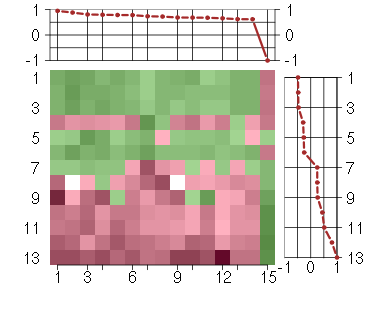

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways, including anabolism and catabolism, by which living organisms transform chemical substances. Metabolic processes typically transform small molecules, but also include macromolecular processes such as DNA repair and replication, and protein synthesis and degradation.
organic acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving organic acids, any acidic compound containing carbon in covalent linkage.
lipid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving lipids, compounds soluble in an organic solvent but not, or sparingly, in an aqueous solvent. Includes fatty acids; neutral fats, other fatty-acid esters, and soaps; long-chain (fatty) alcohols and waxes; sphingoids and other long-chain bases; glycolipids, phospholipids and sphingolipids; and carotenes, polyprenols, sterols, terpenes and other isoprenoids.
fatty acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving fatty acids, aliphatic monocarboxylic acids liberated from naturally occurring fats and oils by hydrolysis.
icosanoid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving icosanoids, any of a group of C20 polyunsaturated fatty acids.
prostanoid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving prostanoids, any compound based on or derived from the prostanoate structure.
prostaglandin metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving prostaglandins, any of a group of biologically active metabolites which contain a cyclopentane ring due to the formation of a bond between two carbons of a fatty acid. They have a wide range of biological activities.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
carboxylic acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving carboxylic acids, any organic acid containing one or more carboxyl (COOH) groups or anions (COO-).
monocarboxylic acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving monocarboxylic acids, any organic acid containing one carboxyl (COOH) group or anion (COO-).
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
primary metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving those compounds which are formed as a part of the normal anabolic and catabolic processes. These processes take place in most, if not all, cells of the organism.
cellular lipid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving lipids, as carried out by individual cells.
all
This term is the most general term possible
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
cellular lipid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving lipids, as carried out by individual cells.
fatty acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving fatty acids, aliphatic monocarboxylic acids liberated from naturally occurring fats and oils by hydrolysis.


molecular_function
Elemental activities, such as catalysis or binding, describing the actions of a gene product at the molecular level. A given gene product may exhibit one or more molecular functions.
catalytic activity
Catalysis of a biochemical reaction at physiological temperatures. In biologically catalyzed reactions, the reactants are known as substrates, and the catalysts are naturally occurring macromolecular substances known as enzymes. Enzymes possess specific binding sites for substrates, and are usually composed wholly or largely of protein, but RNA that has catalytic activity (ribozyme) is often also regarded as enzymatic.
aldo-keto reductase activity
Catalysis of the NADPH-dependent reduction of carbonyl compounds.
oxidoreductase activity
Catalysis of an oxidation-reduction (redox) reaction, a reversible chemical reaction in which the oxidation state of an atom or atoms within a molecule is altered. One substrate acts as a hydrogen or electron donor and becomes oxidized, while the other acts as hydrogen or electron acceptor and becomes reduced.
steroid dehydrogenase activity
Catalysis of an oxidation-reduction (redox) reaction in which one substrate is a sterol derivative.
oxidoreductase activity, acting on CH-OH group of donors
Catalysis of an oxidation-reduction (redox) reaction in which a CH-OH group act as a hydrogen or electron donor and reduces a hydrogen or electron acceptor.
oxidoreductase activity, acting on the CH-OH group of donors, NAD or NADP as acceptor
Catalysis of an oxidation-reduction (redox) reaction in which a CH-OH group acts as a hydrogen or electron donor and reduces NAD+ or NADP.
oxidoreductase activity, acting on the CH-CH group of donors
Catalysis of an oxidation-reduction (redox) reaction in which a CH-CH group acts as a hydrogen or electron donor and reduces a hydrogen or electron acceptor.
oxidoreductase activity, acting on the CH-CH group of donors, NAD or NADP as acceptor
Catalysis of an oxidation-reduction (redox) reaction in which a CH-CH group acts as a hydrogen or electron donor and reduces NAD or NADP.
steroid dehydrogenase activity, acting on the CH-OH group of donors, NAD or NADP as acceptor
Catalysis of an oxidation-reduction (redox) reaction in which a CH-OH group acts as a hydrogen or electron donor and reduces NAD+ or NADP, and in which one substrate is a sterol derivative.
3-alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (A-specific) activity
Catalysis of the reaction: NAD(P)+ + androsterone = NAD(P)H + H+ + 5-alpha-androstane-3,17-dione. The reaction is A-specific (i.e. the pro-R hydrogen is transferred from the 4-position of reduced nicotinamide cofactor) with respect to NAD(P)+.
trans-1,2-dihydrobenzene-1,2-diol dehydrogenase activity
Catalysis of the reaction: NADP+ + trans-1,2-dihydrobenzene-1,2-diol = NADPH + catechol.
all
This term is the most general term possible
steroid dehydrogenase activity, acting on the CH-OH group of donors, NAD or NADP as acceptor
Catalysis of an oxidation-reduction (redox) reaction in which a CH-OH group acts as a hydrogen or electron donor and reduces NAD+ or NADP, and in which one substrate is a sterol derivative.
| Id | Pvalue | ExpCount | Count | Size | Term |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 00980 | 1.965e-02 | 0.1357 | 3 | 37 | Metabolism of xenobiotics by cytochrome P450 |
AKR1B10aldo-keto reductase family 1, member B10 (aldose reductase) (206561_s_at), score: 0.95 AKR1C2aldo-keto reductase family 1, member C2 (dihydrodiol dehydrogenase 2; bile acid binding protein; 3-alpha hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase, type III) (209699_x_at), score: 0.62 AKR1C3aldo-keto reductase family 1, member C3 (3-alpha hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase, type II) (209160_at), score: 0.72 ALDH3A1aldehyde dehydrogenase 3 family, memberA1 (205623_at), score: 0.69 C20orf39chromosome 20 open reading frame 39 (219310_at), score: 0.68 CELSR1cadherin, EGF LAG seven-pass G-type receptor 1 (flamingo homolog, Drosophila) (41660_at), score: 0.78 FCGR2AFc fragment of IgG, low affinity IIa, receptor (CD32) (203561_at), score: 0.68 FGF13fibroblast growth factor 13 (205110_s_at), score: 0.62 GABRA2gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) A receptor, alpha 2 (207014_at), score: 0.65 GREM1gremlin 1, cysteine knot superfamily, homolog (Xenopus laevis) (218469_at), score: -1 IGSF3immunoglobulin superfamily, member 3 (202421_at), score: 0.81 KYNUkynureninase (L-kynurenine hydrolase) (217388_s_at), score: 0.88 LEF1lymphoid enhancer-binding factor 1 (221558_s_at), score: 0.79 MPPED2metallophosphoesterase domain containing 2 (205413_at), score: 0.78 PDGFDplatelet derived growth factor D (219304_s_at), score: 0.73
| Id | sample | Experiment | ExpName | Array | Syndrome | Cell.line |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
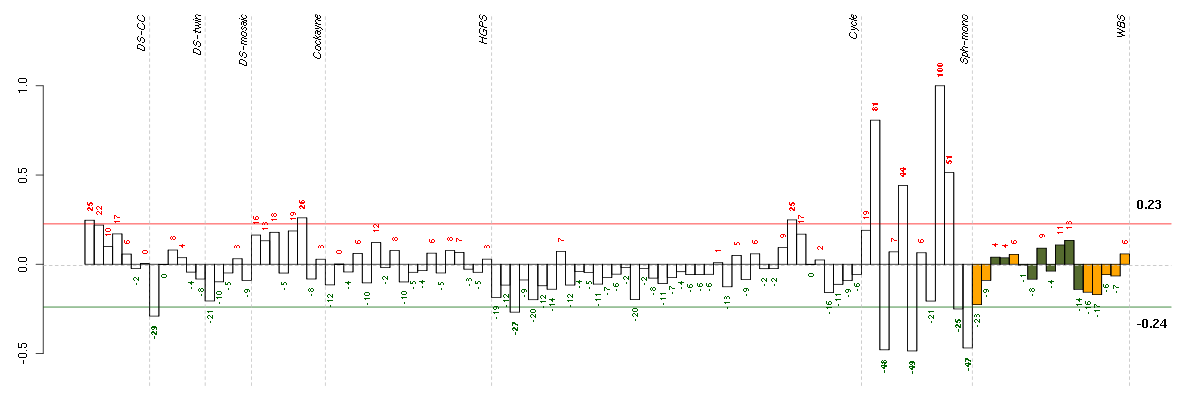
| E-GEOD-4219-raw-cel-1311956358.cel | 10 | 7 | Sph-mono | hgu133plus2 | none | Sph-mon 1 |
| E-GEOD-4219-raw-cel-1311956178.cel | 6 | 7 | Sph-mono | hgu133plus2 | none | Sph-mon 1 |
| E-GEOD-4219-raw-cel-1311956824.cel | 24 | 7 | Sph-mono | hgu133plus2 | none | Sph-mon 1 |
| 1Twin.CEL | 1 | 2 | DS-twin | hgu133plus2 | Down | DS-twin 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485691.cel | 3 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-GEOD-4219-raw-cel-1311956634.cel | 19 | 7 | Sph-mono | hgu133plus2 | none | Sph-mon 1 |
| ctrl a 08-03.CEL | 1 | 1 | DS-CC | hgu133a | none | DS-CC 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486291.cel | 33 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-GEOD-3407-raw-cel-1437949750.cel | 6 | 4 | Cockayne | hgu133a | CS | CSB |
| E-GEOD-4219-raw-cel-1311956321.cel | 9 | 7 | Sph-mono | hgu133plus2 | none | Sph-mon 1 |
| E-GEOD-4219-raw-cel-1311956614.cel | 18 | 7 | Sph-mono | hgu133plus2 | none | Sph-mon 1 |
| E-GEOD-4219-raw-cel-1311956138.cel | 4 | 7 | Sph-mono | hgu133plus2 | none | Sph-mon 1 |
| E-GEOD-4219-raw-cel-1311956457.cel | 14 | 7 | Sph-mono | hgu133plus2 | none | Sph-mon 1 |