
Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

chromosome organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level that results in the formation, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of chromosomes, structures composed of a very long molecule of DNA and associated proteins that carries hereditary information.
chromatin assembly or disassembly
The formation or destruction of chromatin structures.
nucleosome assembly
The aggregation, arrangement and bonding together of a nucleosome, the beadlike structural units of eukaryotic chromatin composed of histones and DNA.
DNA packaging
Any process by which DNA and associated proteins are formed into a compact, orderly structure.
establishment or maintenance of chromatin architecture
Any process that results in the specification, formation or maintenance of the physical structure of eukaryotic chromatin.
organelle organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the formation, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of an organelle within a cell. An organelle is an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
cellular component organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the formation, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of a cellular component.
cellular component assembly
A cellular process that results in the assembly of a part of the cell.
chromatin assembly
The assembly of DNA, histone proteins, and other associated proteins into chromatin structure, beginning with the formation of the basic unit, the nucleosome, followed by organization of the nucleosomes into higher order structures, ultimately giving rise to a complex organization of specific domains within the nucleus.
cellular macromolecular complex subunit organization
Any process carried out at the cellular level by which macromolecules aggregate, disaggregate, or are modified, resulting in the formation, disassembly, or alteration of a macromolecular complex.
cellular macromolecular complex assembly
The aggregation, arrangement and bonding together of a set of macromolecules to form a complex, carried out at the cellular level.
nucleosome organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the formation, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of one or more nucleosomes.
macromolecular complex subunit organization
Any process by which macromolecules aggregate, disaggregate, or are modified, resulting in the formation, disassembly, or alteration of a macromolecular complex.
macromolecular complex assembly
The aggregation, arrangement and bonding together of a set of macromolecules to form a complex.
protein-DNA complex assembly
The aggregation, arrangement and bonding together of proteins and DNA molecules to form a protein-DNA complex.
all
This term is the most general term possible
chromatin assembly
The assembly of DNA, histone proteins, and other associated proteins into chromatin structure, beginning with the formation of the basic unit, the nucleosome, followed by organization of the nucleosomes into higher order structures, ultimately giving rise to a complex organization of specific domains within the nucleus.
macromolecular complex assembly
The aggregation, arrangement and bonding together of a set of macromolecules to form a complex.
cellular macromolecular complex assembly
The aggregation, arrangement and bonding together of a set of macromolecules to form a complex, carried out at the cellular level.
chromatin assembly
The assembly of DNA, histone proteins, and other associated proteins into chromatin structure, beginning with the formation of the basic unit, the nucleosome, followed by organization of the nucleosomes into higher order structures, ultimately giving rise to a complex organization of specific domains within the nucleus.
nucleosome assembly
The aggregation, arrangement and bonding together of a nucleosome, the beadlike structural units of eukaryotic chromatin composed of histones and DNA.
nucleosome assembly
The aggregation, arrangement and bonding together of a nucleosome, the beadlike structural units of eukaryotic chromatin composed of histones and DNA.

intracellular
The living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
chromatin
The ordered and organized complex of DNA and protein that forms the chromosome.
nucleosome
A complex comprised of DNA wound around a multisubunit core and associated proteins, which forms the primary packing unit of DNA into higher order structures.
cellular_component
The part of a cell or its extracellular environment in which a gene product is located. A gene product may be located in one or more parts of a cell and its location may be as specific as a particular macromolecular complex, that is, a stable, persistent association of macromolecules that function together.
cell
The basic structural and functional unit of all organisms. Includes the plasma membrane and any external encapsulating structures such as the cell wall and cell envelope.
chromosome
A structure composed of a very long molecule of DNA and associated proteins (e.g. histones) that carries hereditary information.
macromolecular complex
A stable assembly of two or more macromolecules, i.e. proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates or lipids, in which the constituent parts function together.
protein-DNA complex
A macromolecular complex containing both protein and DNA molecules.
organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
non-membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, not bounded by a lipid bilayer membrane. Includes ribosomes, the cytoskeleton and chromosomes.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular non-membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, not bounded by a lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes ribosomes, the cytoskeleton and chromosomes.
organelle part
Any constituent part of an organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, but excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
chromosomal part
Any constituent part of a chromosome, a structure composed of a very long molecule of DNA and associated proteins (e.g. histones) that carries hereditary information.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
all
This term is the most general term possible
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
organelle part
Any constituent part of an organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, but excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular non-membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, not bounded by a lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes ribosomes, the cytoskeleton and chromosomes.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
nucleosome
A complex comprised of DNA wound around a multisubunit core and associated proteins, which forms the primary packing unit of DNA into higher order structures.
chromosomal part
Any constituent part of a chromosome, a structure composed of a very long molecule of DNA and associated proteins (e.g. histones) that carries hereditary information.
nucleosome
A complex comprised of DNA wound around a multisubunit core and associated proteins, which forms the primary packing unit of DNA into higher order structures.

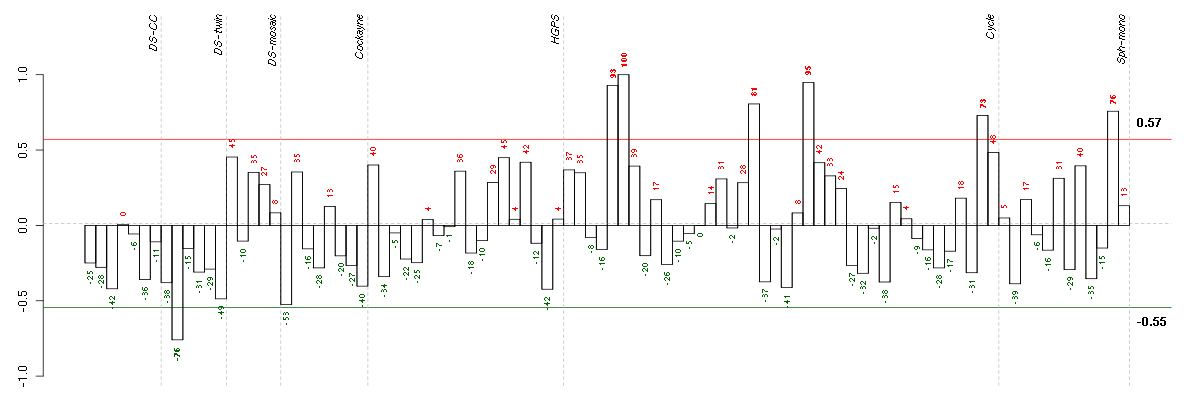
CSN2casein beta (207951_at), score: -0.92 H2BFSH2B histone family, member S (208579_x_at), score: 0.97 HIST1H2BEhistone cluster 1, H2be (208527_x_at), score: 0.96 HIST1H2BFhistone cluster 1, H2bf (208490_x_at), score: 1 HIST1H2BHhistone cluster 1, H2bh (208546_x_at), score: 0.9 HIST1H2BKhistone cluster 1, H2bk (209806_at), score: 0.77 MOAP1modulator of apoptosis 1 (212508_at), score: 0.79 SLC22A4solute carrier family 22 (organic cation/ergothioneine transporter), member 4 (205896_at), score: 0.76
| Id | sample | Experiment | ExpName | Array | Syndrome | Cell.line |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2Twin.CEL | 2 | 2 | DS-twin | hgu133plus2 | none | DS-twin 2 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486411.cel | 39 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-GEOD-4219-raw-cel-1311956634.cel | 19 | 7 | Sph-mono | hgu133plus2 | none | Sph-mon 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485991.cel | 18 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485731.cel | 5 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486091.cel | 23 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485751.cel | 6 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |