
Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

urea cycle
A cyclic metabolic pathway that converts waste nitrogen in the form of ammonium to urea.
metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways, including anabolism and catabolism, by which living organisms transform chemical substances. Metabolic processes typically transform small molecules, but also include macromolecular processes such as DNA repair and replication, and protein synthesis and degradation.
system process
A multicellular organismal process carried out by any of the organs or tissues in an organ system. An organ system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a biological objective.
alcohol metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving alcohols, any of a class of compounds containing one or more hydroxyl groups attached to a saturated carbon atom.
organic acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving organic acids, any acidic compound containing carbon in covalent linkage.
cellular amino acid and derivative metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving amino acids, organic acids containing one or more amino substituents, and compounds derived from amino acids, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular amino acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving amino acids, organic acids containing one or more amino substituents.
lipid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving lipids, compounds soluble in an organic solvent but not, or sparingly, in an aqueous solvent. Includes fatty acids; neutral fats, other fatty-acid esters, and soaps; long-chain (fatty) alcohols and waxes; sphingoids and other long-chain bases; glycolipids, phospholipids and sphingolipids; and carotenes, polyprenols, sterols, terpenes and other isoprenoids.
steroid catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of steroids, compounds with a 1,2,cyclopentanoperhydrophenanthrene nucleus.
nitrogen compound metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving various organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds; includes nitrogen fixation, nitrification, denitrification, assimilatory/dissimilatory nitrate reduction and the interconversion of nitrogenous organic matter and ammonium.
transport
The directed movement of substances (such as macromolecules, small molecules, ions) into, out of, within or between cells, or within a multicellular organism by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
lipid transport
The directed movement of lipids into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore. Lipids are compounds soluble in an organic solvent but not, or sparingly, in an aqueous solvent.
digestion
The whole of the physical, chemical, and biochemical processes carried out by multicellular organisms to break down ingested nutrients into components that may be easily absorbed and directed into metabolism.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
steroid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving steroids, compounds with a 1,2,cyclopentanoperhydrophenanthrene nucleus.
bile acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving bile acids, any of a group of steroid carboxylic acids occurring in bile, where they are present as the sodium salts of their amides with glycine or taurine.
catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of substances, including the breakdown of carbon compounds with the liberation of energy for use by the cell or organism.
biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances; typically the energy-requiring part of metabolism in which simpler substances are transformed into more complex ones.
amine metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving any organic compound that is weakly basic in character and contains an amino or a substituted amino group, as carried out by individual cells. Amines are called primary, secondary, or tertiary according to whether one, two, or three carbon atoms are attached to the nitrogen atom.
response to drug
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a drug stimulus. A drug is a substance used in the diagnosis, treatment or prevention of a disease.
response to external stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an external stimulus.
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
response to extracellular stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an extracellular stimulus.
lipid localization
Any process by which a lipid is transported to, or maintained in, a specific location.
sterol transport
The directed movement of sterols into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore. Sterols are steroids with one or more hydroxyl groups and a hydrocarbon side-chain in the molecule.
lipid catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of lipids, compounds soluble in an organic solvent but not, or sparingly, in an aqueous solvent.
organic acid catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of organic acids, any acidic compound containing carbon in covalent linkage.
drug metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving a drug, a substance used in the diagnosis, treatment or prevention of a disease; as used here antibiotic substances (see antibiotic metabolism) are considered to be drugs, even if not used in medical or veterinary practice.
urea metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving urea, the water soluble compound O=C-(NH2)2, produced in the liver by the ornithine cycle. It is the main nitrogen-containing excretion product in ureotelic animals.
carboxylic acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving carboxylic acids, any organic acid containing one or more carboxyl (COOH) groups or anions (COO-).
digestive system process
A physical, chemical, or biochemical process carried out by living organisms to break down ingested nutrients into components that may be easily absorbed and directed into metabolism.
intestinal cholesterol absorption
Uptake of cholesterol into the blood by absorption from the small intestine.
cholesterol transport
The directed movement of cholesterol, cholest-5-en-3-beta-ol, into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
bile acid catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of bile acids, any of a group of steroid carboxylic acids occurring in bile.
response to nutrient levels
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus reflecting the presence, absence, or concentration of nutrients.
multicellular organismal process
Any biological process, occurring at the level of a multicellular organism, pertinent to its function.
monocarboxylic acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving monocarboxylic acids, any organic acid containing one carboxyl (COOH) group or anion (COO-).
macromolecule localization
Any process by which a macromolecule is transported to, or maintained in, a specific location.
cholesterol efflux
The directed movement of cholesterol, cholest-5-en-3-beta-ol, out of a cell or organelle.
cellular nitrogen compound metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving various organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular ketone metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving any of a class of organic compounds that contain the carbonyl group, CO, and in which the carbonyl group is bonded only to carbon atoms, as carried out by individual cells. The general formula for a ketone is RCOR, where R and R are alkyl or aryl groups.
response to chemical stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a chemical stimulus.
homeostatic process
Any biological process involved in the maintenance of an internal steady-state.
drug catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of a drug, a substance used in the diagnosis, treatment or prevention of a disease.
exogenous drug catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of a drug that has originated externally to the cell or organism.
oxoacid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving any oxoacid; an oxoacid is a compound which contains oxygen, at least one other element, and at least one hydrogen bound to oxygen, and which produces a conjugate base by loss of positive hydrogen ion(s) (hydrons).
cellular amide metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving an amide, any derivative of an oxoacid in which an acidic hydroxy group has been replaced by an amino or substituted amino group, as carried out by individual cells.
amide biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of an amide, any derivative of an oxoacid in which an acidic hydroxy group has been replaced by an amino or substituted amino group.
cellular amine metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving any organic compound that is weakly basic in character and contains an amino or a substituted amino group, as carried out by individual cells. Amines are called primary, secondary, or tertiary according to whether one, two, or three carbon atoms are attached to the nitrogen atom.
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
primary metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving those compounds which are formed as a part of the normal anabolic and catabolic processes. These processes take place in most, if not all, cells of the organism.
lipid digestion
The whole of the physical, chemical, and biochemical processes carried out by living organisms to break down ingested lipids into components that may be easily absorbed and directed into metabolism.
cellular catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of substances, carried out by individual cells.
cellular biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
cellular nitrogen compound biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds.
small molecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving small molecules, any monomeric molecule of small relative molecular mass.
small molecule catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of small molecules, any monomeric molecule of small relative molecular mass.
carboxylic acid catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of carboxylic acids, any organic acid containing one or more carboxyl (-COOH) groups.
chemical homeostasis
Any biological process involved in the maintenance of an internal steady-state of a chemical.
intestinal absorption
Any process by which nutrients are taken up from the contents of the intestine.
response to stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
localization
Any process by which a cell, a substance, or a cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, is transported to, and/or maintained in a specific location.
establishment of localization
The directed movement of a cell, substance or cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, to a specific location.
lipid homeostasis
Any process involved in the maintenance of an internal steady-state of lipid within an organism or cell.
biological regulation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of any biological process, quality or function.
regulation of biological quality
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological quality. A biological quality is a measurable attribute of an organism or part of an organism, such as size, mass, shape, color, etc.
all
NA
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
establishment of localization
The directed movement of a cell, substance or cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, to a specific location.
cellular nitrogen compound metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving various organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of substances, carried out by individual cells.
cellular biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
cellular amino acid and derivative metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving amino acids, organic acids containing one or more amino substituents, and compounds derived from amino acids, as carried out by individual cells.
organic acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving organic acids, any acidic compound containing carbon in covalent linkage.
cellular amino acid and derivative metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving amino acids, organic acids containing one or more amino substituents, and compounds derived from amino acids, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular ketone metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving any of a class of organic compounds that contain the carbonyl group, CO, and in which the carbonyl group is bonded only to carbon atoms, as carried out by individual cells. The general formula for a ketone is RCOR, where R and R are alkyl or aryl groups.
small molecule catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of small molecules, any monomeric molecule of small relative molecular mass.
digestive system process
A physical, chemical, or biochemical process carried out by living organisms to break down ingested nutrients into components that may be easily absorbed and directed into metabolism.
cellular amine metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving any organic compound that is weakly basic in character and contains an amino or a substituted amino group, as carried out by individual cells. Amines are called primary, secondary, or tertiary according to whether one, two, or three carbon atoms are attached to the nitrogen atom.
organic acid catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of organic acids, any acidic compound containing carbon in covalent linkage.
cellular nitrogen compound biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds.
organic acid catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of organic acids, any acidic compound containing carbon in covalent linkage.
drug catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of a drug, a substance used in the diagnosis, treatment or prevention of a disease.
oxoacid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving any oxoacid; an oxoacid is a compound which contains oxygen, at least one other element, and at least one hydrogen bound to oxygen, and which produces a conjugate base by loss of positive hydrogen ion(s) (hydrons).
lipid catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of lipids, compounds soluble in an organic solvent but not, or sparingly, in an aqueous solvent.
lipid transport
The directed movement of lipids into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore. Lipids are compounds soluble in an organic solvent but not, or sparingly, in an aqueous solvent.
cellular amino acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving amino acids, organic acids containing one or more amino substituents.
urea metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving urea, the water soluble compound O=C-(NH2)2, produced in the liver by the ornithine cycle. It is the main nitrogen-containing excretion product in ureotelic animals.
amide biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of an amide, any derivative of an oxoacid in which an acidic hydroxy group has been replaced by an amino or substituted amino group.
exogenous drug catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of a drug that has originated externally to the cell or organism.
steroid catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of steroids, compounds with a 1,2,cyclopentanoperhydrophenanthrene nucleus.
intestinal cholesterol absorption
Uptake of cholesterol into the blood by absorption from the small intestine.
urea cycle
A cyclic metabolic pathway that converts waste nitrogen in the form of ammonium to urea.
bile acid catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of bile acids, any of a group of steroid carboxylic acids occurring in bile.
cellular amino acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving amino acids, organic acids containing one or more amino substituents.
carboxylic acid catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of carboxylic acids, any organic acid containing one or more carboxyl (-COOH) groups.
bile acid catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of bile acids, any of a group of steroid carboxylic acids occurring in bile.
intestinal cholesterol absorption
Uptake of cholesterol into the blood by absorption from the small intestine.
bile acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving bile acids, any of a group of steroid carboxylic acids occurring in bile, where they are present as the sodium salts of their amides with glycine or taurine.

plasma membrane
The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
cell fraction
A generic term for parts of cells prepared by disruptive biochemical techniques.
membrane
Double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
integral to membrane
Penetrating at least one phospholipid bilayer of a membrane. May also refer to the state of being buried in the bilayer with no exposure outside the bilayer. When used to describe a protein, indicates that all or part of the peptide sequence is embedded in the membrane.
extracellular region
The space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.
integral to plasma membrane
Penetrating at least one phospholipid bilayer of a plasma membrane. May also refer to the state of being buried in the bilayer with no exposure outside the bilayer.
cellular_component
The part of a cell or its extracellular environment in which a gene product is located. A gene product may be located in one or more parts of a cell and its location may be as specific as a particular macromolecular complex, that is, a stable, persistent association of macromolecules that function together.
membrane attack complex
A protein complex produced by sequentially activated components of the complement cascade inserted into a target cell membrane and forming a pore leading to cell lysis via ion and water flow.
cell
The basic structural and functional unit of all organisms. Includes the plasma membrane and any external encapsulating structures such as the cell wall and cell envelope.
membrane fraction
That fraction of cells, prepared by disruptive biochemical methods, that includes the plasma and other membranes.
insoluble fraction
That fraction of cells, prepared by disruptive biochemical methods, that is not soluble in water.
microsome
Any of the small, heterogeneous, artifactual, vesicular particles, 50-150 nm in diameter, that are formed when some eukaryotic cells are homogenized and that sediment on centrifugation at 100000 g.
pore complex
Any small opening in a membrane that allows the passage of gases and/or liquids.
intrinsic to membrane
Located in a membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
intrinsic to plasma membrane
Located in the plasma membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
macromolecular complex
A stable assembly of two or more macromolecules, i.e. proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates or lipids, in which the constituent parts function together.
vesicular fraction
Any of the small, heterogeneous, artifactual, vesicular particles that are formed when some cells are homogenized.
protein complex
Any macromolecular complex composed of two or more polypeptide subunits, which may or may not be identical. Protein complexes may have other associated non-protein prosthetic groups, such as nucleotides, metal ions or other small molecules.
membrane part
Any constituent part of a membrane, a double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
plasma membrane part
Any constituent part of the plasma membrane, the membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
all
NA
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
membrane part
Any constituent part of a membrane, a double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
plasma membrane part
Any constituent part of the plasma membrane, the membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
membrane attack complex
A protein complex produced by sequentially activated components of the complement cascade inserted into a target cell membrane and forming a pore leading to cell lysis via ion and water flow.
intrinsic to plasma membrane
Located in the plasma membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
pore complex
Any small opening in a membrane that allows the passage of gases and/or liquids.
integral to plasma membrane
Penetrating at least one phospholipid bilayer of a plasma membrane. May also refer to the state of being buried in the bilayer with no exposure outside the bilayer.
membrane attack complex
A protein complex produced by sequentially activated components of the complement cascade inserted into a target cell membrane and forming a pore leading to cell lysis via ion and water flow.

molecular_function
Elemental activities, such as catalysis or binding, describing the actions of a gene product at the molecular level. A given gene product may exhibit one or more molecular functions.
enzyme inhibitor activity
Stops, prevents or reduces the activity of an enzyme.
endopeptidase inhibitor activity
Stops, prevents or reduces the activity of an endopeptidase, any enzyme that hydrolyzes nonterminal peptide bonds in polypeptides.
transporter activity
Enables the directed movement of substances (such as macromolecules, small molecules, ions) into, out of, within or between cells.
transmembrane transporter activity
Enables the transfer of a substance from one side of a membrane to the other.
organic acid transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of organic acids, any acidic compound containing carbon in covalent linkage, from one side of the membrane to the other.
monocarboxylic acid transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of monocarboxylic acids from one side of the membrane to the other. A monocarboxylic acid is an organic acid with one COOH group.
endopeptidase regulator activity
Modulates the activity of a peptidase, any enzyme that hydrolyzes nonterminal peptide bonds in polypeptides.
bile acid transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of bile acid from one side of the membrane to the other. Bile acids are any of a group of steroid carboxylic acids occurring in bile, where they are present as the sodium salts of their amides with glycine or taurine.
peptidase inhibitor activity
Stops, prevents or reduces the activity of a peptidase, any enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis peptide bonds.
substrate-specific transmembrane transporter activity
Enables the transfer of a specific substance or group of related substances from one side of a membrane to the other.
substrate-specific transporter activity
Enables the directed movement of a specific substance or group of related substances (such as macromolecules, small molecules, ions) into, out of, within or between cells.
enzyme regulator activity
Modulates the activity of an enzyme.
carboxylic acid transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of carboxylic acids from one side of the membrane to the other. Carboxylic acids are organic acids containing one or more carboxyl (COOH) groups or anions (COO-).
peptidase regulator activity
Modulates the activity of a peptidase, any enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis peptide bonds.
all
NA
substrate-specific transmembrane transporter activity
Enables the transfer of a specific substance or group of related substances from one side of a membrane to the other.
peptidase inhibitor activity
Stops, prevents or reduces the activity of a peptidase, any enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis peptide bonds.
endopeptidase inhibitor activity
Stops, prevents or reduces the activity of an endopeptidase, any enzyme that hydrolyzes nonterminal peptide bonds in polypeptides.
| Id | Pvalue | ExpCount | Count | Size | Term |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 00830 | 4.686e-04 | 0.1499 | 4 | 25 | Retinol metabolism |
| 01100 | 5.275e-03 | 4.827 | 13 | 805 | Metabolic pathways |
| 00980 | 1.040e-02 | 0.1559 | 3 | 26 | Metabolism of xenobiotics by cytochrome P450 |
| 00982 | 1.147e-02 | 0.1619 | 3 | 27 | Drug metabolism - cytochrome P450 |
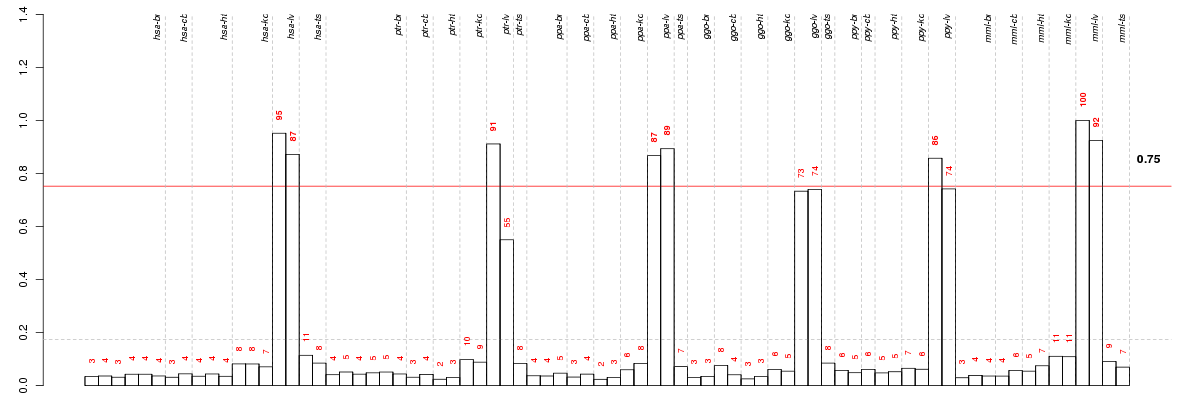
ABCG5ATP-binding cassette, sub-family G (WHITE), member 5 (ENSG00000138075), score: 0.94 ADH4alcohol dehydrogenase 4 (class II), pi polypeptide (ENSG00000198099), score: 0.93 AKR1D1aldo-keto reductase family 1, member D1 (delta 4-3-ketosteroid-5-beta-reductase) (ENSG00000122787), score: 0.96 AQP9aquaporin 9 (ENSG00000103569), score: 0.92 ARG1arginase, liver (ENSG00000118520), score: 0.95 C8Acomplement component 8, alpha polypeptide (ENSG00000157131), score: 0.93 C8Bcomplement component 8, beta polypeptide (ENSG00000021852), score: 0.91 CLDN14claudin 14 (ENSG00000159261), score: 0.91 CYP1A2cytochrome P450, family 1, subfamily A, polypeptide 2 (ENSG00000140505), score: 0.94 CYP3A43cytochrome P450, family 3, subfamily A, polypeptide 43 (ENSG00000021461), score: 0.95 F9coagulation factor IX (ENSG00000101981), score: 0.91 FETUBfetuin B (ENSG00000090512), score: 0.98 FOXA1forkhead box A1 (ENSG00000129514), score: 0.93 GNMTglycine N-methyltransferase (ENSG00000124713), score: 0.91 GPAMglycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase, mitochondrial (ENSG00000119927), score: 0.91 GYS2glycogen synthase 2 (liver) (ENSG00000111713), score: 0.97 HAO1hydroxyacid oxidase (glycolate oxidase) 1 (ENSG00000101323), score: 0.93 IGFALSinsulin-like growth factor binding protein, acid labile subunit (ENSG00000099769), score: 0.93 INHBCinhibin, beta C (ENSG00000175189), score: 0.92 LECT2leukocyte cell-derived chemotaxin 2 (ENSG00000145826), score: 0.97 MAT1Amethionine adenosyltransferase I, alpha (ENSG00000151224), score: 0.91 NPC1L1NPC1 (Niemann-Pick disease, type C1, gene)-like 1 (ENSG00000015520), score: 0.91 NR1I2nuclear receptor subfamily 1, group I, member 2 (ENSG00000144852), score: 0.92 OTCornithine carbamoyltransferase (ENSG00000036473), score: 1 PFKFB16-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-biphosphatase 1 (ENSG00000158571), score: 0.92 PGLYRP2peptidoglycan recognition protein 2 (ENSG00000161031), score: 0.95 PON1paraoxonase 1 (ENSG00000005421), score: 0.93 RDH16retinol dehydrogenase 16 (all-trans) (ENSG00000139547), score: 0.93 SEC14L4SEC14-like 4 (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000133488), score: 0.97 SERPINA11serpin peptidase inhibitor, clade A (alpha-1 antiproteinase, antitrypsin), member 11 (ENSG00000186910), score: 0.92 SERPINA4serpin peptidase inhibitor, clade A (alpha-1 antiproteinase, antitrypsin), member 4 (ENSG00000100665), score: 0.93 SERPINA7serpin peptidase inhibitor, clade A (alpha-1 antiproteinase, antitrypsin), member 7 (ENSG00000123561), score: 0.92 SLC10A1solute carrier family 10 (sodium/bile acid cotransporter family), member 1 (ENSG00000100652), score: 0.96 SLC22A1solute carrier family 22 (organic cation transporter), member 1 (ENSG00000175003), score: 0.91 SLC25A15solute carrier family 25 (mitochondrial carrier; ornithine transporter) member 15 (ENSG00000102743), score: 0.94 SLC38A4solute carrier family 38, member 4 (ENSG00000139209), score: 0.93 SLCO1B1solute carrier organic anion transporter family, member 1B1 (ENSG00000134538), score: 0.92 SLCO1B3solute carrier organic anion transporter family, member 1B3 (ENSG00000111700), score: 0.98 SOAT2sterol O-acyltransferase 2 (ENSG00000167780), score: 1 SPP2secreted phosphoprotein 2, 24kDa (ENSG00000072080), score: 0.99 SULT2A1sulfotransferase family, cytosolic, 2A, dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA)-preferring, member 1 (ENSG00000105398), score: 0.91 TATtyrosine aminotransferase (ENSG00000198650), score: 0.91 TMEM195transmembrane protein 195 (ENSG00000187546), score: 0.91 TTPAtocopherol (alpha) transfer protein (ENSG00000137561), score: 0.94 UNC93Aunc-93 homolog A (C. elegans) (ENSG00000112494), score: 0.91 UROC1urocanase domain containing 1 (ENSG00000159650), score: 0.96 VWCEvon Willebrand factor C and EGF domains (ENSG00000167992), score: 0.95
| Id | species | tissue | sex | individual |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ppy_lv_m_ca1 | ppy | lv | m | _ |
| ppa_lv_m_ca1 | ppa | lv | m | _ |
| hsa_lv_m2_ca1 | hsa | lv | m | 2 |
| ppa_lv_f_ca1 | ppa | lv | f | _ |
| ptr_lv_m_ca1 | ptr | lv | m | _ |
| mml_lv_f_ca1 | mml | lv | f | _ |
| hsa_lv_m1_ca1 | hsa | lv | m | 1 |
| mml_lv_m_ca1 | mml | lv | m | _ |