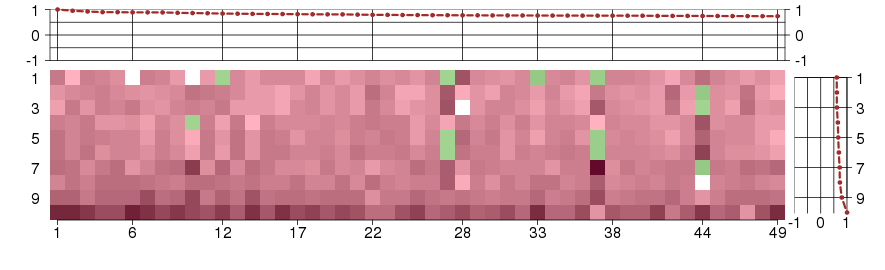

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

cell fate specification
The process involved in the specification of cell identity. Once specification has taken place, a cell will be committed to differentiate down a specific pathway if left in its normal environment.
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
nervous system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of nervous tissue over time, from its formation to its mature state.
central nervous system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the central nervous system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The central nervous system is the core nervous system that serves an integrating and coordinating function. In vertebrates it consists of the brain, spinal cord and spinal nerves. In those invertebrates with a central nervous system it typically consists of a brain, cerebral ganglia and a nerve cord.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
glial cell differentiation
The process whereby a relatively unspecialized cell acquires the specialized features of a glial cell.
positive regulation of cell development
Any process that increases the rate, frequency or extent of the progression of the cell over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Cell development does not include the steps involved in committing a cell to a specific fate.
regulation of gliogenesis
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of gliogenesis, the formation of mature glia.
positive regulation of gliogenesis
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of gliogenesis, the formation of mature glia.
spinal cord development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the spinal cord over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The spinal cord primarily conducts sensory and motor nerve impulses between the brain and the peripheral nervous tissues.
cell differentiation in spinal cord
The process whereby relatively unspecialized cells acquire specialized structural and/or functional features that characterize the cells of the spinal cord. Differentiation includes the processes involved in commitment of a cell to a specific fate.
spinal cord oligodendrocyte cell differentiation
The process whereby neuroepithelial cells in the neural tube acquire specialized structural and/or functional features of oligodendrocytes. Oligodendrocytes are non-neuronal cells. The primary function of oligodendrocytes is the myelination of nerve axons in the central nervous system. Differentiation includes the processes involved in commitment of a cell to a specific fate.
spinal cord oligodendrocyte cell fate specification
The process whereby a cell becomes capable of differentiating autonomously into an oligodendrocyte in an environment that is neutral with respect to the developmental pathway.
oligodendrocyte cell fate specification
The process whereby a cell becomes capable of differentiating autonomously into an oligodendrocyte in an environment that is neutral with respect to the developmental pathway. Upon specification, the cell fate can be reversed.
oligodendrocyte cell fate commitment
The process whereby the developmental fate of a cell becomes restricted such that it will develop into an oligodendrocyte.
glial cell fate specification
The process whereby a cell becomes capable of differentiating autonomously into a glial cell in an environment that is neutral with respect to the developmental pathway. Upon specification, the cell fate can be reversed.
glial cell fate commitment
The process whereby the developmental fate of a cell becomes restricted such that it will develop into a glial cell.
neurogenesis
Generation of cells within the nervous system.
cell differentiation
The process whereby relatively unspecialized cells, e.g. embryonic or regenerative cells, acquire specialized structural and/or functional features that characterize the cells, tissues, or organs of the mature organism or some other relatively stable phase of the organism's life history. Differentiation includes the processes involved in commitment of a cell to a specific fate and its subsequent development to the mature state.
multicellular organismal process
Any biological process, occurring at the level of a multicellular organism, pertinent to its function.
developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an integrated living unit: an anatomical structure (which may be a subcellular structure, cell, tissue, or organ), or organism over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
gliogenesis
The process by which glial cells are generated. This includes the production of glial progenitors and their differentiation into mature glia.
cell fate commitment
The commitment of cells to specific cell fates and their capacity to differentiate into particular kinds of cells. Positional information is established through protein signals that emanate from a localized source within a cell (the initial one-cell zygote) or within a developmental field.
regulation of cell differentiation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell differentiation, the process whereby relatively unspecialized cells acquire specialized structural and functional features.
positive regulation of cell differentiation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cell differentiation.
regulation of glial cell differentiation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of glia cell differentiation.
positive regulation of glial cell differentiation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of glia cell differentiation.
cell development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the cell over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Cell development does not include the steps involved in committing a cell to a specific fate.
positive regulation of biological process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
negative regulation of biological process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
positive regulation of cellular process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
generation of neurons
The process by which nerve cells are generated. This includes the production of neuroblasts and their differentiation into neurons.
oligodendrocyte differentiation
The process whereby a relatively unspecialized cell acquires the specialized features of an oligodendrocyte. An oligodendrocyte is a type of glial cell involved in myelinating the axons of neurons in the central nervous system.
regulation of oligodendrocyte differentiation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of oligodendrocyte differentiation.
positive regulation of oligodendrocyte differentiation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of oligodendrocyte differentiation.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
anatomical structure development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an anatomical structure from an initial condition to its mature state. This process begins with the formation of the structure and ends with the mature structure, whatever form that may be including its natural destruction. An anatomical structure is any biological entity that occupies space and is distinguished from its surroundings. Anatomical structures can be macroscopic such as a carpel, or microscopic such as an acrosome.
cellular developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a cell over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
regulation of neurogenesis
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of neurogenesis, the origin and formation of neurons.
positive regulation of neurogenesis
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of neurogenesis, the origin and formation of neurons.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of developmental process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of development, the biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote, or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
regulation of cellular process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
negative regulation of developmental process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the rate or extent of development, the biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote, or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
positive regulation of developmental process
Any process that activates or increases the rate or extent of development, the biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote, or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
regulation of multicellular organismal process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a multicellular organismal process, the processes pertinent to the function of a multicellular organism above the cellular level; includes the integrated processes of tissues and organs.
regulation of nervous system development
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of nervous system development, the origin and formation of nervous tissue.
regulation of cell development
Any process that modulates the rate, frequency or extent of the progression of the cell over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Cell development does not include the steps involved in committing a cell to a specific fate.
biological regulation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of any biological process, quality or function.
regulation of multicellular organismal development
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of multicellular organismal development.
all
NA
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
cellular developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a cell over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
positive regulation of cellular process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
positive regulation of developmental process
Any process that activates or increases the rate or extent of development, the biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote, or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
negative regulation of developmental process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the rate or extent of development, the biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote, or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
positive regulation of biological process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
negative regulation of biological process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of developmental process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of development, the biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote, or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
regulation of cellular process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
regulation of multicellular organismal process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a multicellular organismal process, the processes pertinent to the function of a multicellular organism above the cellular level; includes the integrated processes of tissues and organs.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
positive regulation of cellular process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
regulation of multicellular organismal development
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of multicellular organismal development.
cell development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the cell over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Cell development does not include the steps involved in committing a cell to a specific fate.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
regulation of cell differentiation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell differentiation, the process whereby relatively unspecialized cells acquire specialized structural and functional features.
negative regulation of developmental process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the rate or extent of development, the biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote, or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
positive regulation of developmental process
Any process that activates or increases the rate or extent of development, the biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote, or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
regulation of multicellular organismal development
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of multicellular organismal development.
positive regulation of cell differentiation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cell differentiation.
cell fate commitment
The commitment of cells to specific cell fates and their capacity to differentiate into particular kinds of cells. Positional information is established through protein signals that emanate from a localized source within a cell (the initial one-cell zygote) or within a developmental field.
regulation of cell differentiation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell differentiation, the process whereby relatively unspecialized cells acquire specialized structural and functional features.
positive regulation of cell differentiation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cell differentiation.
cell development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the cell over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Cell development does not include the steps involved in committing a cell to a specific fate.
cell fate specification
The process involved in the specification of cell identity. Once specification has taken place, a cell will be committed to differentiate down a specific pathway if left in its normal environment.
positive regulation of cell development
Any process that increases the rate, frequency or extent of the progression of the cell over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Cell development does not include the steps involved in committing a cell to a specific fate.
positive regulation of cell differentiation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cell differentiation.
regulation of cell development
Any process that modulates the rate, frequency or extent of the progression of the cell over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Cell development does not include the steps involved in committing a cell to a specific fate.
cell differentiation in spinal cord
The process whereby relatively unspecialized cells acquire specialized structural and/or functional features that characterize the cells of the spinal cord. Differentiation includes the processes involved in commitment of a cell to a specific fate.
glial cell fate commitment
The process whereby the developmental fate of a cell becomes restricted such that it will develop into a glial cell.
positive regulation of neurogenesis
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of neurogenesis, the origin and formation of neurons.
glial cell fate specification
The process whereby a cell becomes capable of differentiating autonomously into a glial cell in an environment that is neutral with respect to the developmental pathway. Upon specification, the cell fate can be reversed.
positive regulation of cell development
Any process that increases the rate, frequency or extent of the progression of the cell over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Cell development does not include the steps involved in committing a cell to a specific fate.
regulation of neurogenesis
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of neurogenesis, the origin and formation of neurons.
central nervous system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the central nervous system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The central nervous system is the core nervous system that serves an integrating and coordinating function. In vertebrates it consists of the brain, spinal cord and spinal nerves. In those invertebrates with a central nervous system it typically consists of a brain, cerebral ganglia and a nerve cord.
neurogenesis
Generation of cells within the nervous system.
regulation of nervous system development
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of nervous system development, the origin and formation of nervous tissue.
spinal cord development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the spinal cord over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The spinal cord primarily conducts sensory and motor nerve impulses between the brain and the peripheral nervous tissues.
oligodendrocyte differentiation
The process whereby a relatively unspecialized cell acquires the specialized features of an oligodendrocyte. An oligodendrocyte is a type of glial cell involved in myelinating the axons of neurons in the central nervous system.
regulation of neurogenesis
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of neurogenesis, the origin and formation of neurons.
positive regulation of glial cell differentiation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of glia cell differentiation.
spinal cord oligodendrocyte cell differentiation
The process whereby neuroepithelial cells in the neural tube acquire specialized structural and/or functional features of oligodendrocytes. Oligodendrocytes are non-neuronal cells. The primary function of oligodendrocytes is the myelination of nerve axons in the central nervous system. Differentiation includes the processes involved in commitment of a cell to a specific fate.
oligodendrocyte cell fate commitment
The process whereby the developmental fate of a cell becomes restricted such that it will develop into an oligodendrocyte.
regulation of oligodendrocyte differentiation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of oligodendrocyte differentiation.
positive regulation of oligodendrocyte differentiation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of oligodendrocyte differentiation.
spinal cord oligodendrocyte cell fate specification
The process whereby a cell becomes capable of differentiating autonomously into an oligodendrocyte in an environment that is neutral with respect to the developmental pathway.
glial cell differentiation
The process whereby a relatively unspecialized cell acquires the specialized features of a glial cell.
positive regulation of gliogenesis
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of gliogenesis, the formation of mature glia.
regulation of neurogenesis
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of neurogenesis, the origin and formation of neurons.
regulation of gliogenesis
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of gliogenesis, the formation of mature glia.
positive regulation of neurogenesis
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of neurogenesis, the origin and formation of neurons.
oligodendrocyte cell fate specification
The process whereby a cell becomes capable of differentiating autonomously into an oligodendrocyte in an environment that is neutral with respect to the developmental pathway. Upon specification, the cell fate can be reversed.
positive regulation of glial cell differentiation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of glia cell differentiation.
positive regulation of oligodendrocyte differentiation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of oligodendrocyte differentiation.
positive regulation of gliogenesis
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of gliogenesis, the formation of mature glia.
regulation of glial cell differentiation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of glia cell differentiation.

membrane
Double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
integral to membrane
Penetrating at least one phospholipid bilayer of a membrane. May also refer to the state of being buried in the bilayer with no exposure outside the bilayer. When used to describe a protein, indicates that all or part of the peptide sequence is embedded in the membrane.
cellular_component
The part of a cell or its extracellular environment in which a gene product is located. A gene product may be located in one or more parts of a cell and its location may be as specific as a particular macromolecular complex, that is, a stable, persistent association of macromolecules that function together.
cell
The basic structural and functional unit of all organisms. Includes the plasma membrane and any external encapsulating structures such as the cell wall and cell envelope.
intrinsic to membrane
Located in a membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
membrane part
Any constituent part of a membrane, a double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
all
NA
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
membrane part
Any constituent part of a membrane, a double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.

regulatory region DNA binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with a DNA region that regulates a DNA-based process. Such processes include transcription, DNA replication, and DNA repair.
molecular_function
Elemental activities, such as catalysis or binding, describing the actions of a gene product at the molecular level. A given gene product may exhibit one or more molecular functions.
nucleic acid binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with any nucleic acid.
DNA binding
Any molecular function by which a gene product interacts selectively with DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid).
sequence-specific DNA binding transcription factor activity
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with a specific DNA sequence in order to modulate transcription. The transcription factor may or may not also interact selectively with a protein or macromolecular complex.
RNA polymerase II transcription factor activity
Functions to initiate or regulate RNA polymerase II transcription.
RNA polymerase II transcription factor activity, enhancer binding
Functions to initiate or regulate RNA polymerase II transcription by binding an enhancer region of DNA.
binding
The selective, non-covalent, often stoichiometric, interaction of a molecule with one or more specific sites on another molecule.
transcription regulator activity
Plays a role in regulating transcription; may bind a promoter or enhancer DNA sequence or interact with a DNA-binding transcription factor.
enhancer binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with an enhancer, a cis-acting sequence that increases the utilization of some eukaryotic promoters, and can function in either orientation and in any location (upstream or downstream) relative to the core promoter.
transcription regulatory region DNA binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with a DNA region that regulates the transcription of a region of DNA, which may be a gene, cistron, or operon. Binding may occur as a sequence specific interaction or as an interaction observed only once a factor has been recruited to the DNA by other factors.
all
NA
RNA polymerase II transcription factor activity, enhancer binding
Functions to initiate or regulate RNA polymerase II transcription by binding an enhancer region of DNA.
RNA polymerase II transcription factor activity, enhancer binding
Functions to initiate or regulate RNA polymerase II transcription by binding an enhancer region of DNA.
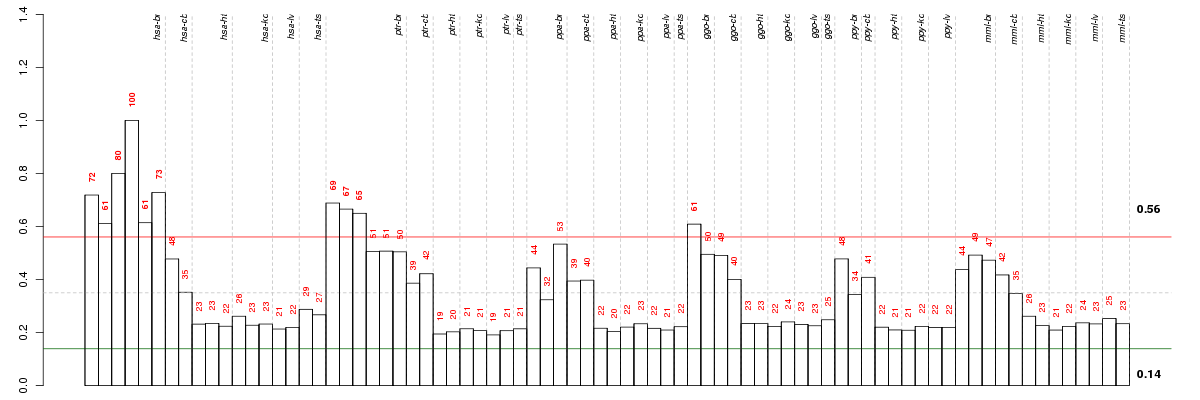
ADAMTS14ADAM metallopeptidase with thrombospondin type 1 motif, 14 (ENSG00000138316), score: 0.77 ATP10BATPase, class V, type 10B (ENSG00000118322), score: 0.76 C11orf9chromosome 11 open reading frame 9 (ENSG00000124920), score: 0.81 C1orf198chromosome 1 open reading frame 198 (ENSG00000119280), score: 0.75 C22orf9chromosome 22 open reading frame 9 (ENSG00000100364), score: 0.77 CD22CD22 molecule (ENSG00000012124), score: 0.95 CDHR1cadherin-related family member 1 (ENSG00000148600), score: 0.75 CERCAMcerebral endothelial cell adhesion molecule (ENSG00000167123), score: 0.84 CHADLchondroadherin-like (ENSG00000100399), score: 0.78 CLCA4chloride channel accessory 4 (ENSG00000016602), score: 0.89 CLDND1claudin domain containing 1 (ENSG00000080822), score: 0.81 CMTM5CKLF-like MARVEL transmembrane domain containing 5 (ENSG00000166091), score: 0.76 CNP2',3'-cyclic nucleotide 3' phosphodiesterase (ENSG00000173786), score: 0.89 DAAM2dishevelled associated activator of morphogenesis 2 (ENSG00000146122), score: 0.78 ENPP2ectonucleotide pyrophosphatase/phosphodiesterase 2 (ENSG00000136960), score: 0.74 ERMNermin, ERM-like protein (ENSG00000136541), score: 0.76 EVI2Aecotropic viral integration site 2A (ENSG00000126860), score: 0.85 FA2Hfatty acid 2-hydroxylase (ENSG00000103089), score: 0.83 FAM124Afamily with sequence similarity 124A (ENSG00000150510), score: 0.87 FFAR1free fatty acid receptor 1 (ENSG00000126266), score: 0.75 GALNT6UDP-N-acetyl-alpha-D-galactosamine:polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase 6 (GalNAc-T6) (ENSG00000139629), score: 0.89 GLDNgliomedin (ENSG00000186417), score: 0.84 GPR37G protein-coupled receptor 37 (endothelin receptor type B-like) (ENSG00000170775), score: 0.76 KCNH8potassium voltage-gated channel, subfamily H (eag-related), member 8 (ENSG00000183960), score: 0.92 KREMEN2kringle containing transmembrane protein 2 (ENSG00000131650), score: 0.86 LGR5leucine-rich repeat-containing G protein-coupled receptor 5 (ENSG00000139292), score: 0.76 LIX1Lix1 homolog (chicken) (ENSG00000145721), score: 0.78 LRIT2leucine-rich repeat, immunoglobulin-like and transmembrane domains 2 (ENSG00000204033), score: 0.76 LYPD5LY6/PLAUR domain containing 5 (ENSG00000159871), score: 0.74 MAGmyelin associated glycoprotein (ENSG00000105695), score: 0.78 MOGmyelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein (ENSG00000204655), score: 0.77 NIPAL4NIPA-like domain containing 4 (ENSG00000172548), score: 1 NKX2-2NK2 homeobox 2 (ENSG00000125820), score: 0.75 NPC1Niemann-Pick disease, type C1 (ENSG00000141458), score: 0.83 OLIG2oligodendrocyte lineage transcription factor 2 (ENSG00000205927), score: 0.75 OPALINoligodendrocytic myelin paranodal and inner loop protein (ENSG00000197430), score: 0.79 P2RX7purinergic receptor P2X, ligand-gated ion channel, 7 (ENSG00000089041), score: 0.76 PIP4K2Aphosphatidylinositol-5-phosphate 4-kinase, type II, alpha (ENSG00000150867), score: 0.82 PMP2peripheral myelin protein 2 (ENSG00000147588), score: 0.79 PREX1phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate-dependent Rac exchange factor 1 (ENSG00000124126), score: 0.74 PRKCQprotein kinase C, theta (ENSG00000065675), score: 0.77 PRR18proline rich 18 (ENSG00000176381), score: 0.89 PTK2PTK2 protein tyrosine kinase 2 (ENSG00000169398), score: 0.81 PTPRHprotein tyrosine phosphatase, receptor type, H (ENSG00000080031), score: 0.74 SIRT2sirtuin 2 (ENSG00000068903), score: 0.82 SLC5A11solute carrier family 5 (sodium/glucose cotransporter), member 11 (ENSG00000158865), score: 0.8 SOX10SRY (sex determining region Y)-box 10 (ENSG00000100146), score: 0.76 SOX8SRY (sex determining region Y)-box 8 (ENSG00000005513), score: 0.77 TMEM144transmembrane protein 144 (ENSG00000164124), score: 0.9
| Id | species | tissue | sex | individual |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ggo_br_m_ca1 | ggo | br | m | _ |
| hsa_br_m2_ca1 | hsa | br | m | 2 |
| hsa_br_m1_ca1 | hsa | br | m | 1 |
| ptr_br_m5_ca1 | ptr | br | m | 5 |
| ptr_br_m2_ca1 | ptr | br | m | 2 |
| ptr_br_m3_ca1 | ptr | br | m | 3 |
| hsa_br_m7_ca1 | hsa | br | m | 7 |
| hsa_br_f_ca1 | hsa | br | f | _ |
| hsa_br_m3_ca1 | hsa | br | m | 3 |
| hsa_br_m6_ca1 | hsa | br | m | 6 |