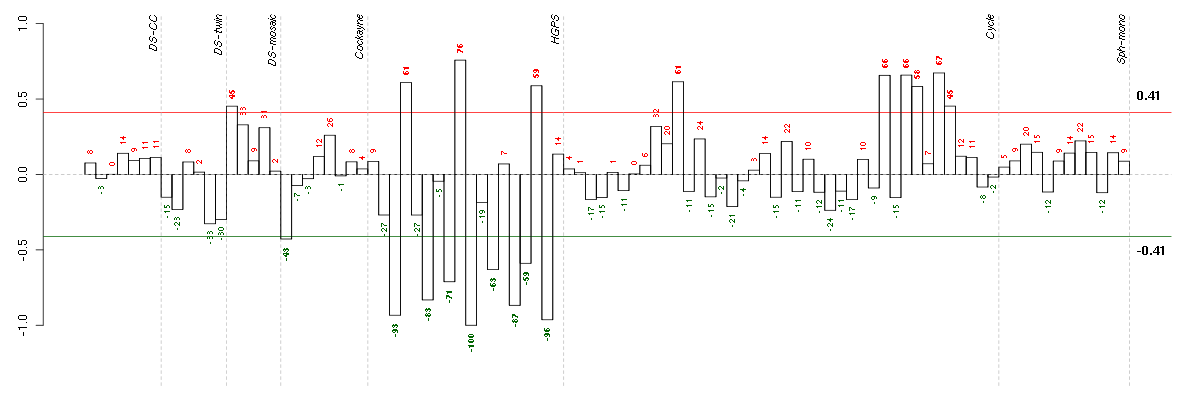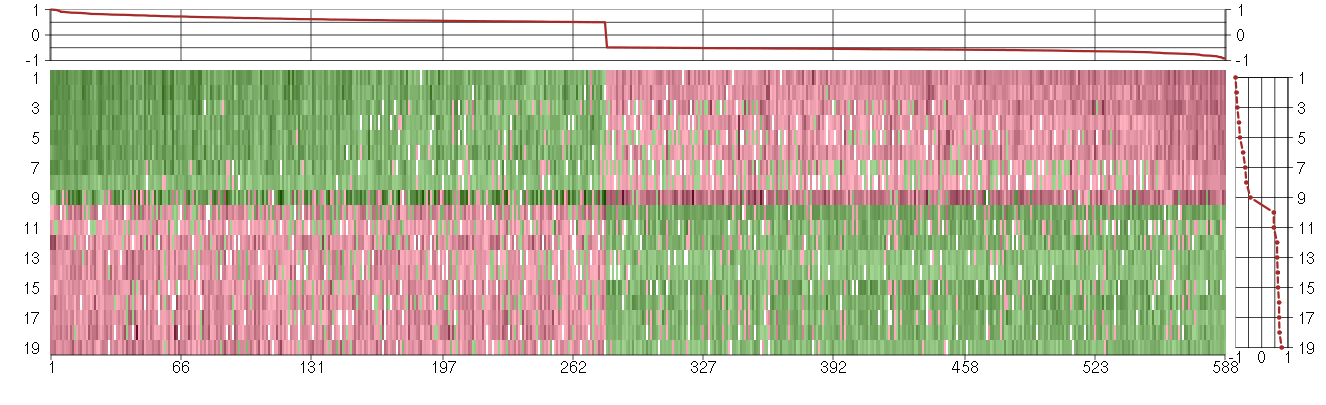

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

DNA replication
The process whereby new strands of DNA are synthesized. The template for replication can either be an existing DNA molecule or RNA.
chromosome segregation
The process by which genetic material, in the form of chromosomes, is organized and then physically separated and apportioned to two or more sets.
chromosome organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level that results in the formation, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of chromosomes, structures composed of a very long molecule of DNA and associated proteins that carries hereditary information.
mitotic sister chromatid segregation
The cell cycle process whereby replicated homologous chromosomes are organized and then physically separated and apportioned to two sets during the mitotic cell cycle. Each replicated chromosome, composed of two sister chromatids, aligns at the cell equator, paired with its homologous partner. One homolog of each morphologic type goes into each of the resulting chromosome sets.
cell cycle checkpoint
The cell cycle regulatory process by which progression through the cycle can be halted until conditions are suitable for the cell to proceed to the next stage.
M phase of mitotic cell cycle
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which a cell progresses through M phase, the part of the mitotic cell cycle during which mitosis takes place.
mitotic cell cycle
Progression through the phases of the mitotic cell cycle, the most common eukaryotic cell cycle, which canonically comprises four successive phases called G1, S, G2, and M and includes replication of the genome and the subsequent segregation of chromosomes into daughter cells. In some variant cell cycles nuclear replication or nuclear division may not be followed by cell division, or G1 and G2 phases may be absent.
M phase
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which a cell progresses through M phase, the part of the cell cycle comprising nuclear division.
nuclear division
A process by which a cell nucleus is divided into two nuclei, with DNA and other nuclear contents distributed between the daughter nuclei.
DNA synthesis during DNA repair
Synthesis of DNA that proceeds from the broken 3' single-strand DNA end uses the homologous intact duplex as the template.
sister chromatid segregation
The process by which sister chromatids are organized and then physically separated and apportioned to two or more sets.
metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways, including anabolism and catabolism, by which living organisms transform chemical substances. Metabolic processes typically transform small molecules, but also include macromolecular processes such as DNA repair and replication, and protein synthesis and degradation.
regulation of cell cycle
Any process that modulates the rate or extent of progression through the cell cycle.
nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
DNA metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving DNA, deoxyribonucleic acid, one of the two main types of nucleic acid, consisting of a long, unbranched macromolecule formed from one, or more commonly, two, strands of linked deoxyribonucleotides.
DNA-dependent DNA replication
The process whereby new strands of DNA are synthesized, using parental DNA as a template for the DNA-dependent DNA polymerases that synthesize the new strands.
DNA replication initiation
The process by which DNA replication is started; this involves the separation of a stretch of the DNA double helix, the recruitment of DNA polymerases and the initiation of polymerase action.
DNA repair
The process of restoring DNA after damage. Genomes are subject to damage by chemical and physical agents in the environment (e.g. UV and ionizing radiations, chemical mutagens, fungal and bacterial toxins, etc.) and by free radicals or alkylating agents endogenously generated in metabolism. DNA is also damaged because of errors during its replication. A variety of different DNA repair pathways have been reported that include direct reversal, base excision repair, nucleotide excision repair, photoreactivation, bypass, double-strand break repair pathway, and mismatch repair pathway.
cell motion
Any process involved in the controlled movement of a cell.
response to stress
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a disturbance in organismal or cellular homeostasis, usually, but not necessarily, exogenous (e.g. temperature, humidity, ionizing radiation).
response to DNA damage stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus indicating damage to its DNA from environmental insults or errors during metabolism.
organelle organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the formation, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of an organelle within a cell. An organelle is an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
cell cycle
The progression of biochemical and morphological phases and events that occur in a cell during successive cell replication or nuclear replication events. Canonically, the cell cycle comprises the replication and segregation of genetic material followed by the division of the cell, but in endocycles or syncytial cells nuclear replication or nuclear division may not be followed by cell division.
mitosis
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell divides; the process involves condensation of chromosomal DNA into a highly compacted form. Canonically, mitosis produces two daughter nuclei whose chromosome complement is identical to that of the mother cell.
mitotic cell cycle checkpoint
A signal transduction-based surveillance mechanism that ensures accurate chromosome replication and segregation by preventing progression through a mitotic cell cycle until conditions are suitable for the cell to proceed to the next stage.
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
regulation of mitotic cell cycle
Any process that modulates the rate or extent of progress through the mitotic cell cycle.
nervous system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of nervous tissue over time, from its formation to its mature state.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances; typically the energy-requiring part of metabolism in which simpler substances are transformed into more complex ones.
macromolecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
cellular component organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the formation, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of a cellular component.
neurogenesis
Generation of cells within the nervous system.
cell cycle process
A cellular process that is involved in the progression of biochemical and morphological phases and events that occur in a cell during successive cell replication or nuclear replication events.
cell cycle phase
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which a cell progresses through one of the biochemical and morphological phases and events that occur during successive cell replication or nuclear replication events.
cell differentiation
The process whereby relatively unspecialized cells, e.g. embryonic or regenerative cells, acquire specialized structural and/or functional features that characterize the cells, tissues, or organs of the mature organism or some other relatively stable phase of the organism's life history. Differentiation includes the processes involved in commitment of a cell to a specific fate.
multicellular organismal process
Any biological process, occurring at the level of a multicellular organism, pertinent to its function.
developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an integrated living unit: an anatomical structure (which may be a subcellular structure, cell, tissue, or organ), or organism over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
cellular response to stress
A change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus indicating the organism is under stress. The stress is usually, but not necessarily, exogenous (e.g. temperature, humidity, ionizing radiation).
cellular macromolecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, carried out by individual cells.
cellular biopolymer metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature, such as polysaccharides and proteins, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular biopolymer biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature, such as polysaccharides and proteins, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular response to DNA damage stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus indicating damage to its DNA from environmental insults or errors during metabolism.
macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
biopolymer metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature, such as polysaccharides and proteins.
biopolymer biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature e.g. polysaccharides and proteins.
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
primary metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving those compounds which are formed as a part of the normal anabolic and catabolic processes. These processes take place in most, if not all, cells of the organism.
cellular biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
cellular macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, as carried out by individual cells.
organelle fission
The creation of two or more organelles by division of one organelle.
cell development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the cell over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Cell development does not include the steps involved in committing a cell to a specific fate.
generation of neurons
The process by which nerve cells are generated. This includes the production of neuroblasts and their differentiation into neurons.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
anatomical structure development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an anatomical structure from an initial condition to its mature state. This process begins with the formation of the structure and ends with the mature structure, whatever form that may be including its natural destruction. An anatomical structure is any biological entity that occupies space and is distinguished from its surroundings. Anatomical structures can be macroscopic such as a carpel, or microscopic such as an acrosome.
cellular developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a cell over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of cellular process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
response to stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
localization
Any process by which a cell, a substance, or a cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, is transported to, and/or maintained in a specific location.
cell division
The process resulting in the physical partitioning and separation of a cell into daughter cells.
S phase
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which a cell progresses through S phase, the part of the cell cycle during which DNA synthesis takes place.
interphase
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which a cell progresses through interphase, the stage of cell cycle between successive rounds of chromosome segregation. Canonically, interphase is the stage of the cell cycle during which the biochemical and physiologic functions of the cell are performed and replication of chromatin occurs.
interphase of mitotic cell cycle
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which a cell progresses through interphase, the stage of cell cycle between successive rounds of mitosis. Canonically, interphase is the stage of the cell cycle during which the biochemical and physiologic functions of the cell are performed and replication of chromatin occurs.
localization of cell
Any process by which a cell is transported to, and/or maintained in, a specific location.
cellular response to stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
biological regulation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of any biological process, quality or function.
all
This term is the most general term possible
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
cellular developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a cell over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
regulation of cellular process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
cellular response to stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
macromolecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
cellular biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
cellular macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, as carried out by individual cells.
nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
cell cycle process
A cellular process that is involved in the progression of biochemical and morphological phases and events that occur in a cell during successive cell replication or nuclear replication events.
sister chromatid segregation
The process by which sister chromatids are organized and then physically separated and apportioned to two or more sets.
regulation of cell cycle
Any process that modulates the rate or extent of progression through the cell cycle.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
cellular response to stress
A change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus indicating the organism is under stress. The stress is usually, but not necessarily, exogenous (e.g. temperature, humidity, ionizing radiation).
cell motion
Any process involved in the controlled movement of a cell.
cellular macromolecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, carried out by individual cells.
biopolymer biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature e.g. polysaccharides and proteins.
cellular macromolecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, carried out by individual cells.
cellular biopolymer metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature, such as polysaccharides and proteins, as carried out by individual cells.
regulation of mitotic cell cycle
Any process that modulates the rate or extent of progress through the mitotic cell cycle.
cell development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the cell over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Cell development does not include the steps involved in committing a cell to a specific fate.
cellular response to DNA damage stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus indicating damage to its DNA from environmental insults or errors during metabolism.
cellular biopolymer biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature, such as polysaccharides and proteins, as carried out by individual cells.
DNA metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving DNA, deoxyribonucleic acid, one of the two main types of nucleic acid, consisting of a long, unbranched macromolecule formed from one, or more commonly, two, strands of linked deoxyribonucleotides.
cellular biopolymer biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature, such as polysaccharides and proteins, as carried out by individual cells.
mitosis
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell divides; the process involves condensation of chromosomal DNA into a highly compacted form. Canonically, mitosis produces two daughter nuclei whose chromosome complement is identical to that of the mother cell.
mitotic cell cycle checkpoint
A signal transduction-based surveillance mechanism that ensures accurate chromosome replication and segregation by preventing progression through a mitotic cell cycle until conditions are suitable for the cell to proceed to the next stage.
sister chromatid segregation
The process by which sister chromatids are organized and then physically separated and apportioned to two or more sets.
M phase of mitotic cell cycle
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which a cell progresses through M phase, the part of the mitotic cell cycle during which mitosis takes place.
mitotic sister chromatid segregation
The cell cycle process whereby replicated homologous chromosomes are organized and then physically separated and apportioned to two sets during the mitotic cell cycle. Each replicated chromosome, composed of two sister chromatids, aligns at the cell equator, paired with its homologous partner. One homolog of each morphologic type goes into each of the resulting chromosome sets.
S phase
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which a cell progresses through S phase, the part of the cell cycle during which DNA synthesis takes place.
interphase of mitotic cell cycle
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which a cell progresses through interphase, the stage of cell cycle between successive rounds of mitosis. Canonically, interphase is the stage of the cell cycle during which the biochemical and physiologic functions of the cell are performed and replication of chromatin occurs.
DNA repair
The process of restoring DNA after damage. Genomes are subject to damage by chemical and physical agents in the environment (e.g. UV and ionizing radiations, chemical mutagens, fungal and bacterial toxins, etc.) and by free radicals or alkylating agents endogenously generated in metabolism. DNA is also damaged because of errors during its replication. A variety of different DNA repair pathways have been reported that include direct reversal, base excision repair, nucleotide excision repair, photoreactivation, bypass, double-strand break repair pathway, and mismatch repair pathway.
neurogenesis
Generation of cells within the nervous system.
DNA replication
The process whereby new strands of DNA are synthesized. The template for replication can either be an existing DNA molecule or RNA.
DNA synthesis during DNA repair
Synthesis of DNA that proceeds from the broken 3' single-strand DNA end uses the homologous intact duplex as the template.
mitosis
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell divides; the process involves condensation of chromosomal DNA into a highly compacted form. Canonically, mitosis produces two daughter nuclei whose chromosome complement is identical to that of the mother cell.
DNA replication initiation
The process by which DNA replication is started; this involves the separation of a stretch of the DNA double helix, the recruitment of DNA polymerases and the initiation of polymerase action.

nuclear chromosome
A chromosome found in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell.
condensed chromosome
A highly compacted molecule of DNA and associated proteins resulting in a cytologically distinct structure.
intracellular
The living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
chromosome, centromeric region
The region of a chromosome that includes the centromere and associated proteins. In monocentric chromosomes, this region corresponds to a single area of the chromosome, whereas in holocentric chromosomes, it is evenly distributed along the chromosome.
kinetochore
A multisubunit complex that is located at the centromeric region of DNA and provides an attachment point for the spindle microtubules.
condensed chromosome kinetochore
A multisubunit complex that is located at the centromeric region of a condensed chromosome and provides an attachment point for the spindle microtubules.
condensed chromosome, centromeric region
The region of a condensed chromosome that includes the centromere and associated proteins, including the kinetochore. In monocentric chromosomes, this region corresponds to a single area of the chromosome, whereas in holocentric chromosomes, it is evenly distributed along the chromosome.
extracellular region
The space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.
cellular_component
The part of a cell or its extracellular environment in which a gene product is located. A gene product may be located in one or more parts of a cell and its location may be as specific as a particular macromolecular complex, that is, a stable, persistent association of macromolecules that function together.
proteinaceous extracellular matrix
A layer consisting mainly of proteins (especially collagen) and glycosaminoglycans (mostly as proteoglycans) that forms a sheet underlying or overlying cells such as endothelial and epithelial cells. The proteins are secreted by cells in the vicinity.
cell
The basic structural and functional unit of all organisms. Includes the plasma membrane and any external encapsulating structures such as the cell wall and cell envelope.
nucleus
A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent.
replication fork
The Y-shaped region of a replicating DNA molecule, resulting from the separation of the DNA strands and in which the synthesis of new strands takes place. Also includes associated protein complexes.
alpha DNA polymerase:primase complex
A complex of four polypeptides, comprising large and small DNA polymerase alpha subunits and two primase subunits, which catalyzes the synthesis of an RNA primer on the lagging strand of replicating DNA; the smaller of the two primase subunits alone can catalyze oligoribonucleotide synthesis.
chromosome
A structure composed of a very long molecule of DNA and associated proteins (e.g. histones) that carries hereditary information.
spindle
The array of microtubules and associated molecules that forms between opposite poles of a eukaryotic cell during mitosis or meiosis and serves to move the duplicated chromosomes apart.
cytoskeleton
Any of the various filamentous elements that form the internal framework of cells, and typically remain after treatment of the cells with mild detergent to remove membrane constituents and soluble components of the cytoplasm. The term embraces intermediate filaments, microfilaments, microtubules, the microtrabecular lattice, and other structures characterized by a polymeric filamentous nature and long-range order within the cell. The various elements of the cytoskeleton not only serve in the maintenance of cellular shape but also have roles in other cellular functions, including cellular movement, cell division, endocytosis, and movement of organelles.
microtubule cytoskeleton
The part of the cytoskeleton (the internal framework of a cell) composed of microtubules and associated proteins.
replisome
A multi-component enzymatic machine at the replication fork which mediates DNA replication. Includes DNA primase, one or more DNA polymerases, DNA helicases, and other proteins.
extracellular matrix
A structure lying external to one or more cells, which provides structural support for cells or tissues; may be completely external to the cell (as in animals) or be part of the cell (as in plants).
macromolecular complex
A stable assembly of two or more macromolecules, i.e. proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates or lipids, in which the constituent parts function together.
protein-DNA complex
A macromolecular complex containing both protein and DNA molecules.
organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
non-membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, not bounded by a lipid bilayer membrane. Includes ribosomes, the cytoskeleton and chromosomes.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular non-membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, not bounded by a lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes ribosomes, the cytoskeleton and chromosomes.
protein complex
Any macromolecular complex composed of two or more polypeptide subunits, which may or may not be identical. Protein complexes may have other associated non-protein prosthetic groups, such as nucleotides, metal ions or carbohydrate groups.
nuclear replication fork
The Y-shaped region of a nuclear replicating DNA molecule, resulting from the separation of the DNA strands and in which the synthesis of new strands takes place. Also includes associated protein complexes.
nuclear replisome
A multi-component enzymatic machine at the nuclear replication fork, which mediates DNA replication. Includes DNA primase, one or more DNA polymerases, DNA helicases, and other proteins.
extracellular region part
Any constituent part of the extracellular region, the space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers constituent parts of the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.
organelle part
Any constituent part of an organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, but excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
chromosomal part
Any constituent part of a chromosome, a structure composed of a very long molecule of DNA and associated proteins (e.g. histones) that carries hereditary information.
nuclear part
Any constituent part of the nucleus, a membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated.
cytoskeletal part
Any constituent part of the cytoskeleton, a cellular scaffolding or skeleton that maintains cell shape, enables some cell motion (using structures such as flagella and cilia), and plays important roles in both intra-cellular transport (e.g. the movement of vesicles and organelles) and cellular division. Includes constituent parts of intermediate filaments, microfilaments, microtubules, and the microtrabecular lattice.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
nuclear chromosome part
Any constituent part of a nuclear chromosome, a chromosome found in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell.
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
all
This term is the most general term possible
extracellular region part
Any constituent part of the extracellular region, the space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers constituent parts of the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
organelle part
Any constituent part of an organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, but excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular non-membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, not bounded by a lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes ribosomes, the cytoskeleton and chromosomes.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
kinetochore
A multisubunit complex that is located at the centromeric region of DNA and provides an attachment point for the spindle microtubules.
kinetochore
A multisubunit complex that is located at the centromeric region of DNA and provides an attachment point for the spindle microtubules.
replisome
A multi-component enzymatic machine at the replication fork which mediates DNA replication. Includes DNA primase, one or more DNA polymerases, DNA helicases, and other proteins.
nuclear chromosome part
Any constituent part of a nuclear chromosome, a chromosome found in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell.
spindle
The array of microtubules and associated molecules that forms between opposite poles of a eukaryotic cell during mitosis or meiosis and serves to move the duplicated chromosomes apart.
alpha DNA polymerase:primase complex
A complex of four polypeptides, comprising large and small DNA polymerase alpha subunits and two primase subunits, which catalyzes the synthesis of an RNA primer on the lagging strand of replicating DNA; the smaller of the two primase subunits alone can catalyze oligoribonucleotide synthesis.
nuclear part
Any constituent part of the nucleus, a membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated.
nuclear chromosome
A chromosome found in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell.
chromosomal part
Any constituent part of a chromosome, a structure composed of a very long molecule of DNA and associated proteins (e.g. histones) that carries hereditary information.
cytoskeletal part
Any constituent part of the cytoskeleton, a cellular scaffolding or skeleton that maintains cell shape, enables some cell motion (using structures such as flagella and cilia), and plays important roles in both intra-cellular transport (e.g. the movement of vesicles and organelles) and cellular division. Includes constituent parts of intermediate filaments, microfilaments, microtubules, and the microtrabecular lattice.
kinetochore
A multisubunit complex that is located at the centromeric region of DNA and provides an attachment point for the spindle microtubules.
replisome
A multi-component enzymatic machine at the replication fork which mediates DNA replication. Includes DNA primase, one or more DNA polymerases, DNA helicases, and other proteins.
alpha DNA polymerase:primase complex
A complex of four polypeptides, comprising large and small DNA polymerase alpha subunits and two primase subunits, which catalyzes the synthesis of an RNA primer on the lagging strand of replicating DNA; the smaller of the two primase subunits alone can catalyze oligoribonucleotide synthesis.
nuclear replication fork
The Y-shaped region of a nuclear replicating DNA molecule, resulting from the separation of the DNA strands and in which the synthesis of new strands takes place. Also includes associated protein complexes.
nuclear replisome
A multi-component enzymatic machine at the nuclear replication fork, which mediates DNA replication. Includes DNA primase, one or more DNA polymerases, DNA helicases, and other proteins.
nuclear chromosome part
Any constituent part of a nuclear chromosome, a chromosome found in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell.
condensed chromosome, centromeric region
The region of a condensed chromosome that includes the centromere and associated proteins, including the kinetochore. In monocentric chromosomes, this region corresponds to a single area of the chromosome, whereas in holocentric chromosomes, it is evenly distributed along the chromosome.
spindle
The array of microtubules and associated molecules that forms between opposite poles of a eukaryotic cell during mitosis or meiosis and serves to move the duplicated chromosomes apart.
condensed chromosome kinetochore
A multisubunit complex that is located at the centromeric region of a condensed chromosome and provides an attachment point for the spindle microtubules.
nuclear replisome
A multi-component enzymatic machine at the nuclear replication fork, which mediates DNA replication. Includes DNA primase, one or more DNA polymerases, DNA helicases, and other proteins.

| Id | Pvalue | ExpCount | Count | Size | Term |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 03030 | 4.512e-10 | 2.443 | 18 | 33 | DNA replication |
| 04110 | 9.759e-07 | 7.255 | 26 | 98 | Cell cycle |
| 04512 | 5.419e-03 | 4.294 | 14 | 58 | ECM-receptor interaction |
| 01430 | 1.959e-02 | 4.368 | 13 | 59 | Cell junctions |
| 05217 | 4.632e-02 | 2.147 | 8 | 29 | Basal cell carcinoma |
ABCC1ATP-binding cassette, sub-family C (CFTR/MRP), member 1 (202804_at), score: 0.57 ABHD4abhydrolase domain containing 4 (218581_at), score: 0.62 ACANaggrecan (205679_x_at), score: 0.69 AGPAT51-acylglycerol-3-phosphate O-acyltransferase 5 (lysophosphatidic acid acyltransferase, epsilon) (218096_at), score: -0.51 AGTR1angiotensin II receptor, type 1 (205357_s_at), score: 0.58 AHRaryl hydrocarbon receptor (202820_at), score: 0.51 AKR1C1aldo-keto reductase family 1, member C1 (dihydrodiol dehydrogenase 1; 20-alpha (3-alpha)-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase) (204151_x_at), score: -0.52 ANK2ankyrin 2, neuronal (202920_at), score: 0.54 ANK3ankyrin 3, node of Ranvier (ankyrin G) (206385_s_at), score: 0.65 ANKRD1ankyrin repeat domain 1 (cardiac muscle) (206029_at), score: 0.74 ANPEPalanyl (membrane) aminopeptidase (202888_s_at), score: -0.65 ANXA3annexin A3 (209369_at), score: 0.66 AOX1aldehyde oxidase 1 (205083_at), score: 0.66 APOBEC3Bapolipoprotein B mRNA editing enzyme, catalytic polypeptide-like 3B (206632_s_at), score: -0.55 APOL1apolipoprotein L, 1 (209546_s_at), score: 0.5 APOL3apolipoprotein L, 3 (221087_s_at), score: 0.6 ARHGAP11ARho GTPase activating protein 11A (204492_at), score: -0.52 ARHGAP19Rho GTPase activating protein 19 (212738_at), score: -0.52 ARID5BAT rich interactive domain 5B (MRF1-like) (212614_at), score: 0.66 ARL4CADP-ribosylation factor-like 4C (202207_at), score: 0.73 ARMC9armadillo repeat containing 9 (219637_at), score: 0.62 ARNTL2aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator-like 2 (220658_s_at), score: -0.61 ASF1BASF1 anti-silencing function 1 homolog B (S. cerevisiae) (218115_at), score: -0.61 ASPMasp (abnormal spindle) homolog, microcephaly associated (Drosophila) (219918_s_at), score: -0.53 ATAD2ATPase family, AAA domain containing 2 (218782_s_at), score: -0.58 ATF3activating transcription factor 3 (202672_s_at), score: 0.73 ATP10DATPase, class V, type 10D (213238_at), score: 0.54 ATXN1ataxin 1 (203232_s_at), score: 0.71 AURKAaurora kinase A (208079_s_at), score: -0.52 AURKBaurora kinase B (209464_at), score: -0.57 AUTS2autism susceptibility candidate 2 (212599_at), score: -0.75 B3GALT2UDP-Gal:betaGlcNAc beta 1,3-galactosyltransferase, polypeptide 2 (217452_s_at), score: 0.73 BAALCbrain and acute leukemia, cytoplasmic (218899_s_at), score: -0.55 BACE2beta-site APP-cleaving enzyme 2 (217867_x_at), score: -0.63 BACH1BTB and CNC homology 1, basic leucine zipper transcription factor 1 (204194_at), score: 0.53 BARD1BRCA1 associated RING domain 1 (205345_at), score: -0.66 BIRC5baculoviral IAP repeat-containing 5 (202095_s_at), score: -0.5 BRCA1breast cancer 1, early onset (204531_s_at), score: -0.59 BST1bone marrow stromal cell antigen 1 (205715_at), score: 0.91 BTN3A3butyrophilin, subfamily 3, member A3 (204820_s_at), score: 0.62 BUB1budding uninhibited by benzimidazoles 1 homolog (yeast) (209642_at), score: -0.5 C13orf27chromosome 13 open reading frame 27 (213346_at), score: -0.58 C14orf1chromosome 14 open reading frame 1 (217188_s_at), score: 0.52 C18orf1chromosome 18 open reading frame 1 (209574_s_at), score: -0.53 C1orf54chromosome 1 open reading frame 54 (219506_at), score: 0.82 C1QTNF3C1q and tumor necrosis factor related protein 3 (220988_s_at), score: -0.52 C21orf45chromosome 21 open reading frame 45 (219004_s_at), score: -0.61 C4orf18chromosome 4 open reading frame 18 (219872_at), score: 0.61 C5orf13chromosome 5 open reading frame 13 (201309_x_at), score: 0.54 C5orf23chromosome 5 open reading frame 23 (219054_at), score: -0.55 C5orf30chromosome 5 open reading frame 30 (221823_at), score: -0.55 C7orf10chromosome 7 open reading frame 10 (219655_at), score: 0.72 C9orf40chromosome 9 open reading frame 40 (218904_s_at), score: -0.6 CA12carbonic anhydrase XII (203963_at), score: -0.64 CALD1caldesmon 1 (201616_s_at), score: 0.51 CAMK2N1calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II inhibitor 1 (218309_at), score: -0.73 CAPGcapping protein (actin filament), gelsolin-like (201850_at), score: -0.68 CASKcalcium/calmodulin-dependent serine protein kinase (MAGUK family) (211208_s_at), score: -0.53 CBX7chromobox homolog 7 (212914_at), score: -0.52 CCDC15coiled-coil domain containing 15 (220466_at), score: -0.56 CCDC81coiled-coil domain containing 81 (220389_at), score: 0.73 CCL2chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 2 (216598_s_at), score: 0.79 CCNA2cyclin A2 (203418_at), score: -0.56 CCND2cyclin D2 (200953_s_at), score: 0.58 CCNE1cyclin E1 (213523_at), score: -0.54 CCNE2cyclin E2 (205034_at), score: -0.65 CCNL1cyclin L1 (220046_s_at), score: 0.53 CCR10chemokine (C-C motif) receptor 10 (220565_at), score: 0.55 CD200CD200 molecule (209583_s_at), score: 0.52 CD44CD44 molecule (Indian blood group) (210916_s_at), score: -0.52 CDC25Acell division cycle 25 homolog A (S. pombe) (204695_at), score: -0.57 CDC45LCDC45 cell division cycle 45-like (S. cerevisiae) (204126_s_at), score: -0.55 CDC6cell division cycle 6 homolog (S. cerevisiae) (203967_at), score: -0.55 CDC7cell division cycle 7 homolog (S. cerevisiae) (204510_at), score: -0.56 CDCA8cell division cycle associated 8 (221520_s_at), score: -0.56 CDH13cadherin 13, H-cadherin (heart) (204726_at), score: 0.69 CDH4cadherin 4, type 1, R-cadherin (retinal) (220227_at), score: -0.66 CDK2cyclin-dependent kinase 2 (204252_at), score: -0.62 CDK7cyclin-dependent kinase 7 (211297_s_at), score: 0.56 CDKN2Dcyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 2D (p19, inhibits CDK4) (210240_s_at), score: -0.57 CDT1chromatin licensing and DNA replication factor 1 (209832_s_at), score: -0.7 CENPEcentromere protein E, 312kDa (205046_at), score: -0.51 CENPFcentromere protein F, 350/400ka (mitosin) (207828_s_at), score: -0.52 CENPIcentromere protein I (214804_at), score: -0.55 CENPMcentromere protein M (218741_at), score: -0.58 CERKceramide kinase (218421_at), score: -0.49 CFHR1complement factor H-related 1 (215388_s_at), score: 0.55 CHAF1Achromatin assembly factor 1, subunit A (p150) (214426_x_at), score: -0.62 CHAF1Bchromatin assembly factor 1, subunit B (p60) (204775_at), score: -0.58 CHPT1choline phosphotransferase 1 (221675_s_at), score: -0.67 CITcitron (rho-interacting, serine/threonine kinase 21) (212801_at), score: -0.64 CKAP2cytoskeleton associated protein 2 (218252_at), score: -0.55 CLEC2BC-type lectin domain family 2, member B (209732_at), score: -0.52 CLEC3BC-type lectin domain family 3, member B (205200_at), score: 0.75 CLGNcalmegin (205830_at), score: -0.73 CLIP3CAP-GLY domain containing linker protein 3 (212358_at), score: 0.55 CNIH3cornichon homolog 3 (Drosophila) (214841_at), score: -0.53 COBLL1COBL-like 1 (203642_s_at), score: 0.81 COL13A1collagen, type XIII, alpha 1 (211343_s_at), score: -0.64 COL4A1collagen, type IV, alpha 1 (211981_at), score: 0.76 COL4A2collagen, type IV, alpha 2 (211966_at), score: 0.67 COL4A5collagen, type IV, alpha 5 (213110_s_at), score: 0.87 COMPcartilage oligomeric matrix protein (205713_s_at), score: -0.57 CORINcorin, serine peptidase (220356_at), score: 0.77 CPA3carboxypeptidase A3 (mast cell) (205624_at), score: 0.58 CTSBcathepsin B (213274_s_at), score: -0.51 CTSCcathepsin C (201487_at), score: 0.65 CYFIP2cytoplasmic FMR1 interacting protein 2 (215785_s_at), score: 0.87 CYP1B1cytochrome P450, family 1, subfamily B, polypeptide 1 (202436_s_at), score: 0.71 DAAM2dishevelled associated activator of morphogenesis 2 (212793_at), score: 0.82 DACT1dapper, antagonist of beta-catenin, homolog 1 (Xenopus laevis) (219179_at), score: 0.64 DBNDD2dysbindin (dystrobrevin binding protein 1) domain containing 2 (218094_s_at), score: 0.7 DCHS1dachsous 1 (Drosophila) (222101_s_at), score: -0.5 DCKdeoxycytidine kinase (203302_at), score: -0.68 DCLRE1BDNA cross-link repair 1B (PSO2 homolog, S. cerevisiae) (219490_s_at), score: -0.54 DDX11DEAD/H (Asp-Glu-Ala-Asp/His) box polypeptide 11 (CHL1-like helicase homolog, S. cerevisiae) (208149_x_at), score: -0.56 DDX54DEAD (Asp-Glu-Ala-Asp) box polypeptide 54 (219111_s_at), score: -0.58 DEPDC6DEP domain containing 6 (218858_at), score: 0.59 DFNA5deafness, autosomal dominant 5 (203695_s_at), score: 0.54 DHCR77-dehydrocholesterol reductase (201790_s_at), score: 0.54 DIRAS3DIRAS family, GTP-binding RAS-like 3 (215506_s_at), score: -0.56 DLEU2deleted in lymphocytic leukemia 2 (non-protein coding) (216870_x_at), score: -0.52 DLEU2Ldeleted in lymphocytic leukemia 2-like (215629_s_at), score: -0.53 DMC1DMC1 dosage suppressor of mck1 homolog, meiosis-specific homologous recombination (yeast) (208382_s_at), score: -0.54 DMDdystrophin (203881_s_at), score: 0.91 DMPKdystrophia myotonica-protein kinase (37996_s_at), score: 0.5 DNA2DNA replication helicase 2 homolog (yeast) (213647_at), score: -0.52 DNM1dynamin 1 (215116_s_at), score: -0.59 DPY19L2P2dpy-19-like 2 pseudogene 2 (C. elegans) (215143_at), score: -0.53 DPYSL2dihydropyrimidinase-like 2 (200762_at), score: 0.54 DRAMdamage-regulated autophagy modulator (218627_at), score: 0.54 DSCC1defective in sister chromatid cohesion 1 homolog (S. cerevisiae) (219000_s_at), score: -0.53 DSN1DSN1, MIND kinetochore complex component, homolog (S. cerevisiae) (219512_at), score: -0.58 DTLdenticleless homolog (Drosophila) (218585_s_at), score: -0.63 DVL3dishevelled, dsh homolog 3 (Drosophila) (201908_at), score: 0.56 E2F1E2F transcription factor 1 (204947_at), score: -0.53 ECOPEGFR-coamplified and overexpressed protein (208091_s_at), score: -0.49 EDIL3EGF-like repeats and discoidin I-like domains 3 (207379_at), score: 0.79 EFEMP1EGF-containing fibulin-like extracellular matrix protein 1 (201842_s_at), score: 0.6 EFHD1EF-hand domain family, member D1 (209343_at), score: 0.57 EIF2S3eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2, subunit 3 gamma, 52kDa (205321_at), score: 0.63 EMP2epithelial membrane protein 2 (204975_at), score: -0.74 EMX2empty spiracles homeobox 2 (221950_at), score: -0.74 ENPP1ectonucleotide pyrophosphatase/phosphodiesterase 1 (205066_s_at), score: -0.91 EPHA5EPH receptor A5 (215664_s_at), score: 0.62 ERAP1endoplasmic reticulum aminopeptidase 1 (214012_at), score: 0.51 ERAP2endoplasmic reticulum aminopeptidase 2 (219759_at), score: 0.51 ERCC6Lexcision repair cross-complementing rodent repair deficiency, complementation group 6-like (219650_at), score: -0.53 EREGepiregulin (205767_at), score: 0.58 ERI2exoribonuclease 2 (213365_at), score: -0.5 ESPL1extra spindle pole bodies homolog 1 (S. cerevisiae) (38158_at), score: -0.54 EVI5ecotropic viral integration site 5 (209717_at), score: 0.59 EXO1exonuclease 1 (204603_at), score: -0.58 EXOSC9exosome component 9 (205061_s_at), score: -0.65 EZH2enhancer of zeste homolog 2 (Drosophila) (203358_s_at), score: -0.62 F2Rcoagulation factor II (thrombin) receptor (203989_x_at), score: 0.71 FAM111Afamily with sequence similarity 111, member A (218248_at), score: -0.51 FAM8A1family with sequence similarity 8, member A1 (203420_at), score: 0.61 FANCAFanconi anemia, complementation group A (203805_s_at), score: -0.53 FANCGFanconi anemia, complementation group G (203564_at), score: -0.56 FANCIFanconi anemia, complementation group I (213007_at), score: -0.49 FEN1flap structure-specific endonuclease 1 (204768_s_at), score: -0.59 FGF1fibroblast growth factor 1 (acidic) (205117_at), score: 0.51 FGFR1OPFGFR1 oncogene partner (205588_s_at), score: -0.52 FHL1four and a half LIM domains 1 (201539_s_at), score: 0.59 FHOD3formin homology 2 domain containing 3 (218980_at), score: -0.72 FIG4FIG4 homolog (S. cerevisiae) (203656_at), score: 0.51 FILIP1Lfilamin A interacting protein 1-like (204135_at), score: 0.52 FLJ14213protor-2 (219383_at), score: -0.52 FLRT2fibronectin leucine rich transmembrane protein 2 (204359_at), score: -0.59 FN3KRPfructosamine 3 kinase related protein (218210_at), score: -0.54 FOLR3folate receptor 3 (gamma) (206371_at), score: -0.63 FOXE1forkhead box E1 (thyroid transcription factor 2) (206912_at), score: 0.62 FOXF2forkhead box F2 (206377_at), score: -0.61 FOXM1forkhead box M1 (202580_x_at), score: -0.52 FOXN3forkhead box N3 (218031_s_at), score: 0.62 FREQfrequenin homolog (Drosophila) (218266_s_at), score: -0.49 FRMD4AFERM domain containing 4A (208476_s_at), score: 0.75 FRMD4BFERM domain containing 4B (213056_at), score: -0.52 FRYfurry homolog (Drosophila) (204072_s_at), score: 0.7 FSTfollistatin (204948_s_at), score: 0.71 FUCA1fucosidase, alpha-L- 1, tissue (202838_at), score: 0.57 FUT8fucosyltransferase 8 (alpha (1,6) fucosyltransferase) (203988_s_at), score: -0.6 FYCO1FYVE and coiled-coil domain containing 1 (218204_s_at), score: 0.74 FZD4frizzled homolog 4 (Drosophila) (218665_at), score: 0.63 FZD7frizzled homolog 7 (Drosophila) (203705_s_at), score: 0.57 GABBR2gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) B receptor, 2 (209990_s_at), score: -0.81 GABRA5gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) A receptor, alpha 5 (206456_at), score: -0.54 GALEUDP-galactose-4-epimerase (202528_at), score: -0.51 GALNT1UDP-N-acetyl-alpha-D-galactosamine:polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase 1 (GalNAc-T1) (201723_s_at), score: 0.54 GALNT3UDP-N-acetyl-alpha-D-galactosamine:polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase 3 (GalNAc-T3) (203397_s_at), score: 0.77 GAS1growth arrest-specific 1 (204457_s_at), score: -0.51 GATA2GATA binding protein 2 (209710_at), score: -0.58 GATA6GATA binding protein 6 (210002_at), score: 0.65 GBP2guanylate binding protein 2, interferon-inducible (202748_at), score: 0.54 GDF15growth differentiation factor 15 (221577_x_at), score: 0.65 GINS1GINS complex subunit 1 (Psf1 homolog) (206102_at), score: -0.6 GINS2GINS complex subunit 2 (Psf2 homolog) (221521_s_at), score: -0.55 GINS3GINS complex subunit 3 (Psf3 homolog) (45633_at), score: -0.5 GINS4GINS complex subunit 4 (Sld5 homolog) (211767_at), score: -0.58 GLI2GLI family zinc finger 2 (207034_s_at), score: 0.51 GMNNgeminin, DNA replication inhibitor (218350_s_at), score: -0.49 GPERG protein-coupled estrogen receptor 1 (210640_s_at), score: -0.83 GPR116G protein-coupled receptor 116 (212950_at), score: 0.78 GPR161G protein-coupled receptor 161 (214104_at), score: -0.56 GPR89AG protein-coupled receptor 89A (222140_s_at), score: -0.5 GPR89BG protein-coupled receptor 89B (220642_x_at), score: -0.54 GRAMD1CGRAM domain containing 1C (219313_at), score: -0.63 GREM2gremlin 2, cysteine knot superfamily, homolog (Xenopus laevis) (220794_at), score: -0.7 GSNgelsolin (amyloidosis, Finnish type) (200696_s_at), score: 0.5 GSTM1glutathione S-transferase mu 1 (204550_x_at), score: 0.5 GSTM3glutathione S-transferase mu 3 (brain) (202554_s_at), score: 0.65 GTDC1glycosyltransferase-like domain containing 1 (219770_at), score: 0.67 GTSE1G-2 and S-phase expressed 1 (204318_s_at), score: -0.56 HAS2hyaluronan synthase 2 (206432_at), score: -0.57 HDAC9histone deacetylase 9 (205659_at), score: 0.57 HEG1HEG homolog 1 (zebrafish) (213069_at), score: 0.64 HERC3hect domain and RLD 3 (206183_s_at), score: -0.6 HES1hairy and enhancer of split 1, (Drosophila) (203394_s_at), score: 0.55 HIP1huntingtin interacting protein 1 (205425_at), score: -0.64 HIVEP1human immunodeficiency virus type I enhancer binding protein 1 (204512_at), score: 0.72 HJURPHolliday junction recognition protein (218726_at), score: -0.51 HMGB3high-mobility group box 3 (203744_at), score: -0.54 HMMRhyaluronan-mediated motility receptor (RHAMM) (207165_at), score: -0.49 HMOX1heme oxygenase (decycling) 1 (203665_at), score: -0.53 HNMThistamine N-methyltransferase (204112_s_at), score: 0.83 HOXA10homeobox A10 (213150_at), score: -0.59 HOXA9homeobox A9 (214651_s_at), score: -0.69 HOXB7homeobox B7 (204779_s_at), score: -0.59 HOXC10homeobox C10 (218959_at), score: -0.56 HOXC11homeobox C11 (206745_at), score: -0.7 HS3ST3A1heparan sulfate (glucosamine) 3-O-sulfotransferase 3A1 (219985_at), score: -0.87 HSPA14heat shock 70kDa protein 14 (219212_at), score: -0.5 HTR1F5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) receptor 1F (221458_at), score: -0.56 HTRA2HtrA serine peptidase 2 (203089_s_at), score: -0.62 ICAM1intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (202638_s_at), score: 0.53 ID1inhibitor of DNA binding 1, dominant negative helix-loop-helix protein (208937_s_at), score: -0.64 IER3immediate early response 3 (201631_s_at), score: 0.54 IFI27interferon, alpha-inducible protein 27 (202411_at), score: 0.6 IFT20intraflagellar transport 20 homolog (Chlamydomonas) (210312_s_at), score: 0.56 IRX5iroquois homeobox 5 (210239_at), score: -0.55 ISLRimmunoglobulin superfamily containing leucine-rich repeat (207191_s_at), score: -0.65 ITGA2integrin, alpha 2 (CD49B, alpha 2 subunit of VLA-2 receptor) (205032_at), score: -0.56 ITGA6integrin, alpha 6 (215177_s_at), score: -0.53 ITGA8integrin, alpha 8 (214265_at), score: 0.69 IVNS1ABPinfluenza virus NS1A binding protein (206245_s_at), score: -0.52 JAG1jagged 1 (Alagille syndrome) (216268_s_at), score: 0.98 KALRNkalirin, RhoGEF kinase (206078_at), score: 0.58 KCND3potassium voltage-gated channel, Shal-related subfamily, member 3 (213832_at), score: 0.66 KCNE4potassium voltage-gated channel, Isk-related family, member 4 (222379_at), score: 0.6 KCNN4potassium intermediate/small conductance calcium-activated channel, subfamily N, member 4 (204401_at), score: -0.57 KCNS3potassium voltage-gated channel, delayed-rectifier, subfamily S, member 3 (205968_at), score: -0.54 KIAA0182KIAA0182 (212057_at), score: -0.56 KIAA0746KIAA0746 protein (212314_at), score: 0.62 KIAA1199KIAA1199 (212942_s_at), score: 0.56 KIF11kinesin family member 11 (204444_at), score: -0.5 KIF14kinesin family member 14 (206364_at), score: -0.52 KIF15kinesin family member 15 (219306_at), score: -0.56 KIF18Bkinesin family member 18B (222039_at), score: -0.56 KIF23kinesin family member 23 (204709_s_at), score: -0.51 KIF2Ckinesin family member 2C (209408_at), score: -0.52 KIF4Akinesin family member 4A (218355_at), score: -0.51 KIFC1kinesin family member C1 (209680_s_at), score: -0.56 KITv-kit Hardy-Zuckerman 4 feline sarcoma viral oncogene homolog (205051_s_at), score: 0.62 KLF9Kruppel-like factor 9 (203543_s_at), score: 0.79 KNTC1kinetochore associated 1 (206316_s_at), score: -0.59 KRT18keratin 18 (201596_x_at), score: 0.77 LAMA5laminin, alpha 5 (210150_s_at), score: 0.66 LGALS3BPlectin, galactoside-binding, soluble, 3 binding protein (200923_at), score: 0.89 LGR5leucine-rich repeat-containing G protein-coupled receptor 5 (213880_at), score: 0.5 LIG1ligase I, DNA, ATP-dependent (202726_at), score: -0.64 LIMS2LIM and senescent cell antigen-like domains 2 (220765_s_at), score: 0.6 LIPGlipase, endothelial (219181_at), score: 0.67 LMCD1LIM and cysteine-rich domains 1 (218574_s_at), score: 0.59 LMNB1lamin B1 (203276_at), score: -0.49 LMNB2lamin B2 (216952_s_at), score: -0.51 LMO2LIM domain only 2 (rhombotin-like 1) (204249_s_at), score: 0.62 LMOD1leiomodin 1 (smooth muscle) (203766_s_at), score: 0.6 LOC731884similar to programmed cell death 6 interacting protein (217520_x_at), score: -0.67 LOC81691exonuclease NEF-sp (208107_s_at), score: -0.5 LPHN2latrophilin 2 (206953_s_at), score: 0.86 LPPR4plasticity related gene 1 (213496_at), score: 0.81 LPXNleupaxin (216250_s_at), score: -0.82 LRP4low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 4 (212850_s_at), score: -0.51 LRP5low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 5 (209468_at), score: 0.68 LRRC15leucine rich repeat containing 15 (213909_at), score: -0.92 LRRC17leucine rich repeat containing 17 (205381_at), score: 0.95 LRRC32leucine rich repeat containing 32 (203835_at), score: 0.77 LRRN3leucine rich repeat neuronal 3 (209841_s_at), score: 0.53 LUZP1leucine zipper protein 1 (221832_s_at), score: 0.57 MAD2L1MAD2 mitotic arrest deficient-like 1 (yeast) (203362_s_at), score: -0.49 MALLmal, T-cell differentiation protein-like (209373_at), score: -0.63 MAN2A2mannosidase, alpha, class 2A, member 2 (202032_s_at), score: 0.53 MANSC1MANSC domain containing 1 (220945_x_at), score: 0.72 MAP3K8mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 8 (205027_s_at), score: 0.77 MAP4K3mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase kinase 3 (218311_at), score: 0.51 MAPRE2microtubule-associated protein, RP/EB family, member 2 (202501_at), score: 0.56 MARCH2membrane-associated ring finger (C3HC4) 2 (210075_at), score: 0.59 MBPmyelin basic protein (210136_at), score: 0.99 MCM10minichromosome maintenance complex component 10 (220651_s_at), score: -0.65 MCM2minichromosome maintenance complex component 2 (202107_s_at), score: -0.58 MCM3minichromosome maintenance complex component 3 (201555_at), score: -0.6 MCM4minichromosome maintenance complex component 4 (212141_at), score: -0.71 MCM5minichromosome maintenance complex component 5 (216237_s_at), score: -0.6 MCM6minichromosome maintenance complex component 6 (201930_at), score: -0.51 MCM7minichromosome maintenance complex component 7 (210983_s_at), score: -0.57 MDFICMyoD family inhibitor domain containing (217599_s_at), score: -0.5 MDM1Mdm1 nuclear protein homolog (mouse) (213761_at), score: -0.5 ME1malic enzyme 1, NADP(+)-dependent, cytosolic (204059_s_at), score: 0.54 ME3malic enzyme 3, NADP(+)-dependent, mitochondrial (204663_at), score: 0.64 MEF2Amyocyte enhancer factor 2A (214684_at), score: 0.56 MEOX2mesenchyme homeobox 2 (206201_s_at), score: 0.73 MESTmesoderm specific transcript homolog (mouse) (202016_at), score: 0.82 METmet proto-oncogene (hepatocyte growth factor receptor) (211599_x_at), score: -0.51 MEX3Dmex-3 homolog D (C. elegans) (91816_f_at), score: -0.6 MFAP3Lmicrofibrillar-associated protein 3-like (205442_at), score: 0.53 MGC87042similar to Six transmembrane epithelial antigen of prostate (217553_at), score: -0.64 MGPmatrix Gla protein (202291_s_at), score: 0.86 MKI67antigen identified by monoclonal antibody Ki-67 (212022_s_at), score: -0.56 MMDmonocyte to macrophage differentiation-associated (203414_at), score: -0.49 MMP14matrix metallopeptidase 14 (membrane-inserted) (202827_s_at), score: -0.53 MMP2matrix metallopeptidase 2 (gelatinase A, 72kDa gelatinase, 72kDa type IV collagenase) (201069_at), score: -0.75 MMP3matrix metallopeptidase 3 (stromelysin 1, progelatinase) (205828_at), score: -0.8 MSCmusculin (activated B-cell factor-1) (209928_s_at), score: 0.59 MSX1msh homeobox 1 (205932_s_at), score: -0.53 MT1Mmetallothionein 1M (217546_at), score: -0.72 MT1Xmetallothionein 1X (204326_x_at), score: -0.59 MYBL1v-myb myeloblastosis viral oncogene homolog (avian)-like 1 (213906_at), score: -0.81 MYCT1myc target 1 (220471_s_at), score: 0.65 MYL5myosin, light chain 5, regulatory (205145_s_at), score: 0.54 MYO19myosin XIX (219320_at), score: -0.58 MYO1Emyosin IE (203072_at), score: 0.78 NBL1neuroblastoma, suppression of tumorigenicity 1 (37005_at), score: -0.72 NCAM1neural cell adhesion molecule 1 (212843_at), score: -0.63 NCAPD3non-SMC condensin II complex, subunit D3 (212789_at), score: -0.51 NCAPG2non-SMC condensin II complex, subunit G2 (219588_s_at), score: -0.56 NCAPHnon-SMC condensin I complex, subunit H (212949_at), score: -0.53 NCLNnicalin homolog (zebrafish) (222206_s_at), score: -0.49 NDNnecdin homolog (mouse) (209550_at), score: -0.63 NDUFA4L2NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) 1 alpha subcomplex, 4-like 2 (218484_at), score: 0.82 NEDD4neural precursor cell expressed, developmentally down-regulated 4 (213012_at), score: -0.56 NEDD9neural precursor cell expressed, developmentally down-regulated 9 (202149_at), score: 0.82 NEO1neogenin homolog 1 (chicken) (204321_at), score: -0.5 NESnestin (218678_at), score: 0.56 NET1neuroepithelial cell transforming 1 (201830_s_at), score: -0.72 NID2nidogen 2 (osteonidogen) (204114_at), score: 0.73 NKX3-1NK3 homeobox 1 (209706_at), score: -0.64 NLRP1NLR family, pyrin domain containing 1 (218380_at), score: 0.53 NOTCH3Notch homolog 3 (Drosophila) (203238_s_at), score: 0.51 NOVnephroblastoma overexpressed gene (214321_at), score: 0.6 NPHP4nephronophthisis 4 (213471_at), score: -0.49 NPR3natriuretic peptide receptor C/guanylate cyclase C (atrionatriuretic peptide receptor C) (219789_at), score: -0.65 NPTX2neuronal pentraxin II (213479_at), score: -0.57 NR2F2nuclear receptor subfamily 2, group F, member 2 (215073_s_at), score: 0.52 NRG1neuregulin 1 (206343_s_at), score: -0.8 NRIP3nuclear receptor interacting protein 3 (219557_s_at), score: -0.79 NRXN3neurexin 3 (205795_at), score: 0.86 NTF3neurotrophin 3 (206706_at), score: -0.52 NUAK1NUAK family, SNF1-like kinase, 1 (204589_at), score: 0.68 NUP155nucleoporin 155kDa (206550_s_at), score: -0.54 NUP85nucleoporin 85kDa (218014_at), score: -0.54 ODZ3odz, odd Oz/ten-m homolog 3 (Drosophila) (219523_s_at), score: -0.58 OLFM1olfactomedin 1 (213131_at), score: -0.75 OLFML3olfactomedin-like 3 (218162_at), score: -0.56 OPN3opsin 3 (219032_x_at), score: 0.68 OPTNoptineurin (202073_at), score: 0.7 ORC1Lorigin recognition complex, subunit 1-like (yeast) (205085_at), score: -0.51 ORC6Lorigin recognition complex, subunit 6 like (yeast) (219105_x_at), score: -0.65 OSBPL10oxysterol binding protein-like 10 (219073_s_at), score: 0.7 OSMRoncostatin M receptor (205729_at), score: 0.62 PAK4p21 protein (Cdc42/Rac)-activated kinase 4 (203154_s_at), score: -0.52 PALLDpalladin, cytoskeletal associated protein (200906_s_at), score: 0.58 PALMparalemmin (203859_s_at), score: 0.51 PAPPApregnancy-associated plasma protein A, pappalysin 1 (201981_at), score: 0.51 PCNTpericentrin (203660_s_at), score: -0.5 PCOLCE2procollagen C-endopeptidase enhancer 2 (219295_s_at), score: -0.49 PDCD4programmed cell death 4 (neoplastic transformation inhibitor) (202731_at), score: 0.75 PDE10Aphosphodiesterase 10A (205501_at), score: 0.61 PDE4Bphosphodiesterase 4B, cAMP-specific (phosphodiesterase E4 dunce homolog, Drosophila) (203708_at), score: -0.69 PDGFAplatelet-derived growth factor alpha polypeptide (205463_s_at), score: 0.77 PDGFRBplatelet-derived growth factor receptor, beta polypeptide (202273_at), score: 0.76 PDGFRLplatelet-derived growth factor receptor-like (205226_at), score: 0.74 PDLIM3PDZ and LIM domain 3 (209621_s_at), score: 0.57 PDLIM5PDZ and LIM domain 5 (216804_s_at), score: 0.57 PELI1pellino homolog 1 (Drosophila) (218319_at), score: 0.52 PENKproenkephalin (213791_at), score: -0.64 PER3period homolog 3 (Drosophila) (221045_s_at), score: -0.5 PGRMC2progesterone receptor membrane component 2 (213227_at), score: 0.56 PIRpirin (iron-binding nuclear protein) (207469_s_at), score: 0.73 PITPNC1phosphatidylinositol transfer protein, cytoplasmic 1 (219155_at), score: -0.63 PITX2paired-like homeodomain 2 (207558_s_at), score: -0.54 PKIAprotein kinase (cAMP-dependent, catalytic) inhibitor alpha (204612_at), score: -0.74 PKMYT1protein kinase, membrane associated tyrosine/threonine 1 (204267_x_at), score: -0.65 PLA2G16phospholipase A2, group XVI (209581_at), score: 0.81 PLD1phospholipase D1, phosphatidylcholine-specific (215723_s_at), score: 0.63 PLK4polo-like kinase 4 (Drosophila) (204887_s_at), score: -0.57 PLSCR4phospholipid scramblase 4 (218901_at), score: 0.69 PLXND1plexin D1 (38671_at), score: 0.8 PMAIP1phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate-induced protein 1 (204285_s_at), score: -0.53 PNMA2paraneoplastic antigen MA2 (209598_at), score: 0.9 POLA1polymerase (DNA directed), alpha 1, catalytic subunit (204835_at), score: -0.64 POLA2polymerase (DNA directed), alpha 2 (70kD subunit) (204441_s_at), score: -0.56 POLD1polymerase (DNA directed), delta 1, catalytic subunit 125kDa (203422_at), score: -0.61 POLD3polymerase (DNA-directed), delta 3, accessory subunit (212836_at), score: -0.67 POLE2polymerase (DNA directed), epsilon 2 (p59 subunit) (205909_at), score: -0.58 POLQpolymerase (DNA directed), theta (219510_at), score: -0.53 POSTNperiostin, osteoblast specific factor (210809_s_at), score: 0.74 PPP3CCprotein phosphatase 3 (formerly 2B), catalytic subunit, gamma isoform (207000_s_at), score: 0.6 PPT2palmitoyl-protein thioesterase 2 (209490_s_at), score: 0.53 PRIM1primase, DNA, polypeptide 1 (49kDa) (205053_at), score: -0.6 PRKAG2protein kinase, AMP-activated, gamma 2 non-catalytic subunit (218292_s_at), score: 0.83 PRKG1protein kinase, cGMP-dependent, type I (207119_at), score: 0.57 PROS1protein S (alpha) (207808_s_at), score: 0.58 PRPS1phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate synthetase 1 (209440_at), score: -0.5 PRRX2paired related homeobox 2 (219729_at), score: -0.66 PRSS23protease, serine, 23 (202458_at), score: 0.51 PSG1pregnancy specific beta-1-glycoprotein 1 (208257_x_at), score: -0.49 PSG3pregnancy specific beta-1-glycoprotein 3 (215821_x_at), score: -0.51 PSG4pregnancy specific beta-1-glycoprotein 4 (208191_x_at), score: -0.57 PSG5pregnancy specific beta-1-glycoprotein 5 (204830_x_at), score: -0.6 PSG7pregnancy specific beta-1-glycoprotein 7 (205602_x_at), score: -0.52 PSG9pregnancy specific beta-1-glycoprotein 9 (209594_x_at), score: -0.57 PSMB9proteasome (prosome, macropain) subunit, beta type, 9 (large multifunctional peptidase 2) (204279_at), score: 0.62 PSMC3IPPSMC3 interacting protein (213951_s_at), score: -0.62 PSMD2proteasome (prosome, macropain) 26S subunit, non-ATPase, 2 (200830_at), score: -0.57 PSME1proteasome (prosome, macropain) activator subunit 1 (PA28 alpha) (200814_at), score: 0.54 PSRC1proline/serine-rich coiled-coil 1 (201896_s_at), score: -0.52 PTGER2prostaglandin E receptor 2 (subtype EP2), 53kDa (206631_at), score: -0.64 PTGER4prostaglandin E receptor 4 (subtype EP4) (204897_at), score: 0.79 PTGISprostaglandin I2 (prostacyclin) synthase (208131_s_at), score: 0.57 PTGS1prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase 1 (prostaglandin G/H synthase and cyclooxygenase) (215813_s_at), score: -0.61 PTK2PTK2 protein tyrosine kinase 2 (207821_s_at), score: 0.51 PTPRZ1protein tyrosine phosphatase, receptor-type, Z polypeptide 1 (204469_at), score: 0.79 PTX3pentraxin-related gene, rapidly induced by IL-1 beta (206157_at), score: 0.65 QSOX1quiescin Q6 sulfhydryl oxidase 1 (201482_at), score: 0.5 RAB15RAB15, member RAS onocogene family (221810_at), score: -0.58 RAB33ARAB33A, member RAS oncogene family (206039_at), score: 0.55 RAB33BRAB33B, member RAS oncogene family (221014_s_at), score: 0.57 RAD51RAD51 homolog (RecA homolog, E. coli) (S. cerevisiae) (205024_s_at), score: -0.58 RAD51AP1RAD51 associated protein 1 (204146_at), score: -0.5 RAD54BRAD54 homolog B (S. cerevisiae) (219494_at), score: -0.74 RAD54LRAD54-like (S. cerevisiae) (204558_at), score: -0.54 RANGAP1Ran GTPase activating protein 1 (212125_at), score: -0.53 RBL1retinoblastoma-like 1 (p107) (205296_at), score: -0.61 RCAN3RCAN family member 3 (219864_s_at), score: -0.53 RELNreelin (205923_at), score: 0.87 RFC3replication factor C (activator 1) 3, 38kDa (204128_s_at), score: -0.67 RFC4replication factor C (activator 1) 4, 37kDa (204023_at), score: -0.53 RFWD3ring finger and WD repeat domain 3 (218564_at), score: -0.63 RHOBras homolog gene family, member B (212099_at), score: 0.56 RMI1RMI1, RecQ mediated genome instability 1, homolog (S. cerevisiae) (218979_at), score: -0.59 RNASEH2Aribonuclease H2, subunit A (203022_at), score: -0.6 RNASET2ribonuclease T2 (217983_s_at), score: 0.67 RNF128ring finger protein 128 (219263_at), score: -0.59 ROR1receptor tyrosine kinase-like orphan receptor 1 (205805_s_at), score: 0.69 RORARAR-related orphan receptor A (210426_x_at), score: -0.53 RRM2ribonucleotide reductase M2 polypeptide (209773_s_at), score: -0.53 RTN1reticulon 1 (203485_at), score: 0.75 RWDD2ARWD domain containing 2A (213555_at), score: 0.54 S100A2S100 calcium binding protein A2 (204268_at), score: -0.73 S1PR1sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 (204642_at), score: -0.61 SC5DLsterol-C5-desaturase (ERG3 delta-5-desaturase homolog, S. cerevisiae)-like (211423_s_at), score: 0.51 SCARA3scavenger receptor class A, member 3 (219416_at), score: -0.75 SCARB1scavenger receptor class B, member 1 (201819_at), score: 0.5 SCN9Asodium channel, voltage-gated, type IX, alpha subunit (206950_at), score: 0.79 SCRG1scrapie responsive protein 1 (205475_at), score: 0.64 SDC1syndecan 1 (201287_s_at), score: -0.66 SDPRserum deprivation response (phosphatidylserine binding protein) (218711_s_at), score: 0.55 SEC61A2Sec61 alpha 2 subunit (S. cerevisiae) (219499_at), score: -0.49 SECTM1secreted and transmembrane 1 (213716_s_at), score: 0.57 SEMA5Asema domain, seven thrombospondin repeats (type 1 and type 1-like), transmembrane domain (TM) and short cytoplasmic domain, (semaphorin) 5A (205405_at), score: 0.53 SERPINB2serpin peptidase inhibitor, clade B (ovalbumin), member 2 (204614_at), score: 0.56 SERPINE2serpin peptidase inhibitor, clade E (nexin, plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1), member 2 (212190_at), score: -0.58 SETBP1SET binding protein 1 (205933_at), score: -0.53 SFRP1secreted frizzled-related protein 1 (202036_s_at), score: -0.59 SHCBP1SHC SH2-domain binding protein 1 (219493_at), score: -0.49 SIM2single-minded homolog 2 (Drosophila) (206558_at), score: 0.6 SIX2SIX homeobox 2 (206510_at), score: 0.62 SLC16A2solute carrier family 16, member 2 (monocarboxylic acid transporter 8) (204462_s_at), score: -0.55 SLC1A4solute carrier family 1 (glutamate/neutral amino acid transporter), member 4 (209610_s_at), score: 0.66 SLC24A3solute carrier family 24 (sodium/potassium/calcium exchanger), member 3 (57588_at), score: 0.58 SLC25A4solute carrier family 25 (mitochondrial carrier; adenine nucleotide translocator), member 4 (202825_at), score: 0.7 SLC2A1solute carrier family 2 (facilitated glucose transporter), member 1 (201250_s_at), score: 0.52 SLC2A14solute carrier family 2 (facilitated glucose transporter), member 14 (222088_s_at), score: 0.55 SLC2A3solute carrier family 2 (facilitated glucose transporter), member 3 (202499_s_at), score: 0.53 SLC46A3solute carrier family 46, member 3 (214719_at), score: 0.66 SLC7A11solute carrier family 7, (cationic amino acid transporter, y+ system) member 11 (217678_at), score: 0.62 SLC7A8solute carrier family 7 (cationic amino acid transporter, y+ system), member 8 (216092_s_at), score: -0.77 SLCO3A1solute carrier organic anion transporter family, member 3A1 (219229_at), score: -0.57 SLIT2slit homolog 2 (Drosophila) (209897_s_at), score: -0.53 SMC2structural maintenance of chromosomes 2 (204240_s_at), score: -0.58 SMURF1SMAD specific E3 ubiquitin protein ligase 1 (212666_at), score: 0.57 SNTB1syntrophin, beta 1 (dystrophin-associated protein A1, 59kDa, basic component 1) (208608_s_at), score: 0.8 SOBPsine oculis binding protein homolog (Drosophila) (218974_at), score: 0.8 SORDsorbitol dehydrogenase (201563_at), score: -0.55 SORT1sortilin 1 (212807_s_at), score: 0.59 SPAG5sperm associated antigen 5 (203145_at), score: -0.55 SPATS2spermatogenesis associated, serine-rich 2 (218324_s_at), score: 0.51 SPINT2serine peptidase inhibitor, Kunitz type, 2 (210715_s_at), score: 0.66 SPOCK1sparc/osteonectin, cwcv and kazal-like domains proteoglycan (testican) 1 (202363_at), score: 0.6 SPON1spondin 1, extracellular matrix protein (209436_at), score: -0.54 SPSB1splA/ryanodine receptor domain and SOCS box containing 1 (219677_at), score: 0.67 SQLEsqualene epoxidase (213562_s_at), score: 0.54 SQRDLsulfide quinone reductase-like (yeast) (217995_at), score: 0.63 SREBF2sterol regulatory element binding transcription factor 2 (201247_at), score: 0.52 SRGNserglycin (201859_at), score: 0.63 SSX2IPsynovial sarcoma, X breakpoint 2 interacting protein (203016_s_at), score: -0.86 ST3GAL4ST3 beta-galactoside alpha-2,3-sialyltransferase 4 (203759_at), score: -0.57 STAT1signal transducer and activator of transcription 1, 91kDa (AFFX-HUMISGF3A/M97935_MA_at), score: 0.73 STAT4signal transducer and activator of transcription 4 (206118_at), score: 0.87 STEAP1six transmembrane epithelial antigen of the prostate 1 (205542_at), score: -0.77 STILSCL/TAL1 interrupting locus (205339_at), score: -0.56 STK38Lserine/threonine kinase 38 like (212572_at), score: 0.7 STMN2stathmin-like 2 (203000_at), score: -0.72 SUSD5sushi domain containing 5 (214954_at), score: 0.5 SUV39H1suppressor of variegation 3-9 homolog 1 (Drosophila) (218619_s_at), score: -0.57 SYNE1spectrin repeat containing, nuclear envelope 1 (209447_at), score: 0.57 SYNGR2synaptogyrin 2 (201079_at), score: 0.75 SYNPOsynaptopodin (202796_at), score: 0.57 SYT11synaptotagmin XI (209198_s_at), score: 0.54 TACC3transforming, acidic coiled-coil containing protein 3 (218308_at), score: -0.58 TAX1BP1Tax1 (human T-cell leukemia virus type I) binding protein 1 (200976_s_at), score: 0.5 TBC1D2BTBC1 domain family, member 2B (212796_s_at), score: 0.53 TCF7transcription factor 7 (T-cell specific, HMG-box) (205255_x_at), score: -0.56 TCF7L1transcription factor 7-like 1 (T-cell specific, HMG-box) (221016_s_at), score: 0.87 TDGthymine-DNA glycosylase (203743_s_at), score: 0.55 TEAD3TEA domain family member 3 (209454_s_at), score: 0.58 TELO2TEL2, telomere maintenance 2, homolog (S. cerevisiae) (34260_at), score: -0.55 TFAP2Ctranscription factor AP-2 gamma (activating enhancer binding protein 2 gamma) (205286_at), score: -0.56 TFPItissue factor pathway inhibitor (lipoprotein-associated coagulation inhibitor) (209676_at), score: 0.8 TFPI2tissue factor pathway inhibitor 2 (209278_s_at), score: -0.63 THBS2thrombospondin 2 (203083_at), score: 0.6 TIMELESStimeless homolog (Drosophila) (203046_s_at), score: -0.5 TINAGL1tubulointerstitial nephritis antigen-like 1 (219058_x_at), score: 0.84 TLR4toll-like receptor 4 (221060_s_at), score: 0.54 TMEM135transmembrane protein 135 (222209_s_at), score: 0.53 TMEM158transmembrane protein 158 (213338_at), score: -0.81 TMEM194Atransmembrane protein 194A (212621_at), score: -0.67 TMEM35transmembrane protein 35 (219685_at), score: 0.64 TMEM38Btransmembrane protein 38B (218772_x_at), score: -0.5 TMPOthymopoietin (209754_s_at), score: -0.57 TMSB15Bthymosin beta 15B (214051_at), score: -0.49 TNCtenascin C (201645_at), score: -0.52 TNFAIP8tumor necrosis factor, alpha-induced protein 8 (210260_s_at), score: 0.53 TNFRSF10Btumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily, member 10b (209295_at), score: 0.71 TNFRSF14tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily, member 14 (herpesvirus entry mediator) (209354_at), score: 0.52 TNFSF4tumor necrosis factor (ligand) superfamily, member 4 (207426_s_at), score: 0.64 TNXAtenascin XA pseudogene (213451_x_at), score: 1 TNXBtenascin XB (216333_x_at), score: 0.99 TOPBP1topoisomerase (DNA) II binding protein 1 (202633_at), score: -0.54 TP53tumor protein p53 (201746_at), score: 0.55 TPCN1two pore segment channel 1 (217914_at), score: 0.56 TPD52L1tumor protein D52-like 1 (203786_s_at), score: 0.59 TRAF5TNF receptor-associated factor 5 (204352_at), score: 0.57 TRAPPC2P1trafficking protein particle complex 2 pseudogene 1 (209751_s_at), score: 0.54 TRIM22tripartite motif-containing 22 (213293_s_at), score: 0.62 TRIP13thyroid hormone receptor interactor 13 (204033_at), score: -0.55 TRPV2transient receptor potential cation channel, subfamily V, member 2 (219282_s_at), score: 0.68 TSC22D1TSC22 domain family, member 1 (215111_s_at), score: 0.51 TSC22D3TSC22 domain family, member 3 (208763_s_at), score: 0.52 TTC28tetratricopeptide repeat domain 28 (215146_s_at), score: 0.56 TTKTTK protein kinase (204822_at), score: -0.57 TUFT1tuftelin 1 (205807_s_at), score: 0.84 TWIST1twist homolog 1 (Drosophila) (213943_at), score: -0.52 TYRO3TYRO3 protein tyrosine kinase (211432_s_at), score: -0.58 UBA7ubiquitin-like modifier activating enzyme 7 (203281_s_at), score: 0.69 UBE2L6ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2L 6 (201649_at), score: 0.53 UGDHUDP-glucose dehydrogenase (203343_at), score: 0.57 UNGuracil-DNA glycosylase (202330_s_at), score: -0.62 USP25ubiquitin specific peptidase 25 (220419_s_at), score: 0.53 VCLvinculin (200930_s_at), score: 0.54 VRK1vaccinia related kinase 1 (203856_at), score: -0.56 WBP2WW domain binding protein 2 (209117_at), score: 0.54 WDR62WD repeat domain 62 (215218_s_at), score: -0.56 WDR76WD repeat domain 76 (205519_at), score: -0.61 WHSC1Wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome candidate 1 (209053_s_at), score: -0.63 WIPI1WD repeat domain, phosphoinositide interacting 1 (203827_at), score: 0.6 WNT5Bwingless-type MMTV integration site family, member 5B (221029_s_at), score: -0.52 WRAP53WD repeat containing, antisense to TP53 (44563_at), score: -0.58 WWP2WW domain containing E3 ubiquitin protein ligase 2 (204022_at), score: 0.7 YPEL5yippee-like 5 (Drosophila) (217783_s_at), score: 0.55 ZNF395zinc finger protein 395 (218149_s_at), score: -0.51 ZNF423zinc finger protein 423 (214761_at), score: 0.89 ZNF512Bzinc finger protein 512B (55872_at), score: 0.5 ZNF536zinc finger protein 536 (206403_at), score: -0.83 ZNF85zinc finger protein 85 (206572_x_at), score: -0.57 ZWILCHZwilch, kinetochore associated, homolog (Drosophila) (218349_s_at), score: -0.52 ZWINTZW10 interactor (204026_s_at), score: -0.49
| Id | sample | Experiment | ExpName | Array | Syndrome | Cell.line |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E-GEOD-3860-raw-cel-1561690344.cel | 10 | 5 | HGPS | hgu133a | none | GM00038C |
| E-GEOD-3860-raw-cel-1561690472.cel | 17 | 5 | HGPS | hgu133a | none | GM00038C |
| E-GEOD-3860-raw-cel-1561690223.cel | 3 | 5 | HGPS | hgu133a | none | GM00038C |
| E-GEOD-3860-raw-cel-1561690392.cel | 14 | 5 | HGPS | hgu133a | none | GMO8398C |
| E-GEOD-3860-raw-cel-1561690256.cel | 6 | 5 | HGPS | hgu133a | none | GMO8398C |
| E-GEOD-3860-raw-cel-1561690304.cel | 8 | 5 | HGPS | hgu133a | none | GMO8398C |
| E-GEOD-3860-raw-cel-1561690360.cel | 12 | 5 | HGPS | hgu133a | none | GM0316B |
| E-GEOD-3860-raw-cel-1561690416.cel | 15 | 5 | HGPS | hgu133a | none | GM0316B |
| E-GEOD-3407-raw-cel-1437949557.cel | 1 | 4 | Cockayne | hgu133a | CS | eGFP |
| 46A.CEL | 1 | 3 | DS-mosaic | hgu133plus2 | none | DS-mosaic 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486351.cel | 36 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486291.cel | 33 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-GEOD-3860-raw-cel-1561690432.cel | 16 | 5 | HGPS | hgu133a | HGPS | AG10750 |
| E-GEOD-3860-raw-cel-1561690231.cel | 4 | 5 | HGPS | hgu133a | HGPS | AG10750 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485851.cel | 11 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486271.cel | 32 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486231.cel | 30 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486331.cel | 35 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-GEOD-3860-raw-cel-1561690336.cel | 9 | 5 | HGPS | hgu133a | HGPS | AG10750 |