
Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

system process
A multicellular organismal process carried out by any of the organs or tissues in an organ system. An organ system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a biological objective.
transport
The directed movement of substances (such as macromolecules, small molecules, ions) into, out of, within or between cells, or within a multicellular organism.
dicarboxylic acid transport
The directed movement of dicarboxylic acids into, out of, within or between cells.
neurological system process
A organ system process carried out by any of the organs or tissues of neurological system.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
organic acid transport
The directed movement of organic acids, any acidic compound containing carbon in covalent linkage, into, out of, within or between cells.
multicellular organismal process
Any biological process, occurring at the level of a multicellular organism, pertinent to its function.
carboxylic acid transport
The directed movement of carboxylic acids into, out of, within or between cells. Carboxylic acids are organic acids containing one or more carboxyl (COOH) groups or anions (COO-).
localization
Any process by which a cell, a substance, or a cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, is transported to, and/or maintained in a specific location.
establishment of localization
The directed movement of a cell, substance or cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, to a specific location.
all
This term is the most general term possible
establishment of localization
The directed movement of a cell, substance or cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, to a specific location.

membrane
Double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
cellular_component
The part of a cell or its extracellular environment in which a gene product is located. A gene product may be located in one or more parts of a cell and its location may be as specific as a particular macromolecular complex, that is, a stable, persistent association of macromolecules that function together.
cell
The basic structural and functional unit of all organisms. Includes the plasma membrane and any external encapsulating structures such as the cell wall and cell envelope.
presynaptic membrane
A specialized area of membrane of the axon terminal that faces the plasma membrane of the neuron or muscle fiber with which the axon terminal establishes a synaptic junction; many synaptic junctions exhibit structural presynaptic characteristics, such as conical, electron-dense internal protrusions, that distinguish it from the remainder of the axon plasma membrane.
synapse part
Any constituent part of a synapse, the junction between a nerve fiber of one neuron and another neuron or muscle fiber or glial cell.
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
synapse
The junction between a nerve fiber of one neuron and another neuron or muscle fiber or glial cell; the site of interneuronal communication. As the nerve fiber approaches the synapse it enlarges into a specialized structure, the presynaptic nerve ending, which contains mitochondria and synaptic vesicles. At the tip of the nerve ending is the presynaptic membrane; facing it, and separated from it by a minute cleft (the synaptic cleft) is a specialized area of membrane on the receiving cell, known as the postsynaptic membrane. In response to the arrival of nerve impulses, the presynaptic nerve ending secretes molecules of neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft. These diffuse across the cleft and transmit the signal to the postsynaptic membrane.
all
This term is the most general term possible
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
synapse part
Any constituent part of a synapse, the junction between a nerve fiber of one neuron and another neuron or muscle fiber or glial cell.
presynaptic membrane
A specialized area of membrane of the axon terminal that faces the plasma membrane of the neuron or muscle fiber with which the axon terminal establishes a synaptic junction; many synaptic junctions exhibit structural presynaptic characteristics, such as conical, electron-dense internal protrusions, that distinguish it from the remainder of the axon plasma membrane.

molecular_function
Elemental activities, such as catalysis or binding, describing the actions of a gene product at the molecular level. A given gene product may exhibit one or more molecular functions.
transporter activity
Enables the directed movement of substances (such as macromolecules, small molecules, ions) into, out of, within or between cells.
transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a substance from one side of a membrane to the other.
dicarboxylic acid transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of dicarboxylic acids from one side of the membrane to the other. A dicarboxylic acid is an organic acid with two COOH groups.
organic acid:sodium symporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a solute or solutes from one side of a membrane to the other according to the reaction: organic acid(out) + Na+(out) = organic acid(in) + Na+(in).
organic acid transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of organic acids, any acidic compound containing carbon in covalent linkage, from one side of the membrane to the other.
secondary active transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a solute from one side of a membrane to the other, up its concentration gradient. The transporter binds the solute and undergoes a series of conformational changes. Transport works equally well in either direction and is driven by a chemiosmotic source of energy. Chemiosmotic sources of energy include uniport, symport or antiport.
cation transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of cation from one side of the membrane to the other.
anion transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a negatively charged ion from one side of a membrane to the other.
ion transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of an ion from one side of a membrane to the other.
symporter activity
Enables the active transport of a solute across a membrane by a mechanism whereby two or more species are transported together in the same direction in a tightly coupled process not directly linked to a form of energy other than chemiosmotic energy.
solute:cation symporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a solute or solutes from one side of a membrane to the other according to the reaction: solute(out) + cation(out) = solute(in) + cation(in).
anion:cation symporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a solute or solutes from one side of a membrane to the other according to the reaction: anion(out) + cation(out) = anion(in) + cation(in).
solute:sodium symporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a solute or solutes from one side of a membrane to the other according to the reaction: solute(out) + Na+(out) = solute(in) + Na+(in).
sodium:dicarboxylate symporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a solute or solutes from one side of a membrane to the other according to the reaction: dicarboxylate(out) + Na+(out) = dicarboxylate(in) + Na+(in).
active transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a specific substance or related group of substances from one side of a membrane to the other, up the solute's concentration gradient. The transporter binds the solute and undergoes a series of conformational changes. Transport works equally well in either direction.
substrate-specific transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a specific substance or group of related substances from one side of a membrane to the other.
substrate-specific transporter activity
Enables the directed movement of a specific substance or group of related substances (such as macromolecules, small molecules, ions) into, out of, within or between cells.
carboxylic acid transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of carboxylic acids from one side of the membrane to the other. Carboxylic acids are organic acids containing one or more carboxyl (COOH) groups or anions (COO-).
all
This term is the most general term possible
substrate-specific transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a specific substance or group of related substances from one side of a membrane to the other.
solute:cation symporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a solute or solutes from one side of a membrane to the other according to the reaction: solute(out) + cation(out) = solute(in) + cation(in).
anion:cation symporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a solute or solutes from one side of a membrane to the other according to the reaction: anion(out) + cation(out) = anion(in) + cation(in).
sodium:dicarboxylate symporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a solute or solutes from one side of a membrane to the other according to the reaction: dicarboxylate(out) + Na+(out) = dicarboxylate(in) + Na+(in).
sodium:dicarboxylate symporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a solute or solutes from one side of a membrane to the other according to the reaction: dicarboxylate(out) + Na+(out) = dicarboxylate(in) + Na+(in).
organic acid:sodium symporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a solute or solutes from one side of a membrane to the other according to the reaction: organic acid(out) + Na+(out) = organic acid(in) + Na+(in).
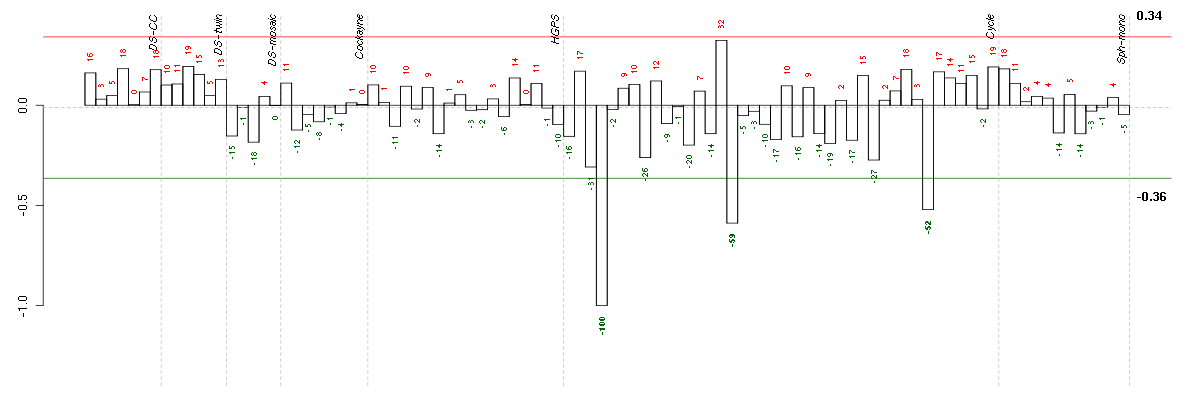
AGTangiotensinogen (serpin peptidase inhibitor, clade A, member 8) (202834_at), score: 0.77 DSPPdentin sialophosphoprotein (221681_s_at), score: 0.78 FLJ21075hypothetical protein FLJ21075 (221172_at), score: 0.86 GPR144G protein-coupled receptor 144 (216289_at), score: 0.83 GPR32G protein-coupled receptor 32 (221469_at), score: 0.89 HAND1heart and neural crest derivatives expressed 1 (220138_at), score: 0.76 ITGALintegrin, alpha L (antigen CD11A (p180), lymphocyte function-associated antigen 1; alpha polypeptide) (213475_s_at), score: 0.79 LRP2low density lipoprotein-related protein 2 (205710_at), score: -0.91 NDPNorrie disease (pseudoglioma) (206022_at), score: -0.81 NRCAMneuronal cell adhesion molecule (216959_x_at), score: 0.75 PPP1R13Bprotein phosphatase 1, regulatory (inhibitor) subunit 13B (216347_s_at), score: 0.86 PTPN6protein tyrosine phosphatase, non-receptor type 6 (206687_s_at), score: 0.76 SLC1A2solute carrier family 1 (glial high affinity glutamate transporter), member 2 (208389_s_at), score: 0.78 SLC1A7solute carrier family 1 (glutamate transporter), member 7 (210923_at), score: 0.81 SNTG1syntrophin, gamma 1 (220405_at), score: -1 SPATA1spermatogenesis associated 1 (221057_at), score: 0.86 SYT1synaptotagmin I (203999_at), score: -0.76 TAL1T-cell acute lymphocytic leukemia 1 (206283_s_at), score: 0.9 TULP2tubby like protein 2 (206733_at), score: 0.74 ZNF460zinc finger protein 460 (216279_at), score: -0.86
| Id | sample | Experiment | ExpName | Array | Syndrome | Cell.line |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485711.cel | 4 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485951.cel | 16 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486311.cel | 34 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |