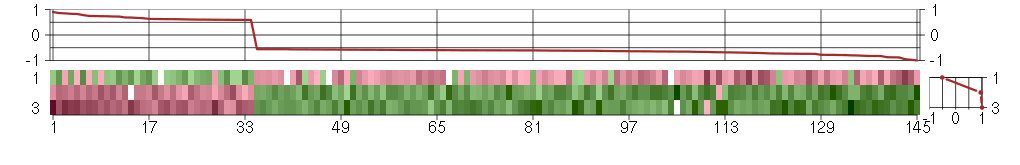

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.
MAPKKK cascade
Cascade of at least three protein kinase activities culminating in the phosphorylation and activation of a MAP kinase. MAPKKK cascades lie downstream of numerous signaling pathways.
activation of MAPK activity
The initiation of the activity of the inactive enzyme MAP kinase by phosphorylation by a MAPKK.
metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways, including anabolism and catabolism, by which living organisms transform chemical substances. Metabolic processes typically transform small molecules, but also include macromolecular processes such as DNA repair and replication, and protein synthesis and degradation.
signal transduction
The cascade of processes by which a signal interacts with a receptor, causing a change in the level or activity of a second messenger or other downstream target, and ultimately effecting a change in the functioning of the cell.
protein modification process
The covalent alteration of one or more amino acids occurring in proteins, peptides and nascent polypeptides (co-translational, post-translational modifications). Includes the modification of charged tRNAs that are destined to occur in a protein (pre-translation modification).
protein amino acid phosphorylation
The process of introducing a phosphate group on to a protein.
phosphorus metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving the nonmetallic element phosphorus or compounds that contain phosphorus, usually in the form of a phosphate group (PO4).
phosphate metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving the phosphate group, the anion or salt of any phosphoric acid.
response to stress
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a disturbance in organismal or cellular homeostasis, usually, but not necessarily, exogenous (e.g. temperature, humidity, ionizing radiation).
cell communication
Any process that mediates interactions between a cell and its surroundings. Encompasses interactions such as signaling or attachment between one cell and another cell, between a cell and an extracellular matrix, or between a cell and any other aspect of its environment.
intracellular signaling cascade
A series of reactions within the cell that occur as a result of a single trigger reaction or compound.
protein kinase cascade
A series of reactions, mediated by protein kinases, which occurs as a result of a single trigger reaction or compound.
JNK cascade
A cascade of protein kinase activities, culminating in the phosphorylation and activation of a member of the JUN kinase subfamily of stress-activated protein kinases, which in turn are a subfamily of mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinases that is activated primarily by cytokines and exposure to environmental stress.
activation of JUN kinase activity
The initiation of the activity of the inactive enzyme JUN kinase by phosphorylation by a JUN kinase kinase (JNKK).
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
phosphorylation
The process of introducing a phosphate group into a molecule, usually with the formation of a phosphoric ester, a phosphoric anhydride or a phosphoric amide.
protein metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving a specific protein, rather than of proteins in general. Includes protein modification.
stress-activated protein kinase signaling pathway
A series of molecular signals in which a stress-activated protein kinase (SAPK) cascade relays one or more of the signals.
cellular response to stress
A change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus indicating the organism is under stress. The stress is usually, but not necessarily, exogenous (e.g. temperature, humidity, ionizing radiation).
positive regulation of kinase activity
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of kinase activity, the catalysis of the transfer of a phosphate group, usually from ATP, to a substrate molecule.
cellular biopolymer metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature, such as polysaccharides and proteins, as carried out by individual cells.
positive regulation of catalytic activity
Any process that activates or increases the activity of an enzyme.
macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
biopolymer metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature, such as polysaccharides and proteins.
regulation of MAP kinase activity
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of MAP kinase activity.
positive regulation of MAP kinase activity
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of MAP kinase activity.
biopolymer modification
The covalent alteration of one or more monomeric units in a polypeptide, polynucleotide, polysaccharide, or other biological polymer, resulting in a change in its properties.
regulation of JUN kinase activity
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of JUN kinase activity.
positive regulation of JUN kinase activity
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of JUN kinase activity.
regulation of kinase activity
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of kinase activity, the catalysis of the transfer of a phosphate group, usually from ATP, to a substrate molecule.
post-translational protein modification
The covalent alteration of one or more amino acids occurring in a protein after the protein has been completely translated and released from the ribosome.
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
primary metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving those compounds which are formed as a part of the normal anabolic and catabolic processes. These processes take place in most, if not all, cells of the organism.
cellular macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular protein metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving a specific protein, rather than of proteins in general, occurring at the level of an individual cell. Includes protein modification.
regulation of protein kinase activity
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of protein kinase activity.
positive regulation of protein kinase activity
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of protein kinase activity.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of catalytic activity
Any process that modulates the activity of an enzyme.
regulation of cellular process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
response to stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
regulation of transferase activity
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of transferase activity, the catalysis of the transfer of a group, e.g. a methyl group, glycosyl group, acyl group, phosphorus-containing, or other groups, from one compound (generally regarded as the donor) to another compound (generally regarded as the acceptor). Transferase is the systematic name for any enzyme of EC class 2.
positive regulation of transferase activity
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of transferase activity, the catalysis of the transfer of a group, e.g. a methyl group, glycosyl group, acyl group, phosphorus-containing, or other groups, from a donor compound to an acceptor.
cellular response to stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
biological regulation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of any biological process, quality or function.
regulation of molecular function
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of molecular functions. Molecular functions are elemental biological activities occurring at the molecular level, such as catalysis or binding.
all
This term is the most general term possible
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
regulation of cellular process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
cellular response to stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
cellular macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, as carried out by individual cells.
signal transduction
The cascade of processes by which a signal interacts with a receptor, causing a change in the level or activity of a second messenger or other downstream target, and ultimately effecting a change in the functioning of the cell.
cellular response to stress
A change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus indicating the organism is under stress. The stress is usually, but not necessarily, exogenous (e.g. temperature, humidity, ionizing radiation).
protein metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving a specific protein, rather than of proteins in general. Includes protein modification.
cellular biopolymer metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature, such as polysaccharides and proteins, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular protein metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving a specific protein, rather than of proteins in general, occurring at the level of an individual cell. Includes protein modification.
protein modification process
The covalent alteration of one or more amino acids occurring in proteins, peptides and nascent polypeptides (co-translational, post-translational modifications). Includes the modification of charged tRNAs that are destined to occur in a protein (pre-translation modification).
stress-activated protein kinase signaling pathway
A series of molecular signals in which a stress-activated protein kinase (SAPK) cascade relays one or more of the signals.
positive regulation of transferase activity
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of transferase activity, the catalysis of the transfer of a group, e.g. a methyl group, glycosyl group, acyl group, phosphorus-containing, or other groups, from a donor compound to an acceptor.
positive regulation of kinase activity
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of kinase activity, the catalysis of the transfer of a phosphate group, usually from ATP, to a substrate molecule.
protein amino acid phosphorylation
The process of introducing a phosphate group on to a protein.
activation of MAPK activity
The initiation of the activity of the inactive enzyme MAP kinase by phosphorylation by a MAPKK.
JNK cascade
A cascade of protein kinase activities, culminating in the phosphorylation and activation of a member of the JUN kinase subfamily of stress-activated protein kinases, which in turn are a subfamily of mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinases that is activated primarily by cytokines and exposure to environmental stress.
positive regulation of protein kinase activity
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of protein kinase activity.
activation of JUN kinase activity
The initiation of the activity of the inactive enzyme JUN kinase by phosphorylation by a JUN kinase kinase (JNKK).
positive regulation of MAP kinase activity
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of MAP kinase activity.
activation of MAPK activity
The initiation of the activity of the inactive enzyme MAP kinase by phosphorylation by a MAPKK.
positive regulation of JUN kinase activity
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of JUN kinase activity.
activation of JUN kinase activity
The initiation of the activity of the inactive enzyme JUN kinase by phosphorylation by a JUN kinase kinase (JNKK).


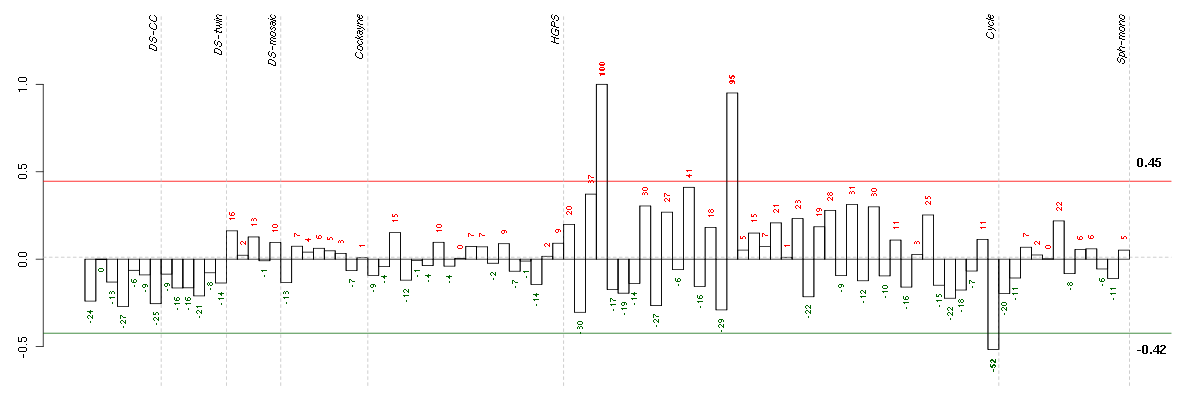
ABL2v-abl Abelson murine leukemia viral oncogene homolog 2 (arg, Abelson-related gene) (206411_s_at), score: -0.57 AFF2AF4/FMR2 family, member 2 (206105_at), score: -0.56 AFPalpha-fetoprotein (204694_at), score: 0.73 AGTangiotensinogen (serpin peptidase inhibitor, clade A, member 8) (202834_at), score: -0.62 ALDH3A1aldehyde dehydrogenase 3 family, memberA1 (205623_at), score: -0.78 ALDH4A1aldehyde dehydrogenase 4 family, member A1 (211552_s_at), score: -0.58 ALPPL2alkaline phosphatase, placental-like 2 (216377_x_at), score: -0.88 ANXA8L2annexin A8-like 2 (203074_at), score: -0.63 AP1G2adaptor-related protein complex 1, gamma 2 subunit (201613_s_at), score: -0.71 APBA1amyloid beta (A4) precursor protein-binding, family A, member 1 (206679_at), score: -0.58 ATMataxia telangiectasia mutated (210858_x_at), score: -0.62 ATP6V1G2ATPase, H+ transporting, lysosomal 13kDa, V1 subunit G2 (214762_at), score: -0.68 BAT2LHLA-B associated transcript 2-like (212068_s_at), score: 0.86 BRS3bombesin-like receptor 3 (207369_at), score: -0.61 C15orf5chromosome 15 open reading frame 5 (208109_s_at), score: -0.66 C17orf63chromosome 17 open reading frame 63 (218464_s_at), score: -0.56 C19orf28chromosome 19 open reading frame 28 (220178_at), score: -0.6 C19orf40chromosome 19 open reading frame 40 (214816_x_at), score: -0.66 C1orf61chromosome 1 open reading frame 61 (205103_at), score: -0.57 C2orf37chromosome 2 open reading frame 37 (220172_at), score: 0.6 C7orf58chromosome 7 open reading frame 58 (220032_at), score: 0.59 CALB2calbindin 2 (205428_s_at), score: -0.6 CCDC40coiled-coil domain containing 40 (220592_at), score: -0.74 CCDC94coiled-coil domain containing 94 (204335_at), score: -0.65 CD70CD70 molecule (206508_at), score: -0.7 CD79BCD79b molecule, immunoglobulin-associated beta (205297_s_at), score: -0.59 CFIcomplement factor I (203854_at), score: -0.63 CLTCL1clathrin, heavy chain-like 1 (205944_s_at), score: -0.6 CNNM2cyclin M2 (206818_s_at), score: -0.56 COL11A2collagen, type XI, alpha 2 (216993_s_at), score: -0.6 CPNE3copine III (202118_s_at), score: 0.59 CTNScystinosis, nephropathic (36566_at), score: -0.57 CTSFcathepsin F (203657_s_at), score: -0.59 CYLC2cylicin, basic protein of sperm head cytoskeleton 2 (207780_at), score: -0.59 DHRS11dehydrogenase/reductase (SDR family) member 11 (218756_s_at), score: 0.67 DKFZp434H1419hypothetical protein DKFZp434H1419 (214717_at), score: -0.6 DMBT1deleted in malignant brain tumors 1 (208250_s_at), score: -0.78 DNAJC2DnaJ (Hsp40) homolog, subfamily C, member 2 (213097_s_at), score: -0.61 DOK4docking protein 4 (209691_s_at), score: 0.72 DSPPdentin sialophosphoprotein (221681_s_at), score: -0.81 DUSP8dual specificity phosphatase 8 (206374_at), score: -0.56 DUSP9dual specificity phosphatase 9 (205777_at), score: -0.88 EPM2Aepilepsy, progressive myoclonus type 2A, Lafora disease (laforin) (205231_s_at), score: -0.62 ERCC6excision repair cross-complementing rodent repair deficiency, complementation group 6 (207347_at), score: 0.74 F11coagulation factor XI (206610_s_at), score: -0.78 F7coagulation factor VII (serum prothrombin conversion accelerator) (207300_s_at), score: -0.64 FAM105Afamily with sequence similarity 105, member A (219694_at), score: 0.59 FCER1GFc fragment of IgE, high affinity I, receptor for; gamma polypeptide (204232_at), score: -0.78 FGL1fibrinogen-like 1 (205305_at), score: -0.62 FLCNfolliculin (215645_at), score: -0.64 FLJ21075hypothetical protein FLJ21075 (221172_at), score: -0.6 FLRT3fibronectin leucine rich transmembrane protein 3 (219250_s_at), score: 0.83 GABARAPL1GABA(A) receptor-associated protein like 1 (208868_s_at), score: -0.6 GABARAPL3GABA(A) receptors associated protein like 3 (pseudogene) (211458_s_at), score: -0.58 GANgigaxonin (220124_at), score: 0.78 GCHFRGTP cyclohydrolase I feedback regulator (204867_at), score: -0.68 GMPRguanosine monophosphate reductase (204187_at), score: 0.6 GP1BAglycoprotein Ib (platelet), alpha polypeptide (207389_at), score: -0.95 GPR144G protein-coupled receptor 144 (216289_at), score: -1 GPR32G protein-coupled receptor 32 (221469_at), score: -0.8 HAB1B1 for mucin (215778_x_at), score: -0.72 HAMPhepcidin antimicrobial peptide (220491_at), score: -0.74 HAND1heart and neural crest derivatives expressed 1 (220138_at), score: -0.82 HAO2hydroxyacid oxidase 2 (long chain) (220801_s_at), score: -0.64 IDI2isopentenyl-diphosphate delta isomerase 2 (217631_at), score: -0.56 IFNA7interferon, alpha 7 (208259_x_at), score: -0.7 IKZF5IKAROS family zinc finger 5 (Pegasus) (220086_at), score: 0.69 IL9Rinterleukin 9 receptor (217212_s_at), score: -0.58 ITGALintegrin, alpha L (antigen CD11A (p180), lymphocyte function-associated antigen 1; alpha polypeptide) (213475_s_at), score: -0.74 KIF26Bkinesin family member 26B (220002_at), score: -0.61 LAT2linker for activation of T cells family, member 2 (211768_at), score: -0.59 LEPREL2leprecan-like 2 (204854_at), score: 0.62 LILRB3leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor, subfamily B (with TM and ITIM domains), member 3 (211133_x_at), score: -0.63 LOC149478hypothetical protein LOC149478 (215462_at), score: -0.6 LOC149501similar to keratin 8 (216821_at), score: -0.69 LRDDleucine-rich repeats and death domain containing (221640_s_at), score: 0.6 LRP2low density lipoprotein-related protein 2 (205710_at), score: 0.83 MAP3K6mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 6 (219278_at), score: 0.62 MAPK10mitogen-activated protein kinase 10 (204813_at), score: -0.74 MEF2Bmyocyte enhancer factor 2B (209926_at), score: -0.72 MEG3maternally expressed 3 (non-protein coding) (210794_s_at), score: -0.56 MEOX1mesenchyme homeobox 1 (205619_s_at), score: -0.62 MGC5590hypothetical protein MGC5590 (220931_at), score: 0.6 MOCS1molybdenum cofactor synthesis 1 (211673_s_at), score: -0.83 MPP2membrane protein, palmitoylated 2 (MAGUK p55 subfamily member 2) (213270_at), score: -0.63 MRPS6mitochondrial ribosomal protein S6 (213167_s_at), score: 0.63 MTMR8myotubularin related protein 8 (220537_at), score: 0.74 NCAM2neural cell adhesion molecule 2 (205669_at), score: -0.65 NDPNorrie disease (pseudoglioma) (206022_at), score: 0.68 NOL10nucleolar protein 10 (218591_s_at), score: -0.65 NOVA2neuro-oncological ventral antigen 2 (206477_s_at), score: -0.69 NRCAMneuronal cell adhesion molecule (216959_x_at), score: -0.65 OLR1oxidized low density lipoprotein (lectin-like) receptor 1 (210004_at), score: -0.58 PCDH24protocadherin 24 (220186_s_at), score: -0.73 PCSK5proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 5 (205559_s_at), score: -0.56 PHF7PHD finger protein 7 (215622_x_at), score: -0.61 PIN1Lpeptidylprolyl cis/trans isomerase, NIMA-interacting 1-like (pseudogene) (207582_at), score: -0.6 PIPOXpipecolic acid oxidase (221605_s_at), score: -0.57 PKLRpyruvate kinase, liver and RBC (222078_at), score: -0.65 PNMAL1PNMA-like 1 (218824_at), score: 0.74 POLR2J4polymerase (RNA) II (DNA directed) polypeptide J4, pseudogene (217610_at), score: -0.6 POM121L2POM121 membrane glycoprotein-like 2 (rat) (216582_at), score: -0.59 POM121L9PPOM121 membrane glycoprotein-like 9 (rat) pseudogene (222253_s_at), score: -0.57 PPP1R13Bprotein phosphatase 1, regulatory (inhibitor) subunit 13B (216347_s_at), score: -0.87 PRLHprolactin releasing hormone (221443_x_at), score: -0.68 PTPN6protein tyrosine phosphatase, non-receptor type 6 (206687_s_at), score: -0.73 PVT1Pvt1 oncogene (non-protein coding) (216249_at), score: -0.59 RALGPS2Ral GEF with PH domain and SH3 binding motif 2 (220338_at), score: -0.66 RASGRP3RAS guanyl releasing protein 3 (calcium and DAG-regulated) (205801_s_at), score: 0.62 RBM38RNA binding motif protein 38 (212430_at), score: -0.64 RNF121ring finger protein 121 (219021_at), score: -0.67 RNF220ring finger protein 220 (219988_s_at), score: 0.6 RPL18AP6ribosomal protein L18a pseudogene 6 (216383_at), score: -0.65 RPRD2regulation of nuclear pre-mRNA domain containing 2 (212553_at), score: 0.61 RPS6KA6ribosomal protein S6 kinase, 90kDa, polypeptide 6 (220738_s_at), score: 0.75 RRHretinal pigment epithelium-derived rhodopsin homolog (208314_at), score: -0.58 SAA4serum amyloid A4, constitutive (207096_at), score: -0.59 SFMBT1Scm-like with four mbt domains 1 (213370_s_at), score: 0.59 SH2D3ASH2 domain containing 3A (222169_x_at), score: -0.58 SHANK2SH3 and multiple ankyrin repeat domains 2 (213307_at), score: -0.62 SLC1A7solute carrier family 1 (glutamate transporter), member 7 (210923_at), score: -0.82 SLCO2A1solute carrier organic anion transporter family, member 2A1 (204368_at), score: -0.79 SNTG1syntrophin, gamma 1 (220405_at), score: 0.85 SORBS1sorbin and SH3 domain containing 1 (218087_s_at), score: -0.56 SPATA1spermatogenesis associated 1 (221057_at), score: -0.97 SRD5A3steroid 5 alpha-reductase 3 (218800_at), score: 0.61 SULT1B1sulfotransferase family, cytosolic, 1B, member 1 (207601_at), score: -0.58 SYT1synaptotagmin I (203999_at), score: 0.66 TAL1T-cell acute lymphocytic leukemia 1 (206283_s_at), score: -0.73 TMCC2transmembrane and coiled-coil domain family 2 (213096_at), score: -0.59 TMPRSS6transmembrane protease, serine 6 (214955_at), score: -0.57 TOM1L2target of myb1-like 2 (chicken) (214840_at), score: 0.62 TULP2tubby like protein 2 (206733_at), score: -0.8 TYMPthymidine phosphorylase (217497_at), score: -0.6 UTF1undifferentiated embryonic cell transcription factor 1 (208275_x_at), score: -0.61 VDRvitamin D (1,25- dihydroxyvitamin D3) receptor (204255_s_at), score: -0.59 VHLvon Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor (203844_at), score: -0.56 WDR78WD repeat domain 78 (220769_s_at), score: -0.57 ZAKsterile alpha motif and leucine zipper containing kinase AZK (218833_at), score: -0.64 ZFYVE26zinc finger, FYVE domain containing 26 (37943_at), score: -0.6 ZNF192zinc finger protein 192 (206579_at), score: 0.6 ZNF362zinc finger protein 362 (214915_at), score: 0.63 ZNF460zinc finger protein 460 (216279_at), score: 0.9 ZNF652zinc finger protein 652 (205594_at), score: -0.6
| Id | sample | Experiment | ExpName | Array | Syndrome | Cell.line |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486431.cel | 40 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485951.cel | 16 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485711.cel | 4 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |