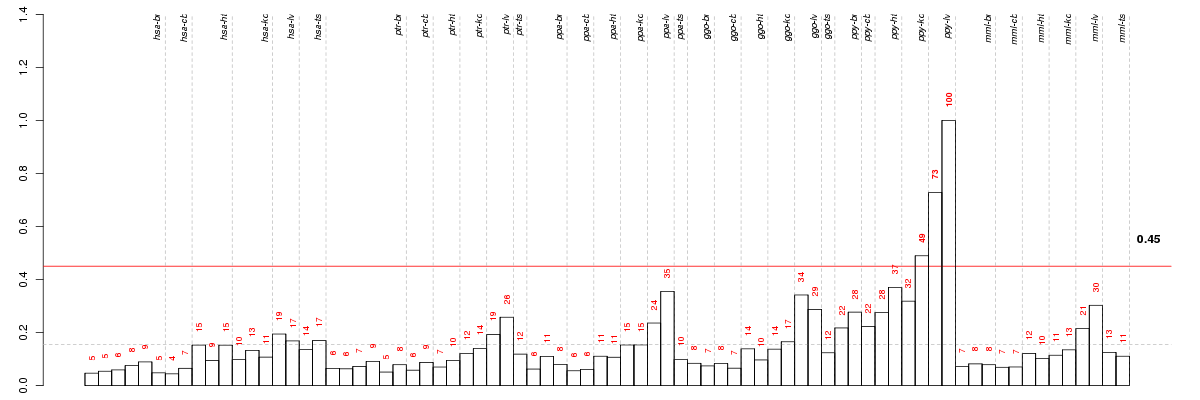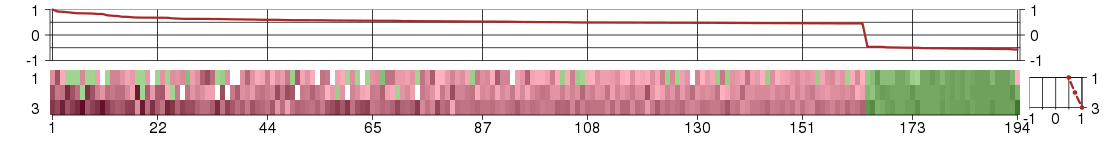

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways, including anabolism and catabolism, by which living organisms transform chemical substances. Metabolic processes typically transform small molecules, but also include macromolecular processes such as DNA repair and replication, and protein synthesis and degradation.
cytokine production
The appearance of a cytokine due to biosynthesis or secretion following a cellular stimulus, resulting in an increase in its intracellular or extracellular levels.
regulation of cytokine production
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of production of a cytokine.
cell killing
Any process in an organism that results in the killing of its own cells or those of another organism, including in some cases the death of the other organism. Killing here refers to the induction of death in one cell by another cell, not cell-autonomous death due to internal or other environmental conditions.
leukocyte mediated cytotoxicity
The directed killing of a target cell by a leukocyte.
immune effector process
Any process of the immune system that occurs as part of an immune response.
immune system process
Any process involved in the development or functioning of the immune system, an organismal system for calibrated responses to potential internal or invasive threats.
leukocyte mediated immunity
Any process involved in the carrying out of an immune response by a leukocyte.
myeloid leukocyte mediated immunity
Any process involved in the carrying out of an immune response by a myeloid leukocyte.
neutrophil mediated immunity
Any process involved in the carrying out of an immune response by a neutrophil.
immune system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system whose objective is to provide calibrated responses by an organism to a potential internal or invasive threat, over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
regulation of immune system process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of an immune system process.
defense response
Reactions, triggered in response to the presence of a foreign body or the occurrence of an injury, which result in restriction of damage to the organism attacked or prevention/recovery from the infection caused by the attack.
defense response to bacterium
Reactions triggered in response to the presence of a bacterium that act to protect the cell or organism.
defense response to fungus
Reactions triggered in response to the presence of a fungus that act to protect the cell or organism.
response to stress
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a disturbance in organismal or cellular homeostasis, usually, but not necessarily, exogenous (e.g. temperature, humidity, ionizing radiation).
immune response
Any immune system process that functions in the calibrated response of an organism to a potential internal or invasive threat.
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
response to biotic stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a biotic stimulus, a stimulus caused or produced by a living organism.
response to other organism
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus from another living organism.
response to bacterium
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus from a bacterium.
response to fungus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus from a fungus.
hemopoiesis
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the myeloid and lymphoid derived organ/tissue systems of the blood and other parts of the body over time, from formation to the mature structure. The site of hemopoiesis is variable during development, but occurs primarily in bone marrow or kidney in many adult vertebrates.
symbiosis, encompassing mutualism through parasitism
An interaction between two organisms living together in more or less intimate association. The term host is usually used for the larger (macro) of the two members of a symbiosis. The smaller (micro) member is called the symbiont organism. Microscopic symbionts are often referred to as endosymbionts. The various forms of symbiosis include parasitism, in which the association is disadvantageous or destructive to one of the organisms; mutualism, in which the association is advantageous, or often necessary to one or both and not harmful to either; and commensalism, in which one member of the association benefits while the other is not affected. However, mutualism, parasitism, and commensalism are often not discrete categories of interactions and should rather be perceived as a continuum of interaction ranging from parasitism to mutualism. In fact, the direction of a symbiotic interaction can change during the lifetime of the symbionts due to developmental changes as well as changes in the biotic/abiotic environment in which the interaction occurs.
killing of cells of another organism
Any process in an organism that results in the killing of cells of another organism, including in some cases the death of the other organism. Killing here refers to the induction of death in one cell by another cell, not cell-autonomous death due to internal or other environmental conditions.
multicellular organismal process
Any biological process, occurring at the level of a multicellular organism, pertinent to its function.
developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an integrated living unit: an anatomical structure (which may be a subcellular structure, cell, tissue, or organ), or organism over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
cytokine biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of cytokines, any of a group of proteins that function to control the survival, growth and differentiation of tissues and cells, and which have autocrine and paracrine activity.
cytokine metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving cytokines, any of a group of proteins or glycoproteins that function to control the survival, growth and differentiation of tissues and cells, and which have autocrine and paracrine activity.
macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
interspecies interaction between organisms
Any process by which an organism has an effect on an organism of a different species.
organ development
Development of a tissue or tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Development pertains to the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a structure over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
hemopoietic or lymphoid organ development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of any organ involved in hemopoiesis or lymphoid cell activation over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Such development includes differentiation of resident cell types (stromal cells) and of migratory cell types dependent on the unique microenvironment afforded by the organ for their proper differentiation.
regulation of response to stimulus
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a response to a stimulus. Response to stimulus is a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
anatomical structure development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an anatomical structure from an initial condition to its mature state. This process begins with the formation of the structure and ends with the mature structure, whatever form that may be including its natural destruction. An anatomical structure is any biological entity that occupies space and is distinguished from its surroundings. Anatomical structures can be macroscopic such as a carpel, or microscopic such as an acrosome.
regulation of immune response
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the immune response, the immunological reaction of an organism to an immunogenic stimulus.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
response to stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
regulation of multicellular organismal process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a multicellular organismal process, the processes pertinent to the function of a multicellular organism above the cellular level; includes the integrated processes of tissues and organs.
interaction with symbiont
An interaction between two organisms living together in more or less intimate association. The term symbiont is used for the smaller (macro) of the two members of a symbiosis; the various forms of symbiosis include parasitism, commensalism and mutualism.
multi-organism process
Any process by which an organism has an effect on another organism of the same or different species.
modification of morphology or physiology of other organism involved in symbiotic interaction
The process by which an organism effects a change in the structure or processes of a second organism, where the two organisms are in a symbiotic interaction.
disruption of cells of other organism involved in symbiotic interaction
A process by which an organism has a negative effect on the functioning of the second organism's cells, where the two organisms are in a symbiotic interaction.
modification by host of symbiont morphology or physiology
The process by which an organism effects a change in the structure or processes of a symbiont organism. The symbiont is defined as the smaller of the organisms involved in a symbiotic interaction.
disruption by host of symbiont cells
Any process by which an organism has a negative effect on the functioning of the symbiont's cells. The symbiont is defined as the smaller of the organisms involved in a symbiotic interaction.
killing by host of symbiont cells
Any process mediated by an organism that results in the death of cells in the symbiont organism. The symbiont is defined as the smaller of the organisms involved in a symbiotic interaction.
killing of cells in other organism involved in symbiotic interaction
Any process mediated by an organism that results in the death of cells in a second organism, where the two organisms are in a symbiotic interaction.
biological regulation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of any biological process, quality or function.
regulation of biological quality
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological quality. A biological quality is a measurable attribute of an organism or part of an organism, such as size, mass, shape, color, etc.
neutrophil mediated cytotoxicity
The directed killing of a target cell by a neutrophil.
neutrophil mediated killing of symbiont cell
The directed killing of a symbiont target cell by a neutrophil.
all
NA
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
regulation of immune system process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of an immune system process.
regulation of multicellular organismal process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a multicellular organismal process, the processes pertinent to the function of a multicellular organism above the cellular level; includes the integrated processes of tissues and organs.
immune response
Any immune system process that functions in the calibrated response of an organism to a potential internal or invasive threat.
regulation of response to stimulus
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a response to a stimulus. Response to stimulus is a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
killing of cells of another organism
Any process in an organism that results in the killing of cells of another organism, including in some cases the death of the other organism. Killing here refers to the induction of death in one cell by another cell, not cell-autonomous death due to internal or other environmental conditions.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
leukocyte mediated cytotoxicity
The directed killing of a target cell by a leukocyte.
immune effector process
Any process of the immune system that occurs as part of an immune response.
regulation of immune response
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the immune response, the immunological reaction of an organism to an immunogenic stimulus.
regulation of cytokine production
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of production of a cytokine.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
regulation of immune response
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the immune response, the immunological reaction of an organism to an immunogenic stimulus.
response to other organism
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus from another living organism.
cytokine biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of cytokines, any of a group of proteins that function to control the survival, growth and differentiation of tissues and cells, and which have autocrine and paracrine activity.
immune system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system whose objective is to provide calibrated responses by an organism to a potential internal or invasive threat, over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
organ development
Development of a tissue or tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Development pertains to the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a structure over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
hemopoietic or lymphoid organ development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of any organ involved in hemopoiesis or lymphoid cell activation over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Such development includes differentiation of resident cell types (stromal cells) and of migratory cell types dependent on the unique microenvironment afforded by the organ for their proper differentiation.
defense response to bacterium
Reactions triggered in response to the presence of a bacterium that act to protect the cell or organism.
defense response to fungus
Reactions triggered in response to the presence of a fungus that act to protect the cell or organism.
interaction with symbiont
An interaction between two organisms living together in more or less intimate association. The term symbiont is used for the smaller (macro) of the two members of a symbiosis; the various forms of symbiosis include parasitism, commensalism and mutualism.
modification of morphology or physiology of other organism involved in symbiotic interaction
The process by which an organism effects a change in the structure or processes of a second organism, where the two organisms are in a symbiotic interaction.
modification by host of symbiont morphology or physiology
The process by which an organism effects a change in the structure or processes of a symbiont organism. The symbiont is defined as the smaller of the organisms involved in a symbiotic interaction.
neutrophil mediated killing of symbiont cell
The directed killing of a symbiont target cell by a neutrophil.
disruption by host of symbiont cells
Any process by which an organism has a negative effect on the functioning of the symbiont's cells. The symbiont is defined as the smaller of the organisms involved in a symbiotic interaction.
killing of cells in other organism involved in symbiotic interaction
Any process mediated by an organism that results in the death of cells in a second organism, where the two organisms are in a symbiotic interaction.
neutrophil mediated cytotoxicity
The directed killing of a target cell by a neutrophil.
killing by host of symbiont cells
Any process mediated by an organism that results in the death of cells in the symbiont organism. The symbiont is defined as the smaller of the organisms involved in a symbiotic interaction.

intracellular
The living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
extracellular region
The space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.
cellular_component
The part of a cell or its extracellular environment in which a gene product is located. A gene product may be located in one or more parts of a cell and its location may be as specific as a particular macromolecular complex, that is, a stable, persistent association of macromolecules that function together.
extracellular space
That part of a multicellular organism outside the cells proper, usually taken to be outside the plasma membranes, and occupied by fluid.
cell
The basic structural and functional unit of all organisms. Includes the plasma membrane and any external encapsulating structures such as the cell wall and cell envelope.
cytoplasm
All of the contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures.
stored secretory granule
A small subcellular vesicle, surrounded by a membrane, that is formed from the Golgi apparatus and contains a highly concentrated protein destined for secretion. Secretory granules move towards the periphery of the cell and upon stimulation, their membranes fuse with the cell membrane, and their protein load is exteriorized. Processing of the contained protein may take place in secretory granules.
cytoplasmic membrane-bounded vesicle
A membrane-bounded vesicle found in the cytoplasm of the cell.
cytoplasmic vesicle
A vesicle formed of membrane or protein, found in the cytoplasm of a cell.
vesicle
Any small, fluid-filled, spherical organelle enclosed by membrane or protein.
membrane-bounded vesicle
Any small, fluid-filled, spherical organelle enclosed by a lipid bilayer.
organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, and prokaryotic structures such as anammoxosomes and pirellulosomes. Excludes the plasma membrane.
membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
extracellular region part
Any constituent part of the extracellular region, the space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers constituent parts of the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
cytoplasmic part
Any constituent part of the cytoplasm, all of the contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures.
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
all
NA
extracellular region part
Any constituent part of the extracellular region, the space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers constituent parts of the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
cytoplasmic vesicle
A vesicle formed of membrane or protein, found in the cytoplasm of a cell.
intracellular membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
cytoplasmic membrane-bounded vesicle
A membrane-bounded vesicle found in the cytoplasm of the cell.
cytoplasmic membrane-bounded vesicle
A membrane-bounded vesicle found in the cytoplasm of the cell.
cytoplasmic part
Any constituent part of the cytoplasm, all of the contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures.
cytoplasmic vesicle
A vesicle formed of membrane or protein, found in the cytoplasm of a cell.

protein binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with any protein or protein complex (a complex of two or more proteins that may include other nonprotein molecules).
molecular_function
Elemental activities, such as catalysis or binding, describing the actions of a gene product at the molecular level. A given gene product may exhibit one or more molecular functions.
receptor binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with one or more specific sites on a receptor molecule, a macromolecule that undergoes combination with a hormone, neurotransmitter, drug or intracellular messenger to initiate a change in cell function.
binding
The selective, non-covalent, often stoichiometric, interaction of a molecule with one or more specific sites on another molecule.
growth factor activity
The function that stimulates a cell to grow or proliferate. Most growth factors have other actions besides the induction of cell growth or proliferation.
all
NA
| Id | Pvalue | ExpCount | Count | Size | Term |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 04060 | 6.768e-03 | 3.2 | 11 | 198 | Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction |
ABHD12Babhydrolase domain containing 12B (ENSG00000131969), score: 0.58 AHSPalpha hemoglobin stabilizing protein (ENSG00000169877), score: 0.48 AKR1CL1aldo-keto reductase family 1, member C-like 1 (ENSG00000196326), score: 0.48 ALAS2aminolevulinate, delta-, synthase 2 (ENSG00000158578), score: 0.56 ALG9asparagine-linked glycosylation 9, alpha-1,2-mannosyltransferase homolog (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000086848), score: 0.51 ANKRD22ankyrin repeat domain 22 (ENSG00000152766), score: 0.53 AP1S3adaptor-related protein complex 1, sigma 3 subunit (ENSG00000152056), score: 0.45 API5apoptosis inhibitor 5 (ENSG00000166181), score: -0.52 AQP8aquaporin 8 (ENSG00000103375), score: 0.62 ARL2BPADP-ribosylation factor-like 2 binding protein (ENSG00000102931), score: -0.49 ARNTaryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator (ENSG00000143437), score: 0.53 ARR3arrestin 3, retinal (X-arrestin) (ENSG00000120500), score: 0.6 ATRIPATR interacting protein (ENSG00000164053), score: 0.52 AZU1azurocidin 1 (ENSG00000172232), score: 0.63 BIRC3baculoviral IAP repeat-containing 3 (ENSG00000023445), score: 0.48 BMP10bone morphogenetic protein 10 (ENSG00000163217), score: 0.49 BPIL1bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein-like 1 (ENSG00000078898), score: 0.85 BPIL3bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein-like 3 (ENSG00000167104), score: 0.68 BRD2bromodomain containing 2 (ENSG00000204256), score: -0.55 BST1bone marrow stromal cell antigen 1 (ENSG00000109743), score: 0.51 BTLAB and T lymphocyte associated (ENSG00000186265), score: 0.54 C16orf54chromosome 16 open reading frame 54 (ENSG00000185905), score: 0.49 C16orf61chromosome 16 open reading frame 61 (ENSG00000103121), score: 0.48 C17orf67chromosome 17 open reading frame 67 (ENSG00000214226), score: 0.65 C1orf192chromosome 1 open reading frame 192 (ENSG00000188931), score: -0.5 C20orf70chromosome 20 open reading frame 70 (ENSG00000131050), score: 0.85 C2CD4BC2 calcium-dependent domain containing 4B (ENSG00000205502), score: 0.53 C2orf66chromosome 2 open reading frame 66 (ENSG00000187944), score: 0.82 C3orf18chromosome 3 open reading frame 18 (ENSG00000088543), score: -0.52 C6orf126chromosome 6 open reading frame 126 (ENSG00000196748), score: 0.61 C7orf68chromosome 7 open reading frame 68 (ENSG00000135245), score: 0.48 CAMPcathelicidin antimicrobial peptide (ENSG00000164047), score: 0.6 CASP4caspase 4, apoptosis-related cysteine peptidase (ENSG00000196954), score: 0.47 CCDC134coiled-coil domain containing 134 (ENSG00000100147), score: 0.51 CCDC92coiled-coil domain containing 92 (ENSG00000119242), score: -0.55 CCL20chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 20 (ENSG00000115009), score: 0.56 CCRL2chemokine (C-C motif) receptor-like 2 (ENSG00000121797), score: 0.55 CD209CD209 molecule (ENSG00000090659), score: 0.53 CD80CD80 molecule (ENSG00000121594), score: 0.54 CEACAM8carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 8 (ENSG00000124469), score: 0.63 CEBPECCAAT/enhancer binding protein (C/EBP), epsilon (ENSG00000092067), score: 0.55 CHAC1ChaC, cation transport regulator homolog 1 (E. coli) (ENSG00000128965), score: 0.51 CHST4carbohydrate (N-acetylglucosamine 6-O) sulfotransferase 4 (ENSG00000140835), score: 0.47 CLEC5AC-type lectin domain family 5, member A (ENSG00000090269), score: 0.69 CRELD2cysteine-rich with EGF-like domains 2 (ENSG00000184164), score: 0.54 CRISP3cysteine-rich secretory protein 3 (ENSG00000096006), score: 0.68 CSF2colony stimulating factor 2 (granulocyte-macrophage) (ENSG00000164400), score: 0.68 CTSGcathepsin G (ENSG00000100448), score: 0.62 CTSKcathepsin K (ENSG00000143387), score: 0.58 CXCR6chemokine (C-X-C motif) receptor 6 (ENSG00000172215), score: 0.56 CYTIPcytohesin 1 interacting protein (ENSG00000115165), score: 0.48 DAPP1dual adaptor of phosphotyrosine and 3-phosphoinositides (ENSG00000070190), score: 0.52 DAXXdeath-domain associated protein (ENSG00000204209), score: -0.53 DDIT4DNA-damage-inducible transcript 4 (ENSG00000168209), score: 0.54 DGAT1diacylglycerol O-acyltransferase 1 (ENSG00000185000), score: 0.47 DNAH11dynein, axonemal, heavy chain 11 (ENSG00000105877), score: 0.58 DOK3docking protein 3 (ENSG00000146094), score: 0.47 DYSFIP1dysferlin interacting protein 1 (ENSG00000182676), score: 0.53 EIF2AK3eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2-alpha kinase 3 (ENSG00000172071), score: 0.49 ELANEelastase, neutrophil expressed (ENSG00000197561), score: 0.65 EMG1EMG1 nucleolar protein homolog (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000126749), score: 0.46 FAM166Afamily with sequence similarity 166, member A (ENSG00000188163), score: -0.49 FAM83Afamily with sequence similarity 83, member A (ENSG00000147689), score: 0.68 FBXO21F-box protein 21 (ENSG00000135108), score: -0.56 FCARFc fragment of IgA, receptor for (ENSG00000186431), score: 0.5 FGF2fibroblast growth factor 2 (basic) (ENSG00000138685), score: -0.54 FGF21fibroblast growth factor 21 (ENSG00000105550), score: 0.46 FGF23fibroblast growth factor 23 (ENSG00000118972), score: 0.57 FRMD8FERM domain containing 8 (ENSG00000126391), score: -0.49 GHRHgrowth hormone releasing hormone (ENSG00000118702), score: 0.54 GNGT1guanine nucleotide binding protein (G protein), gamma transducing activity polypeptide 1 (ENSG00000127928), score: 0.77 GPR107G protein-coupled receptor 107 (ENSG00000148358), score: -0.5 GPR97G protein-coupled receptor 97 (ENSG00000182885), score: 0.63 GPRC5DG protein-coupled receptor, family C, group 5, member D (ENSG00000111291), score: 0.68 GPX2glutathione peroxidase 2 (gastrointestinal) (ENSG00000176153), score: 0.46 GRAP2GRB2-related adaptor protein 2 (ENSG00000100351), score: 0.58 GRHL1grainyhead-like 1 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000134317), score: 0.47 GZMKgranzyme K (granzyme 3; tryptase II) (ENSG00000113088), score: 0.56 HALhistidine ammonia-lyase (ENSG00000084110), score: 0.48 HIST1H1Bhistone cluster 1, H1b (ENSG00000184357), score: 0.85 HPS3Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome 3 (ENSG00000163755), score: 0.6 HPSEheparanase (ENSG00000173083), score: 0.71 HSH2Dhematopoietic SH2 domain containing (ENSG00000196684), score: 0.56 HSPA5heat shock 70kDa protein 5 (glucose-regulated protein, 78kDa) (ENSG00000044574), score: 0.55 IFNAR1interferon (alpha, beta and omega) receptor 1 (ENSG00000142166), score: 0.51 IL1RNinterleukin 1 receptor antagonist (ENSG00000136689), score: 0.46 IL7interleukin 7 (ENSG00000104432), score: 0.46 IL7Rinterleukin 7 receptor (ENSG00000168685), score: 0.48 IRF2interferon regulatory factor 2 (ENSG00000168310), score: 0.46 IRF4interferon regulatory factor 4 (ENSG00000137265), score: 0.63 KIAA0146KIAA0146 (ENSG00000164808), score: 0.49 KLF1Kruppel-like factor 1 (erythroid) (ENSG00000105610), score: 0.58 KRT27keratin 27 (ENSG00000171446), score: 0.89 LAX1lymphocyte transmembrane adaptor 1 (ENSG00000122188), score: 0.63 LILRA5leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor, subfamily A (with TM domain), member 5 (ENSG00000187116), score: 0.49 LOC100134052similar to ubiquitin associated and SH3 domain containing, A (ENSG00000160185), score: 0.47 LONP2lon peptidase 2, peroxisomal (ENSG00000102910), score: 0.52 LTBlymphotoxin beta (TNF superfamily, member 3) (ENSG00000227507), score: 0.46 MADCAM1mucosal vascular addressin cell adhesion molecule 1 (ENSG00000099866), score: 0.49 MANFmesencephalic astrocyte-derived neurotrophic factor (ENSG00000145050), score: 0.46 MED17mediator complex subunit 17 (ENSG00000042429), score: 0.58 MESDC2mesoderm development candidate 2 (ENSG00000117899), score: 0.53 MLANAmelan-A (ENSG00000120215), score: 1 MMABmethylmalonic aciduria (cobalamin deficiency) cblB type (ENSG00000139428), score: 0.46 MMP8matrix metallopeptidase 8 (neutrophil collagenase) (ENSG00000118113), score: 0.82 MPOmyeloperoxidase (ENSG00000005381), score: 0.52 MSMBmicroseminoprotein, beta- (ENSG00000138294), score: 0.87 MTHFD2Lmethylenetetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase (NADP+ dependent) 2-like (ENSG00000163738), score: 0.56 MXD1MAX dimerization protein 1 (ENSG00000059728), score: 0.47 MYBPHmyosin binding protein H (ENSG00000133055), score: 0.68 MYO1Fmyosin IF (ENSG00000142347), score: 0.48 MYO7Amyosin VIIA (ENSG00000137474), score: 0.49 NCR1natural cytotoxicity triggering receptor 1 (ENSG00000189430), score: 0.5 NFE2nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2), 45kDa (ENSG00000123405), score: 0.5 NFIL3nuclear factor, interleukin 3 regulated (ENSG00000165030), score: 0.47 NLRP12NLR family, pyrin domain containing 12 (ENSG00000142405), score: 0.71 NQO1NAD(P)H dehydrogenase, quinone 1 (ENSG00000181019), score: 0.46 NXF1nuclear RNA export factor 1 (ENSG00000162231), score: 0.49 OFD1oral-facial-digital syndrome 1 (ENSG00000046651), score: 0.56 OSMoncostatin M (ENSG00000099985), score: 0.45 PDCD4programmed cell death 4 (neoplastic transformation inhibitor) (ENSG00000150593), score: 0.49 PFDN6prefoldin subunit 6 (ENSG00000204220), score: -0.54 PGLYRP1peptidoglycan recognition protein 1 (ENSG00000008438), score: 0.57 PGM3phosphoglucomutase 3 (ENSG00000013375), score: 0.48 PHF23PHD finger protein 23 (ENSG00000040633), score: 0.6 PLA2G2Aphospholipase A2, group IIA (platelets, synovial fluid) (ENSG00000188257), score: 0.46 POU2AF1POU class 2 associating factor 1 (ENSG00000110777), score: 0.51 PPAPDC1Bphosphatidic acid phosphatase type 2 domain containing 1B (ENSG00000147535), score: 0.47 PPBPpro-platelet basic protein (chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 7) (ENSG00000163736), score: 0.63 PRDM1PR domain containing 1, with ZNF domain (ENSG00000057657), score: 0.63 PRLprolactin (ENSG00000172179), score: 0.91 PRSS53protease, serine, 53 (ENSG00000151006), score: 0.59 PTCRApre T-cell antigen receptor alpha (ENSG00000171611), score: 0.54 PTGS2prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase 2 (prostaglandin G/H synthase and cyclooxygenase) (ENSG00000073756), score: 0.48 R3HDMLR3H domain containing-like (ENSG00000101074), score: 0.58 RAB40ARAB40A, member RAS oncogene family (ENSG00000172476), score: 0.52 RAD54BRAD54 homolog B (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000197275), score: 0.55 RFC2replication factor C (activator 1) 2, 40kDa (ENSG00000049541), score: 0.49 RGL2ral guanine nucleotide dissociation stimulator-like 2 (ENSG00000237441), score: -0.53 RING1ring finger protein 1 (ENSG00000204227), score: -0.55 RNASE7ribonuclease, RNase A family, 7 (ENSG00000165799), score: 0.48 RNMTRNA (guanine-7-) methyltransferase (ENSG00000101654), score: -0.47 RPL37ribosomal protein L37 (ENSG00000145592), score: -0.53 RXRBretinoid X receptor, beta (ENSG00000204231), score: -0.54 S100A12S100 calcium binding protein A12 (ENSG00000163221), score: 0.53 S100PS100 calcium binding protein P (ENSG00000163993), score: 0.5 S1PR4sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 4 (ENSG00000125910), score: 0.46 SAP18Sin3A-associated protein, 18kDa (ENSG00000150459), score: 0.61 SCGB3A2secretoglobin, family 3A, member 2 (ENSG00000164265), score: 0.84 SCYL1SCY1-like 1 (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000142186), score: 0.47 SELLselectin L (ENSG00000188404), score: 0.47 SERPINB10serpin peptidase inhibitor, clade B (ovalbumin), member 10 (ENSG00000242550), score: 0.54 SERPINE1serpin peptidase inhibitor, clade E (nexin, plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1), member 1 (ENSG00000106366), score: 0.46 SIGLEC14sialic acid binding Ig-like lectin 14 (ENSG00000105501), score: 0.57 SLAMF7SLAM family member 7 (ENSG00000026751), score: 0.58 SLC11A2solute carrier family 11 (proton-coupled divalent metal ion transporters), member 2 (ENSG00000110911), score: 0.49 SLC20A1solute carrier family 20 (phosphate transporter), member 1 (ENSG00000144136), score: 0.62 SLC28A3solute carrier family 28 (sodium-coupled nucleoside transporter), member 3 (ENSG00000197506), score: 0.48 SLC39A7solute carrier family 39 (zinc transporter), member 7 (ENSG00000112473), score: -0.53 SNX20sorting nexin 20 (ENSG00000167208), score: 0.48 SPINK1serine peptidase inhibitor, Kazal type 1 (ENSG00000164266), score: 0.53 SPTA1spectrin, alpha, erythrocytic 1 (elliptocytosis 2) (ENSG00000163554), score: 0.57 STX5syntaxin 5 (ENSG00000162236), score: 0.46 TAPBPTAP binding protein (tapasin) (ENSG00000231925), score: -0.51 TBC1D10CTBC1 domain family, member 10C (ENSG00000175463), score: 0.47 TBC1D14TBC1 domain family, member 14 (ENSG00000132405), score: -0.57 TC2Ntandem C2 domains, nuclear (ENSG00000165929), score: 0.48 TCN1transcobalamin I (vitamin B12 binding protein, R binder family) (ENSG00000134827), score: 0.56 TEFthyrotrophic embryonic factor (ENSG00000167074), score: -0.47 TFF1trefoil factor 1 (ENSG00000160182), score: 0.92 TIGITT cell immunoreceptor with Ig and ITIM domains (ENSG00000181847), score: 0.74 TMC3transmembrane channel-like 3 (ENSG00000188869), score: 0.68 TMEM149transmembrane protein 149 (ENSG00000126246), score: 0.48 TNFRSF9tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily, member 9 (ENSG00000049249), score: 0.56 TOB1transducer of ERBB2, 1 (ENSG00000141232), score: 0.54 TRAT1T cell receptor associated transmembrane adaptor 1 (ENSG00000163519), score: 0.76 TREML1triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells-like 1 (ENSG00000161911), score: 0.49 TRIM26tripartite motif-containing 26 (ENSG00000234127), score: -0.52 TXNDC12thioredoxin domain containing 12 (endoplasmic reticulum) (ENSG00000117862), score: 0.48 USP2ubiquitin specific peptidase 2 (ENSG00000036672), score: -0.5 VMO1vitelline membrane outer layer 1 homolog (chicken) (ENSG00000182853), score: 0.49 VNN2vanin 2 (ENSG00000112303), score: 0.6 VPS52vacuolar protein sorting 52 homolog (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000223501), score: -0.55 WDR46WD repeat domain 46 (ENSG00000227057), score: -0.54 WISP1WNT1 inducible signaling pathway protein 1 (ENSG00000104415), score: 0.61 ZBTB22zinc finger and BTB domain containing 22 (ENSG00000236104), score: -0.51 ZDHHC8zinc finger, DHHC-type containing 8 (ENSG00000099904), score: -0.47 ZNF498zinc finger protein 498 (ENSG00000197037), score: 0.63 ZNF629zinc finger protein 629 (ENSG00000102870), score: -0.53 ZNRD1zinc ribbon domain containing 1 (ENSG00000066379), score: -0.5 ZZEF1zinc finger, ZZ-type with EF-hand domain 1 (ENSG00000074755), score: -0.46
| Id | species | tissue | sex | individual |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ppy_kd_f_ca1 | ppy | kd | f | _ |
| ppy_lv_m_ca1 | ppy | lv | m | _ |
| ppy_lv_f_ca1 | ppy | lv | f | _ |