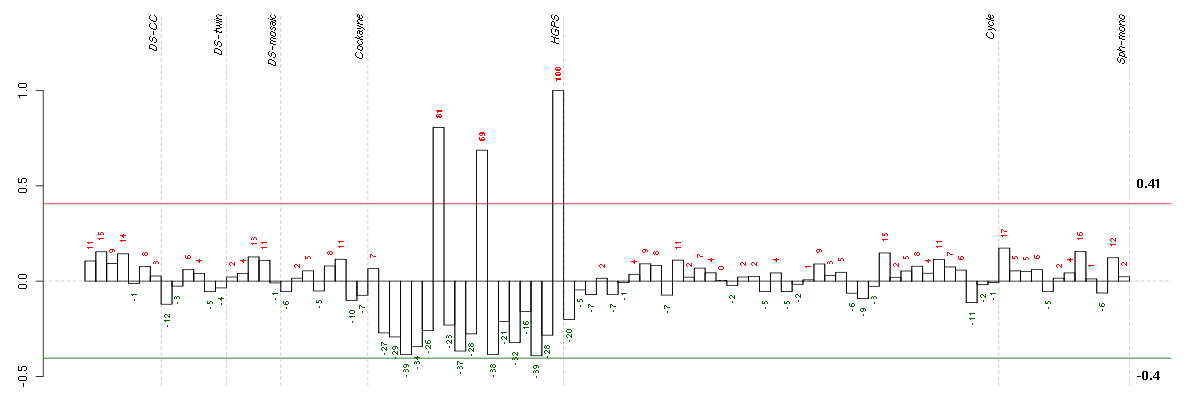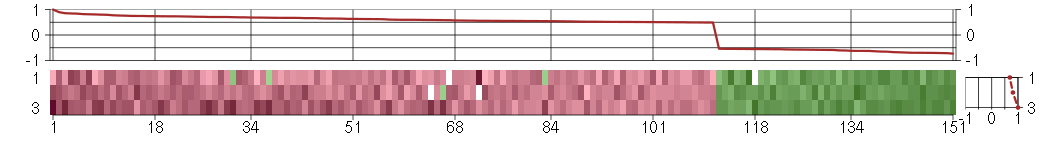

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

blood vessel development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the blood vessel over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The blood vessel is the vasculature carrying blood.
vasculature development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the vasculature over time, from its formation to the mature structure.
adaptive immune response
An immune response based on directed amplification of specific receptors for antigen produced through a somatic diversification process, and allowing for enhanced response to subsequent exposures to the same antigen (immunological memory).
immune system process
Any process involved in the development or functioning of the immune system, an organismal system for calibrated responses to potential internal or invasive threats.
adaptive immune response based on somatic recombination of immune receptors built from immunoglobulin superfamily domains
An immune response based on directed amplification of specific receptors for antigen produced through a somatic diversification process that includes somatic recombination of germline gene segments encoding immunoglobulin superfamily domains, and allowing for enhanced responses upon subsequent exposures to the same antigen (immunological memory). Recombined receptors for antigen encoded by immunoglobulin superfamily domains include T cell receptors and immunoglobulins (antibodies).
acute inflammatory response
Inflammation which comprises a rapid, short-lived, relatively uniform response to acute injury or antigenic challenge and is characterized by accumulations of fluid, plasma proteins, and granulocytic leukocytes. An acute inflammatory response occurs within a matter of minutes or hours, and either resolves within a few days or becomes a chronic inflammatory response.
defense response
Reactions, triggered in response to the presence of a foreign body or the occurrence of an injury, which result in restriction of damage to the organism attacked or prevention/recovery from the infection caused by the attack.
signal transduction
The cascade of processes by which a signal interacts with a receptor, causing a change in the level or activity of a second messenger or other downstream target, and ultimately effecting a change in the functioning of the cell.
response to stress
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a disturbance in organismal or cellular homeostasis, usually, but not necessarily, exogenous (e.g. temperature, humidity, ionizing radiation).
inflammatory response
The immediate defensive reaction (by vertebrate tissue) to infection or injury caused by chemical or physical agents. The process is characterized by local vasodilation, extravasation of plasma into intercellular spaces and accumulation of white blood cells and macrophages.
immune response
Any immune system process that functions in the calibrated response of an organism to a potential internal or invasive threat.
cell communication
Any process that mediates interactions between a cell and its surroundings. Encompasses interactions such as signaling or attachment between one cell and another cell, between a cell and an extracellular matrix, or between a cell and any other aspect of its environment.
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
response to external stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an external stimulus.
response to wounding
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus indicating damage to the organism.
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
multicellular organismal process
Any biological process, occurring at the level of a multicellular organism, pertinent to its function.
developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an integrated living unit: an anatomical structure (which may be a subcellular structure, cell, tissue, or organ), or organism over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
organ development
Development of a tissue or tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Development pertains to the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a structure over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
positive regulation of biological process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of response to stimulus
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a response to a stimulus. Response to stimulus is a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
positive regulation of response to stimulus
Any process that activates, maintains or increases the rate of a response to a stimulus. Response to stimulus is a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
anatomical structure development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an anatomical structure from an initial condition to its mature state. This process begins with the formation of the structure and ends with the mature structure, whatever form that may be including its natural destruction. An anatomical structure is any biological entity that occupies space and is distinguished from its surroundings. Anatomical structures can be macroscopic such as a carpel, or microscopic such as an acrosome.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of cellular process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
response to stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
biological regulation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of any biological process, quality or function.
all
This term is the most general term possible
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
positive regulation of biological process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of cellular process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
immune response
Any immune system process that functions in the calibrated response of an organism to a potential internal or invasive threat.
regulation of response to stimulus
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a response to a stimulus. Response to stimulus is a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
positive regulation of response to stimulus
Any process that activates, maintains or increases the rate of a response to a stimulus. Response to stimulus is a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
signal transduction
The cascade of processes by which a signal interacts with a receptor, causing a change in the level or activity of a second messenger or other downstream target, and ultimately effecting a change in the functioning of the cell.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
positive regulation of response to stimulus
Any process that activates, maintains or increases the rate of a response to a stimulus. Response to stimulus is a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
response to wounding
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus indicating damage to the organism.
organ development
Development of a tissue or tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Development pertains to the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a structure over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
inflammatory response
The immediate defensive reaction (by vertebrate tissue) to infection or injury caused by chemical or physical agents. The process is characterized by local vasodilation, extravasation of plasma into intercellular spaces and accumulation of white blood cells and macrophages.

extracellular region
The space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.
cellular_component
The part of a cell or its extracellular environment in which a gene product is located. A gene product may be located in one or more parts of a cell and its location may be as specific as a particular macromolecular complex, that is, a stable, persistent association of macromolecules that function together.
extracellular space
That part of a multicellular organism outside the cells proper, usually taken to be outside the plasma membranes, and occupied by fluid.
extracellular region part
Any constituent part of the extracellular region, the space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers constituent parts of the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.
all
This term is the most general term possible
extracellular region part
Any constituent part of the extracellular region, the space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers constituent parts of the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.

protein binding
Interacting selectively with any protein or protein complex (a complex of two or more proteins that may include other nonprotein molecules).
pattern binding
Interacting selectively with a repeating or polymeric structure, such as a polysaccharide or peptidoglycan.
molecular_function
Elemental activities, such as catalysis or binding, describing the actions of a gene product at the molecular level. A given gene product may exhibit one or more molecular functions.
receptor binding
Interacting selectively with one or more specific sites on a receptor molecule, a macromolecule that undergoes combination with a hormone, neurotransmitter, drug or intracellular messenger to initiate a change in cell function.
carbohydrate binding
Interacting selectively with any carbohydrate.
cytokine activity
Functions to control the survival, growth, differentiation and effector function of tissues and cells.
binding
The selective, often stoichiometric, interaction of a molecule with one or more specific sites on another molecule.
glycosaminoglycan binding
Interacting selectively with any glycan (polysaccharide) containing a substantial proportion of aminomonosaccharide residues.
polysaccharide binding
Interacting selectively with any polysaccharide.
all
This term is the most general term possible
polysaccharide binding
Interacting selectively with any polysaccharide.
| Id | Pvalue | ExpCount | Count | Size | Term |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 04060 | 2.511e-03 | 2.439 | 11 | 115 | Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction |
ABCA8ATP-binding cassette, sub-family A (ABC1), member 8 (204719_at), score: 0.71 ABCC4ATP-binding cassette, sub-family C (CFTR/MRP), member 4 (203196_at), score: 0.51 ABI3BPABI family, member 3 (NESH) binding protein (220518_at), score: 0.52 ADAMTS3ADAM metallopeptidase with thrombospondin type 1 motif, 3 (214913_at), score: 0.5 ADAMTSL3ADAMTS-like 3 (213974_at), score: 0.73 ADMadrenomedullin (202912_at), score: -0.65 AKR1C3aldo-keto reductase family 1, member C3 (3-alpha hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase, type II) (209160_at), score: 0.71 ALDH3B1aldehyde dehydrogenase 3 family, member B1 (211004_s_at), score: -0.61 ALDH4A1aldehyde dehydrogenase 4 family, member A1 (211552_s_at), score: -0.54 AMFRautocrine motility factor receptor (202203_s_at), score: 0.55 ANKRD1ankyrin repeat domain 1 (cardiac muscle) (206029_at), score: 0.72 ANO3anoctamin 3 (215241_at), score: -0.56 ANXA10annexin A10 (210143_at), score: 0.61 ANXA3annexin A3 (209369_at), score: 0.71 ARSBarylsulfatase B (206129_s_at), score: 0.56 B3GALT4UDP-Gal:betaGlcNAc beta 1,3-galactosyltransferase, polypeptide 4 (210205_at), score: -0.59 BAMBIBMP and activin membrane-bound inhibitor homolog (Xenopus laevis) (203304_at), score: -0.54 BMP6bone morphogenetic protein 6 (206176_at), score: 0.55 BNC2basonuclin 2 (220272_at), score: 0.69 C3complement component 3 (217767_at), score: 0.56 C8orf84chromosome 8 open reading frame 84 (214725_at), score: 0.82 CADPS2Ca++-dependent secretion activator 2 (219572_at), score: 0.6 CCDC68coiled-coil domain containing 68 (220180_at), score: 0.56 CD200CD200 molecule (209583_s_at), score: 0.85 CD34CD34 molecule (209543_s_at), score: 0.74 CD55CD55 molecule, decay accelerating factor for complement (Cromer blood group) (201925_s_at), score: 0.62 CD70CD70 molecule (206508_at), score: 0.58 CEBPGCCAAT/enhancer binding protein (C/EBP), gamma (204203_at), score: 0.51 CENPQcentromere protein Q (219294_at), score: 0.49 CFHcomplement factor H (213800_at), score: 0.8 CFHR1complement factor H-related 1 (215388_s_at), score: 0.67 CHRDL1chordin-like 1 (209763_at), score: 0.67 CLDN1claudin 1 (218182_s_at), score: 0.68 CMAHcytidine monophosphate-N-acetylneuraminic acid hydroxylase (CMP-N-acetylneuraminate monooxygenase) pseudogene (205518_s_at), score: 0.68 COL16A1collagen, type XVI, alpha 1 (204345_at), score: 0.5 CRYBB2crystallin, beta B2 (206777_s_at), score: 0.59 CUGBP2CUG triplet repeat, RNA binding protein 2 (202158_s_at), score: 0.65 CXCL1chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 1 (melanoma growth stimulating activity, alpha) (204470_at), score: 0.76 CXCL6chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 6 (granulocyte chemotactic protein 2) (206336_at), score: 0.62 DAAM1dishevelled associated activator of morphogenesis 1 (216060_s_at), score: 0.63 DDX43DEAD (Asp-Glu-Ala-Asp) box polypeptide 43 (220004_at), score: 0.63 DLEU1deleted in lymphocytic leukemia 1 (non-protein coding) (205677_s_at), score: 0.6 DMPKdystrophia myotonica-protein kinase (37996_s_at), score: -0.55 DOCK9dedicator of cytokinesis 9 (212538_at), score: 0.54 DPYSL3dihydropyrimidinase-like 3 (201431_s_at), score: 0.55 DSG2desmoglein 2 (217901_at), score: 0.75 DUSP4dual specificity phosphatase 4 (204014_at), score: 0.55 EDN1endothelin 1 (218995_s_at), score: 0.64 EIF1AYeukaryotic translation initiation factor 1A, Y-linked (204409_s_at), score: 0.57 ELTD1EGF, latrophilin and seven transmembrane domain containing 1 (219134_at), score: -0.57 EN1engrailed homeobox 1 (220559_at), score: -0.71 EPHA5EPH receptor A5 (215664_s_at), score: 0.75 ERCC6excision repair cross-complementing rodent repair deficiency, complementation group 6 (207347_at), score: 0.54 ERGv-ets erythroblastosis virus E26 oncogene homolog (avian) (213541_s_at), score: 0.84 ESM1endothelial cell-specific molecule 1 (208394_x_at), score: 0.56 FBLN2fibulin 2 (203886_s_at), score: -0.7 FGL2fibrinogen-like 2 (204834_at), score: 1 FKBP1BFK506 binding protein 1B, 12.6 kDa (206857_s_at), score: 0.49 FLI1Friend leukemia virus integration 1 (204236_at), score: 0.51 FMO3flavin containing monooxygenase 3 (40665_at), score: 0.67 FOXD1forkhead box D1 (206307_s_at), score: -0.55 FOXO1forkhead box O1 (202724_s_at), score: 0.57 GALNT12UDP-N-acetyl-alpha-D-galactosamine:polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase 12 (GalNAc-T12) (218885_s_at), score: 0.65 GPR1G protein-coupled receptor 1 (214605_x_at), score: 0.51 GPR126G protein-coupled receptor 126 (213094_at), score: 0.77 GPR4G protein-coupled receptor 4 (206236_at), score: 0.66 GPRC5BG protein-coupled receptor, family C, group 5, member B (203632_s_at), score: 0.68 GSTT2glutathione S-transferase theta 2 (205439_at), score: 0.73 HDAC5histone deacetylase 5 (202455_at), score: -0.54 HGFhepatocyte growth factor (hepapoietin A; scatter factor) (209960_at), score: 0.59 HRH1histamine receptor H1 (205580_s_at), score: 0.59 HSPB8heat shock 22kDa protein 8 (221667_s_at), score: -0.7 HYIhydroxypyruvate isomerase homolog (E. coli) (221435_x_at), score: 0.67 IFI27interferon, alpha-inducible protein 27 (202411_at), score: 0.74 IL12Ainterleukin 12A (natural killer cell stimulatory factor 1, cytotoxic lymphocyte maturation factor 1, p35) (207160_at), score: -0.55 IL18interleukin 18 (interferon-gamma-inducing factor) (206295_at), score: 0.73 IL1Ainterleukin 1, alpha (210118_s_at), score: 0.7 IL1Binterleukin 1, beta (39402_at), score: 0.54 IL21Rinterleukin 21 receptor (219971_at), score: 0.51 IL8interleukin 8 (211506_s_at), score: 0.55 ITM2Aintegral membrane protein 2A (202746_at), score: 0.72 KAL1Kallmann syndrome 1 sequence (205206_at), score: 0.52 KCTD12potassium channel tetramerisation domain containing 12 (212192_at), score: 0.63 KIAA0182KIAA0182 (212057_at), score: -0.56 KIAA0247KIAA0247 (202181_at), score: 0.51 KLF5Kruppel-like factor 5 (intestinal) (209212_s_at), score: 0.59 KRT8keratin 8 (209008_x_at), score: 0.52 LAMC2laminin, gamma 2 (202267_at), score: 0.81 LBHlimb bud and heart development homolog (mouse) (221011_s_at), score: -0.56 LIPGlipase, endothelial (219181_at), score: 0.9 LOC100132214similar to HSPC047 protein (220692_at), score: 0.51 LYPD1LY6/PLAUR domain containing 1 (212909_at), score: 0.74 MAPK3mitogen-activated protein kinase 3 (212046_x_at), score: -0.58 MCTP1multiple C2 domains, transmembrane 1 (220122_at), score: 0.66 MFAP2microfibrillar-associated protein 2 (203417_at), score: -0.68 MFGE8milk fat globule-EGF factor 8 protein (210605_s_at), score: -0.55 MYLKmyosin light chain kinase (202555_s_at), score: -0.73 NAAAN-acylethanolamine acid amidase (214765_s_at), score: -0.57 NFIBnuclear factor I/B (209290_s_at), score: 0.66 NOX4NADPH oxidase 4 (219773_at), score: 0.79 OSBPL1Aoxysterol binding protein-like 1A (209485_s_at), score: -0.62 PAPPApregnancy-associated plasma protein A, pappalysin 1 (201981_at), score: 0.49 PARP3poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase family, member 3 (209940_at), score: -0.7 PDE10Aphosphodiesterase 10A (205501_at), score: 0.53 PDE4Dphosphodiesterase 4D, cAMP-specific (phosphodiesterase E3 dunce homolog, Drosophila) (204491_at), score: 0.52 PDGFRAplatelet-derived growth factor receptor, alpha polypeptide (203131_at), score: -0.62 PDLIM1PDZ and LIM domain 1 (208690_s_at), score: -0.55 PDZRN4PDZ domain containing ring finger 4 (220595_at), score: 0.67 PKP2plakophilin 2 (207717_s_at), score: 0.64 PLCB4phospholipase C, beta 4 (203896_s_at), score: -0.59 PLCL1phospholipase C-like 1 (205934_at), score: 0.51 PLXNA2plexin A2 (213030_s_at), score: 0.76 POPDC3popeye domain containing 3 (219926_at), score: -0.7 PPAP2Aphosphatidic acid phosphatase type 2A (209147_s_at), score: -0.65 PPM1Hprotein phosphatase 1H (PP2C domain containing) (212686_at), score: 0.68 PSPHphosphoserine phosphatase (205048_s_at), score: 0.55 PYGLphosphorylase, glycogen, liver (202990_at), score: 0.49 RAC2ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate 2 (rho family, small GTP binding protein Rac2) (213603_s_at), score: -0.67 ROR1receptor tyrosine kinase-like orphan receptor 1 (205805_s_at), score: 0.56 RPP25ribonuclease P/MRP 25kDa subunit (219143_s_at), score: -0.58 RXRAretinoid X receptor, alpha (202449_s_at), score: -0.55 SCRN1secernin 1 (201462_at), score: -0.69 SLC17A9solute carrier family 17, member 9 (219559_at), score: -0.62 SLC31A2solute carrier family 31 (copper transporters), member 2 (204204_at), score: 0.58 SLC39A8solute carrier family 39 (zinc transporter), member 8 (209267_s_at), score: 0.73 SLC7A5solute carrier family 7 (cationic amino acid transporter, y+ system), member 5 (201195_s_at), score: 0.52 SOX17SRY (sex determining region Y)-box 17 (219993_at), score: 0.84 STBD1starch binding domain 1 (203986_at), score: -0.64 SULT1B1sulfotransferase family, cytosolic, 1B, member 1 (207601_at), score: 0.6 SUSD5sushi domain containing 5 (214954_at), score: 0.55 SWAP70SWAP-70 protein (209307_at), score: 0.53 SYCP2synaptonemal complex protein 2 (206546_at), score: -0.6 TBC1D8TBC1 domain family, member 8 (with GRAM domain) (204526_s_at), score: 0.5 TEKTEK tyrosine kinase, endothelial (206702_at), score: 0.49 THBS2thrombospondin 2 (203083_at), score: 0.54 THY1Thy-1 cell surface antigen (208850_s_at), score: -0.71 TIMP3TIMP metallopeptidase inhibitor 3 (201149_s_at), score: -0.7 TLR4toll-like receptor 4 (221060_s_at), score: 0.81 TNFAIP6tumor necrosis factor, alpha-induced protein 6 (206026_s_at), score: 0.63 TNFAIP8tumor necrosis factor, alpha-induced protein 8 (210260_s_at), score: 0.69 TPK1thiamin pyrophosphokinase 1 (221218_s_at), score: 0.71 UAP1L1UDP-N-acteylglucosamine pyrophosphorylase 1-like 1 (214755_at), score: -0.58 VLDLRvery low density lipoprotein receptor (209822_s_at), score: 0.6 VPS13Avacuolar protein sorting 13 homolog A (S. cerevisiae) (214785_at), score: 0.55 WDTC1WD and tetratricopeptide repeats 1 (40829_at), score: -0.57 YES1v-yes-1 Yamaguchi sarcoma viral oncogene homolog 1 (202932_at), score: 0.5 ZDHHC7zinc finger, DHHC-type containing 7 (218606_at), score: -0.62 ZFHX4zinc finger homeobox 4 (219779_at), score: 0.75 ZFPM2zinc finger protein, multitype 2 (219778_at), score: 0.5 ZNF323zinc finger protein 323 (222016_s_at), score: 0.71 ZNF365zinc finger protein 365 (206448_at), score: 0.62
| Id | sample | Experiment | ExpName | Array | Syndrome | Cell.line |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E-GEOD-3860-raw-cel-1561690352.cel | 11 | 5 | HGPS | hgu133a | HGPS | AG11498 |
| E-GEOD-3860-raw-cel-1561690272.cel | 7 | 5 | HGPS | hgu133a | HGPS | AG11498 |
| E-GEOD-3860-raw-cel-1561690480.cel | 18 | 5 | HGPS | hgu133a | HGPS | AG11498 |