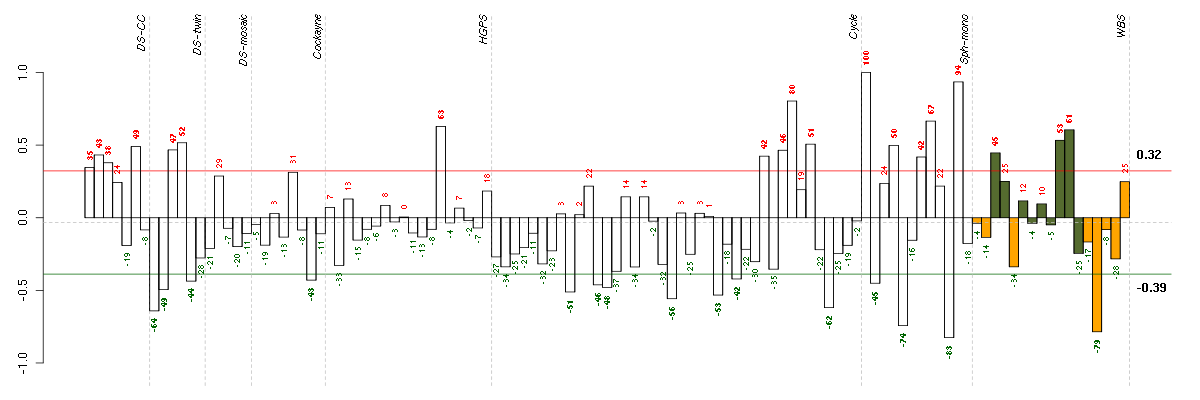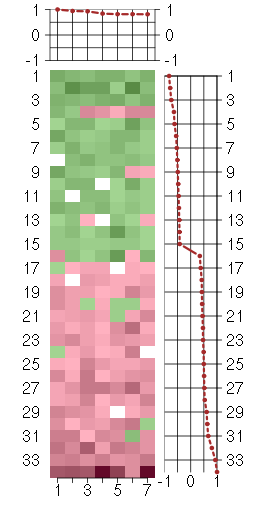

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways, including anabolism and catabolism, by which living organisms transform chemical substances. Metabolic processes typically transform small molecules, but also include macromolecular processes such as DNA repair and replication, and protein synthesis and degradation.
nitrogen compound metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving various organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds; includes nitrogen fixation, nitrification, denitrification, assimilatory/dissimilatory nitrate reduction and the interconversion of nitrogenous organic matter and ammonium.
nitric oxide biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of nitric oxide, nitrogen monoxide (NO), a colorless gas only slightly soluble in water.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances; typically the energy-requiring part of metabolism in which simpler substances are transformed into more complex ones.
regulation of biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances.
positive regulation of biosynthetic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances.
positive regulation of metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism.
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
regulation of metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism.
regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
positive regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
regulation of cellular biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
positive regulation of cellular biosynthetic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
cellular nitrogen compound metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving various organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
cellular biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
nitrogen compound biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds.
regulation of nitric oxide biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of nitric oxide.
positive regulation of nitric oxide biosynthetic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of nitric oxide.
nitric oxide metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving nitric oxide, nitrogen monoxide (NO), a colorless gas only slightly soluble in water.
positive regulation of biological process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
positive regulation of cellular process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of cellular process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
regulation of nitrogen compound metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving nitrogen or nitrogenous compounds.
positive regulation of nitrogen compound metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving nitrogen or nitrogenous compounds.
biological regulation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of any biological process, quality or function.
regulation of biological quality
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological quality. A biological quality is a measurable attribute of an organism or part of an organism, such as size, mass, shape, color, etc.
all
This term is the most general term possible
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
positive regulation of metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism.
positive regulation of cellular process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
regulation of metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism.
positive regulation of biological process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of cellular process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
positive regulation of biosynthetic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances.
positive regulation of nitrogen compound metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving nitrogen or nitrogenous compounds.
regulation of biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances.
positive regulation of metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism.
regulation of nitrogen compound metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving nitrogen or nitrogenous compounds.
regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
positive regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
cellular nitrogen compound metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving various organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
positive regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
positive regulation of cellular process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
positive regulation of nitrogen compound metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving nitrogen or nitrogenous compounds.
positive regulation of biosynthetic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances.
regulation of cellular biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
positive regulation of cellular biosynthetic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
nitrogen compound biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds.
positive regulation of cellular biosynthetic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
positive regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
regulation of cellular biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
nitric oxide biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of nitric oxide, nitrogen monoxide (NO), a colorless gas only slightly soluble in water.
regulation of nitric oxide biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of nitric oxide.
positive regulation of nitric oxide biosynthetic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of nitric oxide.
positive regulation of nitric oxide biosynthetic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of nitric oxide.
positive regulation of cellular biosynthetic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
regulation of nitric oxide biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of nitric oxide.
positive regulation of nitric oxide biosynthetic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of nitric oxide.


ABCA1ATP-binding cassette, sub-family A (ABC1), member 1 (203504_s_at), score: 0.94 CDKN1Ccyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1C (p57, Kip2) (213348_at), score: 0.93 DHRS3dehydrogenase/reductase (SDR family) member 3 (202481_at), score: 0.82 INSRinsulin receptor (213792_s_at), score: 0.84 MXI1MAX interactor 1 (202364_at), score: 0.82 PELI2pellino homolog 2 (Drosophila) (219132_at), score: 0.81 SOD2superoxide dismutase 2, mitochondrial (221477_s_at), score: 1
| Id | sample | Experiment | ExpName | Array | Syndrome | Cell.line |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E-GEOD-4219-raw-cel-1311956614.cel | 18 | 7 | Sph-mono | hgu133plus2 | none | Sph-mon 1 |
| F055_WBS.CEL | 14 | 8 | WBS | hgu133plus2 | WBS | WBS 1 |
| E-GEOD-4219-raw-cel-1311956321.cel | 9 | 7 | Sph-mono | hgu133plus2 | none | Sph-mon 1 |
| 1Twin.CEL | 1 | 2 | DS-twin | hgu133plus2 | Down | DS-twin 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486371.cel | 37 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486031.cel | 20 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486131.cel | 25 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485811.cel | 9 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| 2Twin.CEL | 2 | 2 | DS-twin | hgu133plus2 | none | DS-twin 2 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485891.cel | 13 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485871.cel | 12 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-GEOD-4219-raw-cel-1311956138.cel | 4 | 7 | Sph-mono | hgu133plus2 | none | Sph-mon 1 |
| 5CTwin.CEL | 5 | 2 | DS-twin | hgu133plus2 | Down | DS-twin 5 |
| E-GEOD-3407-raw-cel-1437949854.cel | 7 | 4 | Cockayne | hgu133a | CS | eGFP |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486171.cel | 27 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| ctrl a 08-03.CEL | 1 | 1 | DS-CC | hgu133a | none | DS-CC 1 |
| ctrl c 08-03.CEL | 3 | 1 | DS-CC | hgu133a | none | DS-CC 3 |
| E-GEOD-4219-raw-cel-1311956398.cel | 12 | 7 | Sph-mono | hgu133plus2 | none | Sph-mon 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486231.cel | 30 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| ctrl b 08-03.CEL | 2 | 1 | DS-CC | hgu133a | none | DS-CC 2 |
| 1104_CNTL.CEL | 3 | 8 | WBS | hgu133plus2 | none | WBS 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486271.cel | 32 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| 3Twin.CEL | 3 | 2 | DS-twin | hgu133plus2 | Down | DS-twin 3 |
| t21c 08-03.CEL | 6 | 1 | DS-CC | hgu133a | Down | DS-CC 6 |
| E-GEOD-4219-raw-cel-1311956275.cel | 8 | 7 | Sph-mono | hgu133plus2 | none | Sph-mon 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486331.cel | 35 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| 4Twin.CEL | 4 | 2 | DS-twin | hgu133plus2 | none | DS-twin 4 |
| 8495_CNTL.CEL | 10 | 8 | WBS | hgu133plus2 | none | WBS 1 |
| 9118_CNTL.CEL | 11 | 8 | WBS | hgu133plus2 | none | WBS 1 |
| E-GEOD-3860-raw-cel-1561690376.cel | 13 | 5 | HGPS | hgu133a | HGPS | AG11513 |
| E-GEOD-4219-raw-cel-1311956418.cel | 13 | 7 | Sph-mono | hgu133plus2 | none | Sph-mon 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486291.cel | 33 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-GEOD-4219-raw-cel-1311956634.cel | 19 | 7 | Sph-mono | hgu133plus2 | none | Sph-mon 1 |
| E-GEOD-4219-raw-cel-1311956083.cel | 2 | 7 | Sph-mono | hgu133plus2 | none | Sph-mon 1 |