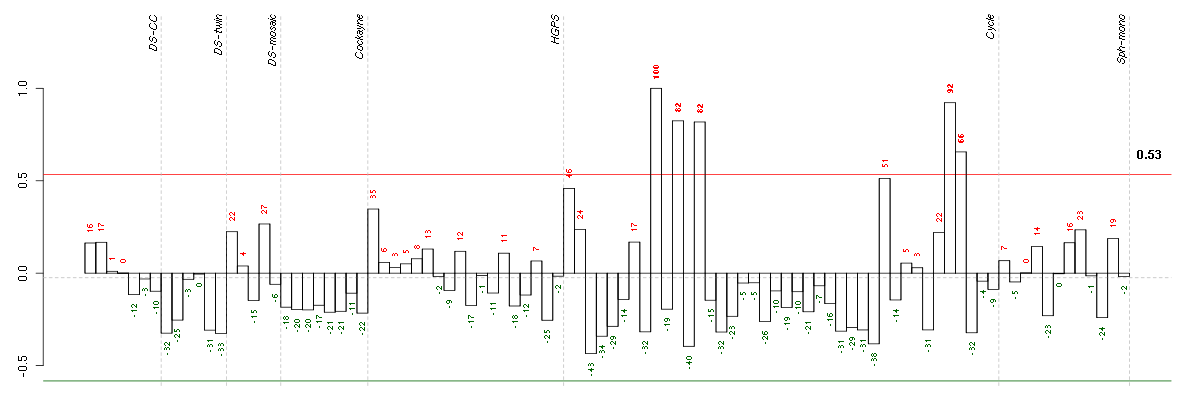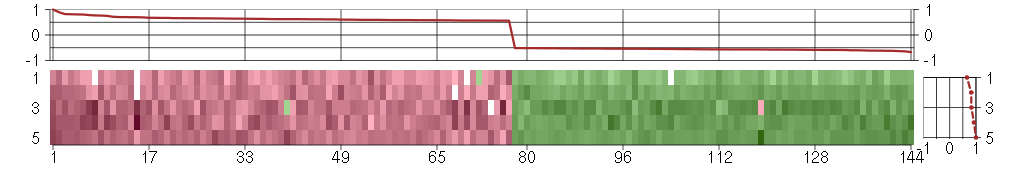

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

chromosome segregation
The process by which genetic material, in the form of chromosomes, is organized and then physically separated and apportioned to two or more sets.
chromosome organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level that results in the formation, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of chromosomes, structures composed of a very long molecule of DNA and associated proteins that carries hereditary information.
mitotic sister chromatid segregation
The cell cycle process whereby replicated homologous chromosomes are organized and then physically separated and apportioned to two sets during the mitotic cell cycle. Each replicated chromosome, composed of two sister chromatids, aligns at the cell equator, paired with its homologous partner. One homolog of each morphologic type goes into each of the resulting chromosome sets.
M phase of mitotic cell cycle
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which a cell progresses through M phase, the part of the mitotic cell cycle during which mitosis takes place.
mitotic cell cycle
Progression through the phases of the mitotic cell cycle, the most common eukaryotic cell cycle, which canonically comprises four successive phases called G1, S, G2, and M and includes replication of the genome and the subsequent segregation of chromosomes into daughter cells. In some variant cell cycles nuclear replication or nuclear division may not be followed by cell division, or G1 and G2 phases may be absent.
M phase
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which a cell progresses through M phase, the part of the cell cycle comprising nuclear division.
nuclear division
A process by which a cell nucleus is divided into two nuclei, with DNA and other nuclear contents distributed between the daughter nuclei.
sister chromatid segregation
The process by which sister chromatids are organized and then physically separated and apportioned to two or more sets.
DNA packaging
Any process by which DNA and associated proteins are formed into a compact, orderly structure.
organelle organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the formation, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of an organelle within a cell. An organelle is an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
cell cycle
The progression of biochemical and morphological phases and events that occur in a cell during successive cell replication or nuclear replication events. Canonically, the cell cycle comprises the replication and segregation of genetic material followed by the division of the cell, but in endocycles or syncytial cells nuclear replication or nuclear division may not be followed by cell division.
mitosis
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell divides; the process involves condensation of chromosomal DNA into a highly compacted form. Canonically, mitosis produces two daughter nuclei whose chromosome complement is identical to that of the mother cell.
mitotic chromosome condensation
The cell cycle process whereby chromatin structure is compacted prior to mitosis in eukaryotic cells.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
cell proliferation
The multiplication or reproduction of cells, resulting in the expansion of a cell population.
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
cellular component organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the formation, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of a cellular component.
cell cycle process
A cellular process that is involved in the progression of biochemical and morphological phases and events that occur in a cell during successive cell replication or nuclear replication events.
cell cycle phase
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which a cell progresses through one of the biochemical and morphological phases and events that occur during successive cell replication or nuclear replication events.
chromosome condensation
The progressive compaction of dispersed interphase chromatin into threadlike chromosomes prior to mitotic or meiotic nuclear division, or during apoptosis, in eukaryotic cells.
organelle fission
The creation of two or more organelles by division of one organelle.
cell division
The process resulting in the physical partitioning and separation of a cell into daughter cells.
all
This term is the most general term possible
cell cycle process
A cellular process that is involved in the progression of biochemical and morphological phases and events that occur in a cell during successive cell replication or nuclear replication events.
sister chromatid segregation
The process by which sister chromatids are organized and then physically separated and apportioned to two or more sets.
mitotic chromosome condensation
The cell cycle process whereby chromatin structure is compacted prior to mitosis in eukaryotic cells.
mitosis
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell divides; the process involves condensation of chromosomal DNA into a highly compacted form. Canonically, mitosis produces two daughter nuclei whose chromosome complement is identical to that of the mother cell.
mitotic chromosome condensation
The cell cycle process whereby chromatin structure is compacted prior to mitosis in eukaryotic cells.
sister chromatid segregation
The process by which sister chromatids are organized and then physically separated and apportioned to two or more sets.
chromosome condensation
The progressive compaction of dispersed interphase chromatin into threadlike chromosomes prior to mitotic or meiotic nuclear division, or during apoptosis, in eukaryotic cells.
M phase of mitotic cell cycle
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which a cell progresses through M phase, the part of the mitotic cell cycle during which mitosis takes place.
mitotic sister chromatid segregation
The cell cycle process whereby replicated homologous chromosomes are organized and then physically separated and apportioned to two sets during the mitotic cell cycle. Each replicated chromosome, composed of two sister chromatids, aligns at the cell equator, paired with its homologous partner. One homolog of each morphologic type goes into each of the resulting chromosome sets.
mitosis
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell divides; the process involves condensation of chromosomal DNA into a highly compacted form. Canonically, mitosis produces two daughter nuclei whose chromosome complement is identical to that of the mother cell.

condensed chromosome
A highly compacted molecule of DNA and associated proteins resulting in a cytologically distinct structure.
intracellular
The living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
chromosome, centromeric region
The region of a chromosome that includes the centromere and associated proteins. In monocentric chromosomes, this region corresponds to a single area of the chromosome, whereas in holocentric chromosomes, it is evenly distributed along the chromosome.
kinetochore
A multisubunit complex that is located at the centromeric region of DNA and provides an attachment point for the spindle microtubules.
condensed chromosome kinetochore
A multisubunit complex that is located at the centromeric region of a condensed chromosome and provides an attachment point for the spindle microtubules.
condensed chromosome, centromeric region
The region of a condensed chromosome that includes the centromere and associated proteins, including the kinetochore. In monocentric chromosomes, this region corresponds to a single area of the chromosome, whereas in holocentric chromosomes, it is evenly distributed along the chromosome.
chromatin
The ordered and organized complex of DNA and protein that forms the chromosome.
cellular_component
The part of a cell or its extracellular environment in which a gene product is located. A gene product may be located in one or more parts of a cell and its location may be as specific as a particular macromolecular complex, that is, a stable, persistent association of macromolecules that function together.
cell
The basic structural and functional unit of all organisms. Includes the plasma membrane and any external encapsulating structures such as the cell wall and cell envelope.
chromosome
A structure composed of a very long molecule of DNA and associated proteins (e.g. histones) that carries hereditary information.
spindle
The array of microtubules and associated molecules that forms between opposite poles of a eukaryotic cell during mitosis or meiosis and serves to move the duplicated chromosomes apart.
cytoskeleton
Any of the various filamentous elements that form the internal framework of cells, and typically remain after treatment of the cells with mild detergent to remove membrane constituents and soluble components of the cytoplasm. The term embraces intermediate filaments, microfilaments, microtubules, the microtrabecular lattice, and other structures characterized by a polymeric filamentous nature and long-range order within the cell. The various elements of the cytoskeleton not only serve in the maintenance of cellular shape but also have roles in other cellular functions, including cellular movement, cell division, endocytosis, and movement of organelles.
microtubule cytoskeleton
The part of the cytoskeleton (the internal framework of a cell) composed of microtubules and associated proteins.
macromolecular complex
A stable assembly of two or more macromolecules, i.e. proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates or lipids, in which the constituent parts function together.
organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
non-membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, not bounded by a lipid bilayer membrane. Includes ribosomes, the cytoskeleton and chromosomes.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular non-membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, not bounded by a lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes ribosomes, the cytoskeleton and chromosomes.
protein complex
Any macromolecular complex composed of two or more polypeptide subunits, which may or may not be identical. Protein complexes may have other associated non-protein prosthetic groups, such as nucleotides, metal ions or carbohydrate groups.
organelle part
Any constituent part of an organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, but excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
chromosomal part
Any constituent part of a chromosome, a structure composed of a very long molecule of DNA and associated proteins (e.g. histones) that carries hereditary information.
cytoskeletal part
Any constituent part of the cytoskeleton, a cellular scaffolding or skeleton that maintains cell shape, enables some cell motion (using structures such as flagella and cilia), and plays important roles in both intra-cellular transport (e.g. the movement of vesicles and organelles) and cellular division. Includes constituent parts of intermediate filaments, microfilaments, microtubules, and the microtrabecular lattice.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
all
This term is the most general term possible
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
organelle part
Any constituent part of an organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, but excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular non-membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, not bounded by a lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes ribosomes, the cytoskeleton and chromosomes.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
kinetochore
A multisubunit complex that is located at the centromeric region of DNA and provides an attachment point for the spindle microtubules.
kinetochore
A multisubunit complex that is located at the centromeric region of DNA and provides an attachment point for the spindle microtubules.
spindle
The array of microtubules and associated molecules that forms between opposite poles of a eukaryotic cell during mitosis or meiosis and serves to move the duplicated chromosomes apart.
chromosomal part
Any constituent part of a chromosome, a structure composed of a very long molecule of DNA and associated proteins (e.g. histones) that carries hereditary information.
cytoskeletal part
Any constituent part of the cytoskeleton, a cellular scaffolding or skeleton that maintains cell shape, enables some cell motion (using structures such as flagella and cilia), and plays important roles in both intra-cellular transport (e.g. the movement of vesicles and organelles) and cellular division. Includes constituent parts of intermediate filaments, microfilaments, microtubules, and the microtrabecular lattice.
kinetochore
A multisubunit complex that is located at the centromeric region of DNA and provides an attachment point for the spindle microtubules.
condensed chromosome, centromeric region
The region of a condensed chromosome that includes the centromere and associated proteins, including the kinetochore. In monocentric chromosomes, this region corresponds to a single area of the chromosome, whereas in holocentric chromosomes, it is evenly distributed along the chromosome.
spindle
The array of microtubules and associated molecules that forms between opposite poles of a eukaryotic cell during mitosis or meiosis and serves to move the duplicated chromosomes apart.
condensed chromosome kinetochore
A multisubunit complex that is located at the centromeric region of a condensed chromosome and provides an attachment point for the spindle microtubules.

ACTR3BARP3 actin-related protein 3 homolog B (yeast) (218868_at), score: 0.65 AHI1Abelson helper integration site 1 (221569_at), score: 0.66 AIM1absent in melanoma 1 (212543_at), score: -0.56 AJAP1adherens junctions associated protein 1 (206460_at), score: 0.59 ANXA10annexin A10 (210143_at), score: 0.56 APOBEC3Bapolipoprotein B mRNA editing enzyme, catalytic polypeptide-like 3B (206632_s_at), score: -0.51 AREGamphiregulin (205239_at), score: 0.7 ARNTLaryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator-like (209824_s_at), score: 0.61 ASF1BASF1 anti-silencing function 1 homolog B (S. cerevisiae) (218115_at), score: -0.57 ATP2A2ATPase, Ca++ transporting, cardiac muscle, slow twitch 2 (212361_s_at), score: 0.57 AURKBaurora kinase B (209464_at), score: -0.59 BIRC5baculoviral IAP repeat-containing 5 (202095_s_at), score: -0.53 BMP2bone morphogenetic protein 2 (205289_at), score: 0.57 BMP6bone morphogenetic protein 6 (206176_at), score: 1 C11orf75chromosome 11 open reading frame 75 (219806_s_at), score: 0.6 C14orf94chromosome 14 open reading frame 94 (218383_at), score: -0.57 C17orf91chromosome 17 open reading frame 91 (214696_at), score: 0.62 C18orf24chromosome 18 open reading frame 24 (217640_x_at), score: -0.57 C2CD2C2 calcium-dependent domain containing 2 (212875_s_at), score: 0.66 CBLBCas-Br-M (murine) ecotropic retroviral transforming sequence b (209682_at), score: 0.59 CBR3carbonyl reductase 3 (205379_at), score: -0.62 CCNB2cyclin B2 (202705_at), score: -0.54 CD55CD55 molecule, decay accelerating factor for complement (Cromer blood group) (201925_s_at), score: 0.58 CDC25Bcell division cycle 25 homolog B (S. pombe) (201853_s_at), score: -0.63 CDC42EP4CDC42 effector protein (Rho GTPase binding) 4 (218062_x_at), score: -0.53 CDCA3cell division cycle associated 3 (221436_s_at), score: -0.58 CDCA8cell division cycle associated 8 (221520_s_at), score: -0.52 CDKN3cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 3 (209714_s_at), score: -0.52 CENPAcentromere protein A (204962_s_at), score: -0.52 CENPEcentromere protein E, 312kDa (205046_at), score: -0.54 CENPFcentromere protein F, 350/400ka (mitosin) (207828_s_at), score: -0.6 CEP68centrosomal protein 68kDa (212677_s_at), score: -0.6 CHMP1Bchromatin modifying protein 1B (218178_s_at), score: 0.57 CITcitron (rho-interacting, serine/threonine kinase 21) (212801_at), score: -0.56 CSGALNACT2chondroitin sulfate N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase 2 (222235_s_at), score: 0.62 CXCL6chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 6 (granulocyte chemotactic protein 2) (206336_at), score: 0.61 DEKDEK oncogene (200934_at), score: -0.54 DEPDC1DEP domain containing 1 (220295_x_at), score: -0.53 DIS3DIS3 mitotic control homolog (S. cerevisiae) (218362_s_at), score: 0.66 DNAJB9DnaJ (Hsp40) homolog, subfamily B, member 9 (202843_at), score: 0.67 E2F8E2F transcription factor 8 (219990_at), score: -0.55 EHMT2euchromatic histone-lysine N-methyltransferase 2 (202326_at), score: -0.53 EIF2AK3eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2-alpha kinase 3 (218696_at), score: 0.64 ENTPD7ectonucleoside triphosphate diphosphohydrolase 7 (220153_at), score: 0.78 ESM1endothelial cell-specific molecule 1 (208394_x_at), score: 0.66 ETV1ets variant 1 (221911_at), score: -0.59 FABP3fatty acid binding protein 3, muscle and heart (mammary-derived growth inhibitor) (214285_at), score: 0.58 FAM64Afamily with sequence similarity 64, member A (221591_s_at), score: -0.58 FERMT1fermitin family homolog 1 (Drosophila) (218796_at), score: 0.81 FGF1fibroblast growth factor 1 (acidic) (205117_at), score: 0.67 FGF7fibroblast growth factor 7 (keratinocyte growth factor) (205782_at), score: 0.69 FOXM1forkhead box M1 (202580_x_at), score: -0.56 GALNT4UDP-N-acetyl-alpha-D-galactosamine:polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase 4 (GalNAc-T4) (220442_at), score: 0.56 GCS1glucosidase I (210627_s_at), score: 0.58 GFPT2glutamine-fructose-6-phosphate transaminase 2 (205100_at), score: 0.57 GHRgrowth hormone receptor (205498_at), score: 0.59 GKglycerol kinase (207387_s_at), score: 0.81 GK3Pglycerol kinase 3 pseudogene (215966_x_at), score: 0.89 GPR183G protein-coupled receptor 183 (205419_at), score: 0.77 GPSM2G-protein signaling modulator 2 (AGS3-like, C. elegans) (221922_at), score: -0.59 GRB14growth factor receptor-bound protein 14 (206204_at), score: 0.66 GTSE1G-2 and S-phase expressed 1 (204318_s_at), score: -0.57 H1F0H1 histone family, member 0 (208886_at), score: -0.57 H1FXH1 histone family, member X (204805_s_at), score: -0.61 HJURPHolliday junction recognition protein (218726_at), score: -0.58 HMMRhyaluronan-mediated motility receptor (RHAMM) (207165_at), score: -0.57 HTR2A5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) receptor 2A (207135_at), score: 0.8 IL1RL1interleukin 1 receptor-like 1 (207526_s_at), score: 0.6 IL33interleukin 33 (209821_at), score: 0.62 ITGB3integrin, beta 3 (platelet glycoprotein IIIa, antigen CD61) (204627_s_at), score: 0.59 ITGB3BPintegrin beta 3 binding protein (beta3-endonexin) (205176_s_at), score: -0.61 KAL1Kallmann syndrome 1 sequence (205206_at), score: 0.64 KCNG1potassium voltage-gated channel, subfamily G, member 1 (214595_at), score: 0.75 KIF15kinesin family member 15 (219306_at), score: -0.59 KIF22kinesin family member 22 (202183_s_at), score: -0.55 KIF4Akinesin family member 4A (218355_at), score: -0.58 KLHL21kelch-like 21 (Drosophila) (203068_at), score: 0.57 LAMC2laminin, gamma 2 (202267_at), score: 0.57 LIG4ligase IV, DNA, ATP-dependent (206235_at), score: 0.6 MAP2microtubule-associated protein 2 (210015_s_at), score: 0.64 MBOAT2membrane bound O-acyltransferase domain containing 2 (213288_at), score: 0.67 MCM7minichromosome maintenance complex component 7 (210983_s_at), score: -0.52 MFAP3microfibrillar-associated protein 3 (213123_at), score: 0.7 MFAP3Lmicrofibrillar-associated protein 3-like (205442_at), score: 0.59 MKI67antigen identified by monoclonal antibody Ki-67 (212022_s_at), score: -0.57 MLXIPMLX interacting protein (202519_at), score: 0.63 MMP10matrix metallopeptidase 10 (stromelysin 2) (205680_at), score: 0.62 MNS1meiosis-specific nuclear structural 1 (219703_at), score: -0.55 MREGmelanoregulin (219648_at), score: 0.62 MTMR9myotubularin related protein 9 (204837_at), score: 0.61 NCALDneurocalcin delta (211685_s_at), score: 0.62 NCAPD2non-SMC condensin I complex, subunit D2 (201774_s_at), score: -0.62 NCAPG2non-SMC condensin II complex, subunit G2 (219588_s_at), score: -0.54 NEIL3nei endonuclease VIII-like 3 (E. coli) (219502_at), score: -0.53 NOX4NADPH oxidase 4 (219773_at), score: 0.65 NPTX1neuronal pentraxin I (204684_at), score: 0.56 NUSAP1nucleolar and spindle associated protein 1 (218039_at), score: -0.57 OIP5Opa interacting protein 5 (213599_at), score: -0.56 OTUB2OTU domain, ubiquitin aldehyde binding 2 (219369_s_at), score: 0.67 PCDH9protocadherin 9 (219737_s_at), score: 0.62 PIGHphosphatidylinositol glycan anchor biosynthesis, class H (209625_at), score: 0.58 PIK3CDphosphoinositide-3-kinase, catalytic, delta polypeptide (203879_at), score: 0.65 PIONpigeon homolog (Drosophila) (222150_s_at), score: 0.6 PLK1polo-like kinase 1 (Drosophila) (202240_at), score: -0.53 POLA1polymerase (DNA directed), alpha 1, catalytic subunit (204835_at), score: -0.57 PPARDperoxisome proliferator-activated receptor delta (37152_at), score: 0.59 PTHLHparathyroid hormone-like hormone (211756_at), score: 0.82 PTTG1pituitary tumor-transforming 1 (203554_x_at), score: -0.54 RFX5regulatory factor X, 5 (influences HLA class II expression) (202963_at), score: -0.6 RNASEH2Aribonuclease H2, subunit A (203022_at), score: -0.57 RNF44ring finger protein 44 (203286_at), score: -0.54 RRP12ribosomal RNA processing 12 homolog (S. cerevisiae) (216913_s_at), score: 0.63 SECISBP2SECIS binding protein 2 (218265_at), score: 0.58 SHMT1serine hydroxymethyltransferase 1 (soluble) (209980_s_at), score: -0.54 SLC25A32solute carrier family 25, member 32 (221020_s_at), score: 0.59 SLC33A1solute carrier family 33 (acetyl-CoA transporter), member 1 (203165_s_at), score: 0.64 SLC35A2solute carrier family 35 (UDP-galactose transporter), member A2 (209326_at), score: 0.62 SLC39A14solute carrier family 39 (zinc transporter), member 14 (212110_at), score: 0.59 SLC4A7solute carrier family 4, sodium bicarbonate cotransporter, member 7 (209884_s_at), score: 0.7 SLC7A6solute carrier family 7 (cationic amino acid transporter, y+ system), member 6 (203578_s_at), score: 0.58 SMAD3SMAD family member 3 (218284_at), score: -0.62 SMC2structural maintenance of chromosomes 2 (204240_s_at), score: -0.55 SNAP25synaptosomal-associated protein, 25kDa (202508_s_at), score: -0.54 SNNstannin (218032_at), score: -0.57 SPAG5sperm associated antigen 5 (203145_at), score: -0.51 SPC25SPC25, NDC80 kinetochore complex component, homolog (S. cerevisiae) (209891_at), score: -0.53 SSTR1somatostatin receptor 1 (208482_at), score: 0.56 SYNE2spectrin repeat containing, nuclear envelope 2 (202761_s_at), score: -0.51 TACC3transforming, acidic coiled-coil containing protein 3 (218308_at), score: -0.58 TFDP2transcription factor Dp-2 (E2F dimerization partner 2) (203588_s_at), score: -0.64 TGDSTDP-glucose 4,6-dehydratase (208249_s_at), score: 0.72 THSD7Athrombospondin, type I, domain containing 7A (214920_at), score: -0.54 TIMELESStimeless homolog (Drosophila) (203046_s_at), score: -0.56 TMEM194Atransmembrane protein 194A (212621_at), score: -0.58 TMEM2transmembrane protein 2 (218113_at), score: 0.65 TMEM39Atransmembrane protein 39A (218615_s_at), score: 0.58 TOM1target of myb1 (chicken) (202807_s_at), score: 0.64 TPX2TPX2, microtubule-associated, homolog (Xenopus laevis) (210052_s_at), score: -0.55 TRPC6transient receptor potential cation channel, subfamily C, member 6 (217287_s_at), score: 0.7 TTLL5tubulin tyrosine ligase-like family, member 5 (214672_at), score: -0.51 URB1URB1 ribosome biogenesis 1 homolog (S. cerevisiae) (212996_s_at), score: 0.76 YRDCyrdC domain containing (E. coli) (218647_s_at), score: 0.63 ZFP36L2zinc finger protein 36, C3H type-like 2 (201367_s_at), score: -0.55 ZNF395zinc finger protein 395 (218149_s_at), score: -0.67
| Id | sample | Experiment | ExpName | Array | Syndrome | Cell.line |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486371.cel | 37 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485891.cel | 13 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485851.cel | 11 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486351.cel | 36 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485811.cel | 9 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |