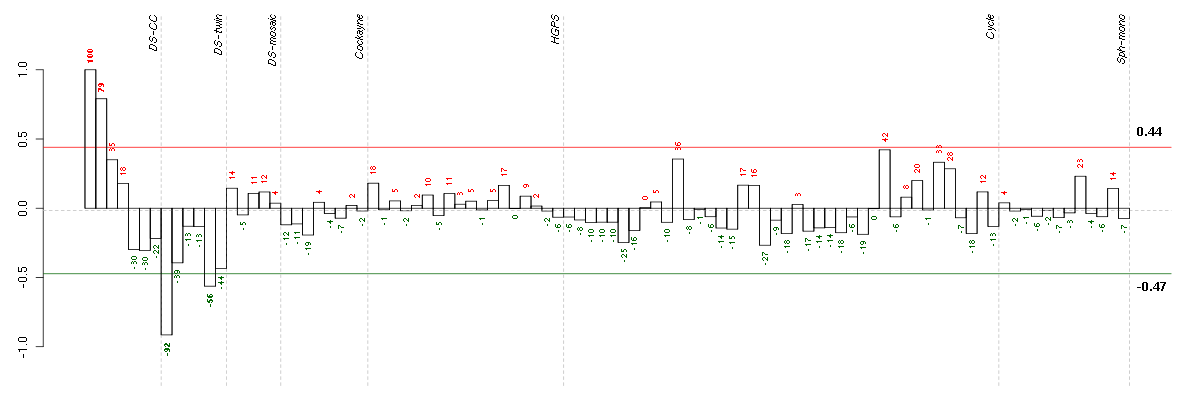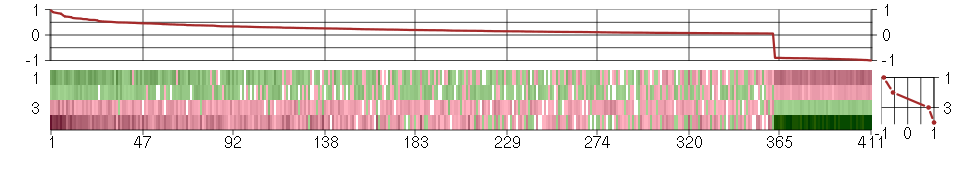

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

reproduction
The production by an organism of new individuals that contain some portion of their genetic material inherited from that organism.
MAPKKK cascade
Cascade of at least three protein kinase activities culminating in the phosphorylation and activation of a MAP kinase. MAPKKK cascades lie downstream of numerous signaling pathways.
cell morphogenesis
The developmental process by which the size or shape of a cell is generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
skeletal system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the skeleton over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The skeleton is the bony framework of the body in vertebrates (endoskeleton) or the hard outer envelope of insects (exoskeleton or dermoskeleton).
ossification
The formation of bone or of a bony substance, or the conversion of fibrous tissue or of cartilage into bone or a bony substance.
angiogenesis
Blood vessel formation when new vessels emerge from the proliferation of pre-existing blood vessels.
blood vessel development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the blood vessel over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The blood vessel is the vasculature carrying blood.
osteoblast differentiation
The process whereby a relatively unspecialized cell acquires the specialized features of an osteoblast, the mesodermal cell that gives rise to bone.
vasculature development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the vasculature over time, from its formation to the mature structure.
immune system process
Any process involved in the development or functioning of the immune system, an organismal system for calibrated responses to potential internal or invasive threats.
immune system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system whose objective is to provide calibrated responses by an organism to a potential internal or invasive threat, over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
regulation of immune system process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of an immune system process.
defense response
Reactions, triggered in response to the presence of a foreign body or the occurrence of an injury, which result in restriction of damage to the organism attacked or prevention/recovery from the infection caused by the attack.
cell adhesion
The attachment of a cell, either to another cell or to an underlying substrate such as the extracellular matrix, via cell adhesion molecules.
signal transduction
The cascade of processes by which a signal interacts with a receptor, causing a change in the level or activity of a second messenger or other downstream target, and ultimately effecting a change in the functioning of the cell.
cell motion
Any process involved in the controlled movement of a cell.
chemotaxis
The directed movement of a motile cell or organism, or the directed growth of a cell guided by a specific chemical concentration gradient. Movement may be towards a higher concentration (positive chemotaxis) or towards a lower concentration (negative chemotaxis).
response to stress
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a disturbance in organismal or cellular homeostasis, usually, but not necessarily, exogenous (e.g. temperature, humidity, ionizing radiation).
inflammatory response
The immediate defensive reaction (by vertebrate tissue) to infection or injury caused by chemical or physical agents. The process is characterized by local vasodilation, extravasation of plasma into intercellular spaces and accumulation of white blood cells and macrophages.
immune response
Any immune system process that functions in the calibrated response of an organism to a potential internal or invasive threat.
humoral immune response
An immune response mediated through a body fluid.
cell communication
Any process that mediates interactions between a cell and its surroundings. Encompasses interactions such as signaling or attachment between one cell and another cell, between a cell and an extracellular matrix, or between a cell and any other aspect of its environment.
cell surface receptor linked signal transduction
Any series of molecular signals initiated by the binding of an extracellular ligand to a receptor on the surface of the target cell.
enzyme linked receptor protein signaling pathway
Any series of molecular signals initiated by the binding of an extracellular ligand to a receptor on the surface of the target cell, where the receptor possesses catalytic activity or is closely associated with an enzyme such as a protein kinase.
intracellular signaling cascade
A series of reactions within the cell that occur as a result of a single trigger reaction or compound.
protein kinase cascade
A series of reactions, mediated by protein kinases, which occurs as a result of a single trigger reaction or compound.
cell-cell signaling
Any process that mediates the transfer of information from one cell to another.
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
anatomical structure morphogenesis
The process by which anatomical structures are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
organ morphogenesis
Morphogenesis of an organ. An organ is defined as a tissue or set of tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Morphogenesis is the process by which anatomical structures are generated and organized. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
tissue development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a tissue over time, from its formation to the mature structure.
female pregnancy
The set of physiological processes that allow an embryo or foetus to develop within the body of a female animal. It covers the time from fertilization of a female ovum by a male spermatozoon until birth.
behavior
The specific actions or reactions of an organism in response to external or internal stimuli. Patterned activity of a whole organism in a manner dependent upon some combination of that organism's internal state and external conditions.
locomotory behavior
The specific movement from place to place of an organism in response to external or internal stimuli. Locomotion of a whole organism in a manner dependent upon some combination of that organism's internal state and external conditions.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
cell proliferation
The multiplication or reproduction of cells, resulting in the expansion of a cell population.
positive regulation of cell proliferation
Any process that activates or increases the rate or extent of cell proliferation.
response to external stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an external stimulus.
response to wounding
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus indicating damage to the organism.
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
cellular component organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the formation, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of a cellular component.
cell migration
The orderly movement of cells from one site to another, often during the development of a multicellular organism or multicellular structure.
reproductive process
A biological process that directly contributes to the process of producing new individuals by one or two organisms. The new individuals inherit some proportion of their genetic material from the parent or parents.
regulation of anatomical structure morphogenesis
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of anatomical structure morphogenesis.
biological adhesion
The attachment of a cell or organism to a substrate or other organism.
cell differentiation
The process whereby relatively unspecialized cells, e.g. embryonic or regenerative cells, acquire specialized structural and/or functional features that characterize the cells, tissues, or organs of the mature organism or some other relatively stable phase of the organism's life history. Differentiation includes the processes involved in commitment of a cell to a specific fate.
regulation of cell migration
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell migration.
positive regulation of cell migration
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cell migration.
multicellular organismal process
Any biological process, occurring at the level of a multicellular organism, pertinent to its function.
developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an integrated living unit: an anatomical structure (which may be a subcellular structure, cell, tissue, or organ), or organism over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
regulation of localization
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of any process by which a cell, a substance, or a cellular entity is transported to, or maintained in, a specific location.
cellular structure morphogenesis
The process by which cellular structures are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
locomotion
Self-propelled movement of a cell or organism from one location to another.
regulation of locomotion
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of locomotion of a cell or organism.
wound healing
The series of events that restore integrity to a damaged tissue, following an injury.
regulation of cell proliferation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell proliferation.
response to chemical stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a chemical stimulus.
taxis
The directed movement of a motile cell or organism in response to an external stimulus.
regulation of cell differentiation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell differentiation, the process whereby relatively unspecialized cells acquire specialized structural and functional features.
positive regulation of cell differentiation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cell differentiation.
regulation of angiogenesis
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of angiogenesis.
organ development
Development of a tissue or tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Development pertains to the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a structure over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
blood vessel morphogenesis
The process by which the anatomical structures of blood vessels are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form. The blood vessel is the vasculature carrying blood.
positive regulation of biological process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
negative regulation of biological process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
positive regulation of cellular process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
hemopoietic or lymphoid organ development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of any organ involved in hemopoiesis or lymphoid cell activation over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Such development includes differentiation of resident cell types (stromal cells) and of migratory cell types dependent on the unique microenvironment afforded by the organ for their proper differentiation.
anatomical structure formation
The process pertaining to the initial formation of an anatomical structure from unspecified parts. This process begins with the specific processes that contribute to the appearance of the discrete structure and ends when the structural rudiment is recognizable. An anatomical structure is any biological entity that occupies space and is distinguished from its surroundings. Anatomical structures can be macroscopic such as a carpel, or microscopic such as an acrosome.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
anatomical structure development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an anatomical structure from an initial condition to its mature state. This process begins with the formation of the structure and ends with the mature structure, whatever form that may be including its natural destruction. An anatomical structure is any biological entity that occupies space and is distinguished from its surroundings. Anatomical structures can be macroscopic such as a carpel, or microscopic such as an acrosome.
cellular developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a cell over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
cell motility
Any process involved in the controlled movement of a cell that results in translocation of the cell from one place to another.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of developmental process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of development, the biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote, or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
regulation of cellular process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
response to stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
negative regulation of developmental process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the rate or extent of development, the biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote, or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
positive regulation of developmental process
Any process that activates or increases the rate or extent of development, the biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote, or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
localization
Any process by which a cell, a substance, or a cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, is transported to, and/or maintained in a specific location.
regulation of multicellular organismal process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a multicellular organismal process, the processes pertinent to the function of a multicellular organism above the cellular level; includes the integrated processes of tissues and organs.
regulation of cell motion
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the movement of a cell.
positive regulation of cell motion
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the movement of a cell.
localization of cell
Any process by which a cell is transported to, and/or maintained in, a specific location.
multi-organism process
Any process by which an organism has an effect on another organism of the same or different species.
bone development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of bone over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Bone is the hard skeletal connective tissue consisting of both mineral and cellular components.
biological regulation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of any biological process, quality or function.
regulation of biological quality
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological quality. A biological quality is a measurable attribute of an organism or part of an organism, such as size, mass, shape, color, etc.
all
This term is the most general term possible
reproductive process
A biological process that directly contributes to the process of producing new individuals by one or two organisms. The new individuals inherit some proportion of their genetic material from the parent or parents.
cell adhesion
The attachment of a cell, either to another cell or to an underlying substrate such as the extracellular matrix, via cell adhesion molecules.
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
cellular developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a cell over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
positive regulation of cellular process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
positive regulation of developmental process
Any process that activates or increases the rate or extent of development, the biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote, or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
negative regulation of developmental process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the rate or extent of development, the biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote, or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
regulation of immune system process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of an immune system process.
regulation of locomotion
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of locomotion of a cell or organism.
positive regulation of biological process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
negative regulation of biological process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of developmental process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of development, the biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote, or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
regulation of cellular process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
regulation of multicellular organismal process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a multicellular organismal process, the processes pertinent to the function of a multicellular organism above the cellular level; includes the integrated processes of tissues and organs.
immune response
Any immune system process that functions in the calibrated response of an organism to a potential internal or invasive threat.
regulation of localization
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of any process by which a cell, a substance, or a cellular entity is transported to, or maintained in, a specific location.
female pregnancy
The set of physiological processes that allow an embryo or foetus to develop within the body of a female animal. It covers the time from fertilization of a female ovum by a male spermatozoon until birth.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
cell motility
Any process involved in the controlled movement of a cell that results in translocation of the cell from one place to another.
positive regulation of cell proliferation
Any process that activates or increases the rate or extent of cell proliferation.
positive regulation of cell motion
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the movement of a cell.
cellular structure morphogenesis
The process by which cellular structures are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
signal transduction
The cascade of processes by which a signal interacts with a receptor, causing a change in the level or activity of a second messenger or other downstream target, and ultimately effecting a change in the functioning of the cell.
regulation of cell proliferation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell proliferation.
positive regulation of cellular process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
regulation of cell motion
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the movement of a cell.
cellular structure morphogenesis
The process by which cellular structures are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
anatomical structure formation
The process pertaining to the initial formation of an anatomical structure from unspecified parts. This process begins with the specific processes that contribute to the appearance of the discrete structure and ends when the structural rudiment is recognizable. An anatomical structure is any biological entity that occupies space and is distinguished from its surroundings. Anatomical structures can be macroscopic such as a carpel, or microscopic such as an acrosome.
anatomical structure morphogenesis
The process by which anatomical structures are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
regulation of anatomical structure morphogenesis
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of anatomical structure morphogenesis.
regulation of cell differentiation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell differentiation, the process whereby relatively unspecialized cells acquire specialized structural and functional features.
negative regulation of developmental process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the rate or extent of development, the biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote, or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
positive regulation of developmental process
Any process that activates or increases the rate or extent of development, the biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote, or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
positive regulation of cell differentiation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cell differentiation.
regulation of cell motion
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the movement of a cell.
response to wounding
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus indicating damage to the organism.
taxis
The directed movement of a motile cell or organism in response to an external stimulus.
chemotaxis
The directed movement of a motile cell or organism, or the directed growth of a cell guided by a specific chemical concentration gradient. Movement may be towards a higher concentration (positive chemotaxis) or towards a lower concentration (negative chemotaxis).
cell motion
Any process involved in the controlled movement of a cell.
regulation of cell migration
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell migration.
positive regulation of cell motion
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the movement of a cell.
positive regulation of cell proliferation
Any process that activates or increases the rate or extent of cell proliferation.
osteoblast differentiation
The process whereby a relatively unspecialized cell acquires the specialized features of an osteoblast, the mesodermal cell that gives rise to bone.
regulation of cell differentiation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell differentiation, the process whereby relatively unspecialized cells acquire specialized structural and functional features.
positive regulation of cell differentiation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cell differentiation.
positive regulation of cell differentiation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cell differentiation.
immune system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system whose objective is to provide calibrated responses by an organism to a potential internal or invasive threat, over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
organ development
Development of a tissue or tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Development pertains to the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a structure over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
regulation of angiogenesis
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of angiogenesis.
regulation of angiogenesis
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of angiogenesis.
organ morphogenesis
Morphogenesis of an organ. An organ is defined as a tissue or set of tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Morphogenesis is the process by which anatomical structures are generated and organized. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
tissue development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a tissue over time, from its formation to the mature structure.
hemopoietic or lymphoid organ development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of any organ involved in hemopoiesis or lymphoid cell activation over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Such development includes differentiation of resident cell types (stromal cells) and of migratory cell types dependent on the unique microenvironment afforded by the organ for their proper differentiation.
ossification
The formation of bone or of a bony substance, or the conversion of fibrous tissue or of cartilage into bone or a bony substance.
positive regulation of cell migration
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cell migration.
regulation of cell migration
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell migration.
positive regulation of cell migration
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cell migration.
inflammatory response
The immediate defensive reaction (by vertebrate tissue) to infection or injury caused by chemical or physical agents. The process is characterized by local vasodilation, extravasation of plasma into intercellular spaces and accumulation of white blood cells and macrophages.
taxis
The directed movement of a motile cell or organism in response to an external stimulus.
bone development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of bone over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Bone is the hard skeletal connective tissue consisting of both mineral and cellular components.
angiogenesis
Blood vessel formation when new vessels emerge from the proliferation of pre-existing blood vessels.
blood vessel morphogenesis
The process by which the anatomical structures of blood vessels are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form. The blood vessel is the vasculature carrying blood.

extracellular region
The space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.
cellular_component
The part of a cell or its extracellular environment in which a gene product is located. A gene product may be located in one or more parts of a cell and its location may be as specific as a particular macromolecular complex, that is, a stable, persistent association of macromolecules that function together.
proteinaceous extracellular matrix
A layer consisting mainly of proteins (especially collagen) and glycosaminoglycans (mostly as proteoglycans) that forms a sheet underlying or overlying cells such as endothelial and epithelial cells. The proteins are secreted by cells in the vicinity.
extracellular space
That part of a multicellular organism outside the cells proper, usually taken to be outside the plasma membranes, and occupied by fluid.
extracellular matrix
A structure lying external to one or more cells, which provides structural support for cells or tissues; may be completely external to the cell (as in animals) or be part of the cell (as in plants).
extracellular region part
Any constituent part of the extracellular region, the space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers constituent parts of the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.
all
This term is the most general term possible
extracellular region part
Any constituent part of the extracellular region, the space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers constituent parts of the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.

protein binding
Interacting selectively with any protein or protein complex (a complex of two or more proteins that may include other nonprotein molecules).
G-protein-coupled receptor binding
Interacting selectively with a G-protein-coupled receptor.
pattern binding
Interacting selectively with a repeating or polymeric structure, such as a polysaccharide or peptidoglycan.
molecular_function
Elemental activities, such as catalysis or binding, describing the actions of a gene product at the molecular level. A given gene product may exhibit one or more molecular functions.
serine-type endopeptidase activity
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of internal, alpha-peptide bonds in a polypeptide chain by a catalytic mechanism that involves a catalytic triad consisting of a serine nucleophile that is activated by a proton relay involving an acidic residue (e.g. aspartate or glutamate) and a basic residue (usually histidine).
catalytic activity
Catalysis of a biochemical reaction at physiological temperatures. In biologically catalyzed reactions, the reactants are known as substrates, and the catalysts are naturally occurring macromolecular substances known as enzymes. Enzymes possess specific binding sites for substrates, and are usually composed wholly or largely of protein, but RNA that has catalytic activity (ribozyme) is often also regarded as enzymatic.
endopeptidase activity
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of internal, alpha-peptide bonds in a polypeptide chain.
serine-type peptidase activity
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of peptide bonds in a polypeptide chain by a catalytic mechanism that involves a catalytic triad consisting of a serine nucleophile that is activated by a proton relay involving an acidic residue (e.g. aspartate or glutamate) and a basic residue (usually histidine).
peptidase activity
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of a peptide bond. A peptide bond is a covalent bond formed when the carbon atom from the carboxyl group of one amino acid shares electrons with the nitrogen atom from the amino group of a second amino acid.
receptor binding
Interacting selectively with one or more specific sites on a receptor molecule, a macromolecule that undergoes combination with a hormone, neurotransmitter, drug or intracellular messenger to initiate a change in cell function.
carbohydrate binding
Interacting selectively with any carbohydrate.
cytokine activity
Functions to control the survival, growth, differentiation and effector function of tissues and cells.
binding
The selective, often stoichiometric, interaction of a molecule with one or more specific sites on another molecule.
glycosaminoglycan binding
Interacting selectively with any glycan (polysaccharide) containing a substantial proportion of aminomonosaccharide residues.
chemokine activity
The function of a family of chemotactic pro-inflammatory activation-inducible cytokines acting primarily upon hemopoietic cells in immunoregulatory processes; all chemokines possess a number of conserved cysteine residues involved in intramolecular disulfide bond formation.
growth factor activity
The function that stimulates a cell to grow or proliferate. Most growth factors have other actions besides the induction of cell growth or proliferation.
heparin binding
Interacting selectively with heparin, any member of a group of glycosaminoglycans found mainly as an intracellular component of mast cells and which consist predominantly of alternating alpha1-4-linked D-galactose and N-acetyl-D-glucosamine-6-sulfate residues.
peptidase activity, acting on L-amino acid peptides
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of peptide bonds formed between L-amino acids.
hydrolase activity
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of various bonds, e.g. C-O, C-N, C-C, phosphoric anhydride bonds, etc. Hydrolase is the systematic name for any enzyme of EC class 3.
serine hydrolase activity
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of a substrate by a catalytic mechanism that involves a catalytic triad consisting of a serine nucleophile that is activated by a proton relay involving an acidic residue (e.g. aspartate or glutamate) and a basic residue (usually histidine).
polysaccharide binding
Interacting selectively with any polysaccharide.
chemokine receptor binding
Interacting selectively with any chemokine receptor.
all
This term is the most general term possible
polysaccharide binding
Interacting selectively with any polysaccharide.
serine-type peptidase activity
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of peptide bonds in a polypeptide chain by a catalytic mechanism that involves a catalytic triad consisting of a serine nucleophile that is activated by a proton relay involving an acidic residue (e.g. aspartate or glutamate) and a basic residue (usually histidine).
serine-type endopeptidase activity
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of internal, alpha-peptide bonds in a polypeptide chain by a catalytic mechanism that involves a catalytic triad consisting of a serine nucleophile that is activated by a proton relay involving an acidic residue (e.g. aspartate or glutamate) and a basic residue (usually histidine).
chemokine activity
The function of a family of chemotactic pro-inflammatory activation-inducible cytokines acting primarily upon hemopoietic cells in immunoregulatory processes; all chemokines possess a number of conserved cysteine residues involved in intramolecular disulfide bond formation.
| Id | Pvalue | ExpCount | Count | Size | Term |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 04060 | 6.634e-06 | 6.289 | 23 | 115 | Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction |
| 04610 | 4.700e-03 | 1.805 | 9 | 33 | Complement and coagulation cascades |
| 04010 | 1.992e-02 | 10.01 | 22 | 183 | MAPK signaling pathway |
| 05218 | 2.263e-02 | 2.789 | 10 | 51 | Melanoma |
ABCA1ATP-binding cassette, sub-family A (ABC1), member 1 (203504_s_at), score: 0.08 ACLYATP citrate lyase (210337_s_at), score: 0.08 ADAMTS12ADAM metallopeptidase with thrombospondin type 1 motif, 12 (221421_s_at), score: 0.13 ADAMTS5ADAM metallopeptidase with thrombospondin type 1 motif, 5 (219935_at), score: 0.12 ADH1Balcohol dehydrogenase 1B (class I), beta polypeptide (209612_s_at), score: 0.85 ADRA2Aadrenergic, alpha-2A-, receptor (209869_at), score: 0.86 AKR1C3aldo-keto reductase family 1, member C3 (3-alpha hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase, type II) (209160_at), score: 0.34 ANGPTL2angiopoietin-like 2 (213004_at), score: 0.3 ANGPTL4angiopoietin-like 4 (221009_s_at), score: 0.59 ANK2ankyrin 2, neuronal (202920_at), score: 0.07 APODapolipoprotein D (201525_at), score: 0.77 AQP1aquaporin 1 (Colton blood group) (209047_at), score: 0.06 ARHGEF11Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) 11 (202914_s_at), score: 0.15 ARHGEF12Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) 12 (201334_s_at), score: -0.91 ATF5activating transcription factor 5 (204999_s_at), score: 0.1 ATN1atrophin 1 (40489_at), score: 0.07 ATP13A3ATPase type 13A3 (219558_at), score: 0.15 AUTS2autism susceptibility candidate 2 (212599_at), score: 0.09 B3GNT2UDP-GlcNAc:betaGal beta-1,3-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase 2 (219326_s_at), score: 0.19 B4GALT1UDP-Gal:betaGlcNAc beta 1,4- galactosyltransferase, polypeptide 1 (201883_s_at), score: 0.28 B4GALT5UDP-Gal:betaGlcNAc beta 1,4- galactosyltransferase, polypeptide 5 (221484_at), score: 0.2 BAIAP2BAI1-associated protein 2 (205294_at), score: 0.07 BCL7AB-cell CLL/lymphoma 7A (203795_s_at), score: 0.06 BHLHE40basic helix-loop-helix family, member e40 (201170_s_at), score: 0.36 BMP2bone morphogenetic protein 2 (205289_at), score: 0.44 BMP6bone morphogenetic protein 6 (206176_at), score: 0.17 BNC1basonuclin 1 (206581_at), score: 0.12 C10orf72chromosome 10 open reading frame 72 (213381_at), score: 0.1 C13orf15chromosome 13 open reading frame 15 (218723_s_at), score: 0.33 C17orf91chromosome 17 open reading frame 91 (214696_at), score: 0.07 C1orf56chromosome 1 open reading frame 56 (221222_s_at), score: 0.14 C1Rcomplement component 1, r subcomponent (212067_s_at), score: 0.49 C1Scomplement component 1, s subcomponent (208747_s_at), score: 0.38 C21orf2chromosome 21 open reading frame 2 (203996_s_at), score: 0.08 C4orf18chromosome 4 open reading frame 18 (219872_at), score: 0.12 C6orf145chromosome 6 open reading frame 145 (212923_s_at), score: 0.19 CADPS2Ca++-dependent secretion activator 2 (219572_at), score: 0.07 CALB2calbindin 2 (205428_s_at), score: 0.07 CBFBcore-binding factor, beta subunit (206788_s_at), score: 0.06 CBLBCas-Br-M (murine) ecotropic retroviral transforming sequence b (209682_at), score: 0.22 CCL2chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 2 (216598_s_at), score: 0.39 CCL7chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 7 (208075_s_at), score: 0.62 CCRL1chemokine (C-C motif) receptor-like 1 (220351_at), score: 0.52 CD302CD302 molecule (203799_at), score: 0.3 CD83CD83 molecule (204440_at), score: 0.08 CDC23cell division cycle 23 homolog (S. cerevisiae) (202892_at), score: -0.91 CDC42SE1CDC42 small effector 1 (218157_x_at), score: 0.32 CDC73cell division cycle 73, Paf1/RNA polymerase II complex component, homolog (S. cerevisiae) (218578_at), score: -0.94 CDH10cadherin 10, type 2 (T2-cadherin) (220115_s_at), score: 0.15 CDKN1Acyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1A (p21, Cip1) (202284_s_at), score: 0.1 CHST2carbohydrate (N-acetylglucosamine-6-O) sulfotransferase 2 (203921_at), score: 0.24 CLCF1cardiotrophin-like cytokine factor 1 (219500_at), score: 0.13 CLDN10claudin 10 (205328_at), score: 0.21 CLEC2BC-type lectin domain family 2, member B (209732_at), score: 0.3 CLGNcalmegin (205830_at), score: 0.1 CLUclusterin (208791_at), score: 0.35 COL14A1collagen, type XIV, alpha 1 (212865_s_at), score: 0.13 COL15A1collagen, type XV, alpha 1 (203477_at), score: 0.34 COL18A1collagen, type XVIII, alpha 1 (209081_s_at), score: 0.12 COL7A1collagen, type VII, alpha 1 (217312_s_at), score: 0.14 COL8A1collagen, type VIII, alpha 1 (214587_at), score: 0.26 COX7A2cytochrome c oxidase subunit VIIa polypeptide 2 (liver) (217249_x_at), score: -0.94 COX7Bcytochrome c oxidase subunit VIIb (202110_at), score: -0.95 COX8Acytochrome c oxidase subunit 8A (ubiquitous) (201119_s_at), score: -0.9 CPOXcoproporphyrinogen oxidase (204172_at), score: -0.9 CREG1cellular repressor of E1A-stimulated genes 1 (201200_at), score: 0.16 CRISPLD2cysteine-rich secretory protein LCCL domain containing 2 (221541_at), score: 0.23 CSF1colony stimulating factor 1 (macrophage) (209716_at), score: 0.27 CTCFCCCTC-binding factor (zinc finger protein) (202521_at), score: -0.93 CTGFconnective tissue growth factor (209101_at), score: 0.07 CTNNB1catenin (cadherin-associated protein), beta 1, 88kDa (201533_at), score: -0.91 CTSAcathepsin A (200661_at), score: 0.07 CTSDcathepsin D (200766_at), score: 0.39 CTSFcathepsin F (203657_s_at), score: 0.49 CTSKcathepsin K (202450_s_at), score: 0.25 CXCL1chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 1 (melanoma growth stimulating activity, alpha) (204470_at), score: 0.26 CXCL2chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 2 (209774_x_at), score: 0.42 CXCL3chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 3 (207850_at), score: 0.54 CXCL6chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 6 (granulocyte chemotactic protein 2) (206336_at), score: 0.12 CXCR7chemokine (C-X-C motif) receptor 7 (212977_at), score: 0.41 CYP2B7P1cytochrome P450, family 2, subfamily B, polypeptide 7 pseudogene 1 (210272_at), score: 0.08 CYP51A1cytochrome P450, family 51, subfamily A, polypeptide 1 (216607_s_at), score: 0.24 DCNdecorin (211896_s_at), score: 0.38 DKK2dickkopf homolog 2 (Xenopus laevis) (219908_at), score: 0.96 DNAJC25-GNG10DNAJC25-GNG10 readthrough transcript (201921_at), score: -0.9 DNM1dynamin 1 (215116_s_at), score: 0.17 DPP4dipeptidyl-peptidase 4 (211478_s_at), score: 0.4 DPTdermatopontin (213068_at), score: 0.7 DRAMdamage-regulated autophagy modulator (218627_at), score: 0.17 DUSP10dual specificity phosphatase 10 (215501_s_at), score: 0.08 DUSP5dual specificity phosphatase 5 (209457_at), score: 0.3 ECM1extracellular matrix protein 1 (209365_s_at), score: 0.13 ECM2extracellular matrix protein 2, female organ and adipocyte specific (206101_at), score: 0.29 EGR2early growth response 2 (Krox-20 homolog, Drosophila) (205249_at), score: 0.33 EGR3early growth response 3 (206115_at), score: 0.59 EN1engrailed homeobox 1 (220559_at), score: 0.12 ENPP4ectonucleotide pyrophosphatase/phosphodiesterase 4 (putative function) (204160_s_at), score: 0.27 EPHX1epoxide hydrolase 1, microsomal (xenobiotic) (202017_at), score: 0.07 ERAP1endoplasmic reticulum aminopeptidase 1 (214012_at), score: 0.09 F10coagulation factor X (205620_at), score: 0.16 F3coagulation factor III (thromboplastin, tissue factor) (204363_at), score: 0.31 FAM38Bfamily with sequence similarity 38, member B (219602_s_at), score: 0.06 FAM46Cfamily with sequence similarity 46, member C (220306_at), score: 0.08 FAPfibroblast activation protein, alpha (209955_s_at), score: 0.45 FBLN1fibulin 1 (202995_s_at), score: 0.34 FBLN2fibulin 2 (203886_s_at), score: 0.28 FBLN5fibulin 5 (203088_at), score: 0.09 FBRSfibrosin (218255_s_at), score: 0.08 FBXO9F-box protein 9 (212987_at), score: -0.96 FBXW7F-box and WD repeat domain containing 7 (218751_s_at), score: 0.44 FCGRTFc fragment of IgG, receptor, transporter, alpha (218831_s_at), score: 0.26 FGF1fibroblast growth factor 1 (acidic) (205117_at), score: 0.44 FGF13fibroblast growth factor 13 (205110_s_at), score: 0.28 FGF2fibroblast growth factor 2 (basic) (204421_s_at), score: 0.31 FGF7fibroblast growth factor 7 (keratinocyte growth factor) (205782_at), score: 0.46 FGFR1fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 (210973_s_at), score: 0.09 FHL2four and a half LIM domains 2 (202949_s_at), score: 0.06 FHOD1formin homology 2 domain containing 1 (218530_at), score: 0.28 FLRT1fibronectin leucine rich transmembrane protein 1 (210414_at), score: 0.15 FN1fibronectin 1 (214701_s_at), score: 0.15 FOSBFBJ murine osteosarcoma viral oncogene homolog B (202768_at), score: 0.88 FOXO3forkhead box O3 (204132_s_at), score: 0.49 FURINfurin (paired basic amino acid cleaving enzyme) (201945_at), score: 0.13 GAAglucosidase, alpha; acid (202812_at), score: 0.49 GBASglioblastoma amplified sequence (201816_s_at), score: -0.95 GBP2guanylate binding protein 2, interferon-inducible (202748_at), score: 0.08 GCH1GTP cyclohydrolase 1 (204224_s_at), score: 0.14 GEMGTP binding protein overexpressed in skeletal muscle (204472_at), score: 0.4 GFPT2glutamine-fructose-6-phosphate transaminase 2 (205100_at), score: 0.34 GPNMBglycoprotein (transmembrane) nmb (201141_at), score: 0.49 GRIA1glutamate receptor, ionotropic, AMPA 1 (209793_at), score: 0.26 GRNgranulin (211284_s_at), score: 0.17 GSTM1glutathione S-transferase mu 1 (204550_x_at), score: 0.06 GYPCglycophorin C (Gerbich blood group) (202947_s_at), score: 0.06 HAS2hyaluronan synthase 2 (206432_at), score: 0.21 HBEGFheparin-binding EGF-like growth factor (203821_at), score: 0.48 HIGD1AHIG1 domain family, member 1A (221896_s_at), score: -0.99 HIPK2homeodomain interacting protein kinase 2 (219028_at), score: 0.18 HIPK3homeodomain interacting protein kinase 3 (210148_at), score: 0.2 HIVEP1human immunodeficiency virus type I enhancer binding protein 1 (204512_at), score: 0.22 HIVEP2human immunodeficiency virus type I enhancer binding protein 2 (212642_s_at), score: 0.42 HK2hexokinase 2 (202934_at), score: 0.2 HLA-Bmajor histocompatibility complex, class I, B (211911_x_at), score: 0.08 HLA-Cmajor histocompatibility complex, class I, C (211799_x_at), score: 0.14 HLXH2.0-like homeobox (214438_at), score: 0.38 HMGCS13-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-Coenzyme A synthase 1 (soluble) (221750_at), score: 0.22 HMGN1high-mobility group nucleosome binding domain 1 (200944_s_at), score: -0.98 HMGN2high-mobility group nucleosomal binding domain 2 (208668_x_at), score: -0.91 HMOX1heme oxygenase (decycling) 1 (203665_at), score: 0.51 HOMER1homer homolog 1 (Drosophila) (213793_s_at), score: 0.09 HOXB6homeobox B6 (205366_s_at), score: 0.18 HS3ST2heparan sulfate (glucosamine) 3-O-sulfotransferase 2 (219697_at), score: 0.12 HSPB6heat shock protein, alpha-crystallin-related, B6 (214767_s_at), score: 0.25 HSPB7heat shock 27kDa protein family, member 7 (cardiovascular) (218934_s_at), score: 0.41 HSPH1heat shock 105kDa/110kDa protein 1 (208744_x_at), score: 0.09 HTR2A5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) receptor 2A (207135_at), score: 0.2 HTRA1HtrA serine peptidase 1 (201185_at), score: 0.11 ICAM1intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (202638_s_at), score: 0.14 IDI1isopentenyl-diphosphate delta isomerase 1 (204615_x_at), score: 0.25 IDUAiduronidase, alpha-L- (205059_s_at), score: 0.12 IL11interleukin 11 (206924_at), score: 0.41 IL1R1interleukin 1 receptor, type I (202948_at), score: 0.25 IL1RAPinterleukin 1 receptor accessory protein (205227_at), score: 0.22 IL1RL1interleukin 1 receptor-like 1 (207526_s_at), score: 0.72 IL1RNinterleukin 1 receptor antagonist (212657_s_at), score: 0.1 IL33interleukin 33 (209821_at), score: 0.15 IL6interleukin 6 (interferon, beta 2) (205207_at), score: 0.38 IL7interleukin 7 (206693_at), score: 0.19 IL8interleukin 8 (211506_s_at), score: 0.45 INHBAinhibin, beta A (210511_s_at), score: 0.24 INSIG1insulin induced gene 1 (201627_s_at), score: 0.53 ISLRimmunoglobulin superfamily containing leucine-rich repeat (207191_s_at), score: 0.16 ITPKCinositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate 3-kinase C (213076_at), score: 0.22 JARID2jumonji, AT rich interactive domain 2 (203297_s_at), score: 0.17 JHDM1Djumonji C domain containing histone demethylase 1 homolog D (S. cerevisiae) (221778_at), score: 0.54 JMJD3jumonji domain containing 3, histone lysine demethylase (213146_at), score: 0.89 JUNBjun B proto-oncogene (201473_at), score: 0.22 JUNDjun D proto-oncogene (203751_x_at), score: 0.62 KCNJ15potassium inwardly-rectifying channel, subfamily J, member 15 (210119_at), score: 0.12 KCNK2potassium channel, subfamily K, member 2 (210261_at), score: 0.33 KIAA0247KIAA0247 (202181_at), score: 0.1 KIAA1024KIAA1024 (215081_at), score: 0.48 KIAA1644KIAA1644 (52837_at), score: 0.27 KLHL21kelch-like 21 (Drosophila) (203068_at), score: 0.11 KPNA4karyopherin alpha 4 (importin alpha 3) (209653_at), score: 0.23 LAMA2laminin, alpha 2 (213519_s_at), score: 0.19 LANCL1LanC lantibiotic synthetase component C-like 1 (bacterial) (202020_s_at), score: -0.91 LARP5La ribonucleoprotein domain family, member 5 (208953_at), score: 0.12 LATS1LATS, large tumor suppressor, homolog 1 (Drosophila) (219813_at), score: 0.07 LDLRlow density lipoprotein receptor (202068_s_at), score: 0.27 LEPROTL1leptin receptor overlapping transcript-like 1 (202594_at), score: -0.91 LHFPlipoma HMGIC fusion partner (218656_s_at), score: 0.07 LIFleukemia inhibitory factor (cholinergic differentiation factor) (205266_at), score: 0.47 LIMS1LIM and senescent cell antigen-like domains 1 (207198_s_at), score: 0.12 LMCD1LIM and cysteine-rich domains 1 (218574_s_at), score: 0.58 LOC100128809similar to hCG2045829 (215707_s_at), score: 0.07 LOH3CR2Aloss of heterozygosity, 3, chromosomal region 2, gene A (220244_at), score: 0.72 LRIG1leucine-rich repeats and immunoglobulin-like domains 1 (211596_s_at), score: 0.11 LRP1low density lipoprotein-related protein 1 (alpha-2-macroglobulin receptor) (200785_s_at), score: 0.35 LRRC15leucine rich repeat containing 15 (213909_at), score: 0.15 LRRC40leucine rich repeat containing 40 (218577_at), score: -0.91 LRRN2leucine rich repeat neuronal 2 (216164_at), score: 0.27 LSM8LSM8 homolog, U6 small nuclear RNA associated (S. cerevisiae) (219119_at), score: -0.9 LTBP2latent transforming growth factor beta binding protein 2 (204682_at), score: 0.14 LUC7L2LUC7-like 2 (S. cerevisiae) (220099_s_at), score: -0.9 LY75lymphocyte antigen 75 (205668_at), score: 0.09 MAFBv-maf musculoaponeurotic fibrosarcoma oncogene homolog B (avian) (218559_s_at), score: 0.07 MAN1A1mannosidase, alpha, class 1A, member 1 (221760_at), score: 0.21 MAN1C1mannosidase, alpha, class 1C, member 1 (218918_at), score: 0.4 MAP1Smicrotubule-associated protein 1S (218522_s_at), score: 0.09 MAP2K3mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 3 (207667_s_at), score: 0.65 MAP3K2mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 2 (221695_s_at), score: 0.13 MAP3K4mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 4 (216199_s_at), score: 0.21 MAP7microtubule-associated protein 7 (202890_at), score: 0.1 MAPKAPK2mitogen-activated protein kinase-activated protein kinase 2 (201461_s_at), score: 0.07 MAT2Amethionine adenosyltransferase II, alpha (200769_s_at), score: 0.31 MAT2Bmethionine adenosyltransferase II, beta (217993_s_at), score: -0.94 MFAP4microfibrillar-associated protein 4 (212713_at), score: 0.64 MLLT11myeloid/lymphoid or mixed-lineage leukemia (trithorax homolog, Drosophila); translocated to, 11 (211071_s_at), score: -0.96 MMP12matrix metallopeptidase 12 (macrophage elastase) (204580_at), score: 0.09 MMRN2multimerin 2 (219091_s_at), score: 0.37 MOBPmyelin-associated oligodendrocyte basic protein (210193_at), score: 0.07 MSCmusculin (activated B-cell factor-1) (209928_s_at), score: 0.48 MSX1msh homeobox 1 (205932_s_at), score: 0.24 MTSS1metastasis suppressor 1 (203037_s_at), score: 0.09 MXRA5matrix-remodelling associated 5 (209596_at), score: 0.06 MYCv-myc myelocytomatosis viral oncogene homolog (avian) (202431_s_at), score: 0.06 MYO1Amyosin IA (211916_s_at), score: 0.21 MYO1Dmyosin ID (212338_at), score: 0.52 NAMPTnicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase (217738_at), score: 0.19 NDUFA6NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) 1 alpha subcomplex, 6, 14kDa (202001_s_at), score: -0.93 NET1neuroepithelial cell transforming 1 (201830_s_at), score: 0.22 NFATC1nuclear factor of activated T-cells, cytoplasmic, calcineurin-dependent 1 (210162_s_at), score: 0.59 NFIL3nuclear factor, interleukin 3 regulated (203574_at), score: 0.24 NFKB1nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells 1 (209239_at), score: 0.28 NFKB2nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells 2 (p49/p100) (207535_s_at), score: 0.1 NGFnerve growth factor (beta polypeptide) (206814_at), score: 0.31 NID1nidogen 1 (202008_s_at), score: 0.15 NINJ1ninjurin 1 (203045_at), score: 0.13 NKX3-1NK3 homeobox 1 (209706_at), score: 0.17 NOTCH2Notch homolog 2 (Drosophila) (210756_s_at), score: 0.09 NPnucleoside phosphorylase (201695_s_at), score: 0.12 NPC2Niemann-Pick disease, type C2 (200701_at), score: 0.22 NPTX1neuronal pentraxin I (204684_at), score: 0.28 NR3C1nuclear receptor subfamily 3, group C, member 1 (glucocorticoid receptor) (201866_s_at), score: 0.2 NR4A1nuclear receptor subfamily 4, group A, member 1 (202340_x_at), score: 0.26 NR4A2nuclear receptor subfamily 4, group A, member 2 (216248_s_at), score: 0.14 NR4A3nuclear receptor subfamily 4, group A, member 3 (209959_at), score: 0.59 OMDosteomodulin (205907_s_at), score: 0.09 OR1E2olfactory receptor, family 1, subfamily E, member 2 (208587_s_at), score: 0.46 PCDHG@protocadherin gamma cluster (215836_s_at), score: 0.17 PCDHGA11protocadherin gamma subfamily A, 11 (211876_x_at), score: 0.2 PDGFAplatelet-derived growth factor alpha polypeptide (205463_s_at), score: 0.16 PDGFDplatelet derived growth factor D (219304_s_at), score: 0.66 PDGFRBplatelet-derived growth factor receptor, beta polypeptide (202273_at), score: 0.07 PDGFRLplatelet-derived growth factor receptor-like (205226_at), score: 0.48 PDK2pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase, isozyme 2 (202590_s_at), score: 0.1 PDPNpodoplanin (221898_at), score: 0.13 PFKFB36-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-biphosphatase 3 (202464_s_at), score: 0.08 PFN2profilin 2 (204992_s_at), score: -0.93 PGK2phosphoglycerate kinase 2 (217009_at), score: 0.17 PICALMphosphatidylinositol binding clathrin assembly protein (215236_s_at), score: 0.08 PIK3CDphosphoinositide-3-kinase, catalytic, delta polypeptide (203879_at), score: 0.31 PIP5K1Aphosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate 5-kinase, type I, alpha (211205_x_at), score: 0.23 PIP5K1Cphosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate 5-kinase, type I, gamma (212518_at), score: 0.06 PLAURplasminogen activator, urokinase receptor (211924_s_at), score: 0.37 PLCL1phospholipase C-like 1 (205934_at), score: 0.08 PLSCR4phospholipid scramblase 4 (218901_at), score: 0.18 PMEPA1prostate transmembrane protein, androgen induced 1 (217875_s_at), score: 0.62 PNPLA2patatin-like phospholipase domain containing 2 (212705_x_at), score: 0.17 POLR1Cpolymerase (RNA) I polypeptide C, 30kDa (207515_s_at), score: 0.07 POM121POM121 membrane glycoprotein (rat) (212178_s_at), score: 0.15 PPAP2Aphosphatidic acid phosphatase type 2A (209147_s_at), score: 0.27 PPIFpeptidylprolyl isomerase F (201490_s_at), score: 0.07 PPLperiplakin (203407_at), score: 0.67 PPP1CCprotein phosphatase 1, catalytic subunit, gamma isoform (200726_at), score: -0.95 PPP4R1protein phosphatase 4, regulatory subunit 1 (201594_s_at), score: -0.93 PPP6Cprotein phosphatase 6, catalytic subunit (203529_at), score: -0.9 PRELPproline/arginine-rich end leucine-rich repeat protein (204223_at), score: 0.13 PROS1protein S (alpha) (207808_s_at), score: 0.08 PRRX1paired related homeobox 1 (205991_s_at), score: 0.09 PRSS7protease, serine, 7 (enterokinase) (217269_s_at), score: 0.43 PSAPprosaposin (200866_s_at), score: 0.23 PSG1pregnancy specific beta-1-glycoprotein 1 (208257_x_at), score: 0.21 PSG2pregnancy specific beta-1-glycoprotein 2 (208134_x_at), score: 0.27 PSG3pregnancy specific beta-1-glycoprotein 3 (215821_x_at), score: 0.33 PSG4pregnancy specific beta-1-glycoprotein 4 (208191_x_at), score: 0.52 PSG5pregnancy specific beta-1-glycoprotein 5 (204830_x_at), score: 0.15 PSG6pregnancy specific beta-1-glycoprotein 6 (209738_x_at), score: 0.26 PSG7pregnancy specific beta-1-glycoprotein 7 (205602_x_at), score: 0.26 PSG9pregnancy specific beta-1-glycoprotein 9 (209594_x_at), score: 0.13 PSMA6proteasome (prosome, macropain) subunit, alpha type, 6 (208805_at), score: -0.95 PTGDSprostaglandin D2 synthase 21kDa (brain) (212187_x_at), score: 0.3 PTGER2prostaglandin E receptor 2 (subtype EP2), 53kDa (206631_at), score: 0.11 PTHLHparathyroid hormone-like hormone (211756_at), score: 0.12 PTMAprothymosin, alpha (216515_x_at), score: -0.93 PTPN12protein tyrosine phosphatase, non-receptor type 12 (216915_s_at), score: 0.08 PTPREprotein tyrosine phosphatase, receptor type, E (221840_at), score: 0.46 PXNpaxillin (211823_s_at), score: 0.11 RANBP2RAN binding protein 2 (201711_x_at), score: 0.32 RASL11BRAS-like, family 11, member B (219142_at), score: 0.06 RBMS1RNA binding motif, single stranded interacting protein 1 (209868_s_at), score: 0.23 RCAN2regulator of calcineurin 2 (203498_at), score: 0.47 RCL1RNA terminal phosphate cyclase-like 1 (218544_s_at), score: 0.3 RELv-rel reticuloendotheliosis viral oncogene homolog (avian) (206036_s_at), score: 0.06 RGS2regulator of G-protein signaling 2, 24kDa (202388_at), score: 0.09 RGS3regulator of G-protein signaling 3 (203823_at), score: 0.4 RNASE4ribonuclease, RNase A family, 4 (205158_at), score: 0.21 RP11-138L21.1similar to cell recognition molecule CASPR3 (220436_at), score: 0.08 RPL24ribosomal protein L24 (200013_at), score: -0.91 RPS11ribosomal protein S11 (213350_at), score: 0.08 RPS20ribosomal protein S20 (216247_at), score: 0.08 RRADRas-related associated with diabetes (204802_at), score: 0.84 RUNX1runt-related transcription factor 1 (209360_s_at), score: 0.17 RYBPRING1 and YY1 binding protein (201846_s_at), score: 0.07 SATB2SATB homeobox 2 (213435_at), score: 0.09 SECTM1secreted and transmembrane 1 (213716_s_at), score: 0.17 SEMA5Asema domain, seven thrombospondin repeats (type 1 and type 1-like), transmembrane domain (TM) and short cytoplasmic domain, (semaphorin) 5A (205405_at), score: 0.1 SEPP1selenoprotein P, plasma, 1 (201427_s_at), score: 0.38 SEPT7septin 7 (213151_s_at), score: -0.94 SERPINB2serpin peptidase inhibitor, clade B (ovalbumin), member 2 (204614_at), score: 0.21 SERPINE1serpin peptidase inhibitor, clade E (nexin, plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1), member 1 (202627_s_at), score: 0.12 SERPINE2serpin peptidase inhibitor, clade E (nexin, plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1), member 2 (212190_at), score: 0.16 SERPINF1serpin peptidase inhibitor, clade F (alpha-2 antiplasmin, pigment epithelium derived factor), member 1 (202283_at), score: 0.29 SERPING1serpin peptidase inhibitor, clade G (C1 inhibitor), member 1 (200986_at), score: 0.16 SGK1serum/glucocorticoid regulated kinase 1 (201739_at), score: 0.12 SHBSrc homology 2 domain containing adaptor protein B (204657_s_at), score: 0.42 SIRPAsignal-regulatory protein alpha (202897_at), score: 0.2 SKILSKI-like oncogene (206675_s_at), score: 0.08 SLC19A2solute carrier family 19 (thiamine transporter), member 2 (209681_at), score: 0.37 SLC25A24solute carrier family 25 (mitochondrial carrier; phosphate carrier), member 24 (204342_at), score: -0.98 SLC35F2solute carrier family 35, member F2 (218826_at), score: 0.2 SLC39A8solute carrier family 39 (zinc transporter), member 8 (209267_s_at), score: 0.15 SLC9A6solute carrier family 9 (sodium/hydrogen exchanger), member 6 (203909_at), score: -0.92 SLIT3slit homolog 3 (Drosophila) (203813_s_at), score: 0.33 SMOXspermine oxidase (210357_s_at), score: 0.53 SNED1sushi, nidogen and EGF-like domains 1 (213488_at), score: 0.12 SOCS3suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 (206359_at), score: 0.08 SOD2superoxide dismutase 2, mitochondrial (221477_s_at), score: 0.39 SOD3superoxide dismutase 3, extracellular (205236_x_at), score: 0.16 SOLHsmall optic lobes homolog (Drosophila) (204275_at), score: 0.14 SOX4SRY (sex determining region Y)-box 4 (201417_at), score: 0.3 SOX9SRY (sex determining region Y)-box 9 (202935_s_at), score: 0.34 SPHK1sphingosine kinase 1 (219257_s_at), score: 0.23 SPON1spondin 1, extracellular matrix protein (209436_at), score: 0.14 SPRED2sprouty-related, EVH1 domain containing 2 (212458_at), score: 0.46 SPRY2sprouty homolog 2 (Drosophila) (204011_at), score: 0.33 SPRY4sprouty homolog 4 (Drosophila) (221489_s_at), score: 0.43 SPSB1splA/ryanodine receptor domain and SOCS box containing 1 (219677_at), score: 0.37 SQLEsqualene epoxidase (213562_s_at), score: 0.14 SRFserum response factor (c-fos serum response element-binding transcription factor) (202401_s_at), score: 0.25 SRPXsushi-repeat-containing protein, X-linked (204955_at), score: 0.07 ST3GAL1ST3 beta-galactoside alpha-2,3-sialyltransferase 1 (208322_s_at), score: 0.25 STAU1staufen, RNA binding protein, homolog 1 (Drosophila) (207320_x_at), score: -0.92 STC1stanniocalcin 1 (204597_x_at), score: 0.14 STK24serine/threonine kinase 24 (STE20 homolog, yeast) (208855_s_at), score: -0.94 STK38Lserine/threonine kinase 38 like (212572_at), score: 0.11 STMN2stathmin-like 2 (203000_at), score: 0.08 SUMO1SMT3 suppressor of mif two 3 homolog 1 (S. cerevisiae) (208761_s_at), score: -0.97 SVEP1sushi, von Willebrand factor type A, EGF and pentraxin domain containing 1 (213247_at), score: 0.34 TBL1XR1transducin (beta)-like 1 X-linked receptor 1 (221428_s_at), score: 0.17 TBX3T-box 3 (219682_s_at), score: 0.45 TBX6T-box 6 (207684_at), score: 0.06 TEX2testis expressed 2 (218099_at), score: 0.11 TGFAtransforming growth factor, alpha (205016_at), score: 0.29 TGFBR1transforming growth factor, beta receptor 1 (206943_at), score: 0.2 THBDthrombomodulin (203887_s_at), score: 0.71 TIMP3TIMP metallopeptidase inhibitor 3 (201149_s_at), score: 0.12 TMEM115transmembrane protein 115 (216267_s_at), score: 0.09 TMEM158transmembrane protein 158 (213338_at), score: 0.19 TMEM41Btransmembrane protein 41B (212623_at), score: 0.34 TMSB10thymosin beta 10 (217733_s_at), score: -0.94 TNFAIP2tumor necrosis factor, alpha-induced protein 2 (202510_s_at), score: 0.26 TNFAIP8tumor necrosis factor, alpha-induced protein 8 (210260_s_at), score: 0.06 TNFRSF11Btumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily, member 11b (204933_s_at), score: 0.19 TNFSF9tumor necrosis factor (ligand) superfamily, member 9 (206907_at), score: 0.19 TNPO1transportin 1 (209225_x_at), score: -0.97 TNS3tensin 3 (217853_at), score: 0.19 TNXAtenascin XA pseudogene (213451_x_at), score: 0.18 TNXBtenascin XB (216333_x_at), score: 0.25 TOB2transducer of ERBB2, 2 (221496_s_at), score: 0.06 TOM1target of myb1 (chicken) (202807_s_at), score: 0.06 TOP2Btopoisomerase (DNA) II beta 180kDa (211987_at), score: -0.97 TP53I11tumor protein p53 inducible protein 11 (214667_s_at), score: 0.49 TPP1tripeptidyl peptidase I (200742_s_at), score: 0.3 TPST1tyrosylprotein sulfotransferase 1 (204140_at), score: 0.11 TRIB1tribbles homolog 1 (Drosophila) (202241_at), score: 0.38 TRIM22tripartite motif-containing 22 (213293_s_at), score: 0.06 TRIP12thyroid hormone receptor interactor 12 (201546_at), score: -0.95 TRMT5TRM5 tRNA methyltransferase 5 homolog (S. cerevisiae) (221952_x_at), score: -0.93 TXNDC9thioredoxin domain containing 9 (203008_x_at), score: -0.98 UBA3ubiquitin-like modifier activating enzyme 3 (209115_at), score: -0.91 UBE2D2ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2D 2 (UBC4/5 homolog, yeast) (201345_s_at), score: -0.96 UBE4Aubiquitination factor E4A (UFD2 homolog, yeast) (202038_at), score: -0.93 UBP1upstream binding protein 1 (LBP-1a) (218082_s_at), score: -0.9 USP12ubiquitin specific peptidase 12 (213327_s_at), score: 0.31 VBP1von Hippel-Lindau binding protein 1 (201472_at), score: -0.92 VDRvitamin D (1,25- dihydroxyvitamin D3) receptor (204255_s_at), score: 0.37 VEGFAvascular endothelial growth factor A (211527_x_at), score: 0.65 VGFVGF nerve growth factor inducible (205586_x_at), score: 0.19 VPS37Bvacuolar protein sorting 37 homolog B (S. cerevisiae) (221704_s_at), score: 0.19 WIPF1WAS/WASL interacting protein family, member 1 (202663_at), score: 0.06 WISP1WNT1 inducible signaling pathway protein 1 (206796_at), score: 0.32 WNT2wingless-type MMTV integration site family member 2 (205648_at), score: 0.07 WTAPWilms tumor 1 associated protein (210285_x_at), score: 0.45 XPO1exportin 1 (CRM1 homolog, yeast) (208775_at), score: -0.91 ZFP36L1zinc finger protein 36, C3H type-like 1 (211965_at), score: 0.5 ZMPSTE24zinc metallopeptidase (STE24 homolog, S. cerevisiae) (202939_at), score: -1 ZNF282zinc finger protein 282 (212892_at), score: 0.34 ZNF35zinc finger protein 35 (206096_at), score: 0.19
| Id | sample | Experiment | ExpName | Array | Syndrome | Cell.line |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1Twin.CEL | 1 | 2 | DS-twin | hgu133plus2 | Down | DS-twin 1 |
| 5CTwin.CEL | 5 | 2 | DS-twin | hgu133plus2 | Down | DS-twin 5 |
| ctrl b 08-03.CEL | 2 | 1 | DS-CC | hgu133a | none | DS-CC 2 |
| ctrl a 08-03.CEL | 1 | 1 | DS-CC | hgu133a | none | DS-CC 1 |