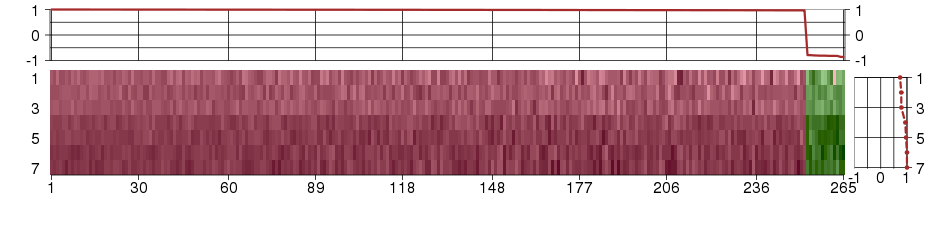

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

reproduction
The production by an organism of new individuals that contain some portion of their genetic material inherited from that organism.
chromosome segregation
The process by which genetic material, in the form of chromosomes, is organized into specific structures and then physically separated and apportioned to two or more sets.
chromosome organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level that results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of chromosomes, structures composed of a very long molecule of DNA and associated proteins that carries hereditary information.
M phase of mitotic cell cycle
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which a cell progresses through M phase, the part of the mitotic cell cycle during which mitosis takes place.
mitotic cell cycle
Progression through the phases of the mitotic cell cycle, the most common eukaryotic cell cycle, which canonically comprises four successive phases called G1, S, G2, and M and includes replication of the genome and the subsequent segregation of chromosomes into daughter cells. In some variant cell cycles nuclear replication or nuclear division may not be followed by cell division, or G1 and G2 phases may be absent.
M phase
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which a cell progresses through M phase, the part of the cell cycle comprising nuclear division.
nuclear division
A process by which a cell nucleus is divided into two nuclei, with DNA and other nuclear contents distributed between the daughter nuclei.
reproductive developmental process
A developmental process by which a progressive change in the state of some part of an organism specifically contributes to its ability to form offspring.
DNA packaging
Any process by which DNA and associated proteins are formed into a compact, orderly structure.
cellular component movement
The directed, self-propelled movement of a cellular component without the involvement of an external agent such as a transporter or a pore.
organelle organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of an organelle within a cell. An organelle is an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
cell cycle
The progression of biochemical and morphological phases and events that occur in a cell during successive cell replication or nuclear replication events. Canonically, the cell cycle comprises the replication and segregation of genetic material followed by the division of the cell, but in endocycles or syncytial cells nuclear replication or nuclear division may not be followed by cell division.
mitosis
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell divides; the process involves condensation of chromosomal DNA into a highly compacted form. Canonically, mitosis produces two daughter nuclei whose chromosome complement is identical to that of the mother cell.
meiosis
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which a cell progresses through the nuclear division phase of a meiotic cell cycle, the specialized nuclear and cell division in which a single diploid cell undergoes two nuclear divisions following a single round of DNA replication in order to produce four daughter cells that contain half the number of chromosomes as the diploid cell. Meiotic division occurs during the formation of gametes from diploid organisms and at the beginning of haplophase in those organisms that alternate between diploid and haploid generations.
gamete generation
The generation and maintenance of gametes in a multicellular organism. A gamete is a haploid reproductive cell.
germ cell development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an immature germ cell over time, from its formation to the mature structure (gamete). A germ cell is any reproductive cell in a multicellular organism.
spermatogenesis
The process of formation of spermatozoa, including spermatocytogenesis and spermiogenesis.
spermatid development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a spermatid over time, from its formation to the mature structure.
single fertilization
The union of male and female gametes to form a zygote.
binding of sperm to zona pellucida
The process by which the sperm binds to the zona pellucida glycoprotein layer of the egg. The process begins with the attachment of the sperm plasma membrane to the zona pellucida and includes attachment of the acrosome inner membrane to the zona pellucida after the acrosomal reaction takes place.
cell recognition
The process by which a cell in a multicellular organism interprets its surroundings.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
fertilization
The union of gametes of opposite sexes during the process of sexual reproduction to form a zygote. It involves the fusion of the gametic nuclei (karyogamy) and cytoplasm (plasmogamy).
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
cell-cell recognition
Cell recognition between cells, usually involving the formation of specialized cell junctions.
cellular component organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of a cellular component.
sexual reproduction
The regular alternation, in the life cycle of haplontic, diplontic and diplohaplontic organisms, of meiosis and fertilization which provides for the production offspring. In diplontic organisms there is a life cycle in which the products of meiosis behave directly as gametes, fusing to form a zygote from which the diploid, or sexually reproductive polyploid, adult organism will develop. In diplohaplontic organisms a haploid phase (gametophyte) exists in the life cycle between meiosis and fertilization (e.g. higher plants, many algae and Fungi); the products of meiosis are spores that develop as haploid individuals from which haploid gametes develop to form a diploid zygote; diplohaplontic organisms show an alternation of haploid and diploid generations. In haplontic organisms meiosis occurs in the zygote, giving rise to four haploid cells (e.g. many algae and protozoa), only the zygote is diploid and this may form a resistant spore, tiding organisms over hard times.
cell cycle process
A cellular process that is involved in the progression of biochemical and morphological phases and events that occur in a cell during successive cell replication or nuclear replication events.
cell cycle phase
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which a cell progresses through one of the biochemical and morphological phases and events that occur during successive cell replication or nuclear replication events.
reproductive process
A biological process that directly contributes to the process of producing new individuals by one or two organisms. The new individuals inherit some proportion of their genetic material from the parent or parents.
cell differentiation
The process whereby relatively unspecialized cells, e.g. embryonic or regenerative cells, acquire specialized structural and/or functional features that characterize the cells, tissues, or organs of the mature organism or some other relatively stable phase of the organism's life history. Differentiation includes the processes involved in commitment of a cell to a specific fate and its subsequent development to the mature state.
sperm motility
Any process involved in the controlled movement of a sperm cell.
multicellular organismal process
Any biological process, occurring at the level of a multicellular organism, pertinent to its function.
developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an integrated living unit: an anatomical structure (which may be a subcellular structure, cell, tissue, or organ), or organism over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
multicellular organism reproduction
The biological process by which new individuals are produced by one or two multicellular organisms. The new individuals inherit some proportion of their genetic material from the parent or parents.
sperm-egg recognition
The initial contact step made between the sperm plasma membrane and outer layer of the egg during fertilization.
locomotion
Self-propelled movement of a cell or organism from one location to another.
male gamete generation
Generation of the male gamete; specialised haploid cells produced by meiosis and along with a female gamete takes part in sexual reproduction.
organelle fission
The creation of two or more organelles by division of one organelle.
cell development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the cell over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Cell development does not include the steps involved in committing a cell to a specific fate.
spermatid differentiation
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a spermatid over time, from initial commitment of the cell to a specific fate, to the fully functional differentiated cell.
reproductive process in a multicellular organism
The process, occurring above the cellular level, that is pertinent to the reproductive function of a multicellular organism. This includes the integrated processes at the level of tissues and organs.
reproductive cellular process
A process, occurring at the cellular level, that is involved in the reproductive function of a multicellular or single-celled organism.
anatomical structure development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an anatomical structure from an initial condition to its mature state. This process begins with the formation of the structure and ends with the mature structure, whatever form that may be including its natural destruction. An anatomical structure is any biological entity that occupies space and is distinguished from its surroundings. Anatomical structures can be macroscopic such as a carpel, or microscopic such as an acrosome.
cellular developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a cell over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
cell motility
Any process involved in the controlled self-propelled movement of a cell that results in translocation of the cell from one place to another.
localization
Any process by which a cell, a substance, or a cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, is transported to, and/or maintained in a specific location.
meiotic cell cycle
Progression through the phases of the meiotic cell cycle, in which canonically a cell replicates to produce four offspring with half the chromosomal content of the progenitor cell.
M phase of meiotic cell cycle
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which a cell progresses through M phase, the part of the meiotic cell cycle during which meiosis takes place.
localization of cell
Any process by which a cell is transported to, and/or maintained in, a specific location.
DNA conformation change
A cellular process that results in a change in the spatial configuration of a DNA molecule. A conformation change can bend DNA, or alter the, twist, writhe, or linking number of a DNA molecule.
all
NA
reproductive process
A biological process that directly contributes to the process of producing new individuals by one or two organisms. The new individuals inherit some proportion of their genetic material from the parent or parents.
organelle organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of an organelle within a cell. An organelle is an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
reproductive cellular process
A process, occurring at the cellular level, that is involved in the reproductive function of a multicellular or single-celled organism.
cell recognition
The process by which a cell in a multicellular organism interprets its surroundings.
multicellular organism reproduction
The biological process by which new individuals are produced by one or two multicellular organisms. The new individuals inherit some proportion of their genetic material from the parent or parents.
reproductive process in a multicellular organism
The process, occurring above the cellular level, that is pertinent to the reproductive function of a multicellular organism. This includes the integrated processes at the level of tissues and organs.
reproductive developmental process
A developmental process by which a progressive change in the state of some part of an organism specifically contributes to its ability to form offspring.
cellular developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a cell over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
fertilization
The union of gametes of opposite sexes during the process of sexual reproduction to form a zygote. It involves the fusion of the gametic nuclei (karyogamy) and cytoplasm (plasmogamy).
reproductive process in a multicellular organism
The process, occurring above the cellular level, that is pertinent to the reproductive function of a multicellular organism. This includes the integrated processes at the level of tissues and organs.
cell motility
Any process involved in the controlled self-propelled movement of a cell that results in translocation of the cell from one place to another.
cell cycle process
A cellular process that is involved in the progression of biochemical and morphological phases and events that occur in a cell during successive cell replication or nuclear replication events.
DNA packaging
Any process by which DNA and associated proteins are formed into a compact, orderly structure.
germ cell development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an immature germ cell over time, from its formation to the mature structure (gamete). A germ cell is any reproductive cell in a multicellular organism.
spermatid differentiation
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a spermatid over time, from initial commitment of the cell to a specific fate, to the fully functional differentiated cell.
gamete generation
The generation and maintenance of gametes in a multicellular organism. A gamete is a haploid reproductive cell.
cell development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the cell over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Cell development does not include the steps involved in committing a cell to a specific fate.
cell motility
Any process involved in the controlled self-propelled movement of a cell that results in translocation of the cell from one place to another.
germ cell development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an immature germ cell over time, from its formation to the mature structure (gamete). A germ cell is any reproductive cell in a multicellular organism.
sperm-egg recognition
The initial contact step made between the sperm plasma membrane and outer layer of the egg during fertilization.
spermatid development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a spermatid over time, from its formation to the mature structure.
cell development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the cell over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Cell development does not include the steps involved in committing a cell to a specific fate.
spermatid differentiation
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a spermatid over time, from initial commitment of the cell to a specific fate, to the fully functional differentiated cell.
germ cell development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an immature germ cell over time, from its formation to the mature structure (gamete). A germ cell is any reproductive cell in a multicellular organism.
sperm-egg recognition
The initial contact step made between the sperm plasma membrane and outer layer of the egg during fertilization.
mitosis
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell divides; the process involves condensation of chromosomal DNA into a highly compacted form. Canonically, mitosis produces two daughter nuclei whose chromosome complement is identical to that of the mother cell.
mitosis
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell divides; the process involves condensation of chromosomal DNA into a highly compacted form. Canonically, mitosis produces two daughter nuclei whose chromosome complement is identical to that of the mother cell.
meiosis
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which a cell progresses through the nuclear division phase of a meiotic cell cycle, the specialized nuclear and cell division in which a single diploid cell undergoes two nuclear divisions following a single round of DNA replication in order to produce four daughter cells that contain half the number of chromosomes as the diploid cell. Meiotic division occurs during the formation of gametes from diploid organisms and at the beginning of haplophase in those organisms that alternate between diploid and haploid generations.
M phase of mitotic cell cycle
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which a cell progresses through M phase, the part of the mitotic cell cycle during which mitosis takes place.
M phase of meiotic cell cycle
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which a cell progresses through M phase, the part of the meiotic cell cycle during which meiosis takes place.
spermatid differentiation
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a spermatid over time, from initial commitment of the cell to a specific fate, to the fully functional differentiated cell.

intracellular
The living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
outer dense fiber
Structure or material found in the flagella of mammalian sperm that surrounds each of the nine microtubule doublets, giving a 9 + 9 + 2 arrangement rather than the 9 + 2 pattern usually seen. These dense fibers are stiff and noncontractile.
acrosomal vesicle
A structure in the head of a spermatozoon that contains acid hydrolases, and is concerned with the breakdown of the outer membrane of the ovum during fertilization. It lies just beneath the plasma membrane and is derived from the lysosome.
axoneme
The bundle of microtubules and associated proteins that forms the core of cilia and flagella in eukaryotic cells and is responsible for their movements.
vacuole
A closed structure, found only in eukaryotic cells, that is completely surrounded by unit membrane and contains liquid material. Cells contain one or several vacuoles, that may have different functions from each other. Vacuoles have a diverse array of functions. They can act as a storage organelle for nutrients or waste products, as a degradative compartment, as a cost-effective way of increasing cell size, and as a homeostatic regulator controlling both turgor pressure and pH of the cytosol.
cellular_component
The part of a cell or its extracellular environment in which a gene product is located. A gene product may be located in one or more parts of a cell and its location may be as specific as a particular macromolecular complex, that is, a stable, persistent association of macromolecules that function together.
cell
The basic structural and functional unit of all organisms. Includes the plasma membrane and any external encapsulating structures such as the cell wall and cell envelope.
nucleus
A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent.
cytoplasm
All of the contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures.
stored secretory granule
A small subcellular vesicle, surrounded by a membrane, that is formed from the Golgi apparatus and contains a highly concentrated protein destined for secretion. Secretory granules move towards the periphery of the cell and upon stimulation, their membranes fuse with the cell membrane, and their protein load is exteriorized. Processing of the contained protein may take place in secretory granules.
cytoskeleton
Any of the various filamentous elements that form the internal framework of cells, and typically remain after treatment of the cells with mild detergent to remove membrane constituents and soluble components of the cytoplasm. The term embraces intermediate filaments, microfilaments, microtubules, the microtrabecular lattice, and other structures characterized by a polymeric filamentous nature and long-range order within the cell. The various elements of the cytoskeleton not only serve in the maintenance of cellular shape but also have roles in other cellular functions, including cellular movement, cell division, endocytosis, and movement of organelles.
microtubule-based flagellum
A long, whiplike protrusion from the surface of a eukaryotic cell, whose undulations drive the cell through a liquid medium; similar in structure to a cilium. The flagellum is based on a 9+2 arrangement of microtubules.
cytoplasmic membrane-bounded vesicle
A membrane-bounded vesicle found in the cytoplasm of the cell.
flagellum
Long whiplike or feathery structures borne either singly or in groups by the motile cells of many bacteria and unicellular eukaryotes and by the motile male gametes of many eukaryotic organisms, which propel the cell through a liquid medium.
cytoplasmic vesicle
A vesicle formed of membrane or protein, found in the cytoplasm of a cell.
vesicle
Any small, fluid-filled, spherical organelle enclosed by membrane or protein.
membrane-bounded vesicle
Any small, fluid-filled, spherical organelle enclosed by a lipid bilayer.
perinuclear theca
A condensed cytoplasmic structure that covers the nucleus of mammalian spermatozoa except for a narrow zone around the insertion of the tail. It shows two distinct regions, a subacrosomal layer and, continuing caudally beyond the acrosomic system, the postacrosomal sheath. The perinuclear theca has been considered a cytoskeletal scaffold responsible for maintaining the overall architecture of the mature sperm head; however, recent studies indicate that the bulk of its constituent proteins are not traditional cytoskeletal proteins but rather a variety of cytosolic proteins.
cytoskeletal calyx
A large cytoskeletal structure located at the posterior end of the perinuclear theca of a mammalian sperm head. The nucleus is tightly associated with the calyx, which contains calicin and basic cylicin proteins.
cell projection
A prolongation or process extending from a cell, e.g. a flagellum or axon.
germ cell nucleus
The nucleus of a germ cell, a reproductive cell in multicellular organisms.
acrosomal matrix
A structural framework, or 'dense core' at the interior of an acrosome. May regulate the distribution of hydrolases within the acrosome and their release during the acrosome reaction.
P granule
A small cytoplasmic, non-membranous RNA/protein complex aggregates in the primordial germ cells of many higher eukaryotes.
organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, and prokaryotic structures such as anammoxosomes and pirellulosomes. Excludes the plasma membrane.
membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
non-membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, not bounded by a lipid bilayer membrane. Includes ribosomes, the cytoskeleton and chromosomes.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular non-membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, not bounded by a lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes ribosomes, the cytoskeleton and chromosomes.
organelle part
Any constituent part of an organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, but excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
cytoskeletal part
Any constituent part of the cytoskeleton, a cellular scaffolding or skeleton that maintains cell shape, enables some cell motion (using structures such as flagella and cilia), and plays important roles in both intra-cellular transport (e.g. the movement of vesicles and organelles) and cellular division. Includes constituent parts of intermediate filaments, microfilaments, microtubules, and the microtrabecular lattice.
cytoplasmic vesicle part
Any constituent part of cytoplasmic vesicle, a vesicle formed of membrane or protein, found in the cytoplasm of a cell.
vacuolar part
Any constituent part of a vacuole, a closed structure, found only in eukaryotic cells, that is completely surrounded by unit membrane and contains liquid material.
cytoplasmic part
Any constituent part of the cytoplasm, all of the contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
axoneme part
Any constituent part of an axoneme, the bundle of microtubules and associated proteins that forms the core of cilia and flagella in eukaryotic cells and is responsible for their movements.
cell projection part
Any constituent part of a cell projection, a prolongation or process extending from a cell, e.g. a flagellum or axon.
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
pole plasm
Differentiated cytoplasm associated with a pole (animal, vegetal, anterior, or posterior) of an oocyte, egg or early embryo.
perinuclear region of cytoplasm
Cytoplasm situated near, or occurring around, the nucleus.
germ plasm
Differentiated cytoplasm associated with a pole of an oocyte, egg or early embryo that will be inherited by the cells that will give rise to the germ line.
all
NA
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
organelle part
Any constituent part of an organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, but excludes the plasma membrane.
cytoplasmic vesicle
A vesicle formed of membrane or protein, found in the cytoplasm of a cell.
intracellular membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular non-membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, not bounded by a lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes ribosomes, the cytoskeleton and chromosomes.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
axoneme part
Any constituent part of an axoneme, the bundle of microtubules and associated proteins that forms the core of cilia and flagella in eukaryotic cells and is responsible for their movements.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
flagellum
Long whiplike or feathery structures borne either singly or in groups by the motile cells of many bacteria and unicellular eukaryotes and by the motile male gametes of many eukaryotic organisms, which propel the cell through a liquid medium.
cell projection part
Any constituent part of a cell projection, a prolongation or process extending from a cell, e.g. a flagellum or axon.
axoneme
The bundle of microtubules and associated proteins that forms the core of cilia and flagella in eukaryotic cells and is responsible for their movements.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
axoneme part
Any constituent part of an axoneme, the bundle of microtubules and associated proteins that forms the core of cilia and flagella in eukaryotic cells and is responsible for their movements.
axoneme
The bundle of microtubules and associated proteins that forms the core of cilia and flagella in eukaryotic cells and is responsible for their movements.
axoneme part
Any constituent part of an axoneme, the bundle of microtubules and associated proteins that forms the core of cilia and flagella in eukaryotic cells and is responsible for their movements.
cytoplasmic vesicle part
Any constituent part of cytoplasmic vesicle, a vesicle formed of membrane or protein, found in the cytoplasm of a cell.
cytoplasmic membrane-bounded vesicle
A membrane-bounded vesicle found in the cytoplasm of the cell.
axoneme
The bundle of microtubules and associated proteins that forms the core of cilia and flagella in eukaryotic cells and is responsible for their movements.
cytoplasmic membrane-bounded vesicle
A membrane-bounded vesicle found in the cytoplasm of the cell.
microtubule-based flagellum
A long, whiplike protrusion from the surface of a eukaryotic cell, whose undulations drive the cell through a liquid medium; similar in structure to a cilium. The flagellum is based on a 9+2 arrangement of microtubules.
acrosomal matrix
A structural framework, or 'dense core' at the interior of an acrosome. May regulate the distribution of hydrolases within the acrosome and their release during the acrosome reaction.
cytoplasmic part
Any constituent part of the cytoplasm, all of the contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures.
vacuole
A closed structure, found only in eukaryotic cells, that is completely surrounded by unit membrane and contains liquid material. Cells contain one or several vacuoles, that may have different functions from each other. Vacuoles have a diverse array of functions. They can act as a storage organelle for nutrients or waste products, as a degradative compartment, as a cost-effective way of increasing cell size, and as a homeostatic regulator controlling both turgor pressure and pH of the cytosol.
cytoplasmic vesicle
A vesicle formed of membrane or protein, found in the cytoplasm of a cell.
cytoskeletal calyx
A large cytoskeletal structure located at the posterior end of the perinuclear theca of a mammalian sperm head. The nucleus is tightly associated with the calyx, which contains calicin and basic cylicin proteins.
P granule
A small cytoplasmic, non-membranous RNA/protein complex aggregates in the primordial germ cells of many higher eukaryotes.
cytoplasmic vesicle part
Any constituent part of cytoplasmic vesicle, a vesicle formed of membrane or protein, found in the cytoplasm of a cell.
vacuolar part
Any constituent part of a vacuole, a closed structure, found only in eukaryotic cells, that is completely surrounded by unit membrane and contains liquid material.
vacuolar part
Any constituent part of a vacuole, a closed structure, found only in eukaryotic cells, that is completely surrounded by unit membrane and contains liquid material.
perinuclear theca
A condensed cytoplasmic structure that covers the nucleus of mammalian spermatozoa except for a narrow zone around the insertion of the tail. It shows two distinct regions, a subacrosomal layer and, continuing caudally beyond the acrosomic system, the postacrosomal sheath. The perinuclear theca has been considered a cytoskeletal scaffold responsible for maintaining the overall architecture of the mature sperm head; however, recent studies indicate that the bulk of its constituent proteins are not traditional cytoskeletal proteins but rather a variety of cytosolic proteins.
cytoskeletal part
Any constituent part of the cytoskeleton, a cellular scaffolding or skeleton that maintains cell shape, enables some cell motion (using structures such as flagella and cilia), and plays important roles in both intra-cellular transport (e.g. the movement of vesicles and organelles) and cellular division. Includes constituent parts of intermediate filaments, microfilaments, microtubules, and the microtrabecular lattice.
cytoskeletal calyx
A large cytoskeletal structure located at the posterior end of the perinuclear theca of a mammalian sperm head. The nucleus is tightly associated with the calyx, which contains calicin and basic cylicin proteins.
perinuclear theca
A condensed cytoplasmic structure that covers the nucleus of mammalian spermatozoa except for a narrow zone around the insertion of the tail. It shows two distinct regions, a subacrosomal layer and, continuing caudally beyond the acrosomic system, the postacrosomal sheath. The perinuclear theca has been considered a cytoskeletal scaffold responsible for maintaining the overall architecture of the mature sperm head; however, recent studies indicate that the bulk of its constituent proteins are not traditional cytoskeletal proteins but rather a variety of cytosolic proteins.
P granule
A small cytoplasmic, non-membranous RNA/protein complex aggregates in the primordial germ cells of many higher eukaryotes.
acrosomal matrix
A structural framework, or 'dense core' at the interior of an acrosome. May regulate the distribution of hydrolases within the acrosome and their release during the acrosome reaction.

molecular_function
Elemental activities, such as catalysis or binding, describing the actions of a gene product at the molecular level. A given gene product may exhibit one or more molecular functions.
lysozyme activity
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of the 1,4-beta-linkages between N-acetylmuramic acid and N-acetyl-D-glucosamine residues in a peptidoglycan and between N-acetyl-D-glucosamine residues in chitodextrins.
catalytic activity
Catalysis of a biochemical reaction at physiological temperatures. In biologically catalyzed reactions, the reactants are known as substrates, and the catalysts are naturally occurring macromolecular substances known as enzymes. Enzymes possess specific binding sites for substrates, and are usually composed wholly or largely of protein, but RNA that has catalytic activity (ribozyme) is often also regarded as enzymatic.
hydrolase activity, hydrolyzing O-glycosyl compounds
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of any O-glycosyl bond.
hydrolase activity
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of various bonds, e.g. C-O, C-N, C-C, phosphoric anhydride bonds, etc. Hydrolase is the systematic name for any enzyme of EC class 3.
hydrolase activity, acting on glycosyl bonds
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of any glycosyl bond.
all
NA
| Id | Pvalue | ExpCount | Count | Size | Term |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 04114 | 9.738e-03 | 0.6569 | 5 | 90 | Oocyte meiosis |
| 04110 | 1.691e-02 | 0.7591 | 5 | 104 | Cell cycle |
ACRacrosin (ENSG00000100312), score: 0.97 ACSBG2acyl-CoA synthetase bubblegum family member 2 (ENSG00000130377), score: 0.98 ACTL7Aactin-like 7A (ENSG00000187003), score: 1 ACTRT2actin-related protein T2 (ENSG00000169717), score: 1 ADAD1adenosine deaminase domain containing 1 (testis-specific) (ENSG00000164113), score: 1 ADAM29ADAM metallopeptidase domain 29 (ENSG00000168594), score: 1 ADAM32ADAM metallopeptidase domain 32 (ENSG00000197140), score: 0.98 AKAP14A kinase (PRKA) anchor protein 14 (ENSG00000186471), score: 0.97 AKAP3A kinase (PRKA) anchor protein 3 (ENSG00000111254), score: 0.98 AKAP4A kinase (PRKA) anchor protein 4 (ENSG00000147081), score: 1 ALS2CR11amyotrophic lateral sclerosis 2 (juvenile) chromosome region, candidate 11 (ENSG00000155754), score: 1 ANP32Aacidic (leucine-rich) nuclear phosphoprotein 32 family, member A (ENSG00000140350), score: -0.8 APLP2amyloid beta (A4) precursor-like protein 2 (ENSG00000084234), score: -0.8 APOBEC4apolipoprotein B mRNA editing enzyme, catalytic polypeptide-like 4 (putative) (ENSG00000173627), score: 0.98 ARMC3armadillo repeat containing 3 (ENSG00000165309), score: 0.99 ARMC4armadillo repeat containing 4 (ENSG00000169126), score: 0.99 ARRDC5arrestin domain containing 5 (ENSG00000205784), score: 0.99 ASB17ankyrin repeat and SOCS box-containing 17 (ENSG00000154007), score: 0.99 ASZ1ankyrin repeat, SAM and basic leucine zipper domain containing 1 (ENSG00000154438), score: 0.99 ATP1A4ATPase, Na+/K+ transporting, alpha 4 polypeptide (ENSG00000132681), score: 0.98 BANF2barrier to autointegration factor 2 (ENSG00000125888), score: 0.99 BOLLbol, boule-like (Drosophila) (ENSG00000152430), score: 1 BRDTbromodomain, testis-specific (ENSG00000137948), score: 1 BRIP1BRCA1 interacting protein C-terminal helicase 1 (ENSG00000136492), score: 0.97 BTG4B-cell translocation gene 4 (ENSG00000137707), score: 0.97 BUB1budding uninhibited by benzimidazoles 1 homolog (yeast) (ENSG00000169679), score: 0.97 C10orf122chromosome 10 open reading frame 122 (ENSG00000175018), score: 0.99 C10orf27chromosome 10 open reading frame 27 (ENSG00000166220), score: 0.97 C10orf82chromosome 10 open reading frame 82 (ENSG00000165863), score: 0.97 C10orf96chromosome 10 open reading frame 96 (ENSG00000182645), score: 1 C11orf88chromosome 11 open reading frame 88 (ENSG00000183644), score: 0.98 C12orf12chromosome 12 open reading frame 12 (ENSG00000197651), score: 1 C12orf50chromosome 12 open reading frame 50 (ENSG00000165805), score: 1 C12orf56chromosome 12 open reading frame 56 (ENSG00000185306), score: 0.99 C13orf28chromosome 13 open reading frame 28 (ENSG00000153498), score: 0.99 C14orf50chromosome 14 open reading frame 50 (ENSG00000165807), score: 0.97 C15orf55chromosome 15 open reading frame 55 (ENSG00000184507), score: 0.99 C15orf60chromosome 15 open reading frame 60 (ENSG00000183324), score: 0.98 C16orf78chromosome 16 open reading frame 78 (ENSG00000166152), score: 1 C17orf46chromosome 17 open reading frame 46 (ENSG00000184361), score: 0.99 C17orf47chromosome 17 open reading frame 47 (ENSG00000181013), score: 0.98 C17orf66chromosome 17 open reading frame 66 (ENSG00000172653), score: 0.98 C17orf74chromosome 17 open reading frame 74 (ENSG00000184560), score: 0.99 C1orf100chromosome 1 open reading frame 100 (ENSG00000173728), score: 0.99 C1orf14chromosome 1 open reading frame 14 (ENSG00000157060), score: 0.99 C1orf141chromosome 1 open reading frame 141 (ENSG00000203963), score: 0.97 C1orf158chromosome 1 open reading frame 158 (ENSG00000157330), score: 0.99 C1orf185chromosome 1 open reading frame 185 (ENSG00000204006), score: 0.99 C1orf189chromosome 1 open reading frame 189 (ENSG00000163263), score: 0.98 C1orf65chromosome 1 open reading frame 65 (ENSG00000178395), score: 0.98 C1orf92chromosome 1 open reading frame 92 (ENSG00000160838), score: 0.99 C1orf94chromosome 1 open reading frame 94 (ENSG00000142698), score: 0.99 C20orf144chromosome 20 open reading frame 144 (ENSG00000149609), score: 0.97 C20orf173chromosome 20 open reading frame 173 (ENSG00000125975), score: 0.99 C20orf195chromosome 20 open reading frame 195 (ENSG00000125531), score: 0.98 C20orf71chromosome 20 open reading frame 71 (ENSG00000131059), score: 1 C20orf79chromosome 20 open reading frame 79 (ENSG00000132631), score: 1 C20orf85chromosome 20 open reading frame 85 (ENSG00000124237), score: 0.99 C2orf53chromosome 2 open reading frame 53 (ENSG00000186143), score: 1 C2orf73chromosome 2 open reading frame 73 (ENSG00000177994), score: 0.98 C2orf78chromosome 2 open reading frame 78 (ENSG00000187833), score: 0.99 C3orf22chromosome 3 open reading frame 22 (ENSG00000180697), score: 0.97 C3orf30chromosome 3 open reading frame 30 (ENSG00000163424), score: 0.99 C3orf77chromosome 3 open reading frame 77 (ENSG00000173769), score: 0.97 C4orf17chromosome 4 open reading frame 17 (ENSG00000138813), score: 1 C4orf35chromosome 4 open reading frame 35 (ENSG00000145309), score: 1 C5orf47chromosome 5 open reading frame 47 (ENSG00000185056), score: 0.98 C5orf50chromosome 5 open reading frame 50 (ENSG00000185662), score: 1 C6orf103chromosome 6 open reading frame 103 (ENSG00000118492), score: 1 C6orf118chromosome 6 open reading frame 118 (ENSG00000112539), score: 0.97 C7orf45chromosome 7 open reading frame 45 (ENSG00000165120), score: 1 C7orf57chromosome 7 open reading frame 57 (ENSG00000164746), score: 0.97 C7orf62chromosome 7 open reading frame 62 (ENSG00000164645), score: 0.99 C8orf74chromosome 8 open reading frame 74 (ENSG00000171060), score: 0.99 CAPN1calpain 1, (mu/I) large subunit (ENSG00000014216), score: -0.82 CAPZA3capping protein (actin filament) muscle Z-line, alpha 3 (ENSG00000177938), score: 0.99 CATSPER4cation channel, sperm associated 4 (ENSG00000188782), score: 0.99 CCDC105coiled-coil domain containing 105 (ENSG00000160994), score: 0.99 CCDC108coiled-coil domain containing 108 (ENSG00000181378), score: 0.98 CCDC116coiled-coil domain containing 116 (ENSG00000161180), score: 0.99 CCDC158coiled-coil domain containing 158 (ENSG00000163749), score: 0.99 CCDC22coiled-coil domain containing 22 (ENSG00000101997), score: -0.86 CCDC27coiled-coil domain containing 27 (ENSG00000162592), score: 1 CCDC38coiled-coil domain containing 38 (ENSG00000165972), score: 0.97 CCDC60coiled-coil domain containing 60 (ENSG00000183273), score: 0.99 CCDC62coiled-coil domain containing 62 (ENSG00000130783), score: 0.99 CCDC63coiled-coil domain containing 63 (ENSG00000173093), score: 0.99 CCDC67coiled-coil domain containing 67 (ENSG00000165325), score: 0.99 CCDC70coiled-coil domain containing 70 (ENSG00000123171), score: 1 CCDC83coiled-coil domain containing 83 (ENSG00000150676), score: 0.99 CCDC87coiled-coil domain containing 87 (ENSG00000182791), score: 0.99 CDC25Ccell division cycle 25 homolog C (S. pombe) (ENSG00000158402), score: 0.97 CEP55centrosomal protein 55kDa (ENSG00000138180), score: 0.97 CETN1centrin, EF-hand protein, 1 (ENSG00000177143), score: 0.98 CPA5carboxypeptidase A5 (ENSG00000158525), score: 0.99 CPXCR1CPX chromosome region, candidate 1 (ENSG00000147183), score: 0.98 CRISP2cysteine-rich secretory protein 2 (ENSG00000124490), score: 0.99 CST8cystatin 8 (cystatin-related epididymal specific) (ENSG00000125815), score: 0.99 CTCFLCCCTC-binding factor (zinc finger protein)-like (ENSG00000124092), score: 0.98 CXorf27chromosome X open reading frame 27 (ENSG00000187516), score: 0.99 CXorf41chromosome X open reading frame 41 (ENSG00000080572), score: 0.97 CXorf61chromosome X open reading frame 61 (ENSG00000204019), score: 0.98 CXorf65chromosome X open reading frame 65 (ENSG00000204165), score: 0.97 CXorf66chromosome X open reading frame 66 (ENSG00000203933), score: 0.99 CYLC1cylicin, basic protein of sperm head cytoskeleton 1 (ENSG00000183035), score: 1 CYLC2cylicin, basic protein of sperm head cytoskeleton 2 (ENSG00000155833), score: 0.99 DAZLdeleted in azoospermia-like (ENSG00000092345), score: 1 DDX4DEAD (Asp-Glu-Ala-Asp) box polypeptide 4 (ENSG00000152670), score: 0.98 DDX43DEAD (Asp-Glu-Ala-Asp) box polypeptide 43 (ENSG00000080007), score: 0.99 DEFB119defensin, beta 119 (ENSG00000180483), score: 0.97 DKFZP781G0119hypothetical protein LOC644041 (ENSG00000206043), score: 0.98 DKKL1dickkopf-like 1 (soggy) (ENSG00000104901), score: 0.98 DLGAP5discs, large (Drosophila) homolog-associated protein 5 (ENSG00000126787), score: 0.97 DMRTB1DMRT-like family B with proline-rich C-terminal, 1 (ENSG00000143006), score: 0.99 DMRTC2DMRT-like family C2 (ENSG00000142025), score: 0.98 DNAH8dynein, axonemal, heavy chain 8 (ENSG00000124721), score: 0.98 DNAI2dynein, axonemal, intermediate chain 2 (ENSG00000171595), score: 0.99 DNAJB8DnaJ (Hsp40) homolog, subfamily B, member 8 (ENSG00000179407), score: 1 DNAJC5BDnaJ (Hsp40) homolog, subfamily C, member 5 beta (ENSG00000147570), score: 0.99 DPEP3dipeptidase 3 (ENSG00000141096), score: 0.97 DTLdenticleless homolog (Drosophila) (ENSG00000143476), score: 0.99 DYDC1DPY30 domain containing 1 (ENSG00000170788), score: 0.99 E2F2E2F transcription factor 2 (ENSG00000007968), score: 0.97 EFCAB6EF-hand calcium binding domain 6 (ENSG00000186976), score: 0.97 EFHBEF-hand domain family, member B (ENSG00000163576), score: 0.98 ENTHD1ENTH domain containing 1 (ENSG00000176177), score: 1 ESCO2establishment of cohesion 1 homolog 2 (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000171320), score: 0.98 EXD1exonuclease 3'-5' domain containing 1 (ENSG00000178997), score: 0.99 FAM154Afamily with sequence similarity 154, member A (ENSG00000155875), score: 0.97 FAM194Afamily with sequence similarity 194, member A (ENSG00000163645), score: 0.98 FAM47Bfamily with sequence similarity 47, member B (ENSG00000189132), score: 0.98 FAM47Cfamily with sequence similarity 47, member C (ENSG00000198173), score: 0.98 FAM71Bfamily with sequence similarity 71, member B (ENSG00000170613), score: 1 FAM71Cfamily with sequence similarity 71, member C (ENSG00000180219), score: 0.99 FAM71Dfamily with sequence similarity 71, member D (ENSG00000172717), score: 0.99 FAM71F1family with sequence similarity 71, member F1 (ENSG00000135248), score: 0.98 FATE1fetal and adult testis expressed 1 (ENSG00000147378), score: 0.97 FBXO39F-box protein 39 (ENSG00000177294), score: 0.98 FBXO43F-box protein 43 (ENSG00000156509), score: 0.99 FLOT2flotillin 2 (ENSG00000132589), score: -0.81 FSCN3fascin homolog 3, actin-bundling protein, testicular (Strongylocentrotus purpuratus) (ENSG00000106328), score: 0.99 FTMTferritin mitochondrial (ENSG00000181867), score: 1 GPR18G protein-coupled receptor 18 (ENSG00000125245), score: 0.97 GSG1germ cell associated 1 (ENSG00000111305), score: 0.99 GSG2germ cell associated 2 (haspin) (ENSG00000177602), score: 0.98 GTSF1gametocyte specific factor 1 (ENSG00000170627), score: 0.98 GTSF1Lgametocyte specific factor 1-like (ENSG00000124196), score: 0.99 H1FNTH1 histone family, member N, testis-specific (ENSG00000187166), score: 0.98 H1FOOH1 histone family, member O, oocyte-specific (ENSG00000178804), score: 0.98 HDAC8histone deacetylase 8 (ENSG00000147099), score: -0.82 HDGFL1hepatoma derived growth factor-like 1 (ENSG00000112273), score: 0.97 HORMAD1HORMA domain containing 1 (ENSG00000143452), score: 1 HSF5heat shock transcription factor family member 5 (ENSG00000176160), score: 0.99 IMP5intramembrane protease 5 (ENSG00000185294), score: 0.97 INSL6insulin-like 6 (ENSG00000120210), score: 0.98 IQCF1IQ motif containing F1 (ENSG00000173389), score: 1 IZUMO2IZUMO family member 2 (ENSG00000161652), score: 0.99 KCNU1potassium channel, subfamily U, member 1 (ENSG00000215262), score: 0.99 KCTD19potassium channel tetramerisation domain containing 19 (ENSG00000168676), score: 0.99 KIF18Akinesin family member 18A (ENSG00000121621), score: 0.99 KIF2Bkinesin family member 2B (ENSG00000141200), score: 1 KLF17Kruppel-like factor 17 (ENSG00000171872), score: 0.99 KLHL10kelch-like 10 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000161594), score: 1 LASS3LAG1 homolog, ceramide synthase 3 (ENSG00000154227), score: 0.99 LDHAL6Blactate dehydrogenase A-like 6B (ENSG00000171989), score: 0.99 LEKR1leucine, glutamate and lysine rich 1 (ENSG00000197980), score: 0.97 LELP1late cornified envelope-like proline-rich 1 (ENSG00000203784), score: 0.99 LOC388946transmembrane protein ENSP00000343375 (ENSG00000242691), score: 1 LRGUKleucine-rich repeats and guanylate kinase domain containing (ENSG00000155530), score: 0.97 LRRC18leucine rich repeat containing 18 (ENSG00000165383), score: 0.97 LRRC52leucine rich repeat containing 52 (ENSG00000162763), score: 0.98 LYPD4LY6/PLAUR domain containing 4 (ENSG00000183103), score: 0.99 LYZL4lysozyme-like 4 (ENSG00000157093), score: 0.97 LYZL6lysozyme-like 6 (ENSG00000161572), score: 0.98 MAGEB10melanoma antigen family B, 10 (ENSG00000177689), score: 0.99 MAGEB3melanoma antigen family B, 3 (ENSG00000198798), score: 0.97 MARCH10membrane-associated ring finger (C3HC4) 10 (ENSG00000173838), score: 0.99 MBD3L1methyl-CpG binding domain protein 3-like 1 (ENSG00000170948), score: 0.99 MS4A5membrane-spanning 4-domains, subfamily A, member 5 (ENSG00000166930), score: 0.99 NAA10N(alpha)-acetyltransferase 10, NatA catalytic subunit (ENSG00000102030), score: -0.81 NCAPHnon-SMC condensin I complex, subunit H (ENSG00000121152), score: 0.98 NUF2NUF2, NDC80 kinetochore complex component, homolog (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000143228), score: 0.97 NUP210Lnucleoporin 210kDa-like (ENSG00000143552), score: 0.99 ODF1outer dense fiber of sperm tails 1 (ENSG00000155087), score: 1 ODF3outer dense fiber of sperm tails 3 (ENSG00000177947), score: 0.99 PAGE1P antigen family, member 1 (prostate associated) (ENSG00000068985), score: 0.98 PAGE3P antigen family, member 3 (prostate associated) (ENSG00000204279), score: 0.98 PDCL2phosducin-like 2 (ENSG00000163440), score: 1 PDHA2pyruvate dehydrogenase (lipoamide) alpha 2 (ENSG00000163114), score: 0.99 PFN4profilin family, member 4 (ENSG00000176732), score: 0.98 PGK1phosphoglycerate kinase 1 (ENSG00000102144), score: -0.79 PIWIL1piwi-like 1 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000125207), score: 1 PLAC1Lplacenta-specific 1-like (ENSG00000149507), score: 0.98 PLCZ1phospholipase C, zeta 1 (ENSG00000139151), score: 0.99 PMFBP1polyamine modulated factor 1 binding protein 1 (ENSG00000118557), score: 0.98 PQBP1polyglutamine binding protein 1 (ENSG00000102103), score: -0.81 PRDX2peroxiredoxin 2 (ENSG00000167815), score: -0.86 PRM3protamine 3 (ENSG00000178257), score: 0.99 PRSS37protease, serine, 37 (ENSG00000165076), score: 0.99 PRSS38protease, serine, 38 (ENSG00000185888), score: 0.99 RBM46RNA binding motif protein 46 (ENSG00000151962), score: 0.99 RIBC2RIB43A domain with coiled-coils 2 (ENSG00000128408), score: 0.97 RNASE11ribonuclease, RNase A family, 11 (non-active) (ENSG00000173464), score: 0.99 RNF113Aring finger protein 113A (ENSG00000125352), score: -0.82 RNF17ring finger protein 17 (ENSG00000132972), score: 0.97 RPGRIP1retinitis pigmentosa GTPase regulator interacting protein 1 (ENSG00000092200), score: 0.99 RPL10Lribosomal protein L10-like (ENSG00000165496), score: 0.99 RSPH6Aradial spoke head 6 homolog A (Chlamydomonas) (ENSG00000104941), score: 0.99 SEL1L2sel-1 suppressor of lin-12-like 2 (C. elegans) (ENSG00000101251), score: 0.98 SEPT14septin 14 (ENSG00000154997), score: 0.98 SERPINB5serpin peptidase inhibitor, clade B (ovalbumin), member 5 (ENSG00000206075), score: 0.98 SGOL2shugoshin-like 2 (S. pombe) (ENSG00000163535), score: 0.98 SLC25A31solute carrier family 25 (mitochondrial carrier; adenine nucleotide translocator), member 31 (ENSG00000151475), score: 0.99 SLCO6A1solute carrier organic anion transporter family, member 6A1 (ENSG00000205359), score: 1 SMC1Bstructural maintenance of chromosomes 1B (ENSG00000077935), score: 1 SMCPsperm mitochondria-associated cysteine-rich protein (ENSG00000163206), score: 0.98 SPACA1sperm acrosome associated 1 (ENSG00000118434), score: 0.98 SPACA3sperm acrosome associated 3 (ENSG00000141316), score: 0.99 SPACA4sperm acrosome associated 4 (ENSG00000177202), score: 0.99 SPAM1sperm adhesion molecule 1 (PH-20 hyaluronidase, zona pellucida binding) (ENSG00000106304), score: 0.98 SPATA19spermatogenesis associated 19 (ENSG00000166118), score: 0.99 SPATA3spermatogenesis associated 3 (ENSG00000173699), score: 1 SPERTspermatid associated (ENSG00000174015), score: 1 SUN5Sad1 and UNC84 domain containing 5 (ENSG00000167098), score: 1 SYCP1synaptonemal complex protein 1 (ENSG00000198765), score: 0.98 TAF7LTAF7-like RNA polymerase II, TATA box binding protein (TBP)-associated factor, 50kDa (ENSG00000102387), score: 0.97 TBX22T-box 22 (ENSG00000122145), score: 0.99 TCP11t-complex 11 homolog (mouse) (ENSG00000124678), score: 0.98 TDRD12tudor domain containing 12 (ENSG00000173809), score: 0.98 TEKT3tektin 3 (ENSG00000125409), score: 0.98 TEX13Atestis expressed 13A (ENSG00000133149), score: 1 TEX15testis expressed 15 (ENSG00000133863), score: 0.97 TKTL2transketolase-like 2 (ENSG00000151005), score: 0.99 TMCO5Atransmembrane and coiled-coil domains 5A (ENSG00000166069), score: 0.99 TMEM146transmembrane protein 146 (ENSG00000174898), score: 1 TMEM217transmembrane protein 217 (ENSG00000172738), score: 0.98 TMEM225transmembrane protein 225 (ENSG00000204300), score: 0.98 TMPRSS12transmembrane (C-terminal) protease, serine 12 (ENSG00000186452), score: 1 TRIM42tripartite motif-containing 42 (ENSG00000155890), score: 1 TRIML1tripartite motif family-like 1 (ENSG00000184108), score: 0.99 TRYX3trypsin X3 (ENSG00000171147), score: 0.99 TSKStestis-specific serine kinase substrate (ENSG00000126467), score: 0.98 TSPYL6TSPY-like 6 (ENSG00000178021), score: 0.97 TTC29tetratricopeptide repeat domain 29 (ENSG00000137473), score: 0.99 TTKTTK protein kinase (ENSG00000112742), score: 0.97 TTLL8tubulin tyrosine ligase-like family, member 8 (ENSG00000138892), score: 0.98 TXNDC2thioredoxin domain containing 2 (spermatozoa) (ENSG00000168454), score: 1 TXNDC3thioredoxin domain containing 3 (spermatozoa) (ENSG00000086288), score: 0.98 UBE2Uubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2U (putative) (ENSG00000177414), score: 1 UBL4Aubiquitin-like 4A (ENSG00000102178), score: -0.79 UBL4Bubiquitin-like 4B (ENSG00000186150), score: 0.98 UBQLN3ubiquilin 3 (ENSG00000175520), score: 1 WBSCR28Williams-Beuren syndrome chromosome region 28 (ENSG00000175877), score: 0.97 WDR38WD repeat domain 38 (ENSG00000136918), score: 0.97 WDR45WD repeat domain 45 (ENSG00000196998), score: -0.82 WDR69WD repeat domain 69 (ENSG00000123977), score: 0.98 WDR87WD repeat domain 87 (ENSG00000171804), score: 1 WFDC6WAP four-disulfide core domain 6 (ENSG00000101448), score: 0.98 ZNRF4zinc and ring finger 4 (ENSG00000105428), score: 0.99 ZPBPzona pellucida binding protein (ENSG00000042813), score: 0.97 ZPBP2zona pellucida binding protein 2 (ENSG00000186075), score: 0.99 ZSWIM2zinc finger, SWIM-type containing 2 (ENSG00000163012), score: 0.97
| Id | species | tissue | sex | individual |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| hsa_ts_m1_ca1 | hsa | ts | m | 1 |
| ggo_ts_m_ca1 | ggo | ts | m | _ |
| hsa_ts_m2_ca1 | hsa | ts | m | 2 |
| ppa_ts_m_ca1 | ppa | ts | m | _ |
| ptr_ts_m_ca1 | ptr | ts | m | _ |
| mml_ts_m2_ca1 | mml | ts | m | 2 |
| mml_ts_m1_ca1 | mml | ts | m | 1 |