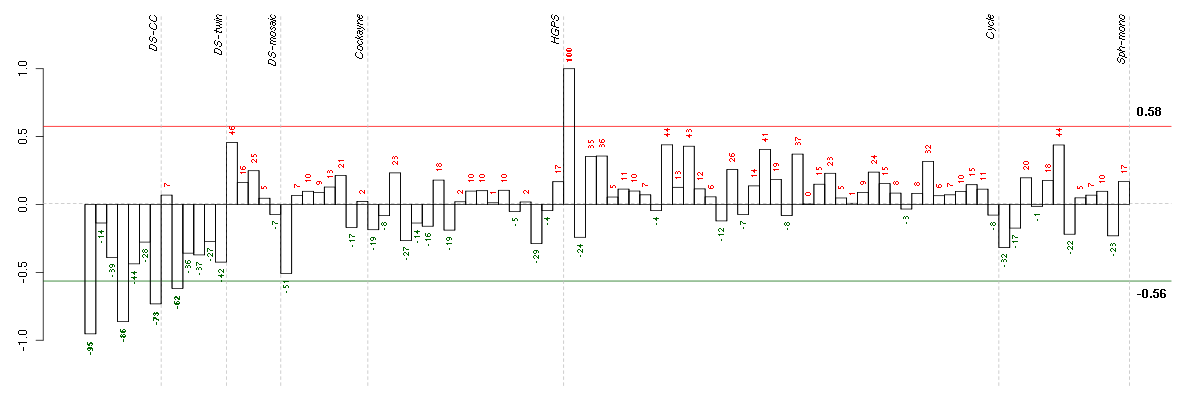

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

system process
A multicellular organismal process carried out by any of the organs or tissues in an organ system. An organ system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a biological objective.
neurological system process
A organ system process carried out by any of the organs or tissues of neurological system.
sensory perception
The series of events required for an organism to receive a sensory stimulus, convert it to a molecular signal, and recognize and characterize the signal.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
multicellular organismal process
Any biological process, occurring at the level of a multicellular organism, pertinent to its function.
cognition
The operation of the mind by which an organism becomes aware of objects of thought or perception; it includes the mental activities associated with thinking, learning, and memory.
all
This term is the most general term possible

plasma membrane
The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
membrane
Double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
integral to membrane
Penetrating at least one phospholipid bilayer of a membrane. May also refer to the state of being buried in the bilayer with no exposure outside the bilayer. When used to describe a protein, indicates that all or part of the peptide sequence is embedded in the membrane.
extracellular region
The space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.
integral to plasma membrane
Penetrating at least one phospholipid bilayer of a plasma membrane. May also refer to the state of being buried in the bilayer with no exposure outside the bilayer.
cellular_component
The part of a cell or its extracellular environment in which a gene product is located. A gene product may be located in one or more parts of a cell and its location may be as specific as a particular macromolecular complex, that is, a stable, persistent association of macromolecules that function together.
cell
The basic structural and functional unit of all organisms. Includes the plasma membrane and any external encapsulating structures such as the cell wall and cell envelope.
intrinsic to membrane
Located in a membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
anchored to membrane
Tethered to a membrane by a covalently attached anchor, such as a lipid moiety, that is embedded in the membrane. When used to describe a protein, indicates that none of the peptide sequence is embedded in the membrane.
intrinsic to plasma membrane
Located in the plasma membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
membrane part
Any constituent part of a membrane, a double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
plasma membrane part
Any constituent part of the plasma membrane, the membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
all
This term is the most general term possible
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
membrane part
Any constituent part of a membrane, a double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
plasma membrane part
Any constituent part of the plasma membrane, the membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
intrinsic to plasma membrane
Located in the plasma membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
integral to plasma membrane
Penetrating at least one phospholipid bilayer of a plasma membrane. May also refer to the state of being buried in the bilayer with no exposure outside the bilayer.

peptide receptor activity
Combining with an extracellular or intracellular peptide to initiate a change in cell activity.
molecular_function
Elemental activities, such as catalysis or binding, describing the actions of a gene product at the molecular level. A given gene product may exhibit one or more molecular functions.
signal transducer activity
Mediates the transfer of a signal from the outside to the inside of a cell by means other than the introduction of the signal molecule itself into the cell.
receptor activity
Combining with an extracellular or intracellular messenger to initiate a change in cell activity.
transmembrane receptor activity
Combining with an extracellular or intracellular messenger to initiate a change in cell activity, and spanning to the membrane of either the cell or an organelle.
G-protein coupled receptor activity
A receptor that binds an extracellular ligand and transmits the signal to a heterotrimeric G-protein complex. These receptors are characteristically seven-transmembrane receptors and are made up of hetero- or homodimers.
transporter activity
Enables the directed movement of substances (such as macromolecules, small molecules, ions) into, out of, within or between cells.
transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a substance from one side of a membrane to the other.
organic acid:sodium symporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a solute or solutes from one side of a membrane to the other according to the reaction: organic acid(out) + Na+(out) = organic acid(in) + Na+(in).
organic acid transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of organic acids, any acidic compound containing carbon in covalent linkage, from one side of the membrane to the other.
secondary active transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a solute from one side of a membrane to the other, up its concentration gradient. The transporter binds the solute and undergoes a series of conformational changes. Transport works equally well in either direction and is driven by a chemiosmotic source of energy. Chemiosmotic sources of energy include uniport, symport or antiport.
binding
The selective, often stoichiometric, interaction of a molecule with one or more specific sites on another molecule.
monocarboxylic acid transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of monocarboxylic acids from one side of the membrane to the other. A monocarboxylic acid is an organic acid with one COOH group.
neuropeptide receptor activity
Combining with a neuropeptide to initiate a change in cell activity.
cation transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of cation from one side of the membrane to the other.
bile acid:sodium symporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a solute or solutes from one side of a membrane to the other according to the reaction: bile acid(out) + Na+(out) = bile acid(in) + Na+(in).
peptide receptor activity, G-protein coupled
Combining with an extracellular or intracellular peptide to initiate a G-protein mediated change in cell activity. A G-protein is a signal transduction molecule that alternates between an inactive GDP-bound and an active GTP-bound state.
ion transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of an ion from one side of a membrane to the other.
bile acid transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of bile acid from one side of the membrane to the other. Bile acids are any of a group of steroid carboxylic acids occurring in bile, where they are present as the sodium salts of their amides with glycine or taurine.
symporter activity
Enables the active transport of a solute across a membrane by a mechanism whereby two or more species are transported together in the same direction in a tightly coupled process not directly linked to a form of energy other than chemiosmotic energy.
solute:cation symporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a solute or solutes from one side of a membrane to the other according to the reaction: solute(out) + cation(out) = solute(in) + cation(in).
solute:sodium symporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a solute or solutes from one side of a membrane to the other according to the reaction: solute(out) + Na+(out) = solute(in) + Na+(in).
active transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a specific substance or related group of substances from one side of a membrane to the other, up the solute's concentration gradient. The transporter binds the solute and undergoes a series of conformational changes. Transport works equally well in either direction.
substrate-specific transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a specific substance or group of related substances from one side of a membrane to the other.
substrate-specific transporter activity
Enables the directed movement of a specific substance or group of related substances (such as macromolecules, small molecules, ions) into, out of, within or between cells.
neurotransmitter receptor activity
Combining with a neurotransmitter to initiate a change in cell activity.
neurotransmitter binding
Interacting selectively with a neurotransmitter, any chemical substance that is capable of transmitting (or inhibiting the transmission of) a nerve impulse from a neuron to another cell.
peptide binding
Interacting selectively with peptides, any of a group of organic compounds comprising two or more amino acids linked by peptide bonds.
neuropeptide binding
Interacting selectively and stoichiometrically with neuropeptides, peptides with direct synaptic effects (peptide neurotransmitters) or indirect modulatory effects on the nervous system (peptide neuromodulators).
carboxylic acid transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of carboxylic acids from one side of the membrane to the other. Carboxylic acids are organic acids containing one or more carboxyl (COOH) groups or anions (COO-).
molecular transducer activity
The molecular function that accepts an input of one form and creates an output of a different form.
all
This term is the most general term possible
substrate-specific transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a specific substance or group of related substances from one side of a membrane to the other.
neuropeptide receptor activity
Combining with a neuropeptide to initiate a change in cell activity.
peptide receptor activity
Combining with an extracellular or intracellular peptide to initiate a change in cell activity.
neurotransmitter receptor activity
Combining with a neurotransmitter to initiate a change in cell activity.
neuropeptide receptor activity
Combining with a neuropeptide to initiate a change in cell activity.
solute:cation symporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a solute or solutes from one side of a membrane to the other according to the reaction: solute(out) + cation(out) = solute(in) + cation(in).
peptide receptor activity, G-protein coupled
Combining with an extracellular or intracellular peptide to initiate a G-protein mediated change in cell activity. A G-protein is a signal transduction molecule that alternates between an inactive GDP-bound and an active GTP-bound state.
organic acid:sodium symporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a solute or solutes from one side of a membrane to the other according to the reaction: organic acid(out) + Na+(out) = organic acid(in) + Na+(in).
bile acid:sodium symporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a solute or solutes from one side of a membrane to the other according to the reaction: bile acid(out) + Na+(out) = bile acid(in) + Na+(in).
A1CFAPOBEC1 complementation factor (220951_s_at), score: -0.75 ABOABO blood group (transferase A, alpha 1-3-N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase; transferase B, alpha 1-3-galactosyltransferase) (216716_at), score: -0.76 ACSL6acyl-CoA synthetase long-chain family member 6 (211207_s_at), score: -0.67 ADAMTS7ADAM metallopeptidase with thrombospondin type 1 motif, 7 (220705_s_at), score: -0.74 ADAMTS9ADAM metallopeptidase with thrombospondin type 1 motif, 9 (220287_at), score: -0.7 APOMapolipoprotein M (205682_x_at), score: -0.71 ASAP3ArfGAP with SH3 domain, ankyrin repeat and PH domain 3 (219103_at), score: -0.69 BRS3bombesin-like receptor 3 (207369_at), score: -0.73 BTNL3butyrophilin-like 3 (217207_s_at), score: -0.81 C7orf28Achromosome 7 open reading frame 28A (201974_s_at), score: -0.73 CA4carbonic anhydrase IV (206209_s_at), score: -0.69 CASZ1castor zinc finger 1 (220015_at), score: -0.67 CCDC9coiled-coil domain containing 9 (206257_at), score: -0.68 CEACAM5carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 5 (201884_at), score: -0.7 CEACAM6carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 6 (non-specific cross reacting antigen) (211657_at), score: -0.76 CLDN10claudin 10 (205328_at), score: -0.72 COL11A2collagen, type XI, alpha 2 (216993_s_at), score: -0.72 CYP2C9cytochrome P450, family 2, subfamily C, polypeptide 9 (214421_x_at), score: -0.68 CYP3A4cytochrome P450, family 3, subfamily A, polypeptide 4 (205998_x_at), score: -0.67 DESdesmin (216947_at), score: -0.73 DRD5dopamine receptor D5 (208486_at), score: -0.83 ELNelastin (212670_at), score: -0.7 FAM38Bfamily with sequence similarity 38, member B (219602_s_at), score: -0.83 GLTSCR1glioma tumor suppressor candidate region gene 1 (219445_at), score: -0.69 GPR12G protein-coupled receptor 12 (214558_at), score: -0.79 HSPB6heat shock protein, alpha-crystallin-related, B6 (214767_s_at), score: -0.74 INE1inactivation escape 1 (non-protein coding) (207252_at), score: -0.66 KCNJ16potassium inwardly-rectifying channel, subfamily J, member 16 (219564_at), score: -0.71 KCNMB4potassium large conductance calcium-activated channel, subfamily M, beta member 4 (219287_at), score: -0.67 KIR3DX1killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor, three domains, X1 (216428_x_at), score: -0.75 KLF1Kruppel-like factor 1 (erythroid) (210504_at), score: -0.8 LHX3LIM homeobox 3 (221670_s_at), score: -0.77 LOC100188945cell division cycle associated 4 pseudogene (215109_at), score: -0.76 LOC286434hypothetical protein LOC286434 (222196_at), score: -0.67 LOC389906similar to Serine/threonine-protein kinase PRKX (Protein kinase PKX1) (59433_at), score: -0.74 LOC80054hypothetical LOC80054 (220465_at), score: -0.73 LOH3CR2Aloss of heterozygosity, 3, chromosomal region 2, gene A (220244_at), score: -0.81 LONRF3LON peptidase N-terminal domain and ring finger 3 (220009_at), score: -0.83 MAPK8IP2mitogen-activated protein kinase 8 interacting protein 2 (205050_s_at), score: -0.74 MBmyoglobin (204179_at), score: -0.76 MEP1Bmeprin A, beta (207251_at), score: -0.7 MFNGMFNG O-fucosylpeptide 3-beta-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase (204153_s_at), score: -0.79 MMP9matrix metallopeptidase 9 (gelatinase B, 92kDa gelatinase, 92kDa type IV collagenase) (203936_s_at), score: -0.67 MMRN2multimerin 2 (219091_s_at), score: -0.87 MOBPmyelin-associated oligodendrocyte basic protein (210193_at), score: -0.81 MUC3Amucin 3A, cell surface associated (217117_x_at), score: -0.75 MYL4myosin, light chain 4, alkali; atrial, embryonic (210088_x_at), score: -0.71 MYO1Amyosin IA (211916_s_at), score: -0.78 NPY2Rneuropeptide Y receptor Y2 (210730_s_at), score: -0.68 NRN1neuritin 1 (218625_at), score: -0.87 NYXnyctalopin (221684_s_at), score: -0.68 OR1E2olfactory receptor, family 1, subfamily E, member 2 (208587_s_at), score: -0.7 OR7E24olfactory receptor, family 7, subfamily E, member 24 (215463_at), score: -0.78 OVOL2ovo-like 2 (Drosophila) (211778_s_at), score: -0.69 PECAM1platelet/endothelial cell adhesion molecule (208982_at), score: -0.89 PGK2phosphoglycerate kinase 2 (217009_at), score: -0.72 PHF20L1PHD finger protein 20-like 1 (222133_s_at), score: -0.7 PLUNCpalate, lung and nasal epithelium associated (220542_s_at), score: -0.72 PNPLA2patatin-like phospholipase domain containing 2 (212705_x_at), score: -0.87 PPP4R4protein phosphatase 4, regulatory subunit 4 (220672_at), score: -0.71 PRB3proline-rich protein BstNI subfamily 3 (206998_x_at), score: -0.67 PROX1prospero homeobox 1 (207401_at), score: -0.68 PRSS7protease, serine, 7 (enterokinase) (217269_s_at), score: -0.96 PYHIN1pyrin and HIN domain family, member 1 (216748_at), score: -0.72 RETret proto-oncogene (205879_x_at), score: -0.67 RP11-35N6.1plasticity related gene 3 (219732_at), score: -0.68 RP3-377H14.5hypothetical LOC285830 (222279_at), score: -0.68 RPGRIP1retinitis pigmentosa GTPase regulator interacting protein 1 (206608_s_at), score: -0.86 S100A14S100 calcium binding protein A14 (218677_at), score: -0.73 SCN10Asodium channel, voltage-gated, type X, alpha subunit (208578_at), score: -0.73 SERPINA1serpin peptidase inhibitor, clade A (alpha-1 antiproteinase, antitrypsin), member 1 (211429_s_at), score: -0.67 SLC10A1solute carrier family 10 (sodium/bile acid cotransporter family), member 1 (207185_at), score: -0.78 SLC10A2solute carrier family 10 (sodium/bile acid cotransporter family), member 2 (207095_at), score: -0.75 SLC15A1solute carrier family 15 (oligopeptide transporter), member 1 (211349_at), score: -0.71 SOCS3suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 (206359_at), score: -0.75 SRCAPSnf2-related CREBBP activator protein (212275_s_at), score: -0.73 ST6GAL1ST6 beta-galactosamide alpha-2,6-sialyltranferase 1 (201998_at), score: -0.68 TACR1tachykinin receptor 1 (208048_at), score: -0.94 TBX21T-box 21 (220684_at), score: -0.78 TBX6T-box 6 (207684_at), score: -0.76 TMEM92transmembrane protein 92 (216791_at), score: -0.67 TRA@T cell receptor alpha locus (216540_at), score: -0.88 VGFVGF nerve growth factor inducible (205586_x_at), score: -1
| Id | sample | Experiment | ExpName | Array | Syndrome | Cell.line |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ctrl a 08-03.CEL | 1 | 1 | DS-CC | hgu133a | none | DS-CC 1 |
| t21a 08-03.CEL | 4 | 1 | DS-CC | hgu133a | Down | DS-CC 4 |
| t21d 08-03.CEL | 7 | 1 | DS-CC | hgu133a | Down | DS-CC 7 |
| 2Twin.CEL | 2 | 2 | DS-twin | hgu133plus2 | none | DS-twin 2 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485651.cel | 1 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |