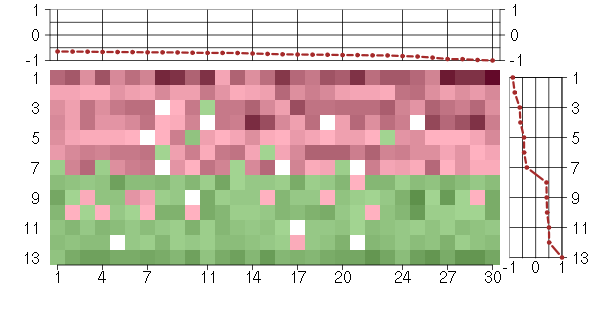

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.
chemotaxis
The directed movement of a motile cell or organism, or the directed growth of a cell guided by a specific chemical concentration gradient. Movement may be towards a higher concentration (positive chemotaxis) or towards a lower concentration (negative chemotaxis).
anatomical structure morphogenesis
The process by which anatomical structures are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
behavior
The specific actions or reactions of an organism in response to external or internal stimuli. Patterned activity of a whole organism in a manner dependent upon some combination of that organism's internal state and external conditions.
locomotory behavior
The specific movement from place to place of an organism in response to external or internal stimuli. Locomotion of a whole organism in a manner dependent upon some combination of that organism's internal state and external conditions.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
response to external stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an external stimulus.
regulation of response to external stimulus
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a response to an external stimulus.
positive regulation of response to external stimulus
Any process that activates, maintains or increases the rate of a response to an external stimulus.
developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an integrated living unit: an anatomical structure (which may be a subcellular structure, cell, tissue, or organ), or organism over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
locomotion
Self-propelled movement of a cell or organism from one location to another.
regulation of locomotion
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of locomotion of a cell or organism.
positive regulation of locomotion
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of locomotion of a cell or organism.
response to chemical stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a chemical stimulus.
taxis
The directed movement of a motile cell or organism in response to an external stimulus.
positive regulation of biological process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
positive regulation of behavior
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of behavior, the specific actions or reactions of an organism in response to external or internal stimuli.
regulation of response to stimulus
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a response to a stimulus. Response to stimulus is a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
positive regulation of response to stimulus
Any process that activates, maintains or increases the rate of a response to a stimulus. Response to stimulus is a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
anatomical structure formation
The process pertaining to the initial formation of an anatomical structure from unspecified parts. This process begins with the specific processes that contribute to the appearance of the discrete structure and ends when the structural rudiment is recognizable. An anatomical structure is any biological entity that occupies space and is distinguished from its surroundings. Anatomical structures can be macroscopic such as a carpel, or microscopic such as an acrosome.
anatomical structure development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an anatomical structure from an initial condition to its mature state. This process begins with the formation of the structure and ends with the mature structure, whatever form that may be including its natural destruction. An anatomical structure is any biological entity that occupies space and is distinguished from its surroundings. Anatomical structures can be macroscopic such as a carpel, or microscopic such as an acrosome.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of behavior
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of behavior, the specific actions or reactions of an organism in response to external or internal stimuli.
response to stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
regulation of chemotaxis
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the directed movement of a motile cell or organism in response to a specific chemical concentration gradient.
positive regulation of chemotaxis
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the directed movement of a motile cell or organism in response to a specific chemical concentration gradient.
biological regulation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of any biological process, quality or function.
all
This term is the most general term possible
positive regulation of locomotion
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of locomotion of a cell or organism.
regulation of locomotion
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of locomotion of a cell or organism.
positive regulation of biological process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of response to stimulus
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a response to a stimulus. Response to stimulus is a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
positive regulation of response to stimulus
Any process that activates, maintains or increases the rate of a response to a stimulus. Response to stimulus is a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
anatomical structure formation
The process pertaining to the initial formation of an anatomical structure from unspecified parts. This process begins with the specific processes that contribute to the appearance of the discrete structure and ends when the structural rudiment is recognizable. An anatomical structure is any biological entity that occupies space and is distinguished from its surroundings. Anatomical structures can be macroscopic such as a carpel, or microscopic such as an acrosome.
anatomical structure morphogenesis
The process by which anatomical structures are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
positive regulation of locomotion
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of locomotion of a cell or organism.
positive regulation of response to stimulus
Any process that activates, maintains or increases the rate of a response to a stimulus. Response to stimulus is a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
positive regulation of behavior
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of behavior, the specific actions or reactions of an organism in response to external or internal stimuli.
regulation of behavior
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of behavior, the specific actions or reactions of an organism in response to external or internal stimuli.
regulation of response to external stimulus
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a response to an external stimulus.
positive regulation of response to external stimulus
Any process that activates, maintains or increases the rate of a response to an external stimulus.
taxis
The directed movement of a motile cell or organism in response to an external stimulus.
chemotaxis
The directed movement of a motile cell or organism, or the directed growth of a cell guided by a specific chemical concentration gradient. Movement may be towards a higher concentration (positive chemotaxis) or towards a lower concentration (negative chemotaxis).
positive regulation of chemotaxis
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the directed movement of a motile cell or organism in response to a specific chemical concentration gradient.
regulation of chemotaxis
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the directed movement of a motile cell or organism in response to a specific chemical concentration gradient.
positive regulation of chemotaxis
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the directed movement of a motile cell or organism in response to a specific chemical concentration gradient.
positive regulation of chemotaxis
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the directed movement of a motile cell or organism in response to a specific chemical concentration gradient.
positive regulation of chemotaxis
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the directed movement of a motile cell or organism in response to a specific chemical concentration gradient.
positive regulation of response to external stimulus
Any process that activates, maintains or increases the rate of a response to an external stimulus.
regulation of chemotaxis
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the directed movement of a motile cell or organism in response to a specific chemical concentration gradient.
positive regulation of behavior
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of behavior, the specific actions or reactions of an organism in response to external or internal stimuli.
regulation of chemotaxis
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the directed movement of a motile cell or organism in response to a specific chemical concentration gradient.
taxis
The directed movement of a motile cell or organism in response to an external stimulus.

extracellular region
The space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.
cellular_component
The part of a cell or its extracellular environment in which a gene product is located. A gene product may be located in one or more parts of a cell and its location may be as specific as a particular macromolecular complex, that is, a stable, persistent association of macromolecules that function together.
extracellular space
That part of a multicellular organism outside the cells proper, usually taken to be outside the plasma membranes, and occupied by fluid.
extracellular region part
Any constituent part of the extracellular region, the space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers constituent parts of the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.
all
This term is the most general term possible
extracellular region part
Any constituent part of the extracellular region, the space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers constituent parts of the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.

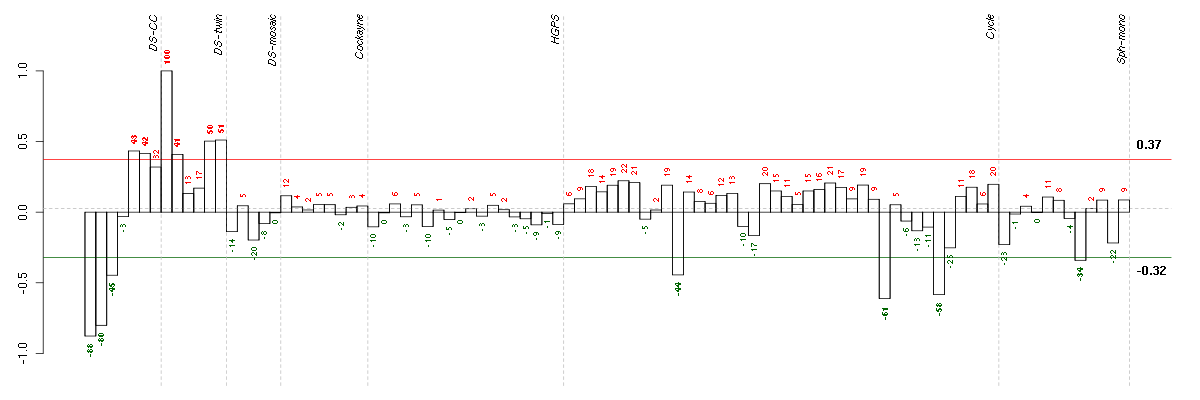
ADH1Balcohol dehydrogenase 1B (class I), beta polypeptide (209612_s_at), score: -0.76 ADRA2Aadrenergic, alpha-2A-, receptor (209869_at), score: -0.68 ANGPTL4angiopoietin-like 4 (221009_s_at), score: -0.8 APODapolipoprotein D (201525_at), score: -0.7 CXCL3chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 3 (207850_at), score: -0.76 DKK2dickkopf homolog 2 (Xenopus laevis) (219908_at), score: -1 DPTdermatopontin (213068_at), score: -0.68 EGR2early growth response 2 (Krox-20 homolog, Drosophila) (205249_at), score: -0.73 EGR3early growth response 3 (206115_at), score: -0.74 FOSBFBJ murine osteosarcoma viral oncogene homolog B (202768_at), score: -0.98 GEMGTP binding protein overexpressed in skeletal muscle (204472_at), score: -0.65 IL1RL1interleukin 1 receptor-like 1 (207526_s_at), score: -0.84 IL6interleukin 6 (interferon, beta 2) (205207_at), score: -0.7 IL8interleukin 8 (211506_s_at), score: -0.67 JHDM1Djumonji C domain containing histone demethylase 1 homolog D (S. cerevisiae) (221778_at), score: -0.77 JMJD3jumonji domain containing 3, histone lysine demethylase (213146_at), score: -0.95 LIFleukemia inhibitory factor (cholinergic differentiation factor) (205266_at), score: -0.68 LMCD1LIM and cysteine-rich domains 1 (218574_s_at), score: -0.71 LOH3CR2Aloss of heterozygosity, 3, chromosomal region 2, gene A (220244_at), score: -0.79 MFAP4microfibrillar-associated protein 4 (212713_at), score: -0.65 NFATC1nuclear factor of activated T-cells, cytoplasmic, calcineurin-dependent 1 (210162_s_at), score: -0.8 NR4A3nuclear receptor subfamily 4, group A, member 3 (209959_at), score: -0.89 PDGFDplatelet derived growth factor D (219304_s_at), score: -0.67 PMEPA1prostate transmembrane protein, androgen induced 1 (217875_s_at), score: -0.79 PPLperiplakin (203407_at), score: -0.83 RCAN2regulator of calcineurin 2 (203498_at), score: -0.65 RRADRas-related associated with diabetes (204802_at), score: -0.94 SMOXspermine oxidase (210357_s_at), score: -0.67 THBDthrombomodulin (203887_s_at), score: -0.77 VEGFAvascular endothelial growth factor A (211527_x_at), score: -0.7
| Id | sample | Experiment | ExpName | Array | Syndrome | Cell.line |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ctrl a 08-03.CEL | 1 | 1 | DS-CC | hgu133a | none | DS-CC 1 |
| ctrl b 08-03.CEL | 2 | 1 | DS-CC | hgu133a | none | DS-CC 2 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486231.cel | 30 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486331.cel | 35 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| ctrl c 08-03.CEL | 3 | 1 | DS-CC | hgu133a | none | DS-CC 3 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485851.cel | 11 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-GEOD-4219-raw-cel-1311956418.cel | 13 | 7 | Sph-mono | hgu133plus2 | none | Sph-mon 1 |
| 2Twin.CEL | 2 | 2 | DS-twin | hgu133plus2 | none | DS-twin 2 |
| t21c 08-03.CEL | 6 | 1 | DS-CC | hgu133a | Down | DS-CC 6 |
| t21b 08-03.CEL | 5 | 1 | DS-CC | hgu133a | Down | DS-CC 5 |
| 5CTwin.CEL | 5 | 2 | DS-twin | hgu133plus2 | Down | DS-twin 5 |
| 6Twin.CEL | 6 | 2 | DS-twin | hgu133plus2 | none | DS-twin 6 |
| 1Twin.CEL | 1 | 2 | DS-twin | hgu133plus2 | Down | DS-twin 1 |