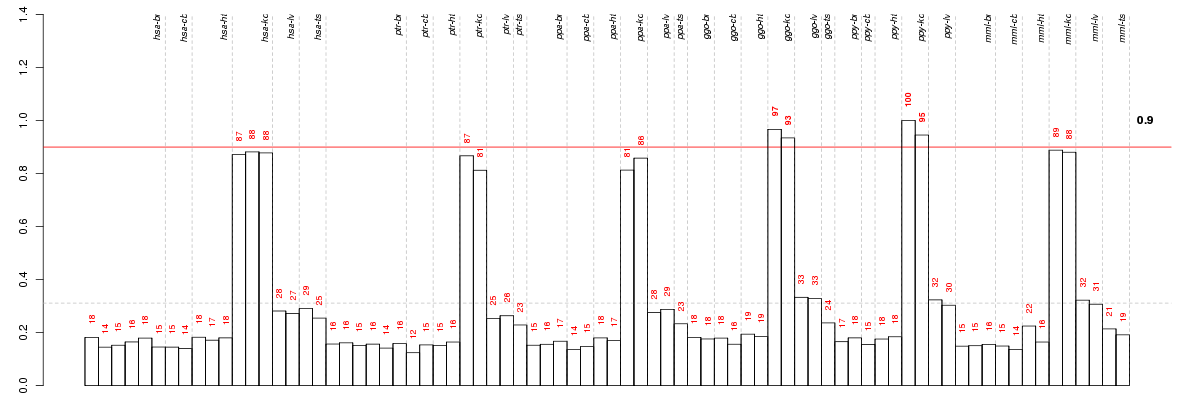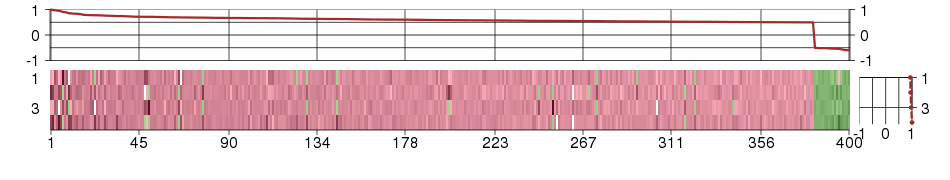

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

skeletal system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the skeleton over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The skeleton is the bony framework of the body in vertebrates (endoskeleton) or the hard outer envelope of insects (exoskeleton or dermoskeleton).
regionalization
The pattern specification process by which an axis or axes is subdivided in space to define an area or volume in which specific patterns of cell differentiation will take place or in which cells interpret a specific environment.
system process
A multicellular organismal process carried out by any of the organs or tissues in an organ system. An organ system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a biological objective.
secretion
The controlled release of a substance by a cell, a group of cells, or a tissue.
transport
The directed movement of substances (such as macromolecules, small molecules, ions) into, out of, within or between cells, or within a multicellular organism by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
ion transport
The directed movement of charged atoms or small charged molecules into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
cation transport
The directed movement of cations, atoms or small molecules with a net positive charge, into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
sodium ion transport
The directed movement of sodium ions (Na+) into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
phosphate transport
The directed movement of phosphate into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
anion transport
The directed movement of anions, atoms or small molecules with a net negative charge, into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
metal ion transport
The directed movement of metal ions, any metal ion with an electric charge, into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
anatomical structure morphogenesis
The process by which anatomical structures are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
embryo development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an embryo from its formation until the end of its embryonic life stage. The end of the embryonic stage is organism-specific. For example, for mammals, the process would begin with zygote formation and end with birth. For insects, the process would begin at zygote formation and end with larval hatching. For plant zygotic embryos, this would be from zygote formation to the end of seed dormancy. For plant vegetative embryos, this would be from the initial determination of the cell or group of cells to form an embryo until the point when the embryo becomes independent of the parent plant.
pattern specification process
Any developmental process that results in the creation of defined areas or spaces within an organism to which cells respond and eventually are instructed to differentiate.
organ morphogenesis
Morphogenesis of an organ. An organ is defined as a tissue or set of tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Morphogenesis is the process by which anatomical structures are generated and organized. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
excretion
The elimination by an organism of the waste products that arise as a result of metabolic activity. These products include water, carbon dioxide (CO2), and nitrogenous compounds.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
embryo development ending in birth or egg hatching
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an embryo over time, from zygote formation until the end of the embryonic life stage. The end of the embryonic life stage is organism-specific and may be somewhat arbitrary; for mammals it is usually considered to be birth, for insects the hatching of the first instar larva from the eggshell.
anterior/posterior pattern formation
The regionalization process by which specific areas of cell differentiation are determined along the anterior-posterior axis. The anterior-posterior axis is defined by a line that runs from the head or mouth of an organism to the tail or opposite end of the organism.
proximal/distal pattern formation
The regionalization process by which specific areas of cell differentiation are determined along a proximal/distal axis. The proximal/distal axis is defined by a line that runs from main body (proximal end) of an organism outward (distal end).
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
monovalent inorganic cation transport
The directed movement of inorganic cations with a valency of one into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore. Inorganic cations are atoms or small molecules with a positive charge which do not contain carbon in covalent linkage.
inorganic anion transport
The directed movement of inorganic anions into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore. Inorganic anions are atoms or small molecules with a negative charge which do not contain carbon in covalent linkage.
organic anion transport
The directed movement of organic anions into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore. Organic anions are atoms or small molecules with a negative charge which contain carbon in covalent linkage.
organic acid transport
The directed movement of organic acids, any acidic compound containing carbon in covalent linkage, into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
thyroid gland development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the thyroid gland over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The thyroid gland is an endoderm-derived gland that produces thyroid hormone.
multicellular organismal process
Any biological process, occurring at the level of a multicellular organism, pertinent to its function.
developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an integrated living unit: an anatomical structure (which may be a subcellular structure, cell, tissue, or organ), or organism over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
endocrine system development
Progression of the endocrine system over time, from its formation to a mature structure. The endocrine system is a system of hormones and ductless glands, where the glands release hormones directly into the blood, lymph or other intercellular fluid, and the hormones circulate within the body to affect distant organs. The major glands that make up the human endocrine system are the hypothalamus, pituitary, thyroid, parathryoids, adrenals, pineal body, and the reproductive glands which include the ovaries and testes.
homeostatic process
Any biological process involved in the maintenance of an internal steady-state.
chordate embryonic development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the embryo over time, from zygote formation through a stage including a notochord and neural tube until birth or egg hatching.
ion homeostasis
Any process involved in the maintenance of an internal steady-state of ions within an organism or cell.
carboxylic acid transport
The directed movement of carboxylic acids into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore. Carboxylic acids are organic acids containing one or more carboxyl (COOH) groups or anions (COO-).
organ development
Development of a tissue or tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Development pertains to the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a structure over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
embryonic organ morphogenesis
Morphogenesis, during the embryonic phase, of a tissue or tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Morphogenesis is the process by which anatomical structures are generated and organized. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
embryonic organ development
Development, taking place during the embryonic phase, of a tissue or tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Development pertains to the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a structure over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
embryonic morphogenesis
The process by which anatomical structures are generated and organized during the embryonic phase. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form. The embryonic phase begins with zygote formation. The end of the embryonic phase is organism-specific. For example, it would be at birth for mammals, larval hatching for insects and seed dormancy in plants.
embryonic skeletal system morphogenesis
The process by which the anatomical structures of the skeleton are generated and organized during the embryonic phase. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
skeletal system morphogenesis
The process by which the anatomical structures of the skeleton are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
embryonic skeletal system development
The process, occurring during the embryonic phase, whose specific outcome is the progression of the skeleton over time, from its formation to the mature structure.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
gland development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a gland over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A gland is an organ specialised for secretion.
anatomical structure development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an anatomical structure from an initial condition to its mature state. This process begins with the formation of the structure and ends with the mature structure, whatever form that may be including its natural destruction. An anatomical structure is any biological entity that occupies space and is distinguished from its surroundings. Anatomical structures can be macroscopic such as a carpel, or microscopic such as an acrosome.
chemical homeostasis
Any biological process involved in the maintenance of an internal steady-state of a chemical.
localization
Any process by which a cell, a substance, or a cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, is transported to, and/or maintained in a specific location.
establishment of localization
The directed movement of a cell, substance or cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, to a specific location.
cation homeostasis
Any process involved in the maintenance of an internal steady-state of cations within an organism or cell.
transmembrane transport
The process whereby a solute is transported from one side of a membrane to the other. This process includes the actual movement of the solute, and any regulation and preparatory steps, such as reduction of the solute.
biological regulation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of any biological process, quality or function.
regulation of biological quality
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological quality. A biological quality is a measurable attribute of an organism or part of an organism, such as size, mass, shape, color, etc.
all
NA
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
establishment of localization
The directed movement of a cell, substance or cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, to a specific location.
embryo development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an embryo from its formation until the end of its embryonic life stage. The end of the embryonic stage is organism-specific. For example, for mammals, the process would begin with zygote formation and end with birth. For insects, the process would begin at zygote formation and end with larval hatching. For plant zygotic embryos, this would be from zygote formation to the end of seed dormancy. For plant vegetative embryos, this would be from the initial determination of the cell or group of cells to form an embryo until the point when the embryo becomes independent of the parent plant.
pattern specification process
Any developmental process that results in the creation of defined areas or spaces within an organism to which cells respond and eventually are instructed to differentiate.
embryonic morphogenesis
The process by which anatomical structures are generated and organized during the embryonic phase. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form. The embryonic phase begins with zygote formation. The end of the embryonic phase is organism-specific. For example, it would be at birth for mammals, larval hatching for insects and seed dormancy in plants.
anatomical structure morphogenesis
The process by which anatomical structures are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
transmembrane transport
The process whereby a solute is transported from one side of a membrane to the other. This process includes the actual movement of the solute, and any regulation and preparatory steps, such as reduction of the solute.
organ development
Development of a tissue or tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Development pertains to the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a structure over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
embryonic organ morphogenesis
Morphogenesis, during the embryonic phase, of a tissue or tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Morphogenesis is the process by which anatomical structures are generated and organized. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
embryonic organ morphogenesis
Morphogenesis, during the embryonic phase, of a tissue or tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Morphogenesis is the process by which anatomical structures are generated and organized. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
organ morphogenesis
Morphogenesis of an organ. An organ is defined as a tissue or set of tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Morphogenesis is the process by which anatomical structures are generated and organized. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
embryonic organ development
Development, taking place during the embryonic phase, of a tissue or tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Development pertains to the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a structure over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
excretion
The elimination by an organism of the waste products that arise as a result of metabolic activity. These products include water, carbon dioxide (CO2), and nitrogenous compounds.
skeletal system morphogenesis
The process by which the anatomical structures of the skeleton are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
embryonic skeletal system morphogenesis
The process by which the anatomical structures of the skeleton are generated and organized during the embryonic phase. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
embryonic skeletal system development
The process, occurring during the embryonic phase, whose specific outcome is the progression of the skeleton over time, from its formation to the mature structure.
thyroid gland development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the thyroid gland over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The thyroid gland is an endoderm-derived gland that produces thyroid hormone.
embryonic skeletal system morphogenesis
The process by which the anatomical structures of the skeleton are generated and organized during the embryonic phase. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
sodium ion transport
The directed movement of sodium ions (Na+) into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.

plasma membrane
The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
proton-transporting two-sector ATPase complex
A large protein complex that catalyzes the synthesis or hydrolysis of ATP by a rotational mechanism, coupled to the transport of protons across a membrane. The complex comprises a membrane sector (F0, V0, or A0) that carries out proton transport and a cytoplasmic compartment sector (F1, V1, or A1) that catalyzes ATP synthesis or hydrolysis. Two major types have been characterized: V-type ATPases couple ATP hydrolysis to the transport of protons across a concentration gradient, whereas F-type ATPases, also known as ATP synthases, normally run in the reverse direction to utilize energy from a proton concentration or electrochemical gradient to synthesize ATP. A third type, A-type ATPases have been found in archaea, and are closely related to eukaryotic V-type ATPases but are reversible.
intracellular
The living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
membrane
Double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
vacuole
A closed structure, found only in eukaryotic cells, that is completely surrounded by unit membrane and contains liquid material. Cells contain one or several vacuoles, that may have different functions from each other. Vacuoles have a diverse array of functions. They can act as a storage organelle for nutrients or waste products, as a degradative compartment, as a cost-effective way of increasing cell size, and as a homeostatic regulator controlling both turgor pressure and pH of the cytosol.
integral to membrane
Penetrating at least one phospholipid bilayer of a membrane. May also refer to the state of being buried in the bilayer with no exposure outside the bilayer. When used to describe a protein, indicates that all or part of the peptide sequence is embedded in the membrane.
extracellular region
The space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.
integral to plasma membrane
Penetrating at least one phospholipid bilayer of a plasma membrane. May also refer to the state of being buried in the bilayer with no exposure outside the bilayer.
collagen
Any of the various assemblies in which collagen chains form a left-handed triple helix; may assemble into higher order structures.
cellular_component
The part of a cell or its extracellular environment in which a gene product is located. A gene product may be located in one or more parts of a cell and its location may be as specific as a particular macromolecular complex, that is, a stable, persistent association of macromolecules that function together.
proteinaceous extracellular matrix
A layer consisting mainly of proteins (especially collagen) and glycosaminoglycans (mostly as proteoglycans) that forms a sheet underlying or overlying cells such as endothelial and epithelial cells. The proteins are secreted by cells in the vicinity. An example of this component is found in Mus musculus.
cell
The basic structural and functional unit of all organisms. Includes the plasma membrane and any external encapsulating structures such as the cell wall and cell envelope.
cytoplasm
All of the contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures.
vacuolar membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding the vacuole and separating its contents from the cytoplasm of the cell.
brush border
Dense covering of microvilli on the apical surface of epithelial cells in tissues such as the intestine, kidney, and choroid plexus; the microvilli aid absorption by increasing the surface area of the cell.
basolateral plasma membrane
The region of the plasma membrane that includes the basal end and sides of the cell. Often used in reference to animal polarized epithelial membranes, where the basal membrane is the part attached to the extracellular matrix, or in plant cells, where the basal membrane is defined with respect to the zygotic axis.
apical plasma membrane
The region of the plasma membrane located at the apical end of the cell.
vacuolar proton-transporting V-type ATPase complex
A proton-transporting two-sector ATPase complex found in the vacuolar membrane, where it acts as a proton pump to mediate acidification of the vacuolar lumen.
sheet-forming collagen
Any collagen polymer in which collagen triple helices associate to form sheet-like networks.
extracellular matrix
A structure lying external to one or more cells, which provides structural support for cells or tissues; may be completely external to the cell (as in animals) or be part of the cell (as in plants).
organelle membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding an organelle.
intrinsic to membrane
Located in a membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
intrinsic to plasma membrane
Located in the plasma membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
cell projection membrane
The portion of the plasma membrane surrounding a cell surface projection.
brush border membrane
The portion of the plasma membrane surrounding the brush border.
macromolecular complex
A stable assembly of two or more macromolecules, i.e. proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates or lipids, in which the constituent parts function together.
proton-transporting V-type ATPase complex
A proton-transporting two-sector ATPase complex that couples ATP hydrolysis to the transport of protons across a concentration gradient. The resulting transmembrane electrochemical potential of H+ is used to drive a variety of (i) secondary active transport systems via H+-dependent symporters and antiporters and (ii) channel-mediated transport systems. The complex comprises a membrane sector (V0) that carries out proton transport and a cytoplasmic compartment sector (V1) that catalyzes ATP hydrolysis. V-type ATPases are found in the membranes of organelles such as vacuoles, endosomes, and lysosomes, and in the plasma membrane.
cell projection
A prolongation or process extending from a cell, e.g. a flagellum or axon.
organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, and prokaryotic structures such as anammoxosomes and pirellulosomes. Excludes the plasma membrane.
membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
protein complex
Any macromolecular complex composed of two or more polypeptide subunits, which may or may not be identical. Protein complexes may have other associated non-protein prosthetic groups, such as nucleotides, metal ions or other small molecules.
extracellular matrix part
Any constituent part of the extracellular matrix, the structure lying external to one or more cells, which provides structural support for cells or tissues; may be completely external to the cell (as in animals) or be part of the cell (as often seen in plants).
extracellular region part
Any constituent part of the extracellular region, the space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers constituent parts of the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.
organelle part
Any constituent part of an organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, but excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
membrane part
Any constituent part of a membrane, a double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
vacuolar part
Any constituent part of a vacuole, a closed structure, found only in eukaryotic cells, that is completely surrounded by unit membrane and contains liquid material.
cytoplasmic part
Any constituent part of the cytoplasm, all of the contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
plasma membrane part
Any constituent part of the plasma membrane, the membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
cell projection part
Any constituent part of a cell projection, a prolongation or process extending from a cell, e.g. a flagellum or axon.
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
apical part of cell
The region of a polarized cell that forms a tip or is distal to a base. For example, in a polarized epithelial cell, the apical region has an exposed surface and lies opposite to the basal lamina that separates the epithelium from other tissue.
all
NA
extracellular region part
Any constituent part of the extracellular region, the space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers constituent parts of the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
organelle part
Any constituent part of an organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, but excludes the plasma membrane.
organelle membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding an organelle.
intracellular membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
extracellular matrix part
Any constituent part of the extracellular matrix, the structure lying external to one or more cells, which provides structural support for cells or tissues; may be completely external to the cell (as in animals) or be part of the cell (as often seen in plants).
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
organelle membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding an organelle.
membrane part
Any constituent part of a membrane, a double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
cell projection part
Any constituent part of a cell projection, a prolongation or process extending from a cell, e.g. a flagellum or axon.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
proton-transporting two-sector ATPase complex
A large protein complex that catalyzes the synthesis or hydrolysis of ATP by a rotational mechanism, coupled to the transport of protons across a membrane. The complex comprises a membrane sector (F0, V0, or A0) that carries out proton transport and a cytoplasmic compartment sector (F1, V1, or A1) that catalyzes ATP synthesis or hydrolysis. Two major types have been characterized: V-type ATPases couple ATP hydrolysis to the transport of protons across a concentration gradient, whereas F-type ATPases, also known as ATP synthases, normally run in the reverse direction to utilize energy from a proton concentration or electrochemical gradient to synthesize ATP. A third type, A-type ATPases have been found in archaea, and are closely related to eukaryotic V-type ATPases but are reversible.
collagen
Any of the various assemblies in which collagen chains form a left-handed triple helix; may assemble into higher order structures.
vacuolar membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding the vacuole and separating its contents from the cytoplasm of the cell.
vacuolar proton-transporting V-type ATPase complex
A proton-transporting two-sector ATPase complex found in the vacuolar membrane, where it acts as a proton pump to mediate acidification of the vacuolar lumen.
plasma membrane part
Any constituent part of the plasma membrane, the membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
cytoplasmic part
Any constituent part of the cytoplasm, all of the contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures.
vacuole
A closed structure, found only in eukaryotic cells, that is completely surrounded by unit membrane and contains liquid material. Cells contain one or several vacuoles, that may have different functions from each other. Vacuoles have a diverse array of functions. They can act as a storage organelle for nutrients or waste products, as a degradative compartment, as a cost-effective way of increasing cell size, and as a homeostatic regulator controlling both turgor pressure and pH of the cytosol.
vacuolar part
Any constituent part of a vacuole, a closed structure, found only in eukaryotic cells, that is completely surrounded by unit membrane and contains liquid material.
apical plasma membrane
The region of the plasma membrane located at the apical end of the cell.
intrinsic to plasma membrane
Located in the plasma membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
cell projection membrane
The portion of the plasma membrane surrounding a cell surface projection.
brush border membrane
The portion of the plasma membrane surrounding the brush border.
vacuolar proton-transporting V-type ATPase complex
A proton-transporting two-sector ATPase complex found in the vacuolar membrane, where it acts as a proton pump to mediate acidification of the vacuolar lumen.
vacuolar part
Any constituent part of a vacuole, a closed structure, found only in eukaryotic cells, that is completely surrounded by unit membrane and contains liquid material.
integral to plasma membrane
Penetrating at least one phospholipid bilayer of a plasma membrane. May also refer to the state of being buried in the bilayer with no exposure outside the bilayer.

molecular_function
Elemental activities, such as catalysis or binding, describing the actions of a gene product at the molecular level. A given gene product may exhibit one or more molecular functions.
nucleic acid binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with any nucleic acid.
DNA binding
Any molecular function by which a gene product interacts selectively with DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid).
sequence-specific DNA binding transcription factor activity
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with a specific DNA sequence in order to modulate transcription. The transcription factor may or may not also interact selectively with a protein or macromolecular complex.
metal ion transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of metal ions from one side of a membrane to the other.
transporter activity
Enables the directed movement of substances (such as macromolecules, small molecules, ions) into, out of, within or between cells.
amine transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of amines, including polyamines, from one side of the membrane to the other. Amines are organic compounds that are weakly basic in character and contain an amino (-NH2) or substituted amino group.
amino acid transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of amino acids from one side of a membrane to the other. Amino acids are organic molecules that contain an amino group and a carboxyl group.
transmembrane transporter activity
Enables the transfer of a substance from one side of a membrane to the other.
organic acid transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of organic acids, any acidic compound containing carbon in covalent linkage, from one side of the membrane to the other.
secondary active transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a solute from one side of a membrane to the other, up its concentration gradient. The transporter binds the solute and undergoes a series of conformational changes. Transport works equally well in either direction and is driven by a chemiosmotic source of energy. Chemiosmotic sources of energy include uniport, symport or antiport.
inorganic anion exchanger activity
NA
binding
The selective, non-covalent, often stoichiometric, interaction of a molecule with one or more specific sites on another molecule.
cation transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of cation from one side of the membrane to the other.
anion transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a negatively charged ion from one side of a membrane to the other.
ion transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of an ion from one side of a membrane to the other.
monovalent inorganic cation transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a inorganic cations with a valency of one from one side of a membrane to the other. Inorganic cations are atoms or small molecules with a positive charge that do not contain carbon in covalent linkage.
sodium ion transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of sodium ions (Na+) from one side of a membrane to the other.
inorganic anion transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of inorganic anions from one side of a membrane to the other. Inorganic anions are atoms or small molecules with a negative charge which do not contain carbon in covalent linkage.
phosphate transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of phosphate (PO4 3-) ions from one side of a membrane to the other.
symporter activity
Enables the active transport of a solute across a membrane by a mechanism whereby two or more species are transported together in the same direction in a tightly coupled process not directly linked to a form of energy other than chemiosmotic energy.
solute:cation symporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a solute or solutes from one side of a membrane to the other according to the reaction: solute(out) + cation(out) = solute(in) + cation(in).
anion:cation symporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a solute or solutes from one side of a membrane to the other according to the reaction: anion(out) + cation(out) = anion(in) + cation(in).
antiporter activity
Enables the active transport of a solute across a membrane by a mechanism whereby two or more species are transported in opposite directions in a tightly coupled process not directly linked to a form of energy other than chemiosmotic energy.
solute:solute antiporter activity
Catalysis of the reaction: solute A(out) + solute B(in) = solute A(in) + solute B(out).
anion:anion antiporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a solute or solutes from one side of a membrane to the other according to the reaction: anion A(out) + anion B(in) = anion A(in) + anion B(out).
sodium-dependent phosphate transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of phosphate (PO4 3-) ions from one side of a membrane to the other, requiring sodium ions.
anion exchanger activity
NA
active transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a specific substance or related group of substances from one side of a membrane to the other, up the solute's concentration gradient. The transporter binds the solute and undergoes a series of conformational changes. Transport works equally well in either direction.
inorganic cation transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of inorganic cations from one side of a membrane to the other. Inorganic cations are atoms or small molecules with a positive charge that do not contain carbon in covalent linkage.
substrate-specific transmembrane transporter activity
Enables the transfer of a specific substance or group of related substances from one side of a membrane to the other.
substrate-specific transporter activity
Enables the directed movement of a specific substance or group of related substances (such as macromolecules, small molecules, ions) into, out of, within or between cells.
sequence-specific DNA binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with DNA of a specific nucleotide composition, e.g. GC-rich DNA binding, or with a specific sequence motif or type of DNA e.g. promotor binding or rDNA binding.
carboxylic acid transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of carboxylic acids from one side of the membrane to the other. Carboxylic acids are organic acids containing one or more carboxyl (COOH) groups or anions (COO-).
all
NA
substrate-specific transmembrane transporter activity
Enables the transfer of a specific substance or group of related substances from one side of a membrane to the other.
amine transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of amines, including polyamines, from one side of the membrane to the other. Amines are organic compounds that are weakly basic in character and contain an amino (-NH2) or substituted amino group.
amino acid transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of amino acids from one side of a membrane to the other. Amino acids are organic molecules that contain an amino group and a carboxyl group.
solute:cation symporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a solute or solutes from one side of a membrane to the other according to the reaction: solute(out) + cation(out) = solute(in) + cation(in).
anion:cation symporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a solute or solutes from one side of a membrane to the other according to the reaction: anion(out) + cation(out) = anion(in) + cation(in).
anion:anion antiporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a solute or solutes from one side of a membrane to the other according to the reaction: anion A(out) + anion B(in) = anion A(in) + anion B(out).
sodium ion transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of sodium ions (Na+) from one side of a membrane to the other.
| Id | Pvalue | ExpCount | Count | Size | Term |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 05322 | 1.510e-04 | 1.627 | 10 | 52 | Systemic lupus erythematosus |
| 04966 | 9.061e-03 | 0.6569 | 5 | 21 | Collecting duct acid secretion |
| 04960 | 1.058e-02 | 1.032 | 6 | 33 | Aldosterone-regulated sodium reabsorption |
ABP1amiloride binding protein 1 (amine oxidase (copper-containing)) (ENSG00000002726), score: 0.56 ACMSDaminocarboxymuconate semialdehyde decarboxylase (ENSG00000153086), score: 0.52 ACPPacid phosphatase, prostate (ENSG00000014257), score: 0.71 ACSF2acyl-CoA synthetase family member 2 (ENSG00000167107), score: 0.58 AGR2anterior gradient homolog 2 (Xenopus laevis) (ENSG00000106541), score: 0.84 AGXT2alanine--glyoxylate aminotransferase 2 (ENSG00000113492), score: 0.55 ALDH3A1aldehyde dehydrogenase 3 family, member A1 (ENSG00000108602), score: 0.56 ALDOCaldolase C, fructose-bisphosphate (ENSG00000109107), score: -0.59 AP1G1adaptor-related protein complex 1, gamma 1 subunit (ENSG00000166747), score: 0.53 AP1M2adaptor-related protein complex 1, mu 2 subunit (ENSG00000129354), score: 0.53 AP1S3adaptor-related protein complex 1, sigma 3 subunit (ENSG00000152056), score: 0.52 AQP2aquaporin 2 (collecting duct) (ENSG00000167580), score: 0.67 AQP6aquaporin 6, kidney specific (ENSG00000086159), score: 0.55 ARHGAP24Rho GTPase activating protein 24 (ENSG00000138639), score: 0.51 ARHGEF38Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) 38 (ENSG00000138784), score: 1 ARSFarylsulfatase F (ENSG00000062096), score: 0.62 ATP2C2ATPase, Ca++ transporting, type 2C, member 2 (ENSG00000064270), score: 0.77 ATP6V0A4ATPase, H+ transporting, lysosomal V0 subunit a4 (ENSG00000105929), score: 0.66 ATP6V0D2ATPase, H+ transporting, lysosomal 38kDa, V0 subunit d2 (ENSG00000147614), score: 0.61 ATP6V1B1ATPase, H+ transporting, lysosomal 56/58kDa, V1 subunit B1 (ENSG00000116039), score: 0.63 ATP6V1G3ATPase, H+ transporting, lysosomal 13kDa, V1 subunit G3 (ENSG00000151418), score: 0.68 ATP8B4ATPase, class I, type 8B, member 4 (ENSG00000104043), score: 0.55 B4GALNT2beta-1,4-N-acetyl-galactosaminyl transferase 2 (ENSG00000167080), score: 0.78 BARX2BARX homeobox 2 (ENSG00000043039), score: 0.52 BBOX1butyrobetaine (gamma), 2-oxoglutarate dioxygenase (gamma-butyrobetaine hydroxylase) 1 (ENSG00000129151), score: 0.5 BICC1bicaudal C homolog 1 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000122870), score: 0.52 BIKBCL2-interacting killer (apoptosis-inducing) (ENSG00000100290), score: 0.54 BMP2bone morphogenetic protein 2 (ENSG00000125845), score: 0.53 BSNDBartter syndrome, infantile, with sensorineural deafness (Barttin) (ENSG00000162399), score: 0.6 BSPRYB-box and SPRY domain containing (ENSG00000119411), score: 0.5 C12orf59chromosome 12 open reading frame 59 (ENSG00000165685), score: 0.69 C14orf149chromosome 14 open reading frame 149 (ENSG00000126790), score: 0.57 C17orf99chromosome 17 open reading frame 99 (ENSG00000187997), score: 0.85 C19orf21chromosome 19 open reading frame 21 (ENSG00000099812), score: 0.56 C1orf106chromosome 1 open reading frame 106 (ENSG00000163362), score: 0.73 C1orf161chromosome 1 open reading frame 161 (ENSG00000173212), score: 0.51 C1orf172chromosome 1 open reading frame 172 (ENSG00000175707), score: 0.54 C1orf85chromosome 1 open reading frame 85 (ENSG00000198715), score: 0.6 C1orf91chromosome 1 open reading frame 91 (ENSG00000160055), score: 0.51 C1QTNF5C1q and tumor necrosis factor related protein 5 (ENSG00000235718), score: 0.5 C2orf62chromosome 2 open reading frame 62 (ENSG00000158428), score: 0.51 C5orf32chromosome 5 open reading frame 32 (ENSG00000120306), score: 0.51 C6orf126chromosome 6 open reading frame 126 (ENSG00000196748), score: 0.64 C9orf71chromosome 9 open reading frame 71 (ENSG00000181778), score: 0.82 C9orf72chromosome 9 open reading frame 72 (ENSG00000147894), score: -0.51 C9orf84chromosome 9 open reading frame 84 (ENSG00000165181), score: 0.77 CA12carbonic anhydrase XII (ENSG00000074410), score: 0.67 CA13carbonic anhydrase XIII (ENSG00000185015), score: 0.54 CALCRcalcitonin receptor (ENSG00000004948), score: 0.58 CARD14caspase recruitment domain family, member 14 (ENSG00000141527), score: 0.64 CASRcalcium-sensing receptor (ENSG00000036828), score: 0.6 CC2D2Acoiled-coil and C2 domain containing 2A (ENSG00000048342), score: 0.53 CCDC127coiled-coil domain containing 127 (ENSG00000164366), score: -0.51 CCL11chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 11 (ENSG00000172156), score: 0.66 CCL19chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 19 (ENSG00000172724), score: 0.65 CDCP1CUB domain containing protein 1 (ENSG00000163814), score: 0.51 CDH16cadherin 16, KSP-cadherin (ENSG00000166589), score: 0.68 CDH17cadherin 17, LI cadherin (liver-intestine) (ENSG00000079112), score: 0.98 CDH3cadherin 3, type 1, P-cadherin (placental) (ENSG00000062038), score: 0.74 CDH6cadherin 6, type 2, K-cadherin (fetal kidney) (ENSG00000113361), score: 0.63 CELSR1cadherin, EGF LAG seven-pass G-type receptor 1 (flamingo homolog, Drosophila) (ENSG00000075275), score: 0.53 CETN2centrin, EF-hand protein, 2 (ENSG00000147400), score: 0.59 CFDP1craniofacial development protein 1 (ENSG00000153774), score: 0.5 CHMP4Cchromatin modifying protein 4C (ENSG00000164695), score: 0.5 CIRH1Acirrhosis, autosomal recessive 1A (cirhin) (ENSG00000141076), score: 0.63 CLCNKAchloride channel Ka (ENSG00000186510), score: 0.63 CLDN16claudin 16 (ENSG00000113946), score: 0.76 CLDN19claudin 19 (ENSG00000164007), score: 0.5 CLDN4claudin 4 (ENSG00000189143), score: 0.63 CLDN8claudin 8 (ENSG00000156284), score: 0.67 CLNKcytokine-dependent hematopoietic cell linker (ENSG00000109684), score: 0.7 CLRN3clarin 3 (ENSG00000180745), score: 0.55 CMBLcarboxymethylenebutenolidase homolog (Pseudomonas) (ENSG00000164237), score: 0.51 COL4A3collagen, type IV, alpha 3 (Goodpasture antigen) (ENSG00000169031), score: 0.63 COL4A4collagen, type IV, alpha 4 (ENSG00000081052), score: 0.55 COL8A1collagen, type VIII, alpha 1 (ENSG00000144810), score: 0.61 COMMD8COMM domain containing 8 (ENSG00000169019), score: 0.52 CPMcarboxypeptidase M (ENSG00000135678), score: 0.63 CPVLcarboxypeptidase, vitellogenic-like (ENSG00000106066), score: 0.5 CPXM2carboxypeptidase X (M14 family), member 2 (ENSG00000121898), score: 0.5 CTSAcathepsin A (ENSG00000064601), score: 0.54 CTSHcathepsin H (ENSG00000103811), score: 0.63 CUBNcubilin (intrinsic factor-cobalamin receptor) (ENSG00000107611), score: 0.67 CWH43cell wall biogenesis 43 C-terminal homolog (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000109182), score: 0.9 CXCL13chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 13 (ENSG00000156234), score: 0.69 CXorf38chromosome X open reading frame 38 (ENSG00000185753), score: 0.5 CYP24A1cytochrome P450, family 24, subfamily A, polypeptide 1 (ENSG00000019186), score: 0.6 DAB2disabled homolog 2, mitogen-responsive phosphoprotein (Drosophila) (ENSG00000153071), score: 0.6 DDCdopa decarboxylase (aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase) (ENSG00000132437), score: 0.5 DEFB1defensin, beta 1 (ENSG00000164825), score: 0.52 DENND1CDENN/MADD domain containing 1C (ENSG00000205744), score: 0.53 DEPDC6DEP domain containing 6 (ENSG00000155792), score: 0.6 DHDHdihydrodiol dehydrogenase (dimeric) (ENSG00000104808), score: 0.63 DHDPSLdihydrodipicolinate synthase-like, mitochondrial (ENSG00000241935), score: 0.53 DMRT2doublesex and mab-3 related transcription factor 2 (ENSG00000173253), score: 0.6 DNTTdeoxynucleotidyltransferase, terminal (ENSG00000107447), score: 0.71 DOCK8dedicator of cytokinesis 8 (ENSG00000107099), score: 0.57 DPEP1dipeptidase 1 (renal) (ENSG00000015413), score: 0.62 DSCR3Down syndrome critical region gene 3 (ENSG00000157538), score: 0.53 DUSP9dual specificity phosphatase 9 (ENSG00000130829), score: 0.6 EAF2ELL associated factor 2 (ENSG00000145088), score: 0.55 ECEL1endothelin converting enzyme-like 1 (ENSG00000171551), score: 0.68 EDARectodysplasin A receptor (ENSG00000135960), score: 0.85 EDN2endothelin 2 (ENSG00000127129), score: 0.64 EGFepidermal growth factor (ENSG00000138798), score: 0.65 EHFets homologous factor (ENSG00000135373), score: 0.7 ELP3elongation protein 3 homolog (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000134014), score: -0.54 ENAMenamelin (ENSG00000132464), score: 0.75 ENOSF1enolase superfamily member 1 (ENSG00000132199), score: 0.61 ENPEPglutamyl aminopeptidase (aminopeptidase A) (ENSG00000138792), score: 0.56 EPCAMepithelial cell adhesion molecule (ENSG00000119888), score: 0.6 EPS8L1EPS8-like 1 (ENSG00000131037), score: 0.71 ESM1endothelial cell-specific molecule 1 (ENSG00000164283), score: 0.53 ESRP1epithelial splicing regulatory protein 1 (ENSG00000104413), score: 0.72 EVC2Ellis van Creveld syndrome 2 (ENSG00000173040), score: 0.6 EVPLenvoplakin (ENSG00000167880), score: 0.57 F2RL1coagulation factor II (thrombin) receptor-like 1 (ENSG00000164251), score: 0.67 FADS2fatty acid desaturase 2 (ENSG00000134824), score: -0.6 FAM26Efamily with sequence similarity 26, member E (ENSG00000178033), score: 0.51 FAM3Bfamily with sequence similarity 3, member B (ENSG00000183844), score: 0.6 FARP1FERM, RhoGEF (ARHGEF) and pleckstrin domain protein 1 (chondrocyte-derived) (ENSG00000152767), score: 0.6 FERMT1fermitin family member 1 (ENSG00000101311), score: 0.93 FGFBP1fibroblast growth factor binding protein 1 (ENSG00000137440), score: 0.83 FMO1flavin containing monooxygenase 1 (ENSG00000010932), score: 0.68 FOXI1forkhead box I1 (ENSG00000168269), score: 0.66 FREM1FRAS1 related extracellular matrix 1 (ENSG00000164946), score: 0.58 FRMD1FERM domain containing 1 (ENSG00000153303), score: 0.5 FUT6fucosyltransferase 6 (alpha (1,3) fucosyltransferase) (ENSG00000156413), score: 0.62 FXYD2FXYD domain containing ion transport regulator 2 (ENSG00000137731), score: 0.67 GALNT10UDP-N-acetyl-alpha-D-galactosamine:polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase 10 (GalNAc-T10) (ENSG00000164574), score: 0.54 GALNT11UDP-N-acetyl-alpha-D-galactosamine:polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase 11 (GalNAc-T11) (ENSG00000178234), score: 0.52 GALNT14UDP-N-acetyl-alpha-D-galactosamine:polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase 14 (GalNAc-T14) (ENSG00000158089), score: 0.53 GATA3GATA binding protein 3 (ENSG00000107485), score: 0.62 GCET2germinal center expressed transcript 2 (ENSG00000174500), score: 0.71 GDF15growth differentiation factor 15 (ENSG00000130513), score: 0.64 GGCTgamma-glutamylcyclotransferase (ENSG00000006625), score: 0.56 GHRHgrowth hormone releasing hormone (ENSG00000118702), score: 0.54 GHRHRgrowth hormone releasing hormone receptor (ENSG00000106128), score: 0.97 GIPC2GIPC PDZ domain containing family, member 2 (ENSG00000137960), score: 0.56 GLYATglycine-N-acyltransferase (ENSG00000149124), score: 0.5 GNPDA1glucosamine-6-phosphate deaminase 1 (ENSG00000113552), score: 0.64 GP2glycoprotein 2 (zymogen granule membrane) (ENSG00000169347), score: 0.66 GPR110G protein-coupled receptor 110 (ENSG00000153292), score: 0.66 GPR124G protein-coupled receptor 124 (ENSG00000020181), score: -0.51 GPR160G protein-coupled receptor 160 (ENSG00000173890), score: 0.64 GPR172BG protein-coupled receptor 172B (ENSG00000132517), score: 0.66 GPRC6AG protein-coupled receptor, family C, group 6, member A (ENSG00000173612), score: 0.78 GRAMD2GRAM domain containing 2 (ENSG00000175318), score: 0.72 GRB7growth factor receptor-bound protein 7 (ENSG00000141738), score: 0.52 GRHL2grainyhead-like 2 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000083307), score: 0.62 GYLTL1Bglycosyltransferase-like 1B (ENSG00000165905), score: 0.51 HEPACAM2HEPACAM family member 2 (ENSG00000188175), score: 0.69 HES2hairy and enhancer of split 2 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000069812), score: 0.57 HIST1H3Ahistone cluster 1, H3a (ENSG00000112727), score: 0.55 HMX2H6 family homeobox 2 (ENSG00000188816), score: 0.61 HNF1BHNF1 homeobox B (ENSG00000108753), score: 0.6 HOXA10homeobox A10 (ENSG00000153807), score: 0.68 HOXA11homeobox A11 (ENSG00000005073), score: 0.77 HOXA3homeobox A3 (ENSG00000105997), score: 0.6 HOXA5homeobox A5 (ENSG00000106004), score: 0.71 HOXA7homeobox A7 (ENSG00000122592), score: 0.58 HOXA9homeobox A9 (ENSG00000078399), score: 0.73 HOXB5homeobox B5 (ENSG00000120075), score: 0.59 HOXB6homeobox B6 (ENSG00000108511), score: 0.67 HOXB7homeobox B7 (ENSG00000120087), score: 0.78 HOXC10homeobox C10 (ENSG00000180818), score: 0.64 HOXC11homeobox C11 (ENSG00000123388), score: 0.52 HOXC6homeobox C6 (ENSG00000197757), score: 0.66 HOXC8homeobox C8 (ENSG00000037965), score: 0.82 HOXC9homeobox C9 (ENSG00000180806), score: 0.68 HOXD1homeobox D1 (ENSG00000128645), score: 0.57 HOXD10homeobox D10 (ENSG00000128710), score: 0.63 HOXD3homeobox D3 (ENSG00000128652), score: 0.74 HOXD4homeobox D4 (ENSG00000170166), score: 0.71 HOXD8homeobox D8 (ENSG00000175879), score: 0.64 HOXD9homeobox D9 (ENSG00000128709), score: 0.63 HSD11B2hydroxysteroid (11-beta) dehydrogenase 2 (ENSG00000176387), score: 0.67 IGBP1immunoglobulin (CD79A) binding protein 1 (ENSG00000089289), score: 0.5 IL18interleukin 18 (interferon-gamma-inducing factor) (ENSG00000150782), score: 0.55 ILDR1immunoglobulin-like domain containing receptor 1 (ENSG00000145103), score: 0.61 IMPA2inositol(myo)-1(or 4)-monophosphatase 2 (ENSG00000141401), score: 0.53 INSRRinsulin receptor-related receptor (ENSG00000027644), score: 0.63 IRF3interferon regulatory factor 3 (ENSG00000126456), score: 0.51 IRF5interferon regulatory factor 5 (ENSG00000128604), score: 0.5 ISXintestine-specific homeobox (ENSG00000175329), score: 0.9 ITGA2integrin, alpha 2 (CD49B, alpha 2 subunit of VLA-2 receptor) (ENSG00000164171), score: 0.5 ITGB3integrin, beta 3 (platelet glycoprotein IIIa, antigen CD61) (ENSG00000056345), score: 0.55 ITGB7integrin, beta 7 (ENSG00000139626), score: 0.52 IVNS1ABPinfluenza virus NS1A binding protein (ENSG00000116679), score: 0.5 KCNH6potassium voltage-gated channel, subfamily H (eag-related), member 6 (ENSG00000173826), score: 0.66 KCNJ1potassium inwardly-rectifying channel, subfamily J, member 1 (ENSG00000151704), score: 0.7 KCNJ16potassium inwardly-rectifying channel, subfamily J, member 16 (ENSG00000153822), score: 0.58 KCNK5potassium channel, subfamily K, member 5 (ENSG00000164626), score: 0.53 KIAA0020KIAA0020 (ENSG00000080608), score: 0.51 KIAA1191KIAA1191 (ENSG00000122203), score: 0.52 KIF12kinesin family member 12 (ENSG00000136883), score: 0.55 KLklotho (ENSG00000133116), score: 0.71 KLHDC7Akelch domain containing 7A (ENSG00000179023), score: 0.65 KRT24keratin 24 (ENSG00000167916), score: 0.58 LAD1ladinin 1 (ENSG00000159166), score: 0.58 LGALS2lectin, galactoside-binding, soluble, 2 (ENSG00000100079), score: 0.55 LIFleukemia inhibitory factor (cholinergic differentiation factor) (ENSG00000128342), score: 0.58 LRP1low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1 (ENSG00000123384), score: -0.54 LRRC19leucine rich repeat containing 19 (ENSG00000184434), score: 0.58 LRRN4leucine rich repeat neuronal 4 (ENSG00000125872), score: 0.79 LTFlactotransferrin (ENSG00000012223), score: 0.69 MACC1metastasis associated in colon cancer 1 (ENSG00000183742), score: 0.56 MAP4K4mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase kinase 4 (ENSG00000071054), score: -0.52 MICAL2microtubule associated monoxygenase, calponin and LIM domain containing 2 (ENSG00000133816), score: -0.52 MIOXmyo-inositol oxygenase (ENSG00000100253), score: 0.67 MMEmembrane metallo-endopeptidase (ENSG00000196549), score: 0.56 MMP7matrix metallopeptidase 7 (matrilysin, uterine) (ENSG00000137673), score: 0.62 MS4A10membrane-spanning 4-domains, subfamily A, member 10 (ENSG00000172689), score: 0.63 MTMR11myotubularin related protein 11 (ENSG00000014914), score: 0.55 MUC1mucin 1, cell surface associated (ENSG00000185499), score: 0.57 MUC20mucin 20, cell surface associated (ENSG00000176945), score: 0.67 MYO3Bmyosin IIIB (ENSG00000071909), score: 0.66 NBEAL1neurobeachin-like 1 (ENSG00000144426), score: 0.51 NEK8NIMA (never in mitosis gene a)- related kinase 8 (ENSG00000160602), score: 0.53 NHEJ1nonhomologous end-joining factor 1 (ENSG00000187736), score: 0.58 NHSNance-Horan syndrome (congenital cataracts and dental anomalies) (ENSG00000188158), score: 0.65 NINJ2ninjurin 2 (ENSG00000171840), score: -0.53 NLRC4NLR family, CARD domain containing 4 (ENSG00000091106), score: 0.56 NOX4NADPH oxidase 4 (ENSG00000086991), score: 0.57 NPHS2nephrosis 2, idiopathic, steroid-resistant (podocin) (ENSG00000116218), score: 0.66 NPNTnephronectin (ENSG00000168743), score: 0.5 NUAK2NUAK family, SNF1-like kinase, 2 (ENSG00000163545), score: 0.52 OCIAD2OCIA domain containing 2 (ENSG00000145247), score: 0.52 OLFM4olfactomedin 4 (ENSG00000102837), score: 0.71 OLR1oxidized low density lipoprotein (lectin-like) receptor 1 (ENSG00000173391), score: 0.68 OSGEPL1O-sialoglycoprotein endopeptidase-like 1 (ENSG00000128694), score: 0.5 OXGR1oxoglutarate (alpha-ketoglutarate) receptor 1 (ENSG00000165621), score: 0.53 PAPPApregnancy-associated plasma protein A, pappalysin 1 (ENSG00000182752), score: 0.52 PAQR5progestin and adipoQ receptor family member V (ENSG00000137819), score: 0.56 PARD6Bpar-6 partitioning defective 6 homolog beta (C. elegans) (ENSG00000124171), score: 0.57 PAX2paired box 2 (ENSG00000075891), score: 0.56 PAX8paired box 8 (ENSG00000125618), score: 0.63 PDZK1IP1PDZK1 interacting protein 1 (ENSG00000162366), score: 0.71 PGPEP1pyroglutamyl-peptidase I (ENSG00000130517), score: 0.56 PID1phosphotyrosine interaction domain containing 1 (ENSG00000153823), score: -0.51 PIGRpolymeric immunoglobulin receptor (ENSG00000162896), score: 0.54 PKHD1polycystic kidney and hepatic disease 1 (autosomal recessive) (ENSG00000170927), score: 0.57 PLA2G4Fphospholipase A2, group IVF (ENSG00000168907), score: 0.67 PLA2R1phospholipase A2 receptor 1, 180kDa (ENSG00000153246), score: 0.59 PLCG2phospholipase C, gamma 2 (phosphatidylinositol-specific) (ENSG00000197943), score: 0.51 PLTPphospholipid transfer protein (ENSG00000100979), score: -0.54 POLMpolymerase (DNA directed), mu (ENSG00000122678), score: 0.53 POU2F3POU class 2 homeobox 3 (ENSG00000137709), score: 0.53 PPA1pyrophosphatase (inorganic) 1 (ENSG00000180817), score: -0.54 PRKAB1protein kinase, AMP-activated, beta 1 non-catalytic subunit (ENSG00000111725), score: 0.56 PROM2prominin 2 (ENSG00000155066), score: 0.61 PRR15proline rich 15 (ENSG00000176532), score: 0.58 PRR15Lproline rich 15-like (ENSG00000167183), score: 0.55 PRSS8protease, serine, 8 (ENSG00000052344), score: 0.54 PSMD9proteasome (prosome, macropain) 26S subunit, non-ATPase, 9 (ENSG00000110801), score: 0.5 PTGER3prostaglandin E receptor 3 (subtype EP3) (ENSG00000050628), score: 0.57 PTH1Rparathyroid hormone 1 receptor (ENSG00000160801), score: 0.51 PTPLAD2protein tyrosine phosphatase-like A domain containing 2 (ENSG00000188921), score: 0.51 R3HDMLR3H domain containing-like (ENSG00000101074), score: 0.69 RAB25RAB25, member RAS oncogene family (ENSG00000132698), score: 0.59 RAB40ARAB40A, member RAS oncogene family (ENSG00000172476), score: 0.53 RAB7L1RAB7, member RAS oncogene family-like 1 (ENSG00000117280), score: 0.57 RABEP2rabaptin, RAB GTPase binding effector protein 2 (ENSG00000177548), score: 0.54 RAG1recombination activating gene 1 (ENSG00000166349), score: 0.5 RASSF6Ras association (RalGDS/AF-6) domain family member 6 (ENSG00000169435), score: 0.54 RBBP8retinoblastoma binding protein 8 (ENSG00000101773), score: 0.59 RBP5retinol binding protein 5, cellular (ENSG00000139194), score: 0.5 RENBPrenin binding protein (ENSG00000102032), score: 0.55 RERGRAS-like, estrogen-regulated, growth inhibitor (ENSG00000134533), score: 0.53 RGL3ral guanine nucleotide dissociation stimulator-like 3 (ENSG00000205517), score: 0.52 RHCGRh family, C glycoprotein (ENSG00000140519), score: 0.61 RILPL2Rab interacting lysosomal protein-like 2 (ENSG00000150977), score: 0.53 RNLSrenalase, FAD-dependent amine oxidase (ENSG00000184719), score: 0.57 RQCD1RCD1 required for cell differentiation1 homolog (S. pombe) (ENSG00000144580), score: -0.57 RTCD1RNA terminal phosphate cyclase domain 1 (ENSG00000137996), score: 0.61 RUFY1RUN and FYVE domain containing 1 (ENSG00000176783), score: 0.51 S100A2S100 calcium binding protein A2 (ENSG00000196754), score: 0.51 SCGB2A1secretoglobin, family 2A, member 1 (ENSG00000124939), score: 0.77 SCINscinderin (ENSG00000006747), score: 0.64 SCNN1Asodium channel, nonvoltage-gated 1 alpha (ENSG00000111319), score: 0.58 SCNN1Bsodium channel, nonvoltage-gated 1, beta (ENSG00000168447), score: 0.55 SCNN1Gsodium channel, nonvoltage-gated 1, gamma (ENSG00000166828), score: 0.61 SCTRsecretin receptor (ENSG00000080293), score: 0.59 SEC23ASec23 homolog A (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000100934), score: -0.56 SEMA3Gsema domain, immunoglobulin domain (Ig), short basic domain, secreted, (semaphorin) 3G (ENSG00000010319), score: 0.53 SERINC3serine incorporator 3 (ENSG00000132824), score: -0.59 SESN2sestrin 2 (ENSG00000130766), score: 0.5 SFXN2sideroflexin 2 (ENSG00000156398), score: 0.55 SH3YL1SH3 domain containing, Ysc84-like 1 (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000035115), score: 0.56 SIM1single-minded homolog 1 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000112246), score: 0.74 SIM2single-minded homolog 2 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000159263), score: 0.55 SLC10A2solute carrier family 10 (sodium/bile acid cotransporter family), member 2 (ENSG00000125255), score: 0.96 SLC12A1solute carrier family 12 (sodium/potassium/chloride transporters), member 1 (ENSG00000074803), score: 0.67 SLC12A3solute carrier family 12 (sodium/chloride transporters), member 3 (ENSG00000070915), score: 0.69 SLC13A1solute carrier family 13 (sodium/sulfate symporters), member 1 (ENSG00000081800), score: 0.69 SLC13A3solute carrier family 13 (sodium-dependent dicarboxylate transporter), member 3 (ENSG00000158296), score: 0.61 SLC15A2solute carrier family 15 (H+/peptide transporter), member 2 (ENSG00000163406), score: 0.52 SLC16A12solute carrier family 16, member 12 (monocarboxylic acid transporter 12) (ENSG00000152779), score: 0.53 SLC16A4solute carrier family 16, member 4 (monocarboxylic acid transporter 5) (ENSG00000168679), score: 0.7 SLC16A9solute carrier family 16, member 9 (monocarboxylic acid transporter 9) (ENSG00000165449), score: 0.53 SLC17A1solute carrier family 17 (sodium phosphate), member 1 (ENSG00000124568), score: 0.57 SLC17A3solute carrier family 17 (sodium phosphate), member 3 (ENSG00000124564), score: 0.6 SLC22A11solute carrier family 22 (organic anion/urate transporter), member 11 (ENSG00000168065), score: 0.66 SLC22A12solute carrier family 22 (organic anion/urate transporter), member 12 (ENSG00000197891), score: 0.75 SLC22A2solute carrier family 22 (organic cation transporter), member 2 (ENSG00000112499), score: 0.72 SLC22A5solute carrier family 22 (organic cation/carnitine transporter), member 5 (ENSG00000197375), score: 0.56 SLC22A6solute carrier family 22 (organic anion transporter), member 6 (ENSG00000197901), score: 0.67 SLC22A8solute carrier family 22 (organic anion transporter), member 8 (ENSG00000149452), score: 0.69 SLC23A3solute carrier family 23 (nucleobase transporters), member 3 (ENSG00000213901), score: 0.52 SLC26A7solute carrier family 26, member 7 (ENSG00000147606), score: 0.67 SLC27A2solute carrier family 27 (fatty acid transporter), member 2 (ENSG00000140284), score: 0.5 SLC2A9solute carrier family 2 (facilitated glucose transporter), member 9 (ENSG00000109667), score: 0.68 SLC30A8solute carrier family 30 (zinc transporter), member 8 (ENSG00000164756), score: 0.76 SLC34A1solute carrier family 34 (sodium phosphate), member 1 (ENSG00000131183), score: 0.72 SLC34A2solute carrier family 34 (sodium phosphate), member 2 (ENSG00000157765), score: 0.61 SLC34A3solute carrier family 34 (sodium phosphate), member 3 (ENSG00000198569), score: 0.7 SLC36A3solute carrier family 36 (proton/amino acid symporter), member 3 (ENSG00000186334), score: 0.52 SLC38A11solute carrier family 38, member 11 (ENSG00000169507), score: 0.53 SLC3A1solute carrier family 3 (cystine, dibasic and neutral amino acid transporters, activator of cystine, dibasic and neutral amino acid transport), member 1 (ENSG00000138079), score: 0.54 SLC3A2solute carrier family 3 (activators of dibasic and neutral amino acid transport), member 2 (ENSG00000168003), score: 0.55 SLC44A4solute carrier family 44, member 4 (ENSG00000204385), score: 0.73 SLC47A1solute carrier family 47, member 1 (ENSG00000142494), score: 0.55 SLC47A2solute carrier family 47, member 2 (ENSG00000180638), score: 0.78 SLC4A1solute carrier family 4, anion exchanger, member 1 (erythrocyte membrane protein band 3, Diego blood group) (ENSG00000004939), score: 0.66 SLC4A9solute carrier family 4, sodium bicarbonate cotransporter, member 9 (ENSG00000113073), score: 0.68 SLC5A10solute carrier family 5 (sodium/glucose cotransporter), member 10 (ENSG00000154025), score: 0.6 SLC5A12solute carrier family 5 (sodium/glucose cotransporter), member 12 (ENSG00000148942), score: 0.75 SLC5A2solute carrier family 5 (sodium/glucose cotransporter), member 2 (ENSG00000140675), score: 0.53 SLC5A9solute carrier family 5 (sodium/glucose cotransporter), member 9 (ENSG00000117834), score: 0.55 SLC6A19solute carrier family 6 (neutral amino acid transporter), member 19 (ENSG00000174358), score: 0.66 SLC7A13solute carrier family 7, (cationic amino acid transporter, y+ system) member 13 (ENSG00000164893), score: 0.64 SLC7A7solute carrier family 7 (cationic amino acid transporter, y+ system), member 7 (ENSG00000155465), score: 0.55 SLC7A8solute carrier family 7 (amino acid transporter, L-type), member 8 (ENSG00000092068), score: 0.65 SLC7A9solute carrier family 7 (cationic amino acid transporter, y+ system), member 9 (ENSG00000021488), score: 0.51 SLC9A4solute carrier family 9 (sodium/hydrogen exchanger), member 4 (ENSG00000180251), score: 0.66 SLCO4C1solute carrier organic anion transporter family, member 4C1 (ENSG00000173930), score: 0.68 SLFN12schlafen family member 12 (ENSG00000172123), score: 0.56 SMTNL2smoothelin-like 2 (ENSG00000188176), score: 0.59 SNX24sorting nexin 24 (ENSG00000064652), score: 0.57 SNX29sorting nexin 29 (ENSG00000048471), score: 0.5 SNX5sorting nexin 5 (ENSG00000089006), score: 0.5 SOSTsclerostin (ENSG00000167941), score: 0.61 SPP1secreted phosphoprotein 1 (ENSG00000118785), score: 0.5 ST14suppression of tumorigenicity 14 (colon carcinoma) (ENSG00000149418), score: 0.58 STK32Bserine/threonine kinase 32B (ENSG00000152953), score: 0.5 STRA6stimulated by retinoic acid gene 6 homolog (mouse) (ENSG00000137868), score: 0.65 SULT1C2sulfotransferase family, cytosolic, 1C, member 2 (ENSG00000198203), score: 0.62 SULT2B1sulfotransferase family, cytosolic, 2B, member 1 (ENSG00000088002), score: 0.77 SUMF1sulfatase modifying factor 1 (ENSG00000144455), score: 0.55 SYT10synaptotagmin X (ENSG00000110975), score: 0.53 TAAR1trace amine associated receptor 1 (ENSG00000146399), score: 0.59 TACSTD2tumor-associated calcium signal transducer 2 (ENSG00000184292), score: 0.5 TBX10T-box 10 (ENSG00000167800), score: 0.88 TBX2T-box 2 (ENSG00000121068), score: 0.52 TFAP2Atranscription factor AP-2 alpha (activating enhancer binding protein 2 alpha) (ENSG00000137203), score: 0.65 TFAP2Btranscription factor AP-2 beta (activating enhancer binding protein 2 beta) (ENSG00000008196), score: 0.51 TFCP2L1transcription factor CP2-like 1 (ENSG00000115112), score: 0.6 TFECtranscription factor EC (ENSG00000105967), score: 0.67 TINAGtubulointerstitial nephritis antigen (ENSG00000137251), score: 0.75 TLCD2TLC domain containing 2 (ENSG00000185561), score: 0.59 TM7SF4transmembrane 7 superfamily member 4 (ENSG00000164935), score: 0.55 TMCC1transmembrane and coiled-coil domain family 1 (ENSG00000172765), score: -0.53 TMEM106Atransmembrane protein 106A (ENSG00000184988), score: 0.57 TMEM138transmembrane protein 138 (ENSG00000149483), score: 0.5 TMEM139transmembrane protein 139 (ENSG00000178826), score: 0.59 TMEM171transmembrane protein 171 (ENSG00000157111), score: 0.72 TMEM174transmembrane protein 174 (ENSG00000164325), score: 0.84 TMEM27transmembrane protein 27 (ENSG00000147003), score: 0.6 TMEM72transmembrane protein 72 (ENSG00000187783), score: 0.61 TMIGD1transmembrane and immunoglobulin domain containing 1 (ENSG00000182271), score: 0.62 TMPRSS2transmembrane protease, serine 2 (ENSG00000184012), score: 0.52 TNFAIP8tumor necrosis factor, alpha-induced protein 8 (ENSG00000145779), score: 0.54 TNFSF15tumor necrosis factor (ligand) superfamily, member 15 (ENSG00000181634), score: 0.66 TPCN2two pore segment channel 2 (ENSG00000162341), score: 0.52 TPH1tryptophan hydroxylase 1 (ENSG00000129167), score: 0.55 TRPV4transient receptor potential cation channel, subfamily V, member 4 (ENSG00000111199), score: 0.58 TSPAN1tetraspanin 1 (ENSG00000117472), score: 0.58 TSPAN10tetraspanin 10 (ENSG00000182612), score: 0.55 UMODuromodulin (ENSG00000169344), score: 0.67 UNC5CLunc-5 homolog C (C. elegans)-like (ENSG00000124602), score: 0.65 UPP2uridine phosphorylase 2 (ENSG00000007001), score: 0.74 USH1CUsher syndrome 1C (autosomal recessive, severe) (ENSG00000006611), score: 0.66 VAV3vav 3 guanine nucleotide exchange factor (ENSG00000134215), score: 0.57 VDRvitamin D (1,25- dihydroxyvitamin D3) receptor (ENSG00000111424), score: 0.79 WDR72WD repeat domain 72 (ENSG00000166415), score: 0.58 WDR73WD repeat domain 73 (ENSG00000177082), score: 0.52 WFDC2WAP four-disulfide core domain 2 (ENSG00000101443), score: 0.6 WNK4WNK lysine deficient protein kinase 4 (ENSG00000126562), score: 0.69 WNT8Bwingless-type MMTV integration site family, member 8B (ENSG00000075290), score: 0.7 XPNPEP2X-prolyl aminopeptidase (aminopeptidase P) 2, membrane-bound (ENSG00000122121), score: 0.51 ZCWPW1zinc finger, CW type with PWWP domain 1 (ENSG00000078487), score: -0.52 ZFATzinc finger and AT hook domain containing (ENSG00000066827), score: 0.52 ZNF467zinc finger protein 467 (ENSG00000181444), score: 0.54 ZNF750zinc finger protein 750 (ENSG00000141579), score: 0.69 ZNF789zinc finger protein 789 (ENSG00000198556), score: 0.57
| Id | species | tissue | sex | individual |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ggo_kd_f_ca1 | ggo | kd | f | _ |
| ppy_kd_f_ca1 | ppy | kd | f | _ |
| ggo_kd_m_ca1 | ggo | kd | m | _ |
| ppy_kd_m_ca1 | ppy | kd | m | _ |