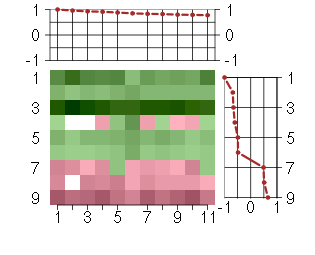

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

angiogenesis
Blood vessel formation when new vessels emerge from the proliferation of pre-existing blood vessels.
blood vessel development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the blood vessel over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The blood vessel is the vasculature carrying blood.
vasculature development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the vasculature over time, from its formation to the mature structure.
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
anatomical structure morphogenesis
The process by which anatomical structures are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
organ morphogenesis
Morphogenesis of an organ. An organ is defined as a tissue or set of tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Morphogenesis is the process by which anatomical structures are generated and organized. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
multicellular organismal process
Any biological process, occurring at the level of a multicellular organism, pertinent to its function.
developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an integrated living unit: an anatomical structure (which may be a subcellular structure, cell, tissue, or organ), or organism over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
organ development
Development of a tissue or tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Development pertains to the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a structure over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
blood vessel morphogenesis
The process by which the anatomical structures of blood vessels are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form. The blood vessel is the vasculature carrying blood.
anatomical structure formation
The process pertaining to the initial formation of an anatomical structure from unspecified parts. This process begins with the specific processes that contribute to the appearance of the discrete structure and ends when the structural rudiment is recognizable. An anatomical structure is any biological entity that occupies space and is distinguished from its surroundings. Anatomical structures can be macroscopic such as a carpel, or microscopic such as an acrosome.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
anatomical structure development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an anatomical structure from an initial condition to its mature state. This process begins with the formation of the structure and ends with the mature structure, whatever form that may be including its natural destruction. An anatomical structure is any biological entity that occupies space and is distinguished from its surroundings. Anatomical structures can be macroscopic such as a carpel, or microscopic such as an acrosome.
all
This term is the most general term possible
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
anatomical structure formation
The process pertaining to the initial formation of an anatomical structure from unspecified parts. This process begins with the specific processes that contribute to the appearance of the discrete structure and ends when the structural rudiment is recognizable. An anatomical structure is any biological entity that occupies space and is distinguished from its surroundings. Anatomical structures can be macroscopic such as a carpel, or microscopic such as an acrosome.
anatomical structure morphogenesis
The process by which anatomical structures are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
organ development
Development of a tissue or tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Development pertains to the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a structure over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
organ morphogenesis
Morphogenesis of an organ. An organ is defined as a tissue or set of tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Morphogenesis is the process by which anatomical structures are generated and organized. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
angiogenesis
Blood vessel formation when new vessels emerge from the proliferation of pre-existing blood vessels.
blood vessel morphogenesis
The process by which the anatomical structures of blood vessels are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form. The blood vessel is the vasculature carrying blood.


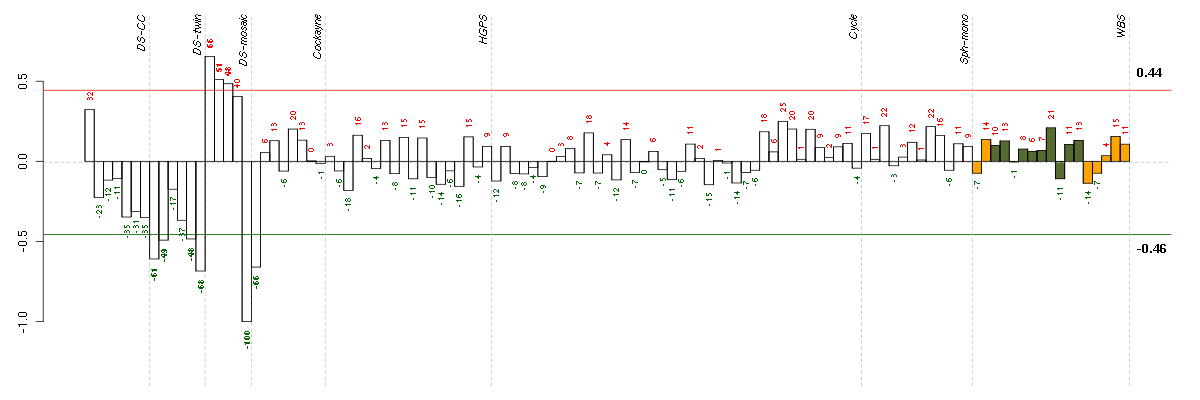
COL15A1collagen, type XV, alpha 1 (203477_at), score: 0.85 ERAP1endoplasmic reticulum aminopeptidase 1 (214012_at), score: 0.78 HHEXhematopoietically expressed homeobox (215933_s_at), score: 0.93 IL23Ainterleukin 23, alpha subunit p19 (211796_s_at), score: 0.79 NINJ1ninjurin 1 (203045_at), score: 0.82 PDLIM3PDZ and LIM domain 3 (209621_s_at), score: 0.83 PKP2plakophilin 2 (207717_s_at), score: 1 PTGDSprostaglandin D2 synthase 21kDa (brain) (212187_x_at), score: 0.88 SCARB1scavenger receptor class B, member 1 (201819_at), score: 0.91 SCG2secretogranin II (chromogranin C) (204035_at), score: 0.96 TM6SF1transmembrane 6 superfamily member 1 (219892_at), score: 0.8
| Id | sample | Experiment | ExpName | Array | Syndrome | Cell.line |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 47C.CEL | 5 | 3 | DS-mosaic | hgu133plus2 | Down mosaic | DS-mosaic 5 |
| 6Twin.CEL | 6 | 2 | DS-twin | hgu133plus2 | none | DS-twin 6 |
| E-GEOD-3407-raw-cel-1437949557.cel | 1 | 4 | Cockayne | hgu133a | CS | eGFP |
| 1Twin.CEL | 1 | 2 | DS-twin | hgu133plus2 | Down | DS-twin 1 |
| 2Twin.CEL | 2 | 2 | DS-twin | hgu133plus2 | none | DS-twin 2 |
| 5CTwin.CEL | 5 | 2 | DS-twin | hgu133plus2 | Down | DS-twin 5 |
| 46C.CEL | 3 | 3 | DS-mosaic | hgu133plus2 | none | DS-mosaic 3 |
| 46B.CEL | 2 | 3 | DS-mosaic | hgu133plus2 | none | DS-mosaic 2 |
| 46A.CEL | 1 | 3 | DS-mosaic | hgu133plus2 | none | DS-mosaic 1 |