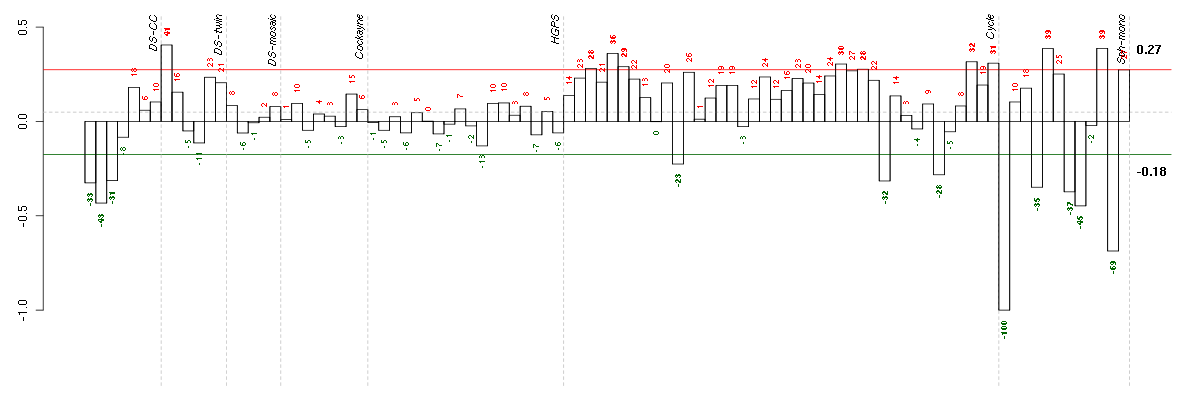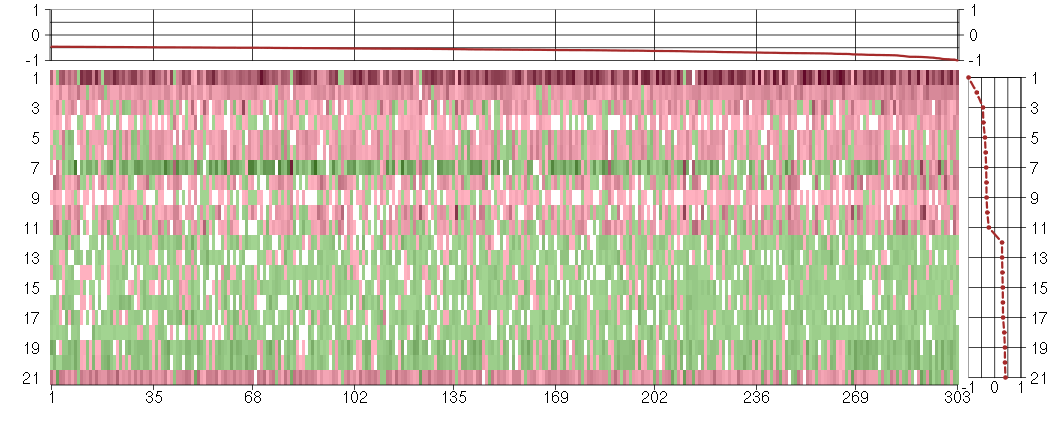

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways, including anabolism and catabolism, by which living organisms transform chemical substances. Metabolic processes typically transform small molecules, but also include macromolecular processes such as DNA repair and replication, and protein synthesis and degradation.
defense response
Reactions, triggered in response to the presence of a foreign body or the occurrence of an injury, which result in restriction of damage to the organism attacked or prevention/recovery from the infection caused by the attack.
nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
transcription
The synthesis of either RNA on a template of DNA or DNA on a template of RNA.
transcription, DNA-dependent
The synthesis of RNA on a template of DNA.
regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of DNA-dependent transcription.
response to stress
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a disturbance in organismal or cellular homeostasis, usually, but not necessarily, exogenous (e.g. temperature, humidity, ionizing radiation).
inflammatory response
The immediate defensive reaction (by vertebrate tissue) to infection or injury caused by chemical or physical agents. The process is characterized by local vasodilation, extravasation of plasma into intercellular spaces and accumulation of white blood cells and macrophages.
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances; typically the energy-requiring part of metabolism in which simpler substances are transformed into more complex ones.
macromolecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
response to external stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an external stimulus.
response to wounding
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus indicating damage to the organism.
regulation of biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances.
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
gene expression
The process by which a gene's coding sequence is converted into a mature gene product or products (proteins or RNA). This includes the production of an RNA transcript as well as any processing to produce a mature RNA product or an mRNA (for protein-coding genes) and the translation of that mRNA into protein. Some protein processing events may be included when they are required to form an active form of a product from an inactive precursor form.
regulation of gene expression
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of gene expression. Gene expression is the process in which a gene's coding sequence is converted into a mature gene product or products (proteins or RNA). This includes the production of an RNA transcript as well as any processing to produce a mature RNA product or an mRNA (for protein-coding genes) and the translation of that mRNA into protein. Some protein processing events may be included when they are required to form an active form of a product from an inactive precursor form.
regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the rate, frequency or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
RNA metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving RNA, ribonucleic acid, one of the two main type of nucleic acid, consisting of a long, unbranched macromolecule formed from ribonucleotides joined in 3',5'-phosphodiester linkage.
regulation of nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
regulation of metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism.
regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
regulation of cellular biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
multicellular organismal process
Any biological process, occurring at the level of a multicellular organism, pertinent to its function.
developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an integrated living unit: an anatomical structure (which may be a subcellular structure, cell, tissue, or organ), or organism over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
RNA biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of RNA, ribonucleic acid, one of the two main type of nucleic acid, consisting of a long, unbranched macromolecule formed from ribonucleotides joined in 3',5'-phosphodiester linkage. Includes polymerization of ribonucleotide monomers.
cellular macromolecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, carried out by individual cells.
cellular biopolymer metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature, such as polysaccharides and proteins, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular biopolymer biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature, such as polysaccharides and proteins, as carried out by individual cells.
macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
biopolymer metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature, such as polysaccharides and proteins.
biopolymer biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature e.g. polysaccharides and proteins.
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
primary metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving those compounds which are formed as a part of the normal anabolic and catabolic processes. These processes take place in most, if not all, cells of the organism.
cellular biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
cellular macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, as carried out by individual cells.
regulation of transcription
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the synthesis of either RNA on a template of DNA or DNA on a template of RNA.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of cellular process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
response to stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
regulation of RNA metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving RNA.
regulation of macromolecule metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
biological regulation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of any biological process, quality or function.
all
This term is the most general term possible
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
regulation of metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism.
regulation of cellular process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances.
macromolecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
regulation of macromolecule metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
cellular biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
cellular macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, as carried out by individual cells.
nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
response to wounding
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus indicating damage to the organism.
regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the rate, frequency or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
regulation of cellular biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
cellular macromolecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, carried out by individual cells.
regulation of cellular biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the rate, frequency or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
regulation of gene expression
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of gene expression. Gene expression is the process in which a gene's coding sequence is converted into a mature gene product or products (proteins or RNA). This includes the production of an RNA transcript as well as any processing to produce a mature RNA product or an mRNA (for protein-coding genes) and the translation of that mRNA into protein. Some protein processing events may be included when they are required to form an active form of a product from an inactive precursor form.
biopolymer biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature e.g. polysaccharides and proteins.
cellular macromolecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, carried out by individual cells.
cellular biopolymer metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature, such as polysaccharides and proteins, as carried out by individual cells.
transcription
The synthesis of either RNA on a template of DNA or DNA on a template of RNA.
regulation of nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
inflammatory response
The immediate defensive reaction (by vertebrate tissue) to infection or injury caused by chemical or physical agents. The process is characterized by local vasodilation, extravasation of plasma into intercellular spaces and accumulation of white blood cells and macrophages.
cellular biopolymer biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature, such as polysaccharides and proteins, as carried out by individual cells.
regulation of transcription
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the synthesis of either RNA on a template of DNA or DNA on a template of RNA.
regulation of transcription
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the synthesis of either RNA on a template of DNA or DNA on a template of RNA.
regulation of RNA metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving RNA.
regulation of transcription
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the synthesis of either RNA on a template of DNA or DNA on a template of RNA.
transcription, DNA-dependent
The synthesis of RNA on a template of DNA.
regulation of transcription
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the synthesis of either RNA on a template of DNA or DNA on a template of RNA.
RNA metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving RNA, ribonucleic acid, one of the two main type of nucleic acid, consisting of a long, unbranched macromolecule formed from ribonucleotides joined in 3',5'-phosphodiester linkage.
cellular biopolymer biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature, such as polysaccharides and proteins, as carried out by individual cells.
RNA biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of RNA, ribonucleic acid, one of the two main type of nucleic acid, consisting of a long, unbranched macromolecule formed from ribonucleotides joined in 3',5'-phosphodiester linkage. Includes polymerization of ribonucleotide monomers.
regulation of RNA metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving RNA.
regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of DNA-dependent transcription.
transcription
The synthesis of either RNA on a template of DNA or DNA on a template of RNA.
regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of DNA-dependent transcription.

extracellular region
The space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.
cellular_component
The part of a cell or its extracellular environment in which a gene product is located. A gene product may be located in one or more parts of a cell and its location may be as specific as a particular macromolecular complex, that is, a stable, persistent association of macromolecules that function together.
extracellular space
That part of a multicellular organism outside the cells proper, usually taken to be outside the plasma membranes, and occupied by fluid.
extracellular region part
Any constituent part of the extracellular region, the space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers constituent parts of the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.
all
This term is the most general term possible
extracellular region part
Any constituent part of the extracellular region, the space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers constituent parts of the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.

protein binding
Interacting selectively with any protein or protein complex (a complex of two or more proteins that may include other nonprotein molecules).
G-protein-coupled receptor binding
Interacting selectively with a G-protein-coupled receptor.
molecular_function
Elemental activities, such as catalysis or binding, describing the actions of a gene product at the molecular level. A given gene product may exhibit one or more molecular functions.
nucleic acid binding
Interacting selectively with any nucleic acid.
DNA binding
Interacting selectively with DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid).
transcription factor activity
The function of binding to a specific DNA sequence in order to modulate transcription. The transcription factor may or may not also interact selectively with a protein or macromolecular complex.
receptor binding
Interacting selectively with one or more specific sites on a receptor molecule, a macromolecule that undergoes combination with a hormone, neurotransmitter, drug or intracellular messenger to initiate a change in cell function.
cytokine activity
Functions to control the survival, growth, differentiation and effector function of tissues and cells.
binding
The selective, often stoichiometric, interaction of a molecule with one or more specific sites on another molecule.
metal ion binding
Interacting selectively with any metal ion.
chemokine activity
The function of a family of chemotactic pro-inflammatory activation-inducible cytokines acting primarily upon hemopoietic cells in immunoregulatory processes; all chemokines possess a number of conserved cysteine residues involved in intramolecular disulfide bond formation.
zinc ion binding
Interacting selectively with zinc (Zn) ions.
transcription regulator activity
Plays a role in regulating transcription; may bind a promoter or enhancer DNA sequence or interact with a DNA-binding transcription factor.
chemokine receptor binding
Interacting selectively with any chemokine receptor.
ion binding
Interacting selectively with ions, charged atoms or groups of atoms.
cation binding
Interacting selectively with cations, charged atoms or groups of atoms with a net positive charge.
transition metal ion binding
Interacting selectively with a transition metal ions; a transition metal is an element whose atom has an incomplete d-subshell of extranuclear electrons, or which gives rise to a cation or cations with an incomplete d-subshell. Transition metals often have more than one valency state. Biologically relevant transition metals include vanadium, manganese, iron, copper, cobalt, nickel, molybdenum and silver.
all
This term is the most general term possible
transcription factor activity
The function of binding to a specific DNA sequence in order to modulate transcription. The transcription factor may or may not also interact selectively with a protein or macromolecular complex.
transition metal ion binding
Interacting selectively with a transition metal ions; a transition metal is an element whose atom has an incomplete d-subshell of extranuclear electrons, or which gives rise to a cation or cations with an incomplete d-subshell. Transition metals often have more than one valency state. Biologically relevant transition metals include vanadium, manganese, iron, copper, cobalt, nickel, molybdenum and silver.
chemokine activity
The function of a family of chemotactic pro-inflammatory activation-inducible cytokines acting primarily upon hemopoietic cells in immunoregulatory processes; all chemokines possess a number of conserved cysteine residues involved in intramolecular disulfide bond formation.
| Id | Pvalue | ExpCount | Count | Size | Term |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 04060 | 9.900e-03 | 3.423 | 12 | 115 | Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction |
| Id | Pvalue | ExpCount | Count | Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-17-5p/20/93.mr/106/519.d | 1.401e-02 | 24.25 | 48 | 633 |
| miR-101 | 1.474e-02 | 16.05 | 36 | 419 |
AASSaminoadipate-semialdehyde synthase (214829_at), score: -0.47 ABCA1ATP-binding cassette, sub-family A (ABC1), member 1 (203504_s_at), score: -0.63 ABCA5ATP-binding cassette, sub-family A (ABC1), member 5 (213353_at), score: -0.46 ABCG1ATP-binding cassette, sub-family G (WHITE), member 1 (204567_s_at), score: -0.8 ACOT11acyl-CoA thioesterase 11 (216103_at), score: -0.53 ACVR2Aactivin A receptor, type IIA (205327_s_at), score: -0.73 ADAM17ADAM metallopeptidase domain 17 (205745_x_at), score: -0.47 ADORA2Aadenosine A2a receptor (205013_s_at), score: -0.87 AKAP8A kinase (PRKA) anchor protein 8 (203848_at), score: -0.54 ALDOAP2aldolase A, fructose-bisphosphate pseudogene 2 (211617_at), score: -0.5 ALMS1Alstrom syndrome 1 (214707_x_at), score: -0.63 AMPD3adenosine monophosphate deaminase (isoform E) (207992_s_at), score: -0.62 ANGPTL4angiopoietin-like 4 (221009_s_at), score: -0.46 ANKHankylosis, progressive homolog (mouse) (220076_at), score: -0.82 ANKRD10ankyrin repeat domain 10 (218093_s_at), score: -0.78 APBB2amyloid beta (A4) precursor protein-binding, family B, member 2 (212972_x_at), score: -0.72 APODapolipoprotein D (201525_at), score: -0.92 ARAP2ArfGAP with RhoGAP domain, ankyrin repeat and PH domain 2 (214102_at), score: -0.54 AREGamphiregulin (205239_at), score: -0.49 ARHGAP5Rho GTPase activating protein 5 (217936_at), score: -0.48 ARHGEF7Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) 7 (202548_s_at), score: -0.52 ARID4AAT rich interactive domain 4A (RBP1-like) (205062_x_at), score: -0.58 ARID4BAT rich interactive domain 4B (RBP1-like) (221230_s_at), score: -0.5 ATAD2BATPase family, AAA domain containing 2B (213387_at), score: -0.59 B4GALT1UDP-Gal:betaGlcNAc beta 1,4- galactosyltransferase, polypeptide 1 (201883_s_at), score: -0.54 B4GALT5UDP-Gal:betaGlcNAc beta 1,4- galactosyltransferase, polypeptide 5 (221484_at), score: -0.63 BACH1BTB and CNC homology 1, basic leucine zipper transcription factor 1 (204194_at), score: -0.56 BACH2BTB and CNC homology 1, basic leucine zipper transcription factor 2 (221234_s_at), score: -0.51 BCL9B-cell CLL/lymphoma 9 (204129_at), score: -0.7 BCORBCL6 co-repressor (219433_at), score: -0.65 BHLHB9basic helix-loop-helix domain containing, class B, 9 (213709_at), score: -0.56 BMP2bone morphogenetic protein 2 (205289_at), score: -0.82 BTAF1BTAF1 RNA polymerase II, B-TFIID transcription factor-associated, 170kDa (Mot1 homolog, S. cerevisiae) (209430_at), score: -0.78 C10orf88chromosome 10 open reading frame 88 (219240_s_at), score: -0.6 C11orf57chromosome 11 open reading frame 57 (218314_s_at), score: -0.66 C12orf35chromosome 12 open reading frame 35 (218614_at), score: -0.5 C12orf49chromosome 12 open reading frame 49 (218867_s_at), score: -0.54 C17orf86chromosome 17 open reading frame 86 (221621_at), score: -0.59 C17orf91chromosome 17 open reading frame 91 (214696_at), score: -0.47 C3complement component 3 (217767_at), score: -0.52 C6orf162chromosome 6 open reading frame 162 (213314_at), score: -0.57 C8orf4chromosome 8 open reading frame 4 (218541_s_at), score: -0.56 CBFA2T2core-binding factor, runt domain, alpha subunit 2; translocated to, 2 (207625_s_at), score: -0.48 CCDC25coiled-coil domain containing 25 (218125_s_at), score: -0.58 CCDC47coiled-coil domain containing 47 (217814_at), score: -0.51 CCNJcyclin J (219470_x_at), score: -0.52 CCT6Bchaperonin containing TCP1, subunit 6B (zeta 2) (206587_at), score: -0.5 CD302CD302 molecule (203799_at), score: -0.61 CDC14ACDC14 cell division cycle 14 homolog A (S. cerevisiae) (205288_at), score: -0.68 CDC42SE1CDC42 small effector 1 (218157_x_at), score: -0.57 CDKN1Ccyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1C (p57, Kip2) (213183_s_at), score: -0.74 CDR1cerebellar degeneration-related protein 1, 34kDa (207276_at), score: -0.55 CGGBP1CGG triplet repeat binding protein 1 (214050_at), score: -0.69 CHI3L1chitinase 3-like 1 (cartilage glycoprotein-39) (209395_at), score: -0.68 CHST2carbohydrate (N-acetylglucosamine-6-O) sulfotransferase 2 (203921_at), score: -0.86 CIRBPcold inducible RNA binding protein (200811_at), score: -0.5 CISD3CDGSH iron sulfur domain 3 (213551_x_at), score: -0.59 CLCA2chloride channel accessory 2 (206165_s_at), score: -0.46 CLEC4EC-type lectin domain family 4, member E (219859_at), score: -0.48 COQ10Bcoenzyme Q10 homolog B (S. cerevisiae) (219397_at), score: -0.59 CPEcarboxypeptidase E (201117_s_at), score: -0.72 CREBZFCREB/ATF bZIP transcription factor (202978_s_at), score: -0.5 CSGALNACT2chondroitin sulfate N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase 2 (222235_s_at), score: -0.48 CUGBP2CUG triplet repeat, RNA binding protein 2 (202158_s_at), score: -0.47 CXCL1chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 1 (melanoma growth stimulating activity, alpha) (204470_at), score: -0.79 CXCL2chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 2 (209774_x_at), score: -1 CXCL3chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 3 (207850_at), score: -0.95 CXCL5chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 5 (214974_x_at), score: -0.68 CXCL6chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 6 (granulocyte chemotactic protein 2) (206336_at), score: -0.53 CYP2C9cytochrome P450, family 2, subfamily C, polypeptide 9 (214421_x_at), score: -0.46 DACT1dapper, antagonist of beta-catenin, homolog 1 (Xenopus laevis) (219179_at), score: -0.52 DAPP1dual adaptor of phosphotyrosine and 3-phosphoinositides (219290_x_at), score: -0.61 DAZ4deleted in azoospermia 4 (216351_x_at), score: -0.49 DKFZp686O1327hypothetical gene supported by BC043549; BX648102 (216877_at), score: -0.67 DKK2dickkopf homolog 2 (Xenopus laevis) (219908_at), score: -0.51 DNAH3dynein, axonemal, heavy chain 3 (220725_x_at), score: -0.65 EEF1Deukaryotic translation elongation factor 1 delta (guanine nucleotide exchange protein) (214395_x_at), score: -0.47 EGR2early growth response 2 (Krox-20 homolog, Drosophila) (205249_at), score: -0.87 EGR3early growth response 3 (206115_at), score: -0.54 EIF4EBP2eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E binding protein 2 (208770_s_at), score: -0.5 ELK4ELK4, ETS-domain protein (SRF accessory protein 1) (206919_at), score: -0.71 EMP1epithelial membrane protein 1 (201325_s_at), score: -0.69 EPB41L1erythrocyte membrane protein band 4.1-like 1 (212339_at), score: -0.62 ERBB4v-erb-a erythroblastic leukemia viral oncogene homolog 4 (avian) (214053_at), score: -0.5 EREGepiregulin (205767_at), score: -0.58 ETS2v-ets erythroblastosis virus E26 oncogene homolog 2 (avian) (201328_at), score: -0.51 EVI5ecotropic viral integration site 5 (209717_at), score: -0.53 FAM134Afamily with sequence similarity 134, member A (222129_at), score: -0.53 FAM60Afamily with sequence similarity 60, member A (220147_s_at), score: -0.5 FBXW12F-box and WD repeat domain containing 12 (215600_x_at), score: -0.47 FCARFc fragment of IgA, receptor for (211305_x_at), score: -0.51 FGD6FYVE, RhoGEF and PH domain containing 6 (219901_at), score: -0.61 FLJ10038hypothetical protein FLJ10038 (205510_s_at), score: -0.57 FLJ11292hypothetical protein FLJ11292 (220828_s_at), score: -0.73 FLJ23172hypothetical LOC389177 (217016_x_at), score: -0.53 FNBP4formin binding protein 4 (212232_at), score: -0.78 FOSBFBJ murine osteosarcoma viral oncogene homolog B (202768_at), score: -0.64 FOXC1forkhead box C1 (213260_at), score: -0.55 FOXN3forkhead box N3 (218031_s_at), score: -0.55 FOXO1forkhead box O1 (202724_s_at), score: -0.61 FUBP1far upstream element (FUSE) binding protein 1 (212847_at), score: -0.65 G3BP1GTPase activating protein (SH3 domain) binding protein 1 (222187_x_at), score: -0.74 GCC2GRIP and coiled-coil domain containing 2 (202832_at), score: -0.62 GCH1GTP cyclohydrolase 1 (204224_s_at), score: -0.71 GCLCglutamate-cysteine ligase, catalytic subunit (202922_at), score: -0.48 GORASP1golgi reassembly stacking protein 1, 65kDa (56919_at), score: -0.48 GPATCH8G patch domain containing 8 (212485_at), score: -0.5 GPM6Bglycoprotein M6B (209167_at), score: -0.72 HCG2P7HLA complex group 2 pseudogene 7 (216229_x_at), score: -0.49 HECAheadcase homolog (Drosophila) (218603_at), score: -0.71 HEY1hairy/enhancer-of-split related with YRPW motif 1 (44783_s_at), score: -0.52 HGFhepatocyte growth factor (hepapoietin A; scatter factor) (209960_at), score: -0.49 HIC2hypermethylated in cancer 2 (212964_at), score: -0.54 HIST1H2AChistone cluster 1, H2ac (215071_s_at), score: -0.5 HIST2H2BEhistone cluster 2, H2be (202708_s_at), score: -0.61 HIVEP1human immunodeficiency virus type I enhancer binding protein 1 (204512_at), score: -0.53 HIVEP2human immunodeficiency virus type I enhancer binding protein 2 (212642_s_at), score: -0.84 HK2hexokinase 2 (202934_at), score: -0.74 HMGCS13-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-Coenzyme A synthase 1 (soluble) (221750_at), score: -0.57 HNRNPDheterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein D (AU-rich element RNA binding protein 1, 37kDa) (213359_at), score: -0.77 HS2ST1heparan sulfate 2-O-sulfotransferase 1 (203285_s_at), score: -0.52 IBD12Inflammatory bowel disease 12 (215373_x_at), score: -0.53 IER3immediate early response 3 (201631_s_at), score: -0.57 IL1Binterleukin 1, beta (39402_at), score: -0.65 IL1RAPinterleukin 1 receptor accessory protein (205227_at), score: -0.95 IL1RL1interleukin 1 receptor-like 1 (207526_s_at), score: -0.49 IL1RNinterleukin 1 receptor antagonist (212657_s_at), score: -0.72 IL24interleukin 24 (206569_at), score: -0.5 IL8interleukin 8 (211506_s_at), score: -0.7 IMAASLC7A5 pseudogene (208118_x_at), score: -0.53 INSRinsulin receptor (213792_s_at), score: -0.85 IPPKinositol 1,3,4,5,6-pentakisphosphate 2-kinase (219092_s_at), score: -0.48 IREB2iron-responsive element binding protein 2 (214666_x_at), score: -0.54 IRS2insulin receptor substrate 2 (209185_s_at), score: -0.49 ISL1ISL LIM homeobox 1 (206104_at), score: -0.48 ITPKBinositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate 3-kinase B (203723_at), score: -0.68 JARID2jumonji, AT rich interactive domain 2 (203297_s_at), score: -0.89 JHDM1Djumonji C domain containing histone demethylase 1 homolog D (S. cerevisiae) (221778_at), score: -0.97 JMJD3jumonji domain containing 3, histone lysine demethylase (213146_at), score: -0.86 KCNJ16potassium inwardly-rectifying channel, subfamily J, member 16 (219564_at), score: -0.5 KIAA0247KIAA0247 (202181_at), score: -0.86 KIAA0562KIAA0562 (204075_s_at), score: -0.48 KIAA1024KIAA1024 (215081_at), score: -0.71 KIAA1128KIAA1128 (209379_s_at), score: -0.51 KIF1Bkinesin family member 1B (209234_at), score: -0.64 KLF11Kruppel-like factor 11 (218486_at), score: -0.54 KLF9Kruppel-like factor 9 (203543_s_at), score: -0.5 KLHL18kelch-like 18 (Drosophila) (212882_at), score: -0.48 LHFPL2lipoma HMGIC fusion partner-like 2 (212658_at), score: -0.61 LOC100128701heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A1-like 2 pseudogene (216497_at), score: -0.63 LOC100128836similar to heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A1 (217353_at), score: -0.58 LOC100134401hypothetical protein LOC100134401 (213605_s_at), score: -0.47 LOC23117PI-3-kinase-related kinase SMG-1 isoform 1 homolog (211996_s_at), score: -0.6 LOC643313similar to hypothetical protein LOC284701 (211050_x_at), score: -0.59 LOC644617hypothetical LOC644617 (221235_s_at), score: -0.78 LOC645139hypothetical LOC645139 (209064_x_at), score: -0.5 LOC647070hypothetical LOC647070 (215467_x_at), score: -0.56 LOC65998hypothetical protein LOC65998 (218641_at), score: -0.59 LOC728844hypothetical LOC728844 (222040_at), score: -0.55 LRIG1leucine-rich repeats and immunoglobulin-like domains 1 (211596_s_at), score: -0.79 LRP4low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 4 (212850_s_at), score: -0.52 MAFFv-maf musculoaponeurotic fibrosarcoma oncogene homolog F (avian) (36711_at), score: -0.47 MAP3K9mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 9 (213927_at), score: -0.52 MCL1myeloid cell leukemia sequence 1 (BCL2-related) (214057_at), score: -0.5 MDN1MDN1, midasin homolog (yeast) (212693_at), score: -0.49 MEF2Amyocyte enhancer factor 2A (214684_at), score: -0.48 MEFVMediterranean fever (208262_x_at), score: -0.47 METAP2methionyl aminopeptidase 2 (202015_x_at), score: -0.6 METTL7Amethyltransferase like 7A (211424_x_at), score: -0.67 MSL2male-specific lethal 2 homolog (Drosophila) (218733_at), score: -0.75 MTHFD2Lmethylenetetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase (NADP+ dependent) 2-like (220346_at), score: -0.49 MXI1MAX interactor 1 (202364_at), score: -0.63 MYNNmyoneurin (218926_at), score: -0.59 NACAnascent polypeptide-associated complex alpha subunit (222018_at), score: -0.79 NAMPTnicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase (217738_at), score: -0.7 NPIPL2nuclear pore complex interacting protein-like 2 (221992_at), score: -0.54 NR4A2nuclear receptor subfamily 4, group A, member 2 (216248_s_at), score: -0.56 NR4A3nuclear receptor subfamily 4, group A, member 3 (209959_at), score: -0.76 NUMBnumb homolog (Drosophila) (207545_s_at), score: -0.5 NUPL1nucleoporin like 1 (204435_at), score: -0.52 P2RY5purinergic receptor P2Y, G-protein coupled, 5 (218589_at), score: -0.58 PARP6poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase family, member 6 (219639_x_at), score: -0.51 PARP8poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase family, member 8 (219033_at), score: -0.47 PBX2pre-B-cell leukemia homeobox 2 (202876_s_at), score: -0.62 PBXIP1pre-B-cell leukemia homeobox interacting protein 1 (214176_s_at), score: -0.47 PCGF2polycomb group ring finger 2 (203793_x_at), score: -0.52 PCMTD2protein-L-isoaspartate (D-aspartate) O-methyltransferase domain containing 2 (212406_s_at), score: -0.56 PELI1pellino homolog 1 (Drosophila) (218319_at), score: -0.77 PELI2pellino homolog 2 (Drosophila) (219132_at), score: -0.94 PER2period homolog 2 (Drosophila) (205251_at), score: -0.67 PFKFB36-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-biphosphatase 3 (202464_s_at), score: -0.67 PHF2PHD finger protein 2 (212726_at), score: -0.5 PHF21APHD finger protein 21A (203278_s_at), score: -0.47 PHF8PHD finger protein 8 (212916_at), score: -0.53 PHLPPPH domain and leucine rich repeat protein phosphatase (212719_at), score: -0.53 PID1phosphotyrosine interaction domain containing 1 (219093_at), score: -0.46 PLCL2phospholipase C-like 2 (213309_at), score: -0.61 POGZpogo transposable element with ZNF domain (215281_x_at), score: -0.51 POLR1Bpolymerase (RNA) I polypeptide B, 128kDa (220113_x_at), score: -0.47 PPARGC1Aperoxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma, coactivator 1 alpha (219195_at), score: -0.58 PPLperiplakin (203407_at), score: -0.48 PRDM2PR domain containing 2, with ZNF domain (203057_s_at), score: -0.5 PRINSpsoriasis associated RNA induced by stress (non-protein coding) (216051_x_at), score: -0.58 PSTPIP2proline-serine-threonine phosphatase interacting protein 2 (219938_s_at), score: -0.48 PTBP2polypyrimidine tract binding protein 2 (218683_at), score: -0.49 PTGESprostaglandin E synthase (210367_s_at), score: -0.68 PTPREprotein tyrosine phosphatase, receptor type, E (221840_at), score: -0.6 RAB11FIP1RAB11 family interacting protein 1 (class I) (219681_s_at), score: -0.57 RAD52RAD52 homolog (S. cerevisiae) (205647_at), score: -0.46 RAPGEF2Rap guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) 2 (203097_s_at), score: -0.68 RGL1ral guanine nucleotide dissociation stimulator-like 1 (209568_s_at), score: -0.6 RGS5regulator of G-protein signaling 5 (218353_at), score: -0.79 RIPK2receptor-interacting serine-threonine kinase 2 (209545_s_at), score: -0.55 RNF139ring finger protein 139 (209510_at), score: -0.51 RNF38ring finger protein 38 (218528_s_at), score: -0.59 RNMTRNA (guanine-7-) methyltransferase (202683_s_at), score: -0.57 RPL21P37ribosomal protein L21 pseudogene 37 (216479_at), score: -0.62 RPL23AP32ribosomal protein L23a pseudogene 32 (207283_at), score: -0.58 RPL35Aribosomal protein L35a (215208_x_at), score: -0.54 RRP15ribosomal RNA processing 15 homolog (S. cerevisiae) (214764_at), score: -0.74 RUNX1runt-related transcription factor 1 (209360_s_at), score: -0.6 SCARF1scavenger receptor class F, member 1 (206995_x_at), score: -0.66 SCD5stearoyl-CoA desaturase 5 (220232_at), score: -0.53 SERF1Bsmall EDRK-rich factor 1B (centromeric) (219982_s_at), score: -0.46 SFRS11splicing factor, arginine/serine-rich 11 (213742_at), score: -0.66 SFRS18splicing factor, arginine/serine-rich 18 (212176_at), score: -0.63 SH3BP2SH3-domain binding protein 2 (217257_at), score: -0.86 SH3GL3SH3-domain GRB2-like 3 (211565_at), score: -0.59 SIAH1seven in absentia homolog 1 (Drosophila) (202981_x_at), score: -0.48 SKP1S-phase kinase-associated protein 1 (200719_at), score: -0.61 SLC17A6solute carrier family 17 (sodium-dependent inorganic phosphate cotransporter), member 6 (220551_at), score: -0.56 SLC19A2solute carrier family 19 (thiamine transporter), member 2 (209681_at), score: -0.8 SLC2A3P1solute carrier family 2 (facilitated glucose transporter), member 3 pseudogene 1 (221751_at), score: -0.54 SLC30A5solute carrier family 30 (zinc transporter), member 5 (220181_x_at), score: -0.63 SLC35F2solute carrier family 35, member F2 (218826_at), score: -0.58 SLC39A14solute carrier family 39 (zinc transporter), member 14 (212110_at), score: -0.54 SLC6A6solute carrier family 6 (neurotransmitter transporter, taurine), member 6 (205921_s_at), score: -0.61 SLKSTE20-like kinase (yeast) (206875_s_at), score: -0.54 SMEK2SMEK homolog 2, suppressor of mek1 (Dictyostelium) (222270_at), score: -0.6 SMOXspermine oxidase (210357_s_at), score: -0.69 SNIP1Smad nuclear interacting protein 1 (219409_at), score: -0.56 SOD2superoxide dismutase 2, mitochondrial (221477_s_at), score: -0.91 SOX4SRY (sex determining region Y)-box 4 (201417_at), score: -0.58 SPATA2spermatogenesis associated 2 (204433_s_at), score: -0.51 SPINLW1serine peptidase inhibitor-like, with Kunitz and WAP domains 1 (eppin) (206318_at), score: -0.69 SPNsialophorin (206057_x_at), score: -0.71 SPRED2sprouty-related, EVH1 domain containing 2 (212458_at), score: -0.89 SPRY2sprouty homolog 2 (Drosophila) (204011_at), score: -0.71 SPTLC3serine palmitoyltransferase, long chain base subunit 3 (220456_at), score: -0.71 STC1stanniocalcin 1 (204597_x_at), score: -0.63 STK38Lserine/threonine kinase 38 like (212572_at), score: -0.72 STX3syntaxin 3 (209238_at), score: -0.47 SVILsupervillin (202565_s_at), score: -0.57 SYCP1synaptonemal complex protein 1 (206740_x_at), score: -0.7 TAAR2trace amine associated receptor 2 (221394_at), score: -0.54 TBX3T-box 3 (219682_s_at), score: -0.63 TFAP2Ctranscription factor AP-2 gamma (activating enhancer binding protein 2 gamma) (205286_at), score: -0.6 THBDthrombomodulin (203887_s_at), score: -0.65 TIMM8Atranslocase of inner mitochondrial membrane 8 homolog A (yeast) (210800_at), score: -0.7 TMEM38Btransmembrane protein 38B (218772_x_at), score: -0.54 TNFAIP2tumor necrosis factor, alpha-induced protein 2 (202510_s_at), score: -0.51 TNFAIP3tumor necrosis factor, alpha-induced protein 3 (202644_s_at), score: -0.53 TP53TG3TP53 target 3 (220167_s_at), score: -0.57 TRAPPC10trafficking protein particle complex 10 (209412_at), score: -0.6 TRIM36tripartite motif-containing 36 (219736_at), score: -0.74 TRIM8tripartite motif-containing 8 (221012_s_at), score: -0.54 TRIT1tRNA isopentenyltransferase 1 (218617_at), score: -0.57 TRPV1transient receptor potential cation channel, subfamily V, member 1 (219632_s_at), score: -0.63 TULP4tubby like protein 4 (218184_at), score: -0.56 UBAP1ubiquitin associated protein 1 (221490_at), score: -0.47 UBE2D1ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2D 1 (UBC4/5 homolog, yeast) (211764_s_at), score: -0.55 UBQLN4ubiquilin 4 (222252_x_at), score: -0.47 UFM1ubiquitin-fold modifier 1 (218050_at), score: -0.52 UGT2B28UDP glucuronosyltransferase 2 family, polypeptide B28 (211682_x_at), score: -0.58 UPP1uridine phosphorylase 1 (203234_at), score: -0.7 USP12ubiquitin specific peptidase 12 (213327_s_at), score: -0.79 USP6ubiquitin specific peptidase 6 (Tre-2 oncogene) (206405_x_at), score: -0.72 VAMP2vesicle-associated membrane protein 2 (synaptobrevin 2) (201557_at), score: -0.72 WASF3WAS protein family, member 3 (204042_at), score: -0.53 WNT6wingless-type MMTV integration site family, member 6 (71933_at), score: -0.49 WRNWerner syndrome (205667_at), score: -0.49 ZBTB39zinc finger and BTB domain containing 39 (205256_at), score: -0.96 ZC3H7Bzinc finger CCCH-type containing 7B (206169_x_at), score: -0.6 ZCCHC14zinc finger, CCHC domain containing 14 (212655_at), score: -0.48 ZCCHC2zinc finger, CCHC domain containing 2 (219062_s_at), score: -0.77 ZDHHC17zinc finger, DHHC-type containing 17 (212982_at), score: -0.47 ZEB2zinc finger E-box binding homeobox 2 (203603_s_at), score: -0.48 ZFC3H1zinc finger, C3H1-type containing (213065_at), score: -0.55 ZFP106zinc finger protein 106 homolog (mouse) (217781_s_at), score: -0.53 ZHX2zinc fingers and homeoboxes 2 (203556_at), score: -0.46 ZMIZ1zinc finger, MIZ-type containing 1 (212124_at), score: -0.53 ZNF432zinc finger protein 432 (219848_s_at), score: -0.71 ZNF468zinc finger protein 468 (214751_at), score: -0.66 ZNF492zinc finger protein 492 (215532_x_at), score: -0.57 ZNF493zinc finger protein 493 (211064_at), score: -0.65 ZNF506zinc finger protein 506 (221626_at), score: -0.55 ZNF528zinc finger protein 528 (215019_x_at), score: -0.48 ZNF639zinc finger protein 639 (218413_s_at), score: -0.59 ZNF770zinc finger protein 770 (220608_s_at), score: -0.76 ZNF816Azinc finger protein 816A (217541_x_at), score: -0.67 ZSCAN12zinc finger and SCAN domain containing 12 (206507_at), score: -0.49
| Id | sample | Experiment | ExpName | Array | Syndrome | Cell.line |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E-GEOD-4219-raw-cel-1311956083.cel | 2 | 7 | Sph-mono | hgu133plus2 | none | Sph-mon 1 |
| E-GEOD-4219-raw-cel-1311956634.cel | 19 | 7 | Sph-mono | hgu133plus2 | none | Sph-mon 1 |
| E-GEOD-4219-raw-cel-1311956418.cel | 13 | 7 | Sph-mono | hgu133plus2 | none | Sph-mon 1 |
| ctrl b 08-03.CEL | 2 | 1 | DS-CC | hgu133a | none | DS-CC 2 |
| E-GEOD-4219-raw-cel-1311956398.cel | 12 | 7 | Sph-mono | hgu133plus2 | none | Sph-mon 1 |
| E-GEOD-4219-raw-cel-1311956275.cel | 8 | 7 | Sph-mono | hgu133plus2 | none | Sph-mon 1 |
| ctrl a 08-03.CEL | 1 | 1 | DS-CC | hgu133a | none | DS-CC 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486231.cel | 30 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| ctrl c 08-03.CEL | 3 | 1 | DS-CC | hgu133a | none | DS-CC 3 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486331.cel | 35 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485851.cel | 11 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486191.cel | 28 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485691.cel | 3 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485751.cel | 6 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486151.cel | 26 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486431.cel | 40 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486391.cel | 38 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485731.cel | 5 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-GEOD-4219-raw-cel-1311956321.cel | 9 | 7 | Sph-mono | hgu133plus2 | none | Sph-mon 1 |
| E-GEOD-4219-raw-cel-1311956614.cel | 18 | 7 | Sph-mono | hgu133plus2 | none | Sph-mon 1 |
| 1Twin.CEL | 1 | 2 | DS-twin | hgu133plus2 | Down | DS-twin 1 |