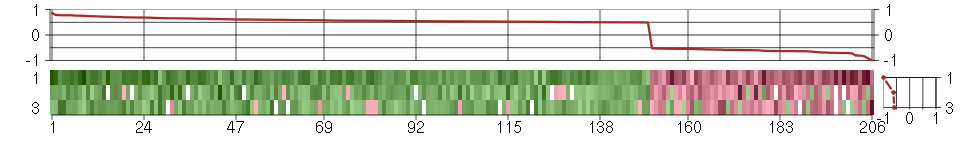

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

cell activation
A change in the morphology or behavior of a cell resulting from exposure to an activating factor such as a cellular or soluble ligand.
cell killing
Any process in an organism that results in the killing of its own cells or those of another organism, including in some cases the death of the other organism. Killing here refers to the induction of death in one cell by another cell, not cell-autonomous death due to internal or other environmental conditions.
leukocyte mediated cytotoxicity
The directed killing of a target cell by a leukocyte.
regulation of leukocyte mediated cytotoxicity
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of leukocyte mediated cytotoxicity.
positive regulation of leukocyte mediated cytotoxicity
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of leukocyte mediated cytotoxicity.
natural killer cell mediated immunity
The promotion of an immune response by natural killer cells through direct recognition of target cells or through the release of cytokines.
adaptive immune response
An immune response based on directed amplification of specific receptors for antigen produced through a somatic diversification process, and allowing for enhanced response to subsequent exposures to the same antigen (immunological memory).
immune effector process
Any process of the immune system that occurs as part of an immune response.
response to tumor cell
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus from a tumor cell.
immune system process
Any process involved in the development or functioning of the immune system, an organismal system for calibrated responses to potential internal or invasive threats.
immune response to tumor cell
An immune system process that functions in the response of an organism to a tumor cell.
natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity directed against tumor cell target
The directed killing of a tumor cell by a natural killer cell through the release of granules containing cytotoxic mediators or through the engagement of death receptors.
natural killer cell mediated immune response to tumor cell
An immune response mediated by a natural killer cell triggered in response to the presence of a tumor cell.
leukocyte mediated immunity
Any process involved in the carrying out of an immune response by a leukocyte.
lymphocyte mediated immunity
Any process involved in the carrying out of an immune response by a lymphocyte.
adaptive immune response based on somatic recombination of immune receptors built from immunoglobulin superfamily domains
An immune response based on directed amplification of specific receptors for antigen produced through a somatic diversification process that includes somatic recombination of germline gene segments encoding immunoglobulin superfamily domains, and allowing for enhanced responses upon subsequent exposures to the same antigen (immunological memory). Recombined receptors for antigen encoded by immunoglobulin superfamily domains include T cell receptors and immunoglobulins (antibodies).
regulation of immune system process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of an immune system process.
positive regulation of immune system process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of an immune system process.
regulation of leukocyte activation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of leukocyte activation.
regulation of immune effector process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of an immune effector process.
positive regulation of immune effector process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of an immune effector process.
regulation of leukocyte mediated immunity
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of leukocyte mediated immunity.
positive regulation of leukocyte mediated immunity
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of leukocyte mediated immunity.
regulation of lymphocyte mediated immunity
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of lymphocyte mediated immunity.
positive regulation of lymphocyte mediated immunity
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of lymphocyte mediated immunity.
regulation of natural killer cell mediated immunity
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of natural killer cell mediated immunity.
positive regulation of natural killer cell mediated immunity
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of natural killer cell mediated immunity.
regulation of response to biotic stimulus
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of a response to biotic stimulus.
positive regulation of response to biotic stimulus
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of a response to biotic stimulus.
regulation of response to tumor cell
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of a response to tumor cell.
positive regulation of response to tumor cell
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of a response to tumor cell.
regulation of immune response to tumor cell
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of an immune response to tumor cell.
positive regulation of immune response to tumor cell
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of an immune response to tumor cell.
regulation of natural killer cell mediated immune response to tumor cell
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of natural killer cell mediated immune response to a tumor cell.
positive regulation of natural killer cell mediated immune response to tumor cell
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of natural killer cell mediated immune response to a tumor cell.
regulation of natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity directed against tumor cell target
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity directed against tumor cell target.
positive regulation of natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity directed against tumor cell target
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity directed against tumor cell target.
defense response
Reactions, triggered in response to the presence of a foreign body or the occurrence of an injury, which result in restriction of damage to the organism attacked or prevention/recovery from the infection caused by the attack.
apoptosis
A form of programmed cell death characterized by rounding-up of the cell, retraction of pseudopodes, reduction of cellular volume (pyknosis), chromatin condensation, nuclear fragmentation (karyorrhexis), classically little or no ultrastructural modifications of cytoplasmic organelles, plasma membrane blebbing (but maintenance of its integrity until the final stages of the process) and engulfment by resident phagocytes. Apoptosis is usually induced by external or internal signals that trigger the activity of proteolytic caspases, whose actions dismantle the cell and result in cell death.
induction of apoptosis
A process that directly activates any of the steps required for cell death by apoptosis.
response to stress
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a disturbance in organismal or cellular homeostasis, usually, but not necessarily, exogenous (e.g. temperature, humidity, ionizing radiation).
immune response
Any immune system process that functions in the calibrated response of an organism to a potential internal or invasive threat.
natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity
The directed killing of a target cell by a natural killer cell through the release of granules containing cytotoxic mediators or through the engagement of death receptors.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
cell death
The specific activation or halting of processes within a cell so that its vital functions markedly cease, rather than simply deteriorating gradually over time, which culminates in cell death.
programmed cell death
Cell death resulting from activation of endogenous cellular processes.
response to biotic stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a biotic stimulus, a stimulus caused or produced by a living organism.
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
induction of programmed cell death
A process which directly activates any of the steps required for programmed cell death.
death
A permanent cessation of all vital functions: the end of life; can be applied to a whole organism or to a part of an organism.
regulation of apoptosis
Any process that modulates the occurrence or rate of cell death by apoptosis.
regulation of cell killing
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell killing, the process by which a cell brings about the death of another cell, either in the same or a different organism.
positive regulation of cell killing
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cell killing.
regulation of defense response
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a defense response.
positive regulation of defense response
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a defense response.
developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an integrated living unit: an anatomical structure (which may be a subcellular structure, cell, tissue, or organ), or organism over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
regulation of natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity.
positive regulation of apoptosis
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cell death by apoptosis.
regulation of programmed cell death
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of programmed cell death, cell death resulting from activation of endogenous cellular processes.
positive regulation of programmed cell death
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of programmed cell death, cell death resulting from activation of endogenous cellular processes.
innate immune response
Innate immune responses are defense responses mediated by germline encoded components that directly recognize components of potential pathogens.
regulation of innate immune response
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the innate immune response, the organism's first line of defense against infection.
positive regulation of innate immune response
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the innate immune response, the organism's first line of defense against infection.
leukocyte activation
A change in morphology and behavior of a leukocyte resulting from exposure to a specific antigen, mitogen, cytokine, cellular ligand, or soluble factor.
positive regulation of natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity.
positive regulation of biological process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
positive regulation of cellular process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
regulation of response to stimulus
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a response to a stimulus. Response to stimulus is a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
positive regulation of response to stimulus
Any process that activates, maintains or increases the rate of a response to a stimulus. Response to stimulus is a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
regulation of immune response
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the immune response, the immunological reaction of an organism to an immunogenic stimulus.
positive regulation of immune response
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the immune response, the immunological reaction of an organism to an immunogenic stimulus.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of developmental process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of development, the biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote, or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
regulation of cellular process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
regulation of cell activation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell activation, the change in the morphology or behavior of a cell resulting from exposure to an activating factor such as a cellular or soluble ligand.
response to stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
positive regulation of developmental process
Any process that activates or increases the rate or extent of development, the biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote, or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
biological regulation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of any biological process, quality or function.
all
This term is the most general term possible
positive regulation of immune system process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of an immune system process.
positive regulation of cell killing
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cell killing.
positive regulation of cellular process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
positive regulation of developmental process
Any process that activates or increases the rate or extent of development, the biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote, or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
regulation of immune system process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of an immune system process.
regulation of cell killing
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell killing, the process by which a cell brings about the death of another cell, either in the same or a different organism.
positive regulation of biological process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of developmental process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of development, the biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote, or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
regulation of cellular process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
immune response
Any immune system process that functions in the calibrated response of an organism to a potential internal or invasive threat.
regulation of response to stimulus
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a response to a stimulus. Response to stimulus is a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
positive regulation of response to stimulus
Any process that activates, maintains or increases the rate of a response to a stimulus. Response to stimulus is a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of leukocyte mediated cytotoxicity
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of leukocyte mediated cytotoxicity.
positive regulation of cell killing
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cell killing.
positive regulation of leukocyte mediated cytotoxicity
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of leukocyte mediated cytotoxicity.
leukocyte mediated cytotoxicity
The directed killing of a target cell by a leukocyte.
positive regulation of immune system process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of an immune system process.
positive regulation of immune effector process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of an immune effector process.
immune effector process
Any process of the immune system that occurs as part of an immune response.
regulation of immune response
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the immune response, the immunological reaction of an organism to an immunogenic stimulus.
positive regulation of immune response
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the immune response, the immunological reaction of an organism to an immunogenic stimulus.
regulation of leukocyte activation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of leukocyte activation.
leukocyte activation
A change in morphology and behavior of a leukocyte resulting from exposure to a specific antigen, mitogen, cytokine, cellular ligand, or soluble factor.
positive regulation of cellular process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
regulation of cell activation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell activation, the change in the morphology or behavior of a cell resulting from exposure to an activating factor such as a cellular or soluble ligand.
cell death
The specific activation or halting of processes within a cell so that its vital functions markedly cease, rather than simply deteriorating gradually over time, which culminates in cell death.
regulation of programmed cell death
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of programmed cell death, cell death resulting from activation of endogenous cellular processes.
positive regulation of developmental process
Any process that activates or increases the rate or extent of development, the biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote, or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
positive regulation of programmed cell death
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of programmed cell death, cell death resulting from activation of endogenous cellular processes.
positive regulation of immune response
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the immune response, the immunological reaction of an organism to an immunogenic stimulus.
positive regulation of response to stimulus
Any process that activates, maintains or increases the rate of a response to a stimulus. Response to stimulus is a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
regulation of immune response
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the immune response, the immunological reaction of an organism to an immunogenic stimulus.
regulation of response to biotic stimulus
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of a response to biotic stimulus.
positive regulation of response to biotic stimulus
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of a response to biotic stimulus.
positive regulation of leukocyte mediated cytotoxicity
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of leukocyte mediated cytotoxicity.
regulation of natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity.
positive regulation of natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity.
regulation of leukocyte mediated cytotoxicity
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of leukocyte mediated cytotoxicity.
positive regulation of immune effector process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of an immune effector process.
regulation of leukocyte mediated immunity
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of leukocyte mediated immunity.
positive regulation of leukocyte mediated cytotoxicity
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of leukocyte mediated cytotoxicity.
positive regulation of leukocyte mediated immunity
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of leukocyte mediated immunity.
regulation of immune effector process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of an immune effector process.
positive regulation of immune response
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the immune response, the immunological reaction of an organism to an immunogenic stimulus.
regulation of immune response to tumor cell
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of an immune response to tumor cell.
positive regulation of immune response to tumor cell
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of an immune response to tumor cell.
regulation of innate immune response
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the innate immune response, the organism's first line of defense against infection.
positive regulation of innate immune response
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the innate immune response, the organism's first line of defense against infection.
regulation of leukocyte activation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of leukocyte activation.
regulation of programmed cell death
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of programmed cell death, cell death resulting from activation of endogenous cellular processes.
positive regulation of programmed cell death
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of programmed cell death, cell death resulting from activation of endogenous cellular processes.
positive regulation of programmed cell death
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of programmed cell death, cell death resulting from activation of endogenous cellular processes.
positive regulation of innate immune response
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the innate immune response, the organism's first line of defense against infection.
positive regulation of response to biotic stimulus
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of a response to biotic stimulus.
positive regulation of defense response
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a defense response.
regulation of innate immune response
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the innate immune response, the organism's first line of defense against infection.
regulation of defense response
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a defense response.
positive regulation of defense response
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a defense response.
innate immune response
Innate immune responses are defense responses mediated by germline encoded components that directly recognize components of potential pathogens.
immune response to tumor cell
An immune system process that functions in the response of an organism to a tumor cell.
regulation of response to tumor cell
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of a response to tumor cell.
positive regulation of response to tumor cell
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of a response to tumor cell.
positive regulation of natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity.
regulation of natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity directed against tumor cell target
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity directed against tumor cell target.
positive regulation of natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity directed against tumor cell target
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity directed against tumor cell target.
natural killer cell mediated immunity
The promotion of an immune response by natural killer cells through direct recognition of target cells or through the release of cytokines.
positive regulation of leukocyte mediated immunity
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of leukocyte mediated immunity.
regulation of lymphocyte mediated immunity
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of lymphocyte mediated immunity.
positive regulation of lymphocyte mediated immunity
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of lymphocyte mediated immunity.
positive regulation of immune response to tumor cell
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of an immune response to tumor cell.
positive regulation of innate immune response
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the innate immune response, the organism's first line of defense against infection.
natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity directed against tumor cell target
The directed killing of a tumor cell by a natural killer cell through the release of granules containing cytotoxic mediators or through the engagement of death receptors.
regulation of natural killer cell mediated immune response to tumor cell
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of natural killer cell mediated immune response to a tumor cell.
positive regulation of natural killer cell mediated immune response to tumor cell
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of natural killer cell mediated immune response to a tumor cell.
natural killer cell mediated immune response to tumor cell
An immune response mediated by a natural killer cell triggered in response to the presence of a tumor cell.
regulation of natural killer cell mediated immunity
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of natural killer cell mediated immunity.
positive regulation of natural killer cell mediated immunity
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of natural killer cell mediated immunity.
natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity
The directed killing of a target cell by a natural killer cell through the release of granules containing cytotoxic mediators or through the engagement of death receptors.
regulation of apoptosis
Any process that modulates the occurrence or rate of cell death by apoptosis.
positive regulation of apoptosis
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cell death by apoptosis.
induction of apoptosis
A process that directly activates any of the steps required for cell death by apoptosis.
positive regulation of apoptosis
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cell death by apoptosis.
positive regulation of immune response to tumor cell
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of an immune response to tumor cell.
positive regulation of response to tumor cell
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of a response to tumor cell.
regulation of immune response to tumor cell
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of an immune response to tumor cell.
positive regulation of natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity directed against tumor cell target
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity directed against tumor cell target.
positive regulation of lymphocyte mediated immunity
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of lymphocyte mediated immunity.
regulation of natural killer cell mediated immunity
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of natural killer cell mediated immunity.
positive regulation of natural killer cell mediated immunity
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of natural killer cell mediated immunity.
positive regulation of natural killer cell mediated immune response to tumor cell
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of natural killer cell mediated immune response to a tumor cell.
regulation of natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity directed against tumor cell target
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity directed against tumor cell target.
positive regulation of natural killer cell mediated immunity
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of natural killer cell mediated immunity.
regulation of natural killer cell mediated immune response to tumor cell
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of natural killer cell mediated immune response to a tumor cell.
regulation of natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity.
positive regulation of natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity directed against tumor cell target
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity directed against tumor cell target.
positive regulation of natural killer cell mediated immune response to tumor cell
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of natural killer cell mediated immune response to a tumor cell.
positive regulation of natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity.
natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity
The directed killing of a target cell by a natural killer cell through the release of granules containing cytotoxic mediators or through the engagement of death receptors.

plasma membrane
The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
membrane
Double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
integral to membrane
Penetrating at least one phospholipid bilayer of a membrane. May also refer to the state of being buried in the bilayer with no exposure outside the bilayer. When used to describe a protein, indicates that all or part of the peptide sequence is embedded in the membrane.
extracellular region
The space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.
integral to plasma membrane
Penetrating at least one phospholipid bilayer of a plasma membrane. May also refer to the state of being buried in the bilayer with no exposure outside the bilayer.
cellular_component
The part of a cell or its extracellular environment in which a gene product is located. A gene product may be located in one or more parts of a cell and its location may be as specific as a particular macromolecular complex, that is, a stable, persistent association of macromolecules that function together.
cell
The basic structural and functional unit of all organisms. Includes the plasma membrane and any external encapsulating structures such as the cell wall and cell envelope.
intrinsic to membrane
Located in a membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
intrinsic to plasma membrane
Located in the plasma membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
membrane part
Any constituent part of a membrane, a double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
plasma membrane part
Any constituent part of the plasma membrane, the membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
all
This term is the most general term possible
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
membrane part
Any constituent part of a membrane, a double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
plasma membrane part
Any constituent part of the plasma membrane, the membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
intrinsic to plasma membrane
Located in the plasma membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
integral to plasma membrane
Penetrating at least one phospholipid bilayer of a plasma membrane. May also refer to the state of being buried in the bilayer with no exposure outside the bilayer.

molecular_function
Elemental activities, such as catalysis or binding, describing the actions of a gene product at the molecular level. A given gene product may exhibit one or more molecular functions.
signal transducer activity
Mediates the transfer of a signal from the outside to the inside of a cell by means other than the introduction of the signal molecule itself into the cell.
receptor activity
Combining with an extracellular or intracellular messenger to initiate a change in cell activity.
transmembrane receptor activity
Combining with an extracellular or intracellular messenger to initiate a change in cell activity, and spanning to the membrane of either the cell or an organelle.
molecular transducer activity
The molecular function that accepts an input of one form and creates an output of a different form.
all
This term is the most general term possible
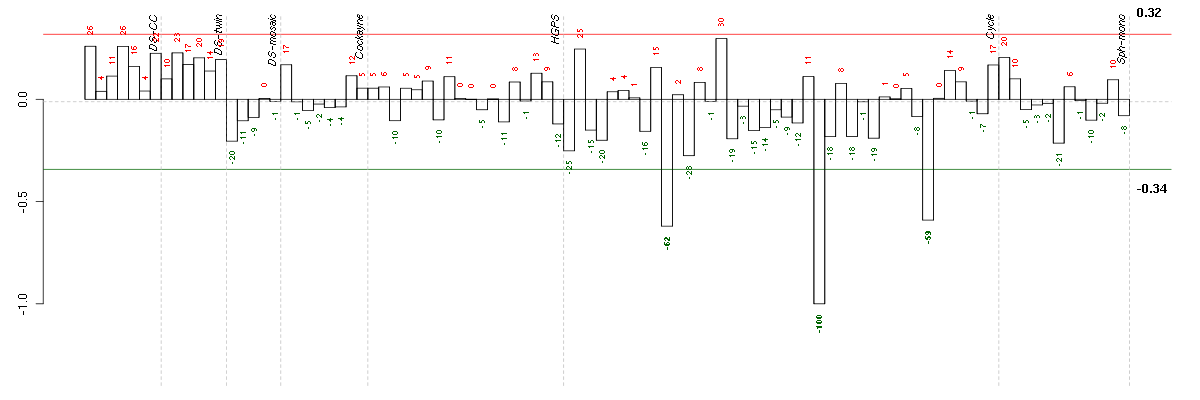
| Id | Pvalue | ExpCount | Count | Size | Term |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 04940 | 2.443e-02 | 0.6481 | 5 | 26 | Type I diabetes mellitus |
| 04060 | 2.807e-02 | 2.866 | 10 | 115 | Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction |
ABOABO blood group (transferase A, alpha 1-3-N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase; transferase B, alpha 1-3-galactosyltransferase) (216716_at), score: 0.52 ADAM21ADAM metallopeptidase domain 21 (207665_at), score: -0.81 ADORA1adenosine A1 receptor (216220_s_at), score: 0.53 AGMATagmatine ureohydrolase (agmatinase) (219792_at), score: 0.77 ALDH1L1aldehyde dehydrogenase 1 family, member L1 (215798_at), score: 0.55 ANKRD36Bankyrin repeat domain 36B (220940_at), score: 0.55 AP4S1adaptor-related protein complex 4, sigma 1 subunit (210278_s_at), score: -0.62 ATF6Bactivating transcription factor 6 beta (203168_at), score: 0.56 B3GALT4UDP-Gal:betaGlcNAc beta 1,3-galactosyltransferase, polypeptide 4 (210205_at), score: 0.56 BAHD1bromo adjacent homology domain containing 1 (203051_at), score: 0.5 BAI2brain-specific angiogenesis inhibitor 2 (204966_at), score: 0.78 BCHEbutyrylcholinesterase (205433_at), score: -0.55 BCL2L11BCL2-like 11 (apoptosis facilitator) (222343_at), score: 0.67 BDH23-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase, type 2 (218285_s_at), score: -0.54 BEANbrain expressed, associated with Nedd4 (214068_at), score: -0.72 BEND5BEN domain containing 5 (219670_at), score: 0.58 BFSP1beaded filament structural protein 1, filensin (206746_at), score: -0.58 BRAFv-raf murine sarcoma viral oncogene homolog B1 (206044_s_at), score: -0.58 BRF2BRF2, subunit of RNA polymerase III transcription initiation factor, BRF1-like (218955_at), score: 0.49 BRS3bombesin-like receptor 3 (207369_at), score: 0.52 BTF3L2basic transcription factor 3, like 2 (217461_x_at), score: 0.52 C11orf1chromosome 11 open reading frame 1 (218925_s_at), score: 0.66 C11orf30chromosome 11 open reading frame 30 (219012_s_at), score: 0.52 C18orf1chromosome 18 open reading frame 1 (209574_s_at), score: -0.62 C1orf69chromosome 1 open reading frame 69 (215490_at), score: 0.51 C22orf30chromosome 22 open reading frame 30 (216555_at), score: 0.72 C4Acomplement component 4A (Rodgers blood group) (214428_x_at), score: 0.76 C7orf28Achromosome 7 open reading frame 28A (201974_s_at), score: 0.53 CACNA1Ccalcium channel, voltage-dependent, L type, alpha 1C subunit (211592_s_at), score: 0.61 CACNB1calcium channel, voltage-dependent, beta 1 subunit (206996_x_at), score: 0.6 CAPN3calpain 3, (p94) (210944_s_at), score: 0.52 CARD8caspase recruitment domain family, member 8 (204950_at), score: 0.56 CASP8caspase 8, apoptosis-related cysteine peptidase (213373_s_at), score: -0.7 CATSPER2cation channel, sperm associated 2 (217588_at), score: 0.56 CC2D1Acoiled-coil and C2 domain containing 1A (58994_at), score: 0.5 CCDC28Acoiled-coil domain containing 28A (209479_at), score: -0.63 CCDC9coiled-coil domain containing 9 (206257_at), score: 0.6 CCL11chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 11 (210133_at), score: 0.57 CD226CD226 molecule (207315_at), score: 0.5 CD70CD70 molecule (206508_at), score: 0.49 CD80CD80 molecule (207176_s_at), score: -0.55 CD83CD83 molecule (204440_at), score: 0.54 CEACAM5carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 5 (201884_at), score: 0.54 CFHR2complement factor H-related 2 (206910_x_at), score: 0.6 CHRM3cholinergic receptor, muscarinic 3 (214596_at), score: -0.63 CLCN2chloride channel 2 (213499_at), score: 0.69 CLDN18claudin 18 (214135_at), score: 0.56 CNNM2cyclin M2 (206818_s_at), score: -0.56 CPEB3cytoplasmic polyadenylation element binding protein 3 (205773_at), score: 0.62 CR1complement component (3b/4b) receptor 1 (Knops blood group) (217484_at), score: 0.64 CYBBcytochrome b-245, beta polypeptide (217431_x_at), score: 0.61 CYorf15Bchromosome Y open reading frame 15B (214131_at), score: 0.59 CYP26B1cytochrome P450, family 26, subfamily B, polypeptide 1 (219825_at), score: 0.53 CYP2B6cytochrome P450, family 2, subfamily B, polypeptide 6 (217133_x_at), score: 0.51 CYP2R1cytochrome P450, family 2, subfamily R, polypeptide 1 (207786_at), score: 0.58 CYSLTR1cysteinyl leukotriene receptor 1 (216288_at), score: 0.59 CYTH4cytohesin 4 (219183_s_at), score: 0.66 DEM1defects in morphology 1 homolog (S. cerevisiae) (219567_s_at), score: 0.77 DHX34DEAH (Asp-Glu-Ala-His) box polypeptide 34 (214017_s_at), score: 0.54 DNAJC2DnaJ (Hsp40) homolog, subfamily C, member 2 (213097_s_at), score: 0.54 EDEM2ER degradation enhancer, mannosidase alpha-like 2 (218282_at), score: -0.57 EFNB1ephrin-B1 (202711_at), score: 0.54 EPN1epsin 1 (221141_x_at), score: 0.55 EPOerythropoietin (217254_s_at), score: 0.57 ETAA1Ewing tumor-associated antigen 1 (219216_at), score: -0.57 F11coagulation factor XI (206610_s_at), score: 0.65 FANCCFanconi anemia, complementation group C (205189_s_at), score: 0.58 FBXO2F-box protein 2 (219305_x_at), score: 0.54 FETUBfetuin B (214417_s_at), score: 0.5 FGF12fibroblast growth factor 12 (207501_s_at), score: 0.61 FGF13fibroblast growth factor 13 (205110_s_at), score: -0.63 FGF9fibroblast growth factor 9 (glia-activating factor) (206404_at), score: -0.6 FKBP10FK506 binding protein 10, 65 kDa (219249_s_at), score: 0.68 FOLH1folate hydrolase (prostate-specific membrane antigen) 1 (217487_x_at), score: 0.59 FZD3frizzled homolog 3 (Drosophila) (219683_at), score: 0.64 G6PC2glucose-6-phosphatase, catalytic, 2 (221453_at), score: 0.52 GABRA5gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) A receptor, alpha 5 (206456_at), score: -0.59 GASTgastrin (208138_at), score: 0.51 GPR65G protein-coupled receptor 65 (214467_at), score: -0.53 HAB1B1 for mucin (215778_x_at), score: 0.55 HAMPhepcidin antimicrobial peptide (220491_at), score: 0.56 HIST1H2AChistone cluster 1, H2ac (215071_s_at), score: -0.59 HIST1H2AGhistone cluster 1, H2ag (207156_at), score: -0.67 HIST1H4Fhistone cluster 1, H4f (208026_at), score: 0.68 HLA-DRB1major histocompatibility complex, class II, DR beta 1 (209312_x_at), score: 0.78 HPNhepsin (204934_s_at), score: 0.63 HSPA6heat shock 70kDa protein 6 (HSP70B') (117_at), score: 0.52 ICAM2intercellular adhesion molecule 2 (204683_at), score: 0.59 IGHG1immunoglobulin heavy constant gamma 1 (G1m marker) (211693_at), score: 0.58 IGLL3immunoglobulin lambda-like polypeptide 3 (215946_x_at), score: 0.56 IL12Ainterleukin 12A (natural killer cell stimulatory factor 1, cytotoxic lymphocyte maturation factor 1, p35) (207160_at), score: 0.56 IL12Binterleukin 12B (natural killer cell stimulatory factor 2, cytotoxic lymphocyte maturation factor 2, p40) (207901_at), score: 0.56 IL22RA1interleukin 22 receptor, alpha 1 (220056_at), score: 0.52 IL27RAinterleukin 27 receptor, alpha (205926_at), score: 0.5 IL2RBinterleukin 2 receptor, beta (205291_at), score: 0.61 INE1inactivation escape 1 (non-protein coding) (207252_at), score: 0.5 IRF6interferon regulatory factor 6 (202597_at), score: 0.74 IRS4insulin receptor substrate 4 (207403_at), score: 0.55 ITGALintegrin, alpha L (antigen CD11A (p180), lymphocyte function-associated antigen 1; alpha polypeptide) (213475_s_at), score: 0.53 ITPR1inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate receptor, type 1 (203710_at), score: -0.83 KERAkeratocan (220504_at), score: -0.71 KIR3DX1killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor, three domains, X1 (216428_x_at), score: -0.68 KMOkynurenine 3-monooxygenase (kynurenine 3-hydroxylase) (205307_s_at), score: -0.91 KSR1kinase suppressor of ras 1 (213769_at), score: 0.68 LATS1LATS, large tumor suppressor, homolog 1 (Drosophila) (219813_at), score: -0.63 LAX1lymphocyte transmembrane adaptor 1 (207734_at), score: 0.6 LILRA5leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor, subfamily A (with TM domain), member 5 (215838_at), score: 0.55 LILRB4leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor, subfamily B (with TM and ITIM domains), member 4 (210152_at), score: 0.77 LOC100128223hypothetical protein LOC100128223 (221264_s_at), score: 0.52 LSRlipolysis stimulated lipoprotein receptor (208190_s_at), score: -0.64 LTBP4latent transforming growth factor beta binding protein 4 (210628_x_at), score: 0.6 MACROD1MACRO domain containing 1 (219188_s_at), score: 0.5 MAPRE3microtubule-associated protein, RP/EB family, member 3 (214270_s_at), score: -0.55 MCTP2multiple C2 domains, transmembrane 2 (220603_s_at), score: 0.56 MEP1Bmeprin A, beta (207251_at), score: 0.71 MGC13053hypothetical MGC13053 (211775_x_at), score: -0.81 MGC5590hypothetical protein MGC5590 (220931_at), score: 0.6 MMP14matrix metallopeptidase 14 (membrane-inserted) (202827_s_at), score: 0.54 MMP17matrix metallopeptidase 17 (membrane-inserted) (206234_s_at), score: 0.52 MOCS3molybdenum cofactor synthesis 3 (206141_at), score: 0.55 MPP3membrane protein, palmitoylated 3 (MAGUK p55 subfamily member 3) (206186_at), score: 0.63 MPPED2metallophosphoesterase domain containing 2 (205413_at), score: -0.7 MSTP9macrophage stimulating, pseudogene 9 (213382_at), score: 0.62 MUC13mucin 13, cell surface associated (218687_s_at), score: 0.52 MUC5ACmucin 5AC, oligomeric mucus/gel-forming (217182_at), score: 0.65 MYBPC1myosin binding protein C, slow type (214087_s_at), score: 0.53 MYO15Amyosin XVA (220288_at), score: 0.54 NDRG3NDRG family member 3 (221082_s_at), score: -0.52 NDRG4NDRG family member 4 (209159_s_at), score: -0.59 OR7E24olfactory receptor, family 7, subfamily E, member 24 (215463_at), score: 0.75 P2RY4pyrimidinergic receptor P2Y, G-protein coupled, 4 (221466_at), score: 0.64 PARD6Apar-6 partitioning defective 6 homolog alpha (C. elegans) (205245_at), score: 0.65 PCNXpecanex homolog (Drosophila) (213159_at), score: 0.51 PCNXL2pecanex-like 2 (Drosophila) (39650_s_at), score: 0.51 PEX13peroxisomal biogenesis factor 13 (205246_at), score: -0.54 PGAP1post-GPI attachment to proteins 1 (213469_at), score: -0.64 PIPOXpipecolic acid oxidase (221605_s_at), score: 0.53 PLXDC1plexin domain containing 1 (219700_at), score: 0.49 POM121L2POM121 membrane glycoprotein-like 2 (rat) (216582_at), score: 0.86 PRLHprolactin releasing hormone (221443_x_at), score: 0.69 PTPRNprotein tyrosine phosphatase, receptor type, N (204945_at), score: 0.53 PTPRUprotein tyrosine phosphatase, receptor type, U (211320_s_at), score: 0.63 RANBP17RAN binding protein 17 (219661_at), score: 0.5 RAP1GAPRAP1 GTPase activating protein (203911_at), score: 0.6 RASGRP2RAS guanyl releasing protein 2 (calcium and DAG-regulated) (214369_s_at), score: 0.69 RBAKRB-associated KRAB zinc finger (219214_s_at), score: 0.5 RBM12BRNA binding motif protein 12B (51228_at), score: -0.54 RBM38RNA binding motif protein 38 (212430_at), score: 0.5 RCAN3RCAN family member 3 (219864_s_at), score: 0.72 RNF121ring finger protein 121 (219021_at), score: 0.62 RNPEPL1arginyl aminopeptidase (aminopeptidase B)-like 1 (218301_at), score: 0.54 RORARAR-related orphan receptor A (210426_x_at), score: 0.5 RPH3ALrabphilin 3A-like (without C2 domains) (221614_s_at), score: -0.63 RUFY2RUN and FYVE domain containing 2 (219957_at), score: 0.5 SCLYselenocysteine lyase (221575_at), score: -0.7 SEPT5septin 5 (209767_s_at), score: 0.73 SERPINB13serpin peptidase inhibitor, clade B (ovalbumin), member 13 (211362_s_at), score: 0.56 SFRS15splicing factor, arginine/serine-rich 15 (222310_at), score: 0.65 SGSHN-sulfoglucosamine sulfohydrolase (35626_at), score: -0.56 SHANK2SH3 and multiple ankyrin repeat domains 2 (213307_at), score: -0.65 SIGLEC6sialic acid binding Ig-like lectin 6 (210796_x_at), score: 0.49 SIK2salt-inducible kinase 2 (213221_s_at), score: -0.59 SLC26A4solute carrier family 26, member 4 (206529_x_at), score: 0.71 SLC5A5solute carrier family 5 (sodium iodide symporter), member 5 (211123_at), score: 0.53 SLC9A8solute carrier family 9 (sodium/hydrogen exchanger), member 8 (212947_at), score: 0.58 SMEK1SMEK homolog 1, suppressor of mek1 (Dictyostelium) (220368_s_at), score: 0.52 SNAP25synaptosomal-associated protein, 25kDa (202508_s_at), score: -1 SORBS1sorbin and SH3 domain containing 1 (218087_s_at), score: 0.69 SPATA6spermatogenesis associated 6 (220298_s_at), score: 0.53 STRA6stimulated by retinoic acid gene 6 homolog (mouse) (221701_s_at), score: 0.56 SUV39H2suppressor of variegation 3-9 homolog 2 (Drosophila) (219262_at), score: -0.59 SYT1synaptotagmin I (203999_at), score: -0.63 SYT5synaptotagmin V (206161_s_at), score: 0.53 TAL1T-cell acute lymphocytic leukemia 1 (206283_s_at), score: 0.68 TAP2transporter 2, ATP-binding cassette, sub-family B (MDR/TAP) (204769_s_at), score: 0.51 TAS2R9taste receptor, type 2, member 9 (221461_at), score: 0.58 TBX10T-box 10 (207689_at), score: 0.64 TBX6T-box 6 (207684_at), score: 0.65 TCF20transcription factor 20 (AR1) (212931_at), score: 0.54 TGIF2TGFB-induced factor homeobox 2 (216262_s_at), score: 0.76 TMPRSS6transmembrane protease, serine 6 (214955_at), score: 0.59 TNFRSF10Dtumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily, member 10d, decoy with truncated death domain (210654_at), score: -0.62 TNFRSF9tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily, member 9 (207536_s_at), score: 0.6 TNFSF13tumor necrosis factor (ligand) superfamily, member 13 (209499_x_at), score: -0.64 TNIKTRAF2 and NCK interacting kinase (213107_at), score: -0.71 TNK1tyrosine kinase, non-receptor, 1 (217149_x_at), score: 0.54 TPK1thiamin pyrophosphokinase 1 (221218_s_at), score: -0.71 TRA@T cell receptor alpha locus (216540_at), score: 0.72 TRIM13tripartite motif-containing 13 (203659_s_at), score: -0.6 TRIM25tripartite motif-containing 25 (206911_at), score: 0.55 TRIM62tripartite motif-containing 62 (219272_at), score: -0.68 TRIP11thyroid hormone receptor interactor 11 (209778_at), score: -0.57 TRMT12tRNA methyltransferase 12 homolog (S. cerevisiae) (219299_at), score: -0.59 TRPA1transient receptor potential cation channel, subfamily A, member 1 (208349_at), score: 0.67 UBE2D4ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2D 4 (putative) (218837_s_at), score: -0.54 ULBP1UL16 binding protein 1 (221323_at), score: 0.71 UTF1undifferentiated embryonic cell transcription factor 1 (208275_x_at), score: 0.66 VGFVGF nerve growth factor inducible (205586_x_at), score: 0.53 WDR4WD repeat domain 4 (221632_s_at), score: 0.51 WDR52WD repeat domain 52 (221103_s_at), score: 0.57 ZNF192zinc finger protein 192 (206579_at), score: -0.57 ZNF33Bzinc finger protein 33B (215022_x_at), score: -0.53 ZNF415zinc finger protein 415 (205514_at), score: -0.55 ZNF440zinc finger protein 440 (215892_at), score: 0.5 ZNF467zinc finger protein 467 (214746_s_at), score: -0.54
| Id | sample | Experiment | ExpName | Array | Syndrome | Cell.line |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486111.cel | 24 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485831.cel | 10 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486311.cel | 34 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |