
Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

reproduction
The production by an organism of new individuals that contain some portion of their genetic material inherited from that organism.
metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways, including anabolism and catabolism, by which living organisms transform chemical substances. Metabolic processes typically transform small molecules, but also include macromolecular processes such as DNA repair and replication, and protein synthesis and degradation.
positive regulation of defense response to virus by host
Any host process that results in the promotion of antiviral immune response mechanisms, thereby limiting viral replication.
immune effector process
Any process of the immune system that occurs as part of an immune response.
immune system process
Any process involved in the development or functioning of the immune system, an organismal system for calibrated responses to potential internal or invasive threats.
regulation of immune system process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of an immune system process.
regulation of immune effector process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of an immune effector process.
regulation of response to biotic stimulus
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of a response to biotic stimulus.
defense response
Reactions, triggered in response to the presence of a foreign body or the occurrence of an injury, which result in restriction of damage to the organism attacked or prevention/recovery from the infection caused by the attack.
response to virus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus from a virus.
nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
transcription
The synthesis of either RNA on a template of DNA or DNA on a template of RNA.
transcription, RNA-dependent
The synthesis of DNA on a template of RNA.
xenobiotic metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving a xenobiotic compound, a compound foreign to living organisms. Used of chemical compounds, e.g. a xenobiotic chemical, such as a pesticide.
response to stress
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a disturbance in organismal or cellular homeostasis, usually, but not necessarily, exogenous (e.g. temperature, humidity, ionizing radiation).
immune response
Any immune system process that functions in the calibrated response of an organism to a potential internal or invasive threat.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
viral genome replication
Any process involved directly in viral genome replication, including viral nucleotide metabolism.
biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances; typically the energy-requiring part of metabolism in which simpler substances are transformed into more complex ones.
macromolecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
viral reproduction
The process by which a virus reproduces. Usually, this is by infection of a host cell, replication of the viral genome, and assembly of progeny virus particles. In some cases the viral genetic material may integrate into the host genome and only subsequently, under particular circumstances, 'complete' its life cycle.
response to xenobiotic stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a xenobiotic compound stimulus. Xenobiotic compounds are compounds foreign to living organisms.
response to biotic stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a biotic stimulus, a stimulus caused or produced by a living organism.
response to other organism
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus from another living organism.
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
gene expression
The process by which a gene's coding sequence is converted into a mature gene product or products (proteins or RNA). This includes the production of an RNA transcript as well as any processing to produce a mature RNA product or an mRNA (for protein-coding genes) and the translation of that mRNA into protein. Some protein processing events may be included when they are required to form an active form of a product from an inactive precursor form.
viral infectious cycle
A set of processes which all viruses follow to ensure survival; includes attachment and entry of the virus particle, decoding of genome information, translation of viral mRNA by host ribosomes, genome replication, and assembly and release of viral particles containing the genome.
reproductive process
A biological process that directly contributes to the process of producing new individuals by one or two organisms. The new individuals inherit some proportion of their genetic material from the parent or parents.
viral reproductive process
A reproductive process involved in viral reproduction. Usually, this is by infection of a host cell, replication of the viral genome, and assembly of progeny virus particles. In some cases the viral genetic material may integrate into the host genome and only subsequently, under particular circumstances, 'complete' its life cycle.
regulation of defense response
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a defense response.
cellular macromolecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, carried out by individual cells.
cellular biopolymer metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature, such as polysaccharides and proteins, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular biopolymer biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature, such as polysaccharides and proteins, as carried out by individual cells.
response to chemical stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a chemical stimulus.
macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
biopolymer metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature, such as polysaccharides and proteins.
biopolymer biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature e.g. polysaccharides and proteins.
regulation of multi-organism process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a multi-organism process, a process by which an organism has an effect on another organism of the same or different species.
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
primary metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving those compounds which are formed as a part of the normal anabolic and catabolic processes. These processes take place in most, if not all, cells of the organism.
cellular biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
cellular macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, as carried out by individual cells.
regulation of viral genome replication
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of viral genome replication.
negative regulation of viral genome replication
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of viral genome replication.
retroviral genome replication
Any process involved in the replication of a retroviral genome. Retroviruses use RNA as their nucleic acid and reverse transcriptase to copy their genome into the DNA of the host cells chromosomes.
regulation of retroviral genome replication
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of retroviral genome replication.
negative regulation of retroviral genome replication
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of retroviral genome replication.
negative regulation of biological process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
negative regulation of viral reproduction
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the viral life cycle, the set of processes by which a virus reproduces and spreads among hosts.
regulation of response to stimulus
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a response to a stimulus. Response to stimulus is a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
regulation of defense response to virus
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the antiviral response of a cell or organism.
regulation of defense response to virus by host
Any host process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of the antiviral response of a host cell or organism.
regulation of immune response
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the immune response, the immunological reaction of an organism to an immunogenic stimulus.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of viral reproduction
Any process that modulates the rate or extent of the viral life cycle, the set of processes by which a virus reproduces and spreads among hosts.
response to stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
defense response to virus
Reactions triggered in response to the presence of a virus that act to protect the cell or organism.
multi-organism process
Any process by which an organism has an effect on another organism of the same or different species.
biological regulation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of any biological process, quality or function.
all
This term is the most general term possible
reproductive process
A biological process that directly contributes to the process of producing new individuals by one or two organisms. The new individuals inherit some proportion of their genetic material from the parent or parents.
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
viral reproductive process
A reproductive process involved in viral reproduction. Usually, this is by infection of a host cell, replication of the viral genome, and assembly of progeny virus particles. In some cases the viral genetic material may integrate into the host genome and only subsequently, under particular circumstances, 'complete' its life cycle.
negative regulation of viral reproduction
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the viral life cycle, the set of processes by which a virus reproduces and spreads among hosts.
regulation of immune system process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of an immune system process.
negative regulation of biological process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of viral reproduction
Any process that modulates the rate or extent of the viral life cycle, the set of processes by which a virus reproduces and spreads among hosts.
immune response
Any immune system process that functions in the calibrated response of an organism to a potential internal or invasive threat.
regulation of response to stimulus
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a response to a stimulus. Response to stimulus is a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
regulation of multi-organism process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a multi-organism process, a process by which an organism has an effect on another organism of the same or different species.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
macromolecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
cellular biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
cellular macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, as carried out by individual cells.
nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
immune effector process
Any process of the immune system that occurs as part of an immune response.
regulation of immune response
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the immune response, the immunological reaction of an organism to an immunogenic stimulus.
negative regulation of viral reproduction
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the viral life cycle, the set of processes by which a virus reproduces and spreads among hosts.
regulation of immune response
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the immune response, the immunological reaction of an organism to an immunogenic stimulus.
regulation of response to biotic stimulus
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of a response to biotic stimulus.
response to other organism
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus from another living organism.
cellular macromolecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, carried out by individual cells.
biopolymer biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature e.g. polysaccharides and proteins.
cellular macromolecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, carried out by individual cells.
cellular biopolymer metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature, such as polysaccharides and proteins, as carried out by individual cells.
transcription
The synthesis of either RNA on a template of DNA or DNA on a template of RNA.
regulation of defense response to virus
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the antiviral response of a cell or organism.
regulation of defense response to virus
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the antiviral response of a cell or organism.
regulation of immune effector process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of an immune effector process.
regulation of viral genome replication
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of viral genome replication.
negative regulation of viral genome replication
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of viral genome replication.
viral genome replication
Any process involved directly in viral genome replication, including viral nucleotide metabolism.
negative regulation of viral genome replication
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of viral genome replication.
regulation of defense response to virus
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the antiviral response of a cell or organism.
regulation of defense response to virus
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the antiviral response of a cell or organism.
regulation of defense response
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a defense response.
defense response to virus
Reactions triggered in response to the presence of a virus that act to protect the cell or organism.
xenobiotic metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving a xenobiotic compound, a compound foreign to living organisms. Used of chemical compounds, e.g. a xenobiotic chemical, such as a pesticide.
defense response to virus
Reactions triggered in response to the presence of a virus that act to protect the cell or organism.
cellular biopolymer biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature, such as polysaccharides and proteins, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular biopolymer biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature, such as polysaccharides and proteins, as carried out by individual cells.
regulation of retroviral genome replication
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of retroviral genome replication.
negative regulation of retroviral genome replication
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of retroviral genome replication.
negative regulation of retroviral genome replication
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of retroviral genome replication.
transcription
The synthesis of either RNA on a template of DNA or DNA on a template of RNA.

intracellular
The living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
extracellular region
The space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.
cellular_component
The part of a cell or its extracellular environment in which a gene product is located. A gene product may be located in one or more parts of a cell and its location may be as specific as a particular macromolecular complex, that is, a stable, persistent association of macromolecules that function together.
proteinaceous extracellular matrix
A layer consisting mainly of proteins (especially collagen) and glycosaminoglycans (mostly as proteoglycans) that forms a sheet underlying or overlying cells such as endothelial and epithelial cells. The proteins are secreted by cells in the vicinity.
cell
The basic structural and functional unit of all organisms. Includes the plasma membrane and any external encapsulating structures such as the cell wall and cell envelope.
nucleus
A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent.
apolipoprotein B mRNA editing enzyme complex
Protein complex that mediates editing of the mRNA encoding apolipoprotein B; catalyzes the deamination of C to U (residue 6666 in the human mRNA). Contains a catalytic subunit, APOBEC-1, and other proteins (e.g. human ASP; rat ASP and KSRP).
extracellular matrix
A structure lying external to one or more cells, which provides structural support for cells or tissues; may be completely external to the cell (as in animals) or be part of the cell (as in plants).
macromolecular complex
A stable assembly of two or more macromolecules, i.e. proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates or lipids, in which the constituent parts function together.
organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
protein complex
Any macromolecular complex composed of two or more polypeptide subunits, which may or may not be identical. Protein complexes may have other associated non-protein prosthetic groups, such as nucleotides, metal ions or carbohydrate groups.
extracellular region part
Any constituent part of the extracellular region, the space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers constituent parts of the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.
organelle part
Any constituent part of an organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, but excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
nuclear part
Any constituent part of the nucleus, a membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
all
This term is the most general term possible
extracellular region part
Any constituent part of the extracellular region, the space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers constituent parts of the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
organelle part
Any constituent part of an organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, but excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
apolipoprotein B mRNA editing enzyme complex
Protein complex that mediates editing of the mRNA encoding apolipoprotein B; catalyzes the deamination of C to U (residue 6666 in the human mRNA). Contains a catalytic subunit, APOBEC-1, and other proteins (e.g. human ASP; rat ASP and KSRP).
nuclear part
Any constituent part of the nucleus, a membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated.

| Id | Pvalue | ExpCount | Count | Size | Term |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 00983 | 1.360e-02 | 0.2913 | 4 | 29 | Drug metabolism - other enzymes |
| 00040 | 1.850e-02 | 0.1306 | 3 | 13 | Pentose and glucuronate interconversions |
ABCB1ATP-binding cassette, sub-family B (MDR/TAP), member 1 (209993_at), score: -1 ADORA2Badenosine A2b receptor (205891_at), score: -0.7 AKR1B10aldo-keto reductase family 1, member B10 (aldose reductase) (206561_s_at), score: -0.85 APOBEC3Fapolipoprotein B mRNA editing enzyme, catalytic polypeptide-like 3F (214995_s_at), score: -0.68 APOBEC3Gapolipoprotein B mRNA editing enzyme, catalytic polypeptide-like 3G (204205_at), score: -0.72 APOL3apolipoprotein L, 3 (221087_s_at), score: -0.7 ARSJarylsulfatase family, member J (219973_at), score: 0.58 C10orf116chromosome 10 open reading frame 116 (203571_s_at), score: 0.74 C3orf64chromosome 3 open reading frame 64 (221935_s_at), score: 0.73 C5orf23chromosome 5 open reading frame 23 (219054_at), score: 0.59 C5orf30chromosome 5 open reading frame 30 (221823_at), score: 0.65 CD24CD24 molecule (266_s_at), score: -0.81 CDKN1Acyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1A (p21, Cip1) (202284_s_at), score: 0.62 COL11A1collagen, type XI, alpha 1 (37892_at), score: 0.68 CRTAPcartilage associated protein (201380_at), score: 0.63 CRYABcrystallin, alpha B (209283_at), score: 0.71 DDX17DEAD (Asp-Glu-Ala-Asp) box polypeptide 17 (208151_x_at), score: -0.76 DDX3YDEAD (Asp-Glu-Ala-Asp) box polypeptide 3, Y-linked (205000_at), score: 0.58 DGKDdiacylglycerol kinase, delta 130kDa (208072_s_at), score: -0.82 DUSP14dual specificity phosphatase 14 (203367_at), score: 0.69 EPHB2EPH receptor B2 (209589_s_at), score: -0.72 FAM105Afamily with sequence similarity 105, member A (219694_at), score: -0.7 FAM169Afamily with sequence similarity 169, member A (213954_at), score: -0.73 FASFas (TNF receptor superfamily, member 6) (204780_s_at), score: 0.66 FAT1FAT tumor suppressor homolog 1 (Drosophila) (201579_at), score: 0.72 FBN2fibrillin 2 (203184_at), score: 0.62 FKBP9FK506 binding protein 9, 63 kDa (212169_at), score: 0.63 GABREgamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) A receptor, epsilon (204537_s_at), score: -0.76 GAGE4G antigen 4 (207086_x_at), score: -0.95 GAGE6G antigen 6 (208155_x_at), score: -0.91 GATA3GATA binding protein 3 (209604_s_at), score: -0.85 GHRgrowth hormone receptor (205498_at), score: 0.62 GLSglutaminase (203159_at), score: 0.67 GREM1gremlin 1, cysteine knot superfamily, homolog (Xenopus laevis) (218469_at), score: 0.59 HAS2hyaluronan synthase 2 (206432_at), score: 0.64 HERC5hect domain and RLD 5 (219863_at), score: -0.91 HGSNATheparan-alpha-glucosaminide N-acetyltransferase (218017_s_at), score: 0.7 HSPB7heat shock 27kDa protein family, member 7 (cardiovascular) (218934_s_at), score: 0.67 IGSF3immunoglobulin superfamily, member 3 (202421_at), score: -0.73 KYNUkynureninase (L-kynurenine hydrolase) (217388_s_at), score: -0.71 LEF1lymphoid enhancer-binding factor 1 (221558_s_at), score: -0.83 LIPAlipase A, lysosomal acid, cholesterol esterase (201847_at), score: 0.61 LOC728855hypothetical LOC728855 (222001_x_at), score: -0.84 LRRC2leucine rich repeat containing 2 (219949_at), score: 0.68 LTBP2latent transforming growth factor beta binding protein 2 (204682_at), score: 0.72 LUMlumican (201744_s_at), score: 0.6 MAN2A1mannosidase, alpha, class 2A, member 1 (205105_at), score: 0.71 MARCH2membrane-associated ring finger (C3HC4) 2 (210075_at), score: 0.68 MFAP3Lmicrofibrillar-associated protein 3-like (205442_at), score: 0.63 MFAP5microfibrillar associated protein 5 (213764_s_at), score: 0.69 MXRA5matrix-remodelling associated 5 (209596_at), score: 0.58 MXRA8matrix-remodelling associated 8 (213422_s_at), score: 0.59 MYO1Dmyosin ID (212338_at), score: 0.59 NCALDneurocalcin delta (211685_s_at), score: 0.58 NEK7NIMA (never in mitosis gene a)-related kinase 7 (212530_at), score: 0.62 NMUneuromedin U (206023_at), score: -0.69 NRGNneurogranin (protein kinase C substrate, RC3) (204081_at), score: -0.67 OASL2'-5'-oligoadenylate synthetase-like (210797_s_at), score: -0.99 PCLOpiccolo (presynaptic cytomatrix protein) (213558_at), score: -0.79 PDGFCplatelet derived growth factor C (218718_at), score: 0.59 PILRBpaired immunoglobin-like type 2 receptor beta (220954_s_at), score: -0.73 PSMB8proteasome (prosome, macropain) subunit, beta type, 8 (large multifunctional peptidase 7) (209040_s_at), score: -0.76 QPCTglutaminyl-peptide cyclotransferase (205174_s_at), score: 0.64 RAD23BRAD23 homolog B (S. cerevisiae) (201223_s_at), score: 0.69 RBM3RNA binding motif (RNP1, RRM) protein 3 (222026_at), score: 0.58 RECKreversion-inducing-cysteine-rich protein with kazal motifs (205407_at), score: 0.61 SERPINB7serpin peptidase inhibitor, clade B (ovalbumin), member 7 (206421_s_at), score: 0.59 SGCDsarcoglycan, delta (35kDa dystrophin-associated glycoprotein) (213543_at), score: 0.58 SLC30A1solute carrier family 30 (zinc transporter), member 1 (212907_at), score: 0.71 SLC4A4solute carrier family 4, sodium bicarbonate cotransporter, member 4 (203908_at), score: 0.75 SLC7A11solute carrier family 7, (cationic amino acid transporter, y+ system) member 11 (217678_at), score: -0.72 SNCAsynuclein, alpha (non A4 component of amyloid precursor) (204466_s_at), score: -0.69 SSR3signal sequence receptor, gamma (translocon-associated protein gamma) (217790_s_at), score: 0.7 SYTL2synaptotagmin-like 2 (220613_s_at), score: -0.71 TBC1D3TBC1 domain family, member 3 (209403_at), score: -0.67 TBC1D8TBC1 domain family, member 8 (with GRAM domain) (204526_s_at), score: -0.71 TCEAL2transcription elongation factor A (SII)-like 2 (211276_at), score: -0.85 TIMP2TIMP metallopeptidase inhibitor 2 (203167_at), score: 0.64 TMEM204transmembrane protein 204 (219315_s_at), score: 0.63 TMEM47transmembrane protein 47 (209656_s_at), score: 0.68 TMEM51transmembrane protein 51 (218815_s_at), score: -0.76 TNS1tensin 1 (221748_s_at), score: 0.8 TOB1transducer of ERBB2, 1 (202704_at), score: 0.69 TRIM16tripartite motif-containing 16 (204341_at), score: -0.7 TSPAN13tetraspanin 13 (217979_at), score: 0.74 TSPYL1TSPY-like 1 (221493_at), score: 0.62 TSPYL5TSPY-like 5 (213122_at), score: 0.65 UAP1UDP-N-acteylglucosamine pyrophosphorylase 1 (209340_at), score: 0.64 UBL3ubiquitin-like 3 (201535_at), score: 0.7 UGT1A1UDP glucuronosyltransferase 1 family, polypeptide A1 (207126_x_at), score: -0.87 UGT1A6UDP glucuronosyltransferase 1 family, polypeptide A6 (206094_x_at), score: -0.84 UGT1A9UDP glucuronosyltransferase 1 family, polypeptide A9 (204532_x_at), score: -0.83 WT1Wilms tumor 1 (206067_s_at), score: -0.8 ZNF281zinc finger protein 281 (218401_s_at), score: 0.62
| Id | sample | Experiment | ExpName | Array | Syndrome | Cell.line |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
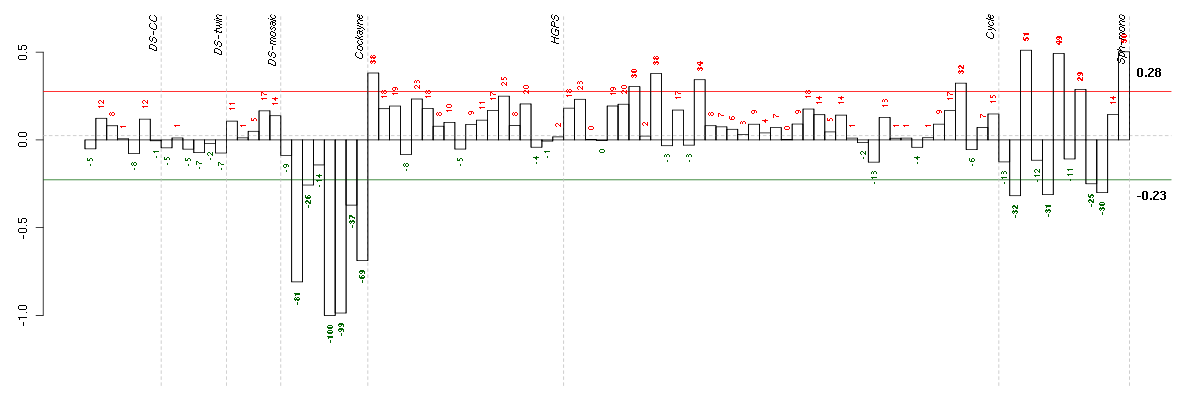
| E-GEOD-3407-raw-cel-1437949721.cel | 5 | 4 | Cockayne | hgu133a | CS | CSB |
| E-GEOD-3407-raw-cel-1437949750.cel | 6 | 4 | Cockayne | hgu133a | CS | CSB |
| E-GEOD-3407-raw-cel-1437949579.cel | 2 | 4 | Cockayne | hgu133a | none | CSB |
| E-GEOD-3407-raw-cel-1437949938.cel | 8 | 4 | Cockayne | hgu133a | none | CSB |
| E-GEOD-3407-raw-cel-1437949854.cel | 7 | 4 | Cockayne | hgu133a | CS | eGFP |
| E-GEOD-4219-raw-cel-1311956138.cel | 4 | 7 | Sph-mono | hgu133plus2 | none | Sph-mon 1 |
| E-GEOD-4219-raw-cel-1311956321.cel | 9 | 7 | Sph-mono | hgu133plus2 | none | Sph-mon 1 |
| E-GEOD-4219-raw-cel-1311956614.cel | 18 | 7 | Sph-mono | hgu133plus2 | none | Sph-mon 1 |
| E-GEOD-3407-raw-cel-1437949655.cel | 3 | 4 | Cockayne | hgu133a | none | CSB |
| E-GEOD-4219-raw-cel-1311956457.cel | 14 | 7 | Sph-mono | hgu133plus2 | none | Sph-mon 1 |
| E-GEOD-4219-raw-cel-1311956418.cel | 13 | 7 | Sph-mono | hgu133plus2 | none | Sph-mon 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485771.cel | 7 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486371.cel | 37 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485891.cel | 13 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485811.cel | 9 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-GEOD-3860-raw-cel-1561690199.cel | 1 | 5 | HGPS | hgu133a | none | GM0316B |
| E-GEOD-4219-raw-cel-1311956358.cel | 10 | 7 | Sph-mono | hgu133plus2 | none | Sph-mon 1 |
| E-GEOD-4219-raw-cel-1311956824.cel | 24 | 7 | Sph-mono | hgu133plus2 | none | Sph-mon 1 |
| E-GEOD-4219-raw-cel-1311956178.cel | 6 | 7 | Sph-mono | hgu133plus2 | none | Sph-mon 1 |