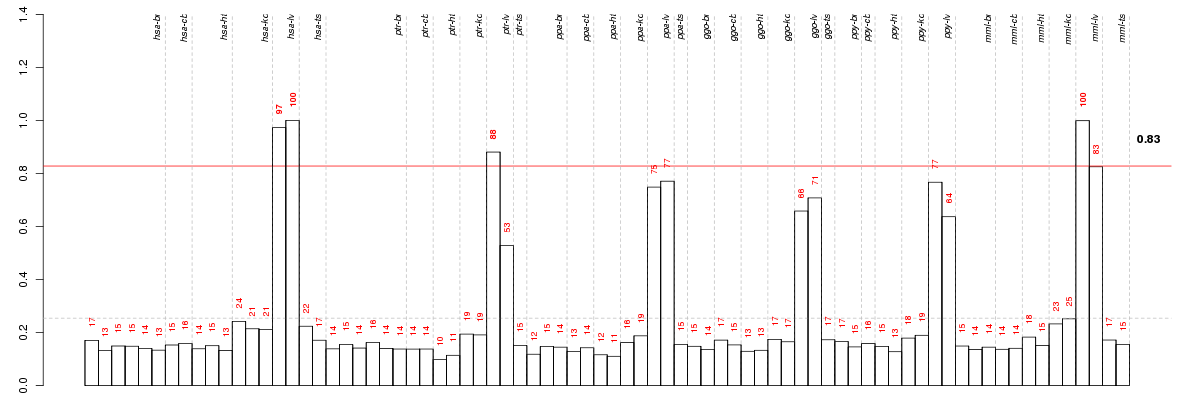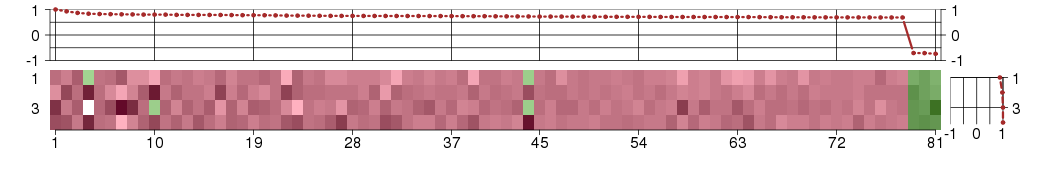

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

reproduction
The production by an organism of new individuals that contain some portion of their genetic material inherited from that organism.
metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways, including anabolism and catabolism, by which living organisms transform chemical substances. Metabolic processes typically transform small molecules, but also include macromolecular processes such as DNA repair and replication, and protein synthesis and degradation.
urogenital system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the urogenital system over time, from its formation to the mature structure.
reproductive developmental process
A developmental process by which a progressive change in the state of some part of an organism specifically contributes to its ability to form offspring.
system process
A multicellular organismal process carried out by any of the organs or tissues in an organ system. An organ system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a biological objective.
alcohol metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving alcohols, any of a class of compounds containing one or more hydroxyl groups attached to a saturated carbon atom.
organic acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving organic acids, any acidic compound containing carbon in covalent linkage.
cellular amino acid and derivative metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving amino acids, organic acids containing one or more amino substituents, and compounds derived from amino acids, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular amino acid derivative metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving compounds derived from amino acids, organic acids containing one or more amino substituents.
cellular biogenic amine metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways occurring at the level of individual cells involving any of a group of naturally occurring, biologically active amines, such as norepinephrine, histamine, and serotonin, many of which act as neurotransmitters.
lipid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving lipids, compounds soluble in an organic solvent but not, or sparingly, in an aqueous solvent. Includes fatty acids; neutral fats, other fatty-acid esters, and soaps; long-chain (fatty) alcohols and waxes; sphingoids and other long-chain bases; glycolipids, phospholipids and sphingolipids; and carotenes, polyprenols, sterols, terpenes and other isoprenoids.
phospholipid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving phospholipids, any lipid containing phosphoric acid as a mono- or diester.
glycerophospholipid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving glycerophospholipids, any derivative of glycerophosphate that contains at least one O-acyl, O-alkyl, or O-alkenyl group attached to the glycerol residue.
glycerol ether metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving glycerol ethers, any anhydride formed between two organic hydroxy compounds, one of which is glycerol.
steroid catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of steroids, compounds with a 1,2,cyclopentanoperhydrophenanthrene nucleus.
nitrogen compound metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving various organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds; includes nitrogen fixation, nitrification, denitrification, assimilatory/dissimilatory nitrate reduction and the interconversion of nitrogenous organic matter and ammonium.
transport
The directed movement of substances (such as macromolecules, small molecules, ions) into, out of, within or between cells, or within a multicellular organism by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
lipid transport
The directed movement of lipids into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore. Lipids are compounds soluble in an organic solvent but not, or sparingly, in an aqueous solvent.
cell communication
Any process that mediates interactions between a cell and its surroundings. Encompasses interactions such as signaling or attachment between one cell and another cell, between a cell and an extracellular matrix, or between a cell and any other aspect of its environment.
cell-cell signaling
Any process that mediates the transfer of information from one cell to another.
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
digestion
The whole of the physical, chemical, and biochemical processes carried out by multicellular organisms to break down ingested nutrients into components that may be easily absorbed and directed into metabolism.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
steroid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving steroids, compounds with a 1,2,cyclopentanoperhydrophenanthrene nucleus.
cholesterol metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving cholesterol, cholest-5-en-3 beta-ol, the principal sterol of vertebrates and the precursor of many steroids, including bile acids and steroid hormones. It is a component of the plasma membrane lipid bilayer and of plasma lipoproteins and can be found in all animal tissues.
androgen metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving androgens, C19 steroid hormones that can stimulate the development of male sexual characteristics.
lipid biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of lipids, compounds soluble in an organic solvent but not, or sparingly, in an aqueous solvent.
catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of substances, including the breakdown of carbon compounds with the liberation of energy for use by the cell or organism.
biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances; typically the energy-requiring part of metabolism in which simpler substances are transformed into more complex ones.
amine metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving any organic compound that is weakly basic in character and contains an amino or a substituted amino group, as carried out by individual cells. Amines are called primary, secondary, or tertiary according to whether one, two, or three carbon atoms are attached to the nitrogen atom.
response to drug
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a drug stimulus. A drug is a substance used in the diagnosis, treatment or prevention of a disease.
phospholipid catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of phospholipids, any lipid containing phosphoric acid as a mono- or diester.
response to external stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an external stimulus.
response to endogenous stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus arising within the organism.
response to hormone stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a hormone stimulus.
negative regulation of metabolic process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism.
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
response to extracellular stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an extracellular stimulus.
response to organic substance
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an organic substance stimulus.
regulation of hormone levels
Any process that modulates the levels of hormone within an organism or a tissue. A hormone is any substance formed in very small amounts in one specialized organ or group of cells and carried (sometimes in the bloodstream) to another organ or group of cells in the same organism, upon which it has a specific regulatory action.
lipid localization
Any process by which a lipid is transported to, or maintained in, a specific location.
sterol transport
The directed movement of sterols into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore. Sterols are steroids with one or more hydroxyl groups and a hydrocarbon side-chain in the molecule.
lipid catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of lipids, compounds soluble in an organic solvent but not, or sparingly, in an aqueous solvent.
sterol metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving sterols, steroids with one or more hydroxyl groups and a hydrocarbon side-chain in the molecule.
drug metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving a drug, a substance used in the diagnosis, treatment or prevention of a disease; as used here antibiotic substances (see antibiotic metabolism) are considered to be drugs, even if not used in medical or veterinary practice.
organic ether metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving organic ethers, any anhydride of the general formula R1-O-R2, formed between two identical or nonidentical organic hydroxy compounds.
regulation of metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism.
organophosphate metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving organophosphates, any phosphate-containing organic compound.
carboxylic acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving carboxylic acids, any organic acid containing one or more carboxyl (COOH) groups or anions (COO-).
reproductive process
A biological process that directly contributes to the process of producing new individuals by one or two organisms. The new individuals inherit some proportion of their genetic material from the parent or parents.
digestive system process
A physical, chemical, or biochemical process carried out by living organisms to break down ingested nutrients into components that may be easily absorbed and directed into metabolism.
signaling
The entirety of a process whereby information is transmitted. This process begins with the initiation of the signal and ends when a response has been triggered.
intestinal cholesterol absorption
Uptake of cholesterol into the blood by absorption from the small intestine.
cholesterol transport
The directed movement of cholesterol, cholest-5-en-3-beta-ol, into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
prostate gland development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the prostate gland over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The prostate gland is a partly muscular, partly glandular body that is situated near the base of the mammalian male urethra and secretes an alkaline viscid fluid which is a major constituent of the ejaculatory fluid.
regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
negative regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
response to nutrient levels
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus reflecting the presence, absence, or concentration of nutrients.
multicellular organismal process
Any biological process, occurring at the level of a multicellular organism, pertinent to its function.
developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an integrated living unit: an anatomical structure (which may be a subcellular structure, cell, tissue, or organ), or organism over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
monocarboxylic acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving monocarboxylic acids, any organic acid containing one carboxyl (COOH) group or anion (COO-).
macromolecule localization
Any process by which a macromolecule is transported to, or maintained in, a specific location.
regulation of cellular amine metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform amines.
negative regulation of cellular amine metabolic process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving amines.
carbohydrate homeostasis
A homeostatic process involved in the maintenance of an internal steady-state of a carbohydrate within an organism or cell.
phosphatidylcholine catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of phosphatidylcholines, any of a class of glycerophospholipids in which the phosphatidyl group is esterified to the hydroxyl group of choline.
cellular nitrogen compound metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving various organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular hormone metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving any hormone, naturally occurring substances secreted by specialized cells that affects the metabolism or behavior of other cells possessing functional receptors for the hormone, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular ketone metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving any of a class of organic compounds that contain the carbonyl group, CO, and in which the carbonyl group is bonded only to carbon atoms, as carried out by individual cells. The general formula for a ketone is RCOR, where R and R are alkyl or aryl groups.
response to chemical stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a chemical stimulus.
ethanolamine and derivative metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving ethanolamine (2-aminoethanol) and compounds derived from it.
hormone metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving any hormone, naturally occurring substances secreted by specialized cells that affects the metabolism or behavior of other cells possessing functional receptors for the hormone.
homeostatic process
Any biological process involved in the maintenance of an internal steady-state.
glucose homeostasis
Any process involved in the maintenance of an internal steady-state of glucose within an organism or cell.
cholesterol homeostasis
Any process involved in the maintenance of an internal steady-state of cholesterol within an organism or cell.
drug catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of a drug, a substance used in the diagnosis, treatment or prevention of a disease.
exogenous drug catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of a drug that has originated externally to the cell or organism.
oxoacid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving any oxoacid; an oxoacid is a compound which contains oxygen, at least one other element, and at least one hydrogen bound to oxygen, and which produces a conjugate base by loss of positive hydrogen ion(s) (hydrons).
cellular amine metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving any organic compound that is weakly basic in character and contains an amino or a substituted amino group, as carried out by individual cells. Amines are called primary, secondary, or tertiary according to whether one, two, or three carbon atoms are attached to the nitrogen atom.
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
primary metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving those compounds which are formed as a part of the normal anabolic and catabolic processes. These processes take place in most, if not all, cells of the organism.
lipid digestion
The whole of the physical, chemical, and biochemical processes carried out by living organisms to break down ingested lipids into components that may be easily absorbed and directed into metabolism.
cellular lipid catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of lipids, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of substances, carried out by individual cells.
cellular lipid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving lipids, as carried out by individual cells.
small molecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving small molecules, any monomeric molecule of small relative molecular mass.
small molecule catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of small molecules, any monomeric molecule of small relative molecular mass.
small molecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of small molecules, any monomeric molecule of small relative molecular mass.
alcohol catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of alcohols, any of a class of compounds containing one or more hydroxyl groups attached to a saturated carbon atom.
phosphatidylcholine metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving phosphatidylcholines, any of a class of glycerophospholipids in which the phosphatidyl group is esterified to the hydroxyl group of choline. They are important constituents of cell membranes.
glycerophospholipid catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of glycerophospholipids, any derivative of glycerophosphate that contains at least one O-acyl, O-alkyl, or O-alkenyl group attached to the glycerol residue.
glycerolipid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving glycerolipids, any lipid with a glycerol backbone. Diacylglycerol and phosphatidate are key lipid intermediates of glycerolipid biosynthesis.
glycerolipid catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of glycerolipids, any lipid with a glycerol backbone.
organ development
Development of a tissue or tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Development pertains to the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a structure over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
negative regulation of biological process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
negative regulation of cellular process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
response to steroid hormone stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a steroid hormone stimulus.
reproductive structure development
The reproductive developmental process whose specific outcome is the progression of structures that will be used in the process of creating new individuals from one or more parents, from their formation to the mature structures.
reproductive cellular process
A process, occurring at the cellular level, that is involved in the reproductive function of a multicellular or single-celled organism.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
gland development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a gland over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A gland is an organ specialised for secretion.
anatomical structure development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an anatomical structure from an initial condition to its mature state. This process begins with the formation of the structure and ends with the mature structure, whatever form that may be including its natural destruction. An anatomical structure is any biological entity that occupies space and is distinguished from its surroundings. Anatomical structures can be macroscopic such as a carpel, or microscopic such as an acrosome.
chemical homeostasis
Any biological process involved in the maintenance of an internal steady-state of a chemical.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of cellular process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
intestinal absorption
Any process by which nutrients are taken up from the contents of the intestine.
response to stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
regulation of nitrogen compound metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving nitrogen or nitrogenous compounds.
negative regulation of nitrogen compound metabolic process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving nitrogen or nitrogenous compounds.
localization
Any process by which a cell, a substance, or a cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, is transported to, and/or maintained in a specific location.
establishment of localization
The directed movement of a cell, substance or cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, to a specific location.
lipid homeostasis
Any process involved in the maintenance of an internal steady-state of lipid within an organism or cell.
sterol homeostasis
Any process involved in the maintenance of an internal steady-state of sterol within an organism or cell.
epithelial-mesenchymal cell signaling
Any process that results in the transfer of information from an epithelial cell to a mesenchymal cell where it is interpreted.
epithelial-mesenchymal signaling involved in prostate gland development
Any process that results in the transfer of information from an epithelial cell to a mesenchymal cell where it is interpreted and contributes to the progression of the prostate gland over time.
biological regulation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of any biological process, quality or function.
regulation of biological quality
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological quality. A biological quality is a measurable attribute of an organism or part of an organism, such as size, mass, shape, color, etc.
all
NA
reproductive process
A biological process that directly contributes to the process of producing new individuals by one or two organisms. The new individuals inherit some proportion of their genetic material from the parent or parents.
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
reproductive cellular process
A process, occurring at the cellular level, that is involved in the reproductive function of a multicellular or single-celled organism.
reproductive developmental process
A developmental process by which a progressive change in the state of some part of an organism specifically contributes to its ability to form offspring.
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
negative regulation of metabolic process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism.
negative regulation of cellular process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
regulation of metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism.
negative regulation of biological process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of cellular process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
establishment of localization
The directed movement of a cell, substance or cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, to a specific location.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
negative regulation of nitrogen compound metabolic process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving nitrogen or nitrogenous compounds.
negative regulation of metabolic process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism.
regulation of nitrogen compound metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving nitrogen or nitrogenous compounds.
regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
negative regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
cellular nitrogen compound metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving various organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular hormone metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving any hormone, naturally occurring substances secreted by specialized cells that affects the metabolism or behavior of other cells possessing functional receptors for the hormone, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of substances, carried out by individual cells.
cellular amino acid and derivative metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving amino acids, organic acids containing one or more amino substituents, and compounds derived from amino acids, as carried out by individual cells.
organic acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving organic acids, any acidic compound containing carbon in covalent linkage.
cellular amino acid and derivative metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving amino acids, organic acids containing one or more amino substituents, and compounds derived from amino acids, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular ketone metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving any of a class of organic compounds that contain the carbonyl group, CO, and in which the carbonyl group is bonded only to carbon atoms, as carried out by individual cells. The general formula for a ketone is RCOR, where R and R are alkyl or aryl groups.
small molecule catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of small molecules, any monomeric molecule of small relative molecular mass.
small molecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of small molecules, any monomeric molecule of small relative molecular mass.
cell-cell signaling
Any process that mediates the transfer of information from one cell to another.
negative regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
negative regulation of cellular process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
digestive system process
A physical, chemical, or biochemical process carried out by living organisms to break down ingested nutrients into components that may be easily absorbed and directed into metabolism.
reproductive structure development
The reproductive developmental process whose specific outcome is the progression of structures that will be used in the process of creating new individuals from one or more parents, from their formation to the mature structures.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
cellular amine metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving any organic compound that is weakly basic in character and contains an amino or a substituted amino group, as carried out by individual cells. Amines are called primary, secondary, or tertiary according to whether one, two, or three carbon atoms are attached to the nitrogen atom.
negative regulation of nitrogen compound metabolic process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving nitrogen or nitrogenous compounds.
cellular lipid catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of lipids, as carried out by individual cells.
negative regulation of cellular amine metabolic process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving amines.
negative regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
regulation of cellular amine metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform amines.
drug catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of a drug, a substance used in the diagnosis, treatment or prevention of a disease.
oxoacid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving any oxoacid; an oxoacid is a compound which contains oxygen, at least one other element, and at least one hydrogen bound to oxygen, and which produces a conjugate base by loss of positive hydrogen ion(s) (hydrons).
phospholipid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving phospholipids, any lipid containing phosphoric acid as a mono- or diester.
cellular lipid catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of lipids, as carried out by individual cells.
lipid biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of lipids, compounds soluble in an organic solvent but not, or sparingly, in an aqueous solvent.
lipid catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of lipids, compounds soluble in an organic solvent but not, or sparingly, in an aqueous solvent.
cellular lipid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving lipids, as carried out by individual cells.
alcohol catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of alcohols, any of a class of compounds containing one or more hydroxyl groups attached to a saturated carbon atom.
epithelial-mesenchymal signaling involved in prostate gland development
Any process that results in the transfer of information from an epithelial cell to a mesenchymal cell where it is interpreted and contributes to the progression of the prostate gland over time.
organ development
Development of a tissue or tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Development pertains to the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a structure over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
response to hormone stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a hormone stimulus.
lipid transport
The directed movement of lipids into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore. Lipids are compounds soluble in an organic solvent but not, or sparingly, in an aqueous solvent.
hormone metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving any hormone, naturally occurring substances secreted by specialized cells that affects the metabolism or behavior of other cells possessing functional receptors for the hormone.
regulation of cellular amine metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform amines.
negative regulation of cellular amine metabolic process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving amines.
negative regulation of cellular amine metabolic process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving amines.
phospholipid catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of phospholipids, any lipid containing phosphoric acid as a mono- or diester.
exogenous drug catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of a drug that has originated externally to the cell or organism.
glycerophospholipid catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of glycerophospholipids, any derivative of glycerophosphate that contains at least one O-acyl, O-alkyl, or O-alkenyl group attached to the glycerol residue.
cellular biogenic amine metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways occurring at the level of individual cells involving any of a group of naturally occurring, biologically active amines, such as norepinephrine, histamine, and serotonin, many of which act as neurotransmitters.
glycerophospholipid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving glycerophospholipids, any derivative of glycerophosphate that contains at least one O-acyl, O-alkyl, or O-alkenyl group attached to the glycerol residue.
glycerolipid catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of glycerolipids, any lipid with a glycerol backbone.
steroid catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of steroids, compounds with a 1,2,cyclopentanoperhydrophenanthrene nucleus.
androgen metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving androgens, C19 steroid hormones that can stimulate the development of male sexual characteristics.
sterol metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving sterols, steroids with one or more hydroxyl groups and a hydrocarbon side-chain in the molecule.
phosphatidylcholine metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving phosphatidylcholines, any of a class of glycerophospholipids in which the phosphatidyl group is esterified to the hydroxyl group of choline. They are important constituents of cell membranes.
epithelial-mesenchymal signaling involved in prostate gland development
Any process that results in the transfer of information from an epithelial cell to a mesenchymal cell where it is interpreted and contributes to the progression of the prostate gland over time.
intestinal cholesterol absorption
Uptake of cholesterol into the blood by absorption from the small intestine.
prostate gland development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the prostate gland over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The prostate gland is a partly muscular, partly glandular body that is situated near the base of the mammalian male urethra and secretes an alkaline viscid fluid which is a major constituent of the ejaculatory fluid.
prostate gland development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the prostate gland over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The prostate gland is a partly muscular, partly glandular body that is situated near the base of the mammalian male urethra and secretes an alkaline viscid fluid which is a major constituent of the ejaculatory fluid.
ethanolamine and derivative metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving ethanolamine (2-aminoethanol) and compounds derived from it.
glycerophospholipid catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of glycerophospholipids, any derivative of glycerophosphate that contains at least one O-acyl, O-alkyl, or O-alkenyl group attached to the glycerol residue.
phosphatidylcholine catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of phosphatidylcholines, any of a class of glycerophospholipids in which the phosphatidyl group is esterified to the hydroxyl group of choline.
intestinal cholesterol absorption
Uptake of cholesterol into the blood by absorption from the small intestine.

intracellular
The living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
cell fraction
A generic term for parts of cells prepared by disruptive biochemical techniques.
extracellular region
The space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.
endoplasmic reticulum
The irregular network of unit membranes, visible only by electron microscopy, that occurs in the cytoplasm of many eukaryotic cells. The membranes form a complex meshwork of tubular channels, which are often expanded into slitlike cavities called cisternae. The ER takes two forms, rough (or granular), with ribosomes adhering to the outer surface, and smooth (with no ribosomes attached).
cellular_component
The part of a cell or its extracellular environment in which a gene product is located. A gene product may be located in one or more parts of a cell and its location may be as specific as a particular macromolecular complex, that is, a stable, persistent association of macromolecules that function together.
extracellular space
That part of a multicellular organism outside the cells proper, usually taken to be outside the plasma membranes, and occupied by fluid.
cell
The basic structural and functional unit of all organisms. Includes the plasma membrane and any external encapsulating structures such as the cell wall and cell envelope.
membrane fraction
That fraction of cells, prepared by disruptive biochemical methods, that includes the plasma and other membranes.
insoluble fraction
That fraction of cells, prepared by disruptive biochemical methods, that is not soluble in water.
cytoplasm
All of the contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures.
macromolecular complex
A stable assembly of two or more macromolecules, i.e. proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates or lipids, in which the constituent parts function together.
protein-lipid complex
A macromolecular complex containing both protein and lipid molecules.
plasma lipoprotein particle
A spherical particle with a hydrophobic core of triglycerides and/or cholesterol esters, surrounded by an amphipathic monolayer of phospholipids, cholesterol and apolipoproteins. Plasma lipoprotein particles transport lipids, which are non-covalently associated with the particles, in the blood or lymph.
high-density lipoprotein particle
A lipoprotein particle with a high density (typically 1.063-1.21 g/ml) and a diameter of 5-10 nm that contains APOAs and may contain APOCs and APOE; found in blood and carries lipids from body tissues to the liver as part of the reverse cholesterol transport process.
vesicular fraction
Any of the small, heterogeneous, artifactual, vesicular particles that are formed when some cells are homogenized.
organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, and prokaryotic structures such as anammoxosomes and pirellulosomes. Excludes the plasma membrane.
membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
extracellular region part
Any constituent part of the extracellular region, the space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers constituent parts of the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
cytoplasmic part
Any constituent part of the cytoplasm, all of the contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures.
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
all
NA
extracellular region part
Any constituent part of the extracellular region, the space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers constituent parts of the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
plasma lipoprotein particle
A spherical particle with a hydrophobic core of triglycerides and/or cholesterol esters, surrounded by an amphipathic monolayer of phospholipids, cholesterol and apolipoproteins. Plasma lipoprotein particles transport lipids, which are non-covalently associated with the particles, in the blood or lymph.
intracellular membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
plasma lipoprotein particle
A spherical particle with a hydrophobic core of triglycerides and/or cholesterol esters, surrounded by an amphipathic monolayer of phospholipids, cholesterol and apolipoproteins. Plasma lipoprotein particles transport lipids, which are non-covalently associated with the particles, in the blood or lymph.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
cytoplasmic part
Any constituent part of the cytoplasm, all of the contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures.
endoplasmic reticulum
The irregular network of unit membranes, visible only by electron microscopy, that occurs in the cytoplasm of many eukaryotic cells. The membranes form a complex meshwork of tubular channels, which are often expanded into slitlike cavities called cisternae. The ER takes two forms, rough (or granular), with ribosomes adhering to the outer surface, and smooth (with no ribosomes attached).

molecular_function
Elemental activities, such as catalysis or binding, describing the actions of a gene product at the molecular level. A given gene product may exhibit one or more molecular functions.
catalytic activity
Catalysis of a biochemical reaction at physiological temperatures. In biologically catalyzed reactions, the reactants are known as substrates, and the catalysts are naturally occurring macromolecular substances known as enzymes. Enzymes possess specific binding sites for substrates, and are usually composed wholly or largely of protein, but RNA that has catalytic activity (ribozyme) is often also regarded as enzymatic.
oxidoreductase activity
Catalysis of an oxidation-reduction (redox) reaction, a reversible chemical reaction in which the oxidation state of an atom or atoms within a molecule is altered. One substrate acts as a hydrogen or electron donor and becomes oxidized, while the other acts as hydrogen or electron acceptor and becomes reduced.
steroid dehydrogenase activity
Catalysis of an oxidation-reduction (redox) reaction in which one substrate is a sterol derivative.
kinase activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a phosphate group, usually from ATP, to a substrate molecule.
oxidoreductase activity, acting on the CH-CH group of donors
Catalysis of an oxidation-reduction (redox) reaction in which a CH-CH group acts as a hydrogen or electron donor and reduces a hydrogen or electron acceptor.
transferase activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a group, e.g. a methyl group, glycosyl group, acyl group, phosphorus-containing, or other groups, from one compound (generally regarded as the donor) to another compound (generally regarded as the acceptor). Transferase is the systematic name for any enzyme of EC class 2.
transferase activity, transferring phosphorus-containing groups
Catalysis of the transfer of a phosphorus-containing group from one compound (donor) to another (acceptor).
carbohydrate kinase activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a phosphate group, usually from ATP, to a carbohydrate substrate molecule.
steroid dehydrogenase activity, acting on the CH-CH group of donors
Catalysis of an oxidation-reduction (redox) reaction in which a CH-CH group acts as a hydrogen or electron donor and reduces a hydrogen or electron acceptor, and in which one substrate is a sterol derivative.
all
NA
steroid dehydrogenase activity, acting on the CH-CH group of donors
Catalysis of an oxidation-reduction (redox) reaction in which a CH-CH group acts as a hydrogen or electron donor and reduces a hydrogen or electron acceptor, and in which one substrate is a sterol derivative.
| Id | Pvalue | ExpCount | Count | Size | Term |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 01100 | 6.393e-03 | 7.345 | 17 | 805 | Metabolic pathways |
| 04950 | 7.438e-03 | 0.1369 | 3 | 15 | Maturity onset diabetes of the young |
| 00232 | 1.101e-02 | 0.0365 | 2 | 4 | Caffeine metabolism |
| 00140 | 1.958e-02 | 0.2007 | 3 | 22 | Steroid hormone biosynthesis |
| 00830 | 2.696e-02 | 0.2281 | 3 | 25 | Retinol metabolism |
| 00980 | 2.937e-02 | 0.2372 | 3 | 26 | Metabolism of xenobiotics by cytochrome P450 |
| 00350 | 4.786e-02 | 0.292 | 3 | 32 | Tyrosine metabolism |
ABCG5ATP-binding cassette, sub-family G (WHITE), member 5 (ENSG00000138075), score: 0.72 ADH4alcohol dehydrogenase 4 (class II), pi polypeptide (ENSG00000198099), score: 0.71 AKR1D1aldo-keto reductase family 1, member D1 (delta 4-3-ketosteroid-5-beta-reductase) (ENSG00000122787), score: 0.72 APOC1apolipoprotein C-I (ENSG00000130208), score: 0.7 APOFapolipoprotein F (ENSG00000175336), score: 0.74 ARG1arginase, liver (ENSG00000118520), score: 0.69 ARID3CAT rich interactive domain 3C (BRIGHT-like) (ENSG00000205143), score: 0.76 C14orf21chromosome 14 open reading frame 21 (ENSG00000196943), score: 0.8 C20orf194chromosome 20 open reading frame 194 (ENSG00000088854), score: -0.71 CIDEBcell death-inducing DFFA-like effector b (ENSG00000136305), score: 0.72 CLDN14claudin 14 (ENSG00000159261), score: 0.73 COMTcatechol-O-methyltransferase (ENSG00000093010), score: 0.7 CYP1A2cytochrome P450, family 1, subfamily A, polypeptide 2 (ENSG00000140505), score: 0.87 EI24etoposide induced 2.4 mRNA (ENSG00000149547), score: 0.79 EPHX1epoxide hydrolase 1, microsomal (xenobiotic) (ENSG00000143819), score: 0.69 F7coagulation factor VII (serum prothrombin conversion accelerator) (ENSG00000057593), score: 0.69 FCER1AFc fragment of IgE, high affinity I, receptor for; alpha polypeptide (ENSG00000179639), score: 0.74 FETUBfetuin B (ENSG00000090512), score: 0.74 FOXA1forkhead box A1 (ENSG00000129514), score: 0.78 FOXA3forkhead box A3 (ENSG00000170608), score: 0.69 GCKglucokinase (hexokinase 4) (ENSG00000106633), score: 0.75 GCKRglucokinase (hexokinase 4) regulator (ENSG00000084734), score: 0.69 GLYATL3glycine-N-acyltransferase-like 3 (ENSG00000203972), score: 0.81 GNEglucosamine (UDP-N-acetyl)-2-epimerase/N-acetylmannosamine kinase (ENSG00000159921), score: 0.7 GPAMglycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase, mitochondrial (ENSG00000119927), score: 0.71 GUCA2Bguanylate cyclase activator 2B (uroguanylin) (ENSG00000044012), score: 1 GYS2glycogen synthase 2 (liver) (ENSG00000111713), score: 0.72 HAO1hydroxyacid oxidase (glycolate oxidase) 1 (ENSG00000101323), score: 0.71 HSD17B13hydroxysteroid (17-beta) dehydrogenase 13 (ENSG00000170509), score: 0.75 IGFALSinsulin-like growth factor binding protein, acid labile subunit (ENSG00000099769), score: 0.8 INHBCinhibin, beta C (ENSG00000175189), score: 0.71 INHBEinhibin, beta E (ENSG00000139269), score: 0.79 JMJD5jumonji domain containing 5 (ENSG00000155666), score: 0.75 LECT2leukocyte cell-derived chemotaxin 2 (ENSG00000145826), score: 0.73 LIPClipase, hepatic (ENSG00000166035), score: 0.78 LRRC3leucine rich repeat containing 3 (ENSG00000160233), score: 0.71 LRRC31leucine rich repeat containing 31 (ENSG00000114248), score: 0.79 LYPD2LY6/PLAUR domain containing 2 (ENSG00000197353), score: 0.73 MINPP1multiple inositol-polyphosphate phosphatase 1 (ENSG00000107789), score: 0.75 NAT2N-acetyltransferase 2 (arylamine N-acetyltransferase) (ENSG00000156006), score: 0.69 NPC1L1NPC1 (Niemann-Pick disease, type C1, gene)-like 1 (ENSG00000015520), score: 0.74 NR1I2nuclear receptor subfamily 1, group I, member 2 (ENSG00000144852), score: 0.74 ONECUT2one cut homeobox 2 (ENSG00000119547), score: 0.77 OTCornithine carbamoyltransferase (ENSG00000036473), score: 0.75 OXER1oxoeicosanoid (OXE) receptor 1 (ENSG00000162881), score: 0.79 PEMTphosphatidylethanolamine N-methyltransferase (ENSG00000133027), score: 0.74 PFKFB16-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-biphosphatase 1 (ENSG00000158571), score: 0.72 PGAM5phosphoglycerate mutase family member 5 (ENSG00000176894), score: 0.75 PGLYRP2peptidoglycan recognition protein 2 (ENSG00000161031), score: 0.77 PKLRpyruvate kinase, liver and RBC (ENSG00000143627), score: 0.71 RABGAP1RAB GTPase activating protein 1 (ENSG00000011454), score: -0.74 RDH16retinol dehydrogenase 16 (all-trans) (ENSG00000139547), score: 0.71 RFNGRFNG O-fucosylpeptide 3-beta-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase (ENSG00000169733), score: 0.7 SEC14L4SEC14-like 4 (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000133488), score: 0.79 SERPINA4serpin peptidase inhibitor, clade A (alpha-1 antiproteinase, antitrypsin), member 4 (ENSG00000100665), score: 0.76 SHHsonic hedgehog (ENSG00000164690), score: 0.76 SIGMAR1sigma non-opioid intracellular receptor 1 (ENSG00000147955), score: 0.75 SLC10A1solute carrier family 10 (sodium/bile acid cotransporter family), member 1 (ENSG00000100652), score: 0.73 SLC16A11solute carrier family 16, member 11 (monocarboxylic acid transporter 11) (ENSG00000174326), score: 0.78 SLC16A13solute carrier family 16, member 13 (monocarboxylic acid transporter 13) (ENSG00000174327), score: 0.7 SLC17A2solute carrier family 17 (sodium phosphate), member 2 (ENSG00000112337), score: 0.71 SLC22A1solute carrier family 22 (organic cation transporter), member 1 (ENSG00000175003), score: 0.71 SLC25A36solute carrier family 25, member 36 (ENSG00000114120), score: -0.71 SLC25A47solute carrier family 25, member 47 (ENSG00000140107), score: 0.74 SLCO1B1solute carrier organic anion transporter family, member 1B1 (ENSG00000134538), score: 0.69 SLCO1B3solute carrier organic anion transporter family, member 1B3 (ENSG00000111700), score: 0.72 SOAT2sterol O-acyltransferase 2 (ENSG00000167780), score: 0.81 SPP2secreted phosphoprotein 2, 24kDa (ENSG00000072080), score: 0.74 SRD5A2steroid-5-alpha-reductase, alpha polypeptide 2 (3-oxo-5 alpha-steroid delta 4-dehydrogenase alpha 2) (ENSG00000049319), score: 0.93 SYVN1synovial apoptosis inhibitor 1, synoviolin (ENSG00000162298), score: 0.71 THtyrosine hydroxylase (ENSG00000180176), score: 0.71 THRSPthyroid hormone responsive (ENSG00000151365), score: 0.69 TM4SF4transmembrane 4 L six family member 4 (ENSG00000169903), score: 0.69 TMEM195transmembrane protein 195 (ENSG00000187546), score: 0.75 TMEM86Btransmembrane protein 86B (ENSG00000180089), score: 0.69 TTPAtocopherol (alpha) transfer protein (ENSG00000137561), score: 0.69 TTPALtocopherol (alpha) transfer protein-like (ENSG00000124120), score: 0.7 UROC1urocanase domain containing 1 (ENSG00000159650), score: 0.82 USH2AUsher syndrome 2A (autosomal recessive, mild) (ENSG00000042781), score: 0.8 VWCEvon Willebrand factor C and EGF domains (ENSG00000167992), score: 0.82 ZG16zymogen granule protein 16 homolog (rat) (ENSG00000174992), score: 0.84
| Id | species | tissue | sex | individual |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ptr_lv_m_ca1 | ptr | lv | m | _ |
| hsa_lv_m1_ca1 | hsa | lv | m | 1 |
| mml_lv_m_ca1 | mml | lv | m | _ |
| hsa_lv_m2_ca1 | hsa | lv | m | 2 |