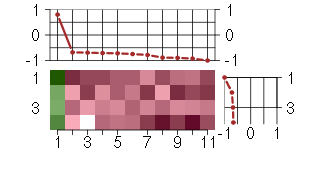

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

cell activation
A change in the morphology or behavior of a cell resulting from exposure to an activating factor such as a cellular or soluble ligand.
immune system process
Any process involved in the development or functioning of the immune system, an organismal system for calibrated responses to potential internal or invasive threats.
immune system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system whose objective is to provide calibrated responses by an organism to a potential internal or invasive threat, over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
leukocyte differentiation
The process whereby a relatively unspecialized hemopoietic precursor cell acquires the specialized features of a plasmacytoid dendritic cell or any cell of the myeloid leukocyte or lymphocyte lineages.
regulation of immune system process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of an immune system process.
negative regulation of immune system process
Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate, or extent of an immune system process.
regulation of leukocyte activation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of leukocyte activation.
negative regulation of leukocyte activation
Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate, or extent of leukocyte activation.
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
hemopoiesis
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the myeloid and lymphoid derived organ/tissue systems of the blood and other parts of the body over time, from formation to the mature structure. The site of hemopoiesis is variable during development, but occurs primarily in bone marrow or kidney in many adult vertebrates.
lymphocyte differentiation
The process whereby a relatively unspecialized precursor cell acquires specialized features of B cells, T cells, or natural killer cells.
cell differentiation
The process whereby relatively unspecialized cells, e.g. embryonic or regenerative cells, acquire specialized structural and/or functional features that characterize the cells, tissues, or organs of the mature organism or some other relatively stable phase of the organism's life history. Differentiation includes the processes involved in commitment of a cell to a specific fate.
B cell differentiation
The process whereby a precursor cell type acquires the specialized features of a B cell.
multicellular organismal process
Any biological process, occurring at the level of a multicellular organism, pertinent to its function.
developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an integrated living unit: an anatomical structure (which may be a subcellular structure, cell, tissue, or organ), or organism over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
B cell activation
The change in morphology and behavior of a mature or immature B cell resulting from exposure to a mitogen, cytokine, chemokine, cellular ligand, or an antigen for which it is specific.
leukocyte activation
A change in morphology and behavior of a leukocyte resulting from exposure to a specific antigen, mitogen, cytokine, cellular ligand, or soluble factor.
regulation of B cell differentiation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of B cell differentiation.
regulation of cell differentiation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell differentiation, the process whereby relatively unspecialized cells acquire specialized structural and functional features.
regulation of lymphocyte differentiation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of lymphocyte differentiation.
lymphocyte activation
A change in morphology and behavior of a lymphocyte resulting from exposure to a specific antigen, mitogen, cytokine, chemokine, cellular ligand, or soluble factor.
organ development
Development of a tissue or tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Development pertains to the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a structure over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
negative regulation of biological process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
negative regulation of cellular process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
hemopoietic or lymphoid organ development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of any organ involved in hemopoiesis or lymphoid cell activation over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Such development includes differentiation of resident cell types (stromal cells) and of migratory cell types dependent on the unique microenvironment afforded by the organ for their proper differentiation.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
anatomical structure development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an anatomical structure from an initial condition to its mature state. This process begins with the formation of the structure and ends with the mature structure, whatever form that may be including its natural destruction. An anatomical structure is any biological entity that occupies space and is distinguished from its surroundings. Anatomical structures can be macroscopic such as a carpel, or microscopic such as an acrosome.
cellular developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a cell over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of developmental process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of development, the biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote, or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
regulation of cellular process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
regulation of B cell activation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of B cell activation.
regulation of cell activation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell activation, the change in the morphology or behavior of a cell resulting from exposure to an activating factor such as a cellular or soluble ligand.
negative regulation of cell activation
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of cell activation.
negative regulation of B cell activation
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of B cell activation.
regulation of multicellular organismal process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a multicellular organismal process, the processes pertinent to the function of a multicellular organism above the cellular level; includes the integrated processes of tissues and organs.
regulation of lymphocyte activation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of lymphocyte activation.
negative regulation of lymphocyte activation
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of lymphocyte activation.
biological regulation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of any biological process, quality or function.
all
This term is the most general term possible
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
cellular developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a cell over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
negative regulation of immune system process
Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate, or extent of an immune system process.
negative regulation of cellular process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
regulation of immune system process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of an immune system process.
negative regulation of biological process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of developmental process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of development, the biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote, or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
regulation of cellular process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
regulation of multicellular organismal process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a multicellular organismal process, the processes pertinent to the function of a multicellular organism above the cellular level; includes the integrated processes of tissues and organs.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
negative regulation of immune system process
Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate, or extent of an immune system process.
regulation of leukocyte activation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of leukocyte activation.
negative regulation of leukocyte activation
Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate, or extent of leukocyte activation.
leukocyte activation
A change in morphology and behavior of a leukocyte resulting from exposure to a specific antigen, mitogen, cytokine, cellular ligand, or soluble factor.
negative regulation of cell activation
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of cell activation.
negative regulation of cellular process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
regulation of cell activation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell activation, the change in the morphology or behavior of a cell resulting from exposure to an activating factor such as a cellular or soluble ligand.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
regulation of cell differentiation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell differentiation, the process whereby relatively unspecialized cells acquire specialized structural and functional features.
negative regulation of leukocyte activation
Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate, or extent of leukocyte activation.
regulation of lymphocyte activation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of lymphocyte activation.
negative regulation of lymphocyte activation
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of lymphocyte activation.
regulation of leukocyte activation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of leukocyte activation.
negative regulation of cell activation
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of cell activation.
negative regulation of leukocyte activation
Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate, or extent of leukocyte activation.
regulation of cell differentiation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell differentiation, the process whereby relatively unspecialized cells acquire specialized structural and functional features.
regulation of lymphocyte differentiation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of lymphocyte differentiation.
immune system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system whose objective is to provide calibrated responses by an organism to a potential internal or invasive threat, over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
organ development
Development of a tissue or tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Development pertains to the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a structure over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
hemopoietic or lymphoid organ development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of any organ involved in hemopoiesis or lymphoid cell activation over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Such development includes differentiation of resident cell types (stromal cells) and of migratory cell types dependent on the unique microenvironment afforded by the organ for their proper differentiation.
leukocyte differentiation
The process whereby a relatively unspecialized hemopoietic precursor cell acquires the specialized features of a plasmacytoid dendritic cell or any cell of the myeloid leukocyte or lymphocyte lineages.
regulation of lymphocyte differentiation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of lymphocyte differentiation.
negative regulation of lymphocyte activation
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of lymphocyte activation.
regulation of lymphocyte differentiation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of lymphocyte differentiation.
B cell differentiation
The process whereby a precursor cell type acquires the specialized features of a B cell.
regulation of B cell activation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of B cell activation.
negative regulation of B cell activation
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of B cell activation.
lymphocyte differentiation
The process whereby a relatively unspecialized precursor cell acquires specialized features of B cells, T cells, or natural killer cells.
regulation of B cell differentiation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of B cell differentiation.
negative regulation of B cell activation
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of B cell activation.
regulation of B cell differentiation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of B cell differentiation.


ADD2adducin 2 (beta) (205268_s_at), score: -0.71 CD24CD24 molecule (209771_x_at), score: -0.9 EPHA4EPH receptor A4 (206114_at), score: -0.78 GABRA5gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) A receptor, alpha 5 (206456_at), score: -0.69 INHBAinhibin, beta A (210511_s_at), score: 0.8 MAFv-maf musculoaponeurotic fibrosarcoma oncogene homolog (avian) (209348_s_at), score: -0.93 NCAM1neural cell adhesion molecule 1 (212843_at), score: -0.68 PLAC8placenta-specific 8 (219014_at), score: -1 PPP2R2Bprotein phosphatase 2 (formerly 2A), regulatory subunit B, beta isoform (213849_s_at), score: -0.89 PRR7proline rich 7 (synaptic) (219742_at), score: -0.72 RUNX3runt-related transcription factor 3 (204198_s_at), score: -0.75
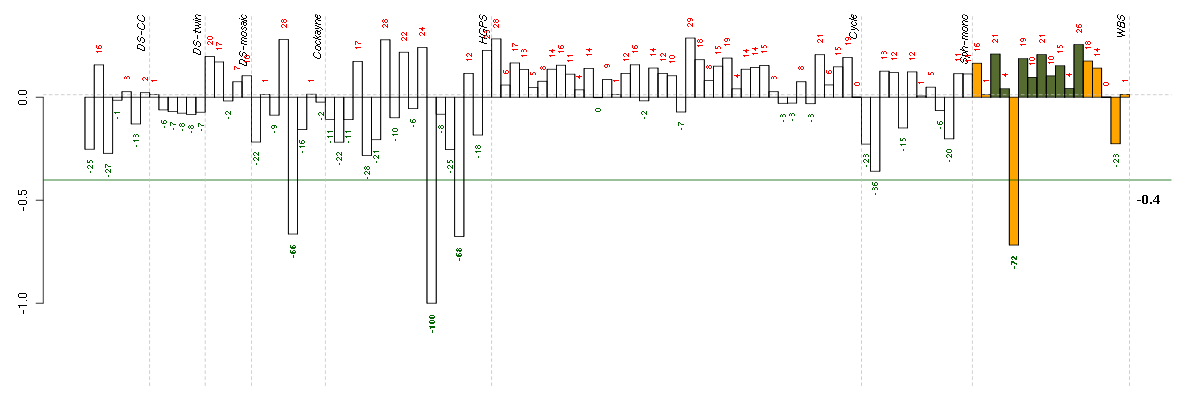
| Id | sample | Experiment | ExpName | Array | Syndrome | Cell.line |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E-GEOD-3860-raw-cel-1561690360.cel | 12 | 5 | HGPS | hgu133a | none | GM0316B |
| 4319_WBS.CEL | 5 | 8 | WBS | hgu133plus2 | WBS | WBS 1 |
| E-GEOD-3860-raw-cel-1561690416.cel | 15 | 5 | HGPS | hgu133a | none | GM0316B |
| E-GEOD-3407-raw-cel-1437949721.cel | 5 | 4 | Cockayne | hgu133a | CS | CSB |