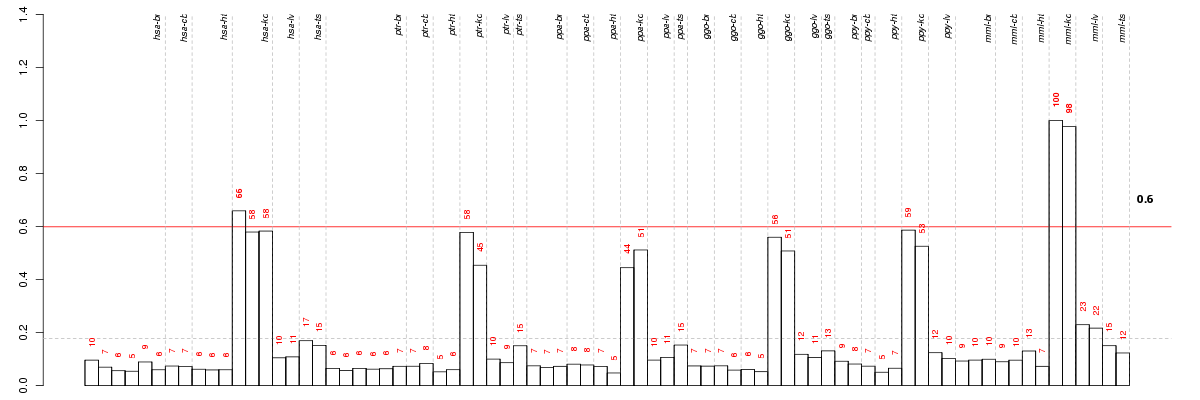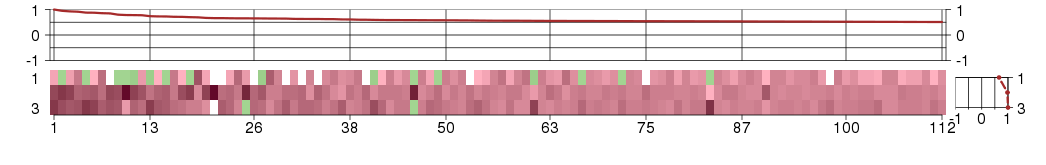

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

reproduction
The production by an organism of new individuals that contain some portion of their genetic material inherited from that organism.
metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways, including anabolism and catabolism, by which living organisms transform chemical substances. Metabolic processes typically transform small molecules, but also include macromolecular processes such as DNA repair and replication, and protein synthesis and degradation.
system process
A multicellular organismal process carried out by any of the organs or tissues in an organ system. An organ system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a biological objective.
renal system process
A organ system process carried out by any of the organs or tissues of the renal system. The renal system is responsible for fluid volume regulation and detoxification in an organism.
regulation of diuresis
Any process that modulates the rate of diuresis. Diuresis is the process of renal water excretion.
renal water homeostasis
Renal process involved in the maintenance of internal steady-state of water in the body.
secretion
The controlled release of a substance by a cell, a group of cells, or a tissue.
transport
The directed movement of substances (such as macromolecules, small molecules, ions) into, out of, within or between cells, or within a multicellular organism by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
cell communication
Any process that mediates interactions between a cell and its surroundings. Encompasses interactions such as signaling or attachment between one cell and another cell, between a cell and an extracellular matrix, or between a cell and any other aspect of its environment.
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
tissue development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a tissue over time, from its formation to the mature structure.
female pregnancy
The set of physiological processes that allow an embryo or foetus to develop within the body of a female animal. It covers the time from fertilization of a female ovum by a male spermatozoon until birth.
response to nutrient
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a nutrient stimulus.
excretion
The elimination by an organism of the waste products that arise as a result of metabolic activity. These products include water, carbon dioxide (CO2), and nitrogenous compounds.
body fluid secretion
The controlled release of a fluid by a cell or group of cells in a multicellular organism.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
response to external stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an external stimulus.
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
response to extracellular stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an extracellular stimulus.
regulation of vitamin D 24-hydroxylase activity
Any process that modulates the rate, frequency or extent of vitamin D 24-hydroxylase activity. Vitamin D 24-hydroxylase activity catalyzes the hydroxylation of C-24 of any form of vitamin D.
positive regulation of vitamin D 24-hydroxylase activity
Any process that increases the rate, frequency or extent of vitamin D 24-hydroxylase activity. Vitamin D 24-hydroxylase activity catalyzes the hydroxylation of C-24 of any form of vitamin D.
regulation of metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism.
reproductive process
A biological process that directly contributes to the process of producing new individuals by one or two organisms. The new individuals inherit some proportion of their genetic material from the parent or parents.
signaling pathway
The series of molecular events whereby information is sent from one location to another within a living organism or between living organisms.
intracellular signaling pathway
The series of molecular events whereby information is sent from one location to another within a cell.
signaling
The entirety of a process whereby information is transmitted. This process begins with the initiation of the signal and ends when a response has been triggered.
water homeostasis
Any process involved in the maintenance of an internal steady-state of water within an organism or cell.
diuresis
The process of renal water excretion.
cell differentiation
The process whereby relatively unspecialized cells, e.g. embryonic or regenerative cells, acquire specialized structural and/or functional features that characterize the cells, tissues, or organs of the mature organism or some other relatively stable phase of the organism's life history. Differentiation includes the processes involved in commitment of a cell to a specific fate and its subsequent development to the mature state.
intracellular receptor mediated signaling pathway
Any series of molecular signals initiated by a ligand binding to an receptor located within a cell.
epithelial cell differentiation
The process whereby a relatively unspecialized cell acquires specialized features of an epithelial cell, any of the cells making up an epithelium.
response to nutrient levels
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus reflecting the presence, absence, or concentration of nutrients.
cellular response to extracellular stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an extracellular stimulus.
cellular response to nutrient levels
A change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus reflecting the presence, absence, or concentration of nutrients.
cellular response to nutrient
A change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a nutrient stimulus.
multicellular organismal process
Any biological process, occurring at the level of a multicellular organism, pertinent to its function.
developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an integrated living unit: an anatomical structure (which may be a subcellular structure, cell, tissue, or organ), or organism over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
regulation of homeostatic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of a homeostatic process.
regulation of localization
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of any process by which a cell, a substance, or a cellular entity is transported to, or maintained in, a specific location.
response to vitamin
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a vitamin stimulus.
response to vitamin D
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a vitamin D stimulus.
response to chemical stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a chemical stimulus.
homeostatic process
Any biological process involved in the maintenance of an internal steady-state.
positive regulation of catalytic activity
Any process that activates or increases the activity of an enzyme.
regulation of system process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a system process, a multicellular organismal process carried out by any of the organs or tissues in an organ system.
regulation of excretion
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of excretion, the elimination by an organism of the waste products that arise as a result of metabolic activity.
positive regulation of molecular function
Any process that activates or increases the rate or extent of a molecular function, an elemental biological activity occurring at the molecular level, such as catalysis or binding.
organ development
Development of a tissue or tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Development pertains to the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a structure over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
anatomical structure development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an anatomical structure from an initial condition to its mature state. This process begins with the formation of the structure and ends with the mature structure, whatever form that may be including its natural destruction. An anatomical structure is any biological entity that occupies space and is distinguished from its surroundings. Anatomical structures can be macroscopic such as a carpel, or microscopic such as an acrosome.
cellular developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a cell over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
chemical homeostasis
Any biological process involved in the maintenance of an internal steady-state of a chemical.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of catalytic activity
Any process that modulates the activity of an enzyme.
regulation of body fluid levels
Any process that modulates the levels of body fluids.
multicellular organismal water homeostasis
Any process involved in the maintenance of an internal steady-state of water within a tissue, organ, or a multicellular organism.
response to stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
regulation of secretion
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the controlled release of a substance from a cell or group of cells.
regulation of transport
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the directed movement of substances (such as macromolecules, small molecules, ions) into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
localization
Any process by which a cell, a substance, or a cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, is transported to, and/or maintained in a specific location.
establishment of localization
The directed movement of a cell, substance or cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, to a specific location.
regulation of multicellular organismal process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a multicellular organismal process, the processes pertinent to the function of a multicellular organism above the cellular level; includes the integrated processes of tissues and organs.
regulation of oxidoreductase activity
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of oxidoreductase activity, the catalysis of an oxidation-reduction (redox) reaction, a reversible chemical reaction in which the oxidation state of an atom or atoms within a molecule is altered. One substrate acts as a hydrogen or electron donor and becomes oxidized, while the other acts as hydrogen or electron acceptor and becomes reduced.
positive regulation of oxidoreductase activity
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of oxidoreductase activity, the catalysis of an oxidation-reduction (redox) reaction, a reversible chemical reaction in which the oxidation state of an atom or atoms within a molecule is altered.
multi-organism process
Any process by which an organism has an effect on another organism of the same or different species.
cellular response to stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
epithelium development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an epithelium over time, from its formation to the mature structure. An epithelium is a tissue that covers the internal or external surfaces of an anatomical structure.
biological regulation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of any biological process, quality or function.
regulation of biological quality
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological quality. A biological quality is a measurable attribute of an organism or part of an organism, such as size, mass, shape, color, etc.
regulation of molecular function
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a molecular function, an elemental biological activity occurring at the molecular level, such as catalysis or binding.
vitamin D receptor signaling pathway
The series of molecular signals generated as a consequence of a vitamin D receptor binding to one of its physiological ligands.
cellular response to chemical stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a chemical stimulus.
cellular response to vitamin
A change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a vitamin stimulus.
cellular response to vitamin D
A change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a vitamin D stimulus.
cellular response to external stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an external stimulus.
all
NA
reproductive process
A biological process that directly contributes to the process of producing new individuals by one or two organisms. The new individuals inherit some proportion of their genetic material from the parent or parents.
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
cellular developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a cell over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
regulation of metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism.
regulation of multicellular organismal process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a multicellular organismal process, the processes pertinent to the function of a multicellular organism above the cellular level; includes the integrated processes of tissues and organs.
cellular response to stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
regulation of localization
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of any process by which a cell, a substance, or a cellular entity is transported to, or maintained in, a specific location.
establishment of localization
The directed movement of a cell, substance or cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, to a specific location.
female pregnancy
The set of physiological processes that allow an embryo or foetus to develop within the body of a female animal. It covers the time from fertilization of a female ovum by a male spermatozoon until birth.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
cellular response to extracellular stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an extracellular stimulus.
regulation of system process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a system process, a multicellular organismal process carried out by any of the organs or tissues in an organ system.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
cellular response to chemical stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a chemical stimulus.
regulation of transport
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the directed movement of substances (such as macromolecules, small molecules, ions) into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
regulation of body fluid levels
Any process that modulates the levels of body fluids.
regulation of catalytic activity
Any process that modulates the activity of an enzyme.
diuresis
The process of renal water excretion.
regulation of excretion
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of excretion, the elimination by an organism of the waste products that arise as a result of metabolic activity.
organ development
Development of a tissue or tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Development pertains to the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a structure over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
diuresis
The process of renal water excretion.
renal water homeostasis
Renal process involved in the maintenance of internal steady-state of water in the body.
tissue development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a tissue over time, from its formation to the mature structure.
cellular response to extracellular stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an extracellular stimulus.
cellular response to extracellular stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an extracellular stimulus.
cellular response to nutrient
A change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a nutrient stimulus.
excretion
The elimination by an organism of the waste products that arise as a result of metabolic activity. These products include water, carbon dioxide (CO2), and nitrogenous compounds.
body fluid secretion
The controlled release of a fluid by a cell or group of cells in a multicellular organism.
regulation of secretion
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the controlled release of a substance from a cell or group of cells.
regulation of homeostatic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of a homeostatic process.
positive regulation of catalytic activity
Any process that activates or increases the activity of an enzyme.
positive regulation of oxidoreductase activity
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of oxidoreductase activity, the catalysis of an oxidation-reduction (redox) reaction, a reversible chemical reaction in which the oxidation state of an atom or atoms within a molecule is altered.
cellular response to nutrient
A change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a nutrient stimulus.
diuresis
The process of renal water excretion.
regulation of diuresis
Any process that modulates the rate of diuresis. Diuresis is the process of renal water excretion.
regulation of diuresis
Any process that modulates the rate of diuresis. Diuresis is the process of renal water excretion.
epithelial cell differentiation
The process whereby a relatively unspecialized cell acquires specialized features of an epithelial cell, any of the cells making up an epithelium.
regulation of excretion
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of excretion, the elimination by an organism of the waste products that arise as a result of metabolic activity.
response to nutrient
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a nutrient stimulus.
cellular response to nutrient levels
A change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus reflecting the presence, absence, or concentration of nutrients.
cellular response to vitamin
A change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a vitamin stimulus.
positive regulation of vitamin D 24-hydroxylase activity
Any process that increases the rate, frequency or extent of vitamin D 24-hydroxylase activity. Vitamin D 24-hydroxylase activity catalyzes the hydroxylation of C-24 of any form of vitamin D.
cellular response to vitamin D
A change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a vitamin D stimulus.
multicellular organismal water homeostasis
Any process involved in the maintenance of an internal steady-state of water within a tissue, organ, or a multicellular organism.
vitamin D receptor signaling pathway
The series of molecular signals generated as a consequence of a vitamin D receptor binding to one of its physiological ligands.

plasma membrane
The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
membrane
Double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
integral to membrane
Penetrating at least one phospholipid bilayer of a membrane. May also refer to the state of being buried in the bilayer with no exposure outside the bilayer. When used to describe a protein, indicates that all or part of the peptide sequence is embedded in the membrane.
extracellular region
The space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.
cellular_component
The part of a cell or its extracellular environment in which a gene product is located. A gene product may be located in one or more parts of a cell and its location may be as specific as a particular macromolecular complex, that is, a stable, persistent association of macromolecules that function together.
cell
The basic structural and functional unit of all organisms. Includes the plasma membrane and any external encapsulating structures such as the cell wall and cell envelope.
apical plasma membrane
The region of the plasma membrane located at the apical end of the cell.
intrinsic to membrane
Located in a membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
membrane part
Any constituent part of a membrane, a double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
plasma membrane part
Any constituent part of the plasma membrane, the membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
apical part of cell
The region of a polarized cell that forms a tip or is distal to a base. For example, in a polarized epithelial cell, the apical region has an exposed surface and lies opposite to the basal lamina that separates the epithelium from other tissue.
all
NA
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
membrane part
Any constituent part of a membrane, a double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
plasma membrane part
Any constituent part of the plasma membrane, the membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
apical plasma membrane
The region of the plasma membrane located at the apical end of the cell.

molecular_function
Elemental activities, such as catalysis or binding, describing the actions of a gene product at the molecular level. A given gene product may exhibit one or more molecular functions.
transporter activity
Enables the directed movement of substances (such as macromolecules, small molecules, ions) into, out of, within or between cells.
amine transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of amines, including polyamines, from one side of the membrane to the other. Amines are organic compounds that are weakly basic in character and contain an amino (-NH2) or substituted amino group.
transmembrane transporter activity
Enables the transfer of a substance from one side of a membrane to the other.
secondary active transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a solute from one side of a membrane to the other, up its concentration gradient. The transporter binds the solute and undergoes a series of conformational changes. Transport works equally well in either direction and is driven by a chemiosmotic source of energy. Chemiosmotic sources of energy include uniport, symport or antiport.
cation transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of cation from one side of the membrane to the other.
ion transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of an ion from one side of a membrane to the other.
organic cation transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of organic cations from one side of a membrane to the other. Organic cations are atoms or small molecules with a positive charge that contain carbon in covalent linkage.
symporter activity
Enables the active transport of a solute across a membrane by a mechanism whereby two or more species are transported together in the same direction in a tightly coupled process not directly linked to a form of energy other than chemiosmotic energy.
active transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a specific substance or related group of substances from one side of a membrane to the other, up the solute's concentration gradient. The transporter binds the solute and undergoes a series of conformational changes. Transport works equally well in either direction.
substrate-specific transmembrane transporter activity
Enables the transfer of a specific substance or group of related substances from one side of a membrane to the other.
substrate-specific transporter activity
Enables the directed movement of a specific substance or group of related substances (such as macromolecules, small molecules, ions) into, out of, within or between cells.
all
NA
substrate-specific transmembrane transporter activity
Enables the transfer of a specific substance or group of related substances from one side of a membrane to the other.
amine transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of amines, including polyamines, from one side of the membrane to the other. Amines are organic compounds that are weakly basic in character and contain an amino (-NH2) or substituted amino group.
A2LD1AIG2-like domain 1 (ENSG00000134864), score: 0.61 ABCC4ATP-binding cassette, sub-family C (CFTR/MRP), member 4 (ENSG00000125257), score: 0.55 AGR3anterior gradient homolog 3 (Xenopus laevis) (ENSG00000173467), score: 0.85 AQP2aquaporin 2 (collecting duct) (ENSG00000167580), score: 0.52 ARSBarylsulfatase B (ENSG00000113273), score: 0.52 ARSFarylsulfatase F (ENSG00000062096), score: 0.54 ATP10DATPase, class V, type 10D (ENSG00000145246), score: 0.54 ATP12AATPase, H+/K+ transporting, nongastric, alpha polypeptide (ENSG00000075673), score: 0.86 B4GALNT2beta-1,4-N-acetyl-galactosaminyl transferase 2 (ENSG00000167080), score: 0.65 BTCbetacellulin (ENSG00000174808), score: 0.6 C17orf78chromosome 17 open reading frame 78 (ENSG00000167230), score: 0.78 C1orf116chromosome 1 open reading frame 116 (ENSG00000182795), score: 0.62 C2orf54chromosome 2 open reading frame 54 (ENSG00000172478), score: 0.54 CA13carbonic anhydrase XIII (ENSG00000185015), score: 0.66 CALCRcalcitonin receptor (ENSG00000004948), score: 0.52 CASRcalcium-sensing receptor (ENSG00000036828), score: 0.6 CD164L2CD164 sialomucin-like 2 (ENSG00000174950), score: 0.71 CLDN16claudin 16 (ENSG00000113946), score: 0.52 CLDN19claudin 19 (ENSG00000164007), score: 0.65 CLDN8claudin 8 (ENSG00000156284), score: 0.53 COCHcoagulation factor C homolog, cochlin (Limulus polyphemus) (ENSG00000100473), score: 0.59 COL19A1collagen, type XIX, alpha 1 (ENSG00000082293), score: 0.54 CSN2casein beta (ENSG00000135222), score: 0.78 CUBNcubilin (intrinsic factor-cobalamin receptor) (ENSG00000107611), score: 0.55 CYP24A1cytochrome P450, family 24, subfamily A, polypeptide 1 (ENSG00000019186), score: 0.56 CYP27B1cytochrome P450, family 27, subfamily B, polypeptide 1 (ENSG00000111012), score: 0.56 DEFB4Bdefensin, beta 4B (ENSG00000171711), score: 0.95 DOCK8dedicator of cytokinesis 8 (ENSG00000107099), score: 0.52 ELF5E74-like factor 5 (ets domain transcription factor) (ENSG00000135374), score: 0.64 ESRP1epithelial splicing regulatory protein 1 (ENSG00000104413), score: 0.53 FAM83Cfamily with sequence similarity 83, member C (ENSG00000125998), score: 0.53 FGFBP1fibroblast growth factor binding protein 1 (ENSG00000137440), score: 0.63 FMO1flavin containing monooxygenase 1 (ENSG00000010932), score: 0.53 FOXI1forkhead box I1 (ENSG00000168269), score: 0.53 FOXN1forkhead box N1 (ENSG00000109101), score: 0.65 GCM1glial cells missing homolog 1 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000137270), score: 0.69 GCNT3glucosaminyl (N-acetyl) transferase 3, mucin type (ENSG00000140297), score: 0.51 GDPD3glycerophosphodiester phosphodiesterase domain containing 3 (ENSG00000102886), score: 0.55 GP2glycoprotein 2 (zymogen granule membrane) (ENSG00000169347), score: 0.63 GPRC6AG protein-coupled receptor, family C, group 6, member A (ENSG00000173612), score: 0.64 GRHL2grainyhead-like 2 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000083307), score: 0.54 GYLTL1Bglycosyltransferase-like 1B (ENSG00000165905), score: 0.55 HMX2H6 family homeobox 2 (ENSG00000188816), score: 0.55 HOXA2homeobox A2 (ENSG00000105996), score: 0.63 HOXB5homeobox B5 (ENSG00000120075), score: 0.53 HOXC10homeobox C10 (ENSG00000180818), score: 0.53 HOXC5homeobox C5 (ENSG00000172789), score: 0.56 HRASLS2HRAS-like suppressor 2 (ENSG00000133328), score: 0.59 HSD11B2hydroxysteroid (11-beta) dehydrogenase 2 (ENSG00000176387), score: 0.53 HTR1D5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) receptor 1D (ENSG00000179546), score: 0.65 IGFL3IGF-like family member 3 (ENSG00000188624), score: 0.56 IL12Binterleukin 12B (natural killer cell stimulatory factor 2, cytotoxic lymphocyte maturation factor 2, p40) (ENSG00000113302), score: 0.74 INSRRinsulin receptor-related receptor (ENSG00000027644), score: 0.53 KIAA1609KIAA1609 (ENSG00000140950), score: 0.51 KRT3keratin 3 (ENSG00000186442), score: 0.8 LAMB4laminin, beta 4 (ENSG00000091128), score: 0.87 LRRC19leucine rich repeat containing 19 (ENSG00000184434), score: 0.52 MATN3matrilin 3 (ENSG00000132031), score: 0.55 MCCD1mitochondrial coiled-coil domain 1 (ENSG00000204511), score: 0.56 MCM10minichromosome maintenance complex component 10 (ENSG00000065328), score: 0.59 MIOXmyo-inositol oxygenase (ENSG00000100253), score: 0.51 MMP13matrix metallopeptidase 13 (collagenase 3) (ENSG00000137745), score: 0.67 MS4A10membrane-spanning 4-domains, subfamily A, member 10 (ENSG00000172689), score: 0.66 MSLNLmesothelin-like (ENSG00000162006), score: 0.7 MTMR8myotubularin related protein 8 (ENSG00000102043), score: 0.65 MTNR1Amelatonin receptor 1A (ENSG00000168412), score: 0.61 NRG1neuregulin 1 (ENSG00000157168), score: 0.51 OR10Q1olfactory receptor, family 10, subfamily Q, member 1 (ENSG00000180475), score: 0.73 OXGR1oxoglutarate (alpha-ketoglutarate) receptor 1 (ENSG00000165621), score: 0.58 OXToxytocin, prepropeptide (ENSG00000101405), score: 0.53 PAPLNpapilin, proteoglycan-like sulfated glycoprotein (ENSG00000100767), score: 0.55 PARD6Bpar-6 partitioning defective 6 homolog beta (C. elegans) (ENSG00000124171), score: 0.52 PAX2paired box 2 (ENSG00000075891), score: 0.54 PKHD1polycystic kidney and hepatic disease 1 (autosomal recessive) (ENSG00000170927), score: 0.54 PLA2G3phospholipase A2, group III (ENSG00000100078), score: 0.93 PNPLA1patatin-like phospholipase domain containing 1 (ENSG00000180316), score: 0.71 PPYpancreatic polypeptide (ENSG00000108849), score: 0.54 PRLRprolactin receptor (ENSG00000113494), score: 0.54 PTPLAD2protein tyrosine phosphatase-like A domain containing 2 (ENSG00000188921), score: 0.57 RAB19RAB19, member RAS oncogene family (ENSG00000146955), score: 0.58 RENrenin (ENSG00000143839), score: 0.58 SIM1single-minded homolog 1 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000112246), score: 0.51 SLC12A3solute carrier family 12 (sodium/chloride transporters), member 3 (ENSG00000070915), score: 0.53 SLC15A5solute carrier family 15, member 5 (ENSG00000188991), score: 0.88 SLC16A9solute carrier family 16, member 9 (monocarboxylic acid transporter 9) (ENSG00000165449), score: 0.55 SLC18A1solute carrier family 18 (vesicular monoamine), member 1 (ENSG00000036565), score: 0.57 SLC22A11solute carrier family 22 (organic anion/urate transporter), member 11 (ENSG00000168065), score: 0.51 SLC22A13solute carrier family 22 (organic anion transporter), member 13 (ENSG00000172940), score: 0.56 SLC22A2solute carrier family 22 (organic cation transporter), member 2 (ENSG00000112499), score: 0.52 SLC22A4solute carrier family 22 (organic cation/ergothioneine transporter), member 4 (ENSG00000197208), score: 0.56 SLC23A3solute carrier family 23 (nucleobase transporters), member 3 (ENSG00000213901), score: 0.54 SLC5A8solute carrier family 5 (iodide transporter), member 8 (ENSG00000139357), score: 0.62 SLC6A19solute carrier family 6 (neutral amino acid transporter), member 19 (ENSG00000174358), score: 0.57 SLC6A4solute carrier family 6 (neurotransmitter transporter, serotonin), member 4 (ENSG00000108576), score: 0.58 SLC7A13solute carrier family 7, (cationic amino acid transporter, y+ system) member 13 (ENSG00000164893), score: 0.58 SLC9A4solute carrier family 9 (sodium/hydrogen exchanger), member 4 (ENSG00000180251), score: 0.58 SOX14SRY (sex determining region Y)-box 14 (ENSG00000168875), score: 0.66 STRA6stimulated by retinoic acid gene 6 homolog (mouse) (ENSG00000137868), score: 0.54 TAAR2trace amine associated receptor 2 (ENSG00000146378), score: 0.58 TFECtranscription factor EC (ENSG00000105967), score: 0.59 TINAGtubulointerstitial nephritis antigen (ENSG00000137251), score: 0.51 TMEM72transmembrane protein 72 (ENSG00000187783), score: 0.55 TMIGD1transmembrane and immunoglobulin domain containing 1 (ENSG00000182271), score: 0.73 TMPRSS13transmembrane protease, serine 13 (ENSG00000137747), score: 0.78 TNFSF15tumor necrosis factor (ligand) superfamily, member 15 (ENSG00000181634), score: 0.63 TUBAL3tubulin, alpha-like 3 (ENSG00000178462), score: 0.55 UCMAupper zone of growth plate and cartilage matrix associated (ENSG00000165623), score: 0.54 UCN3urocortin 3 (stresscopin) (ENSG00000178473), score: 1 UPK2uroplakin 2 (ENSG00000110375), score: 0.91 VDRvitamin D (1,25- dihydroxyvitamin D3) receptor (ENSG00000111424), score: 0.51 XPNPEP2X-prolyl aminopeptidase (aminopeptidase P) 2, membrane-bound (ENSG00000122121), score: 0.52
| Id | species | tissue | sex | individual |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| hsa_kd_m1_ca1 | hsa | kd | m | 1 |
| mml_kd_f_ca1 | mml | kd | f | _ |
| mml_kd_m_ca1 | mml | kd | m | _ |