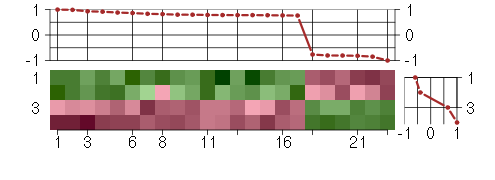

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways, including anabolism and catabolism, by which living organisms transform chemical substances. Metabolic processes typically transform small molecules, but also include macromolecular processes such as DNA repair and replication, and protein synthesis and degradation.
regulation of protein amino acid phosphorylation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of addition of phosphate groups into an amino acid in a protein.
positive regulation of protein amino acid phosphorylation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of addition of phosphate groups to amino acids within a protein.
signal transduction
The cascade of processes by which a signal interacts with a receptor, causing a change in the level or activity of a second messenger or other downstream target, and ultimately effecting a change in the functioning of the cell.
protein modification process
The covalent alteration of one or more amino acids occurring in proteins, peptides and nascent polypeptides (co-translational, post-translational modifications). Includes the modification of charged tRNAs that are destined to occur in a protein (pre-translation modification).
protein amino acid phosphorylation
The process of introducing a phosphate group on to a protein.
phosphorus metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving the nonmetallic element phosphorus or compounds that contain phosphorus, usually in the form of a phosphate group (PO4).
phosphate metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving the phosphate group, the anion or salt of any phosphoric acid.
cell communication
Any process that mediates interactions between a cell and its surroundings. Encompasses interactions such as signaling or attachment between one cell and another cell, between a cell and an extracellular matrix, or between a cell and any other aspect of its environment.
intracellular signaling cascade
A series of reactions within the cell that occur as a result of a single trigger reaction or compound.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
positive regulation of metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism.
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
positive regulation of phosphorus metabolic process
Any process that increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving phosphorus or compounds containing phosphorus.
positive regulation of macromolecule metabolic process
Any process that increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
phosphorylation
The process of introducing a phosphate group into a molecule, usually with the formation of a phosphoric ester, a phosphoric anhydride or a phosphoric amide.
peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation
The posttranslational phosphorylation of peptidyl-tyrosine to form peptidyl-O4'-phospho-L-tyrosine.
peptidyl-amino acid modification
The alteration of an amino acid residue in a peptide.
peptidyl-tyrosine modification
The modification of peptidyl-tyrosine.
regulation of phosphate metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving phosphates.
regulation of metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism.
protein metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving a specific protein, rather than of proteins in general. Includes protein modification.
regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
positive regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
regulation of protein modification process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the covalent alteration of one or more amino acid residues within a protein.
positive regulation of protein modification process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the covalent alteration of one or more amino acid residues within a protein.
regulation of cellular protein metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving a protein, occurring at the level of an individual cell.
positive regulation of cellular protein metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving a protein, occurring at the level of an individual cell.
cellular biopolymer metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature, such as polysaccharides and proteins, as carried out by individual cells.
regulation of phosphorylation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of addition of phosphate groups into a molecule.
positive regulation of phosphorylation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of addition of phosphate groups to a molecule.
macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
biopolymer metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature, such as polysaccharides and proteins.
biopolymer modification
The covalent alteration of one or more monomeric units in a polypeptide, polynucleotide, polysaccharide, or other biological polymer, resulting in a change in its properties.
post-translational protein modification
The covalent alteration of one or more amino acids occurring in a protein after the protein has been completely translated and released from the ribosome.
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
primary metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving those compounds which are formed as a part of the normal anabolic and catabolic processes. These processes take place in most, if not all, cells of the organism.
cellular macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular protein metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving a specific protein, rather than of proteins in general, occurring at the level of an individual cell. Includes protein modification.
positive regulation of phosphate metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving phosphates.
positive regulation of biological process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
positive regulation of cellular process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the phosphorylation of peptidyl-tyrosine.
positive regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the phosphorylation of peptidyl-tyrosine.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of cellular process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
regulation of phosphorus metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving phosphorus or compounds containing phosphorus.
regulation of protein metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving a protein.
positive regulation of protein metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving a protein.
regulation of macromolecule metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
biological regulation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of any biological process, quality or function.
all
This term is the most general term possible
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
positive regulation of metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism.
positive regulation of cellular process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
regulation of metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism.
positive regulation of biological process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of cellular process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
positive regulation of metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism.
positive regulation of macromolecule metabolic process
Any process that increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
regulation of macromolecule metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
positive regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
cellular macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, as carried out by individual cells.
positive regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
signal transduction
The cascade of processes by which a signal interacts with a receptor, causing a change in the level or activity of a second messenger or other downstream target, and ultimately effecting a change in the functioning of the cell.
regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
positive regulation of cellular process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
positive regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
positive regulation of macromolecule metabolic process
Any process that increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
protein metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving a specific protein, rather than of proteins in general. Includes protein modification.
cellular biopolymer metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature, such as polysaccharides and proteins, as carried out by individual cells.
positive regulation of phosphorus metabolic process
Any process that increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving phosphorus or compounds containing phosphorus.
regulation of phosphorus metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving phosphorus or compounds containing phosphorus.
regulation of protein metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving a protein.
positive regulation of protein metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving a protein.
positive regulation of cellular protein metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving a protein, occurring at the level of an individual cell.
positive regulation of cellular protein metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving a protein, occurring at the level of an individual cell.
positive regulation of phosphorus metabolic process
Any process that increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving phosphorus or compounds containing phosphorus.
regulation of cellular protein metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving a protein, occurring at the level of an individual cell.
positive regulation of protein metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving a protein.
cellular protein metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving a specific protein, rather than of proteins in general, occurring at the level of an individual cell. Includes protein modification.
regulation of phosphate metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving phosphates.
positive regulation of phosphate metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving phosphates.
protein modification process
The covalent alteration of one or more amino acids occurring in proteins, peptides and nascent polypeptides (co-translational, post-translational modifications). Includes the modification of charged tRNAs that are destined to occur in a protein (pre-translation modification).
regulation of cellular protein metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving a protein, occurring at the level of an individual cell.
positive regulation of cellular protein metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving a protein, occurring at the level of an individual cell.
positive regulation of protein modification process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the covalent alteration of one or more amino acid residues within a protein.
positive regulation of phosphate metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving phosphates.
regulation of protein modification process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the covalent alteration of one or more amino acid residues within a protein.
positive regulation of protein modification process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the covalent alteration of one or more amino acid residues within a protein.
regulation of phosphorylation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of addition of phosphate groups into a molecule.
positive regulation of phosphorylation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of addition of phosphate groups to a molecule.
positive regulation of protein amino acid phosphorylation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of addition of phosphate groups to amino acids within a protein.
positive regulation of protein amino acid phosphorylation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of addition of phosphate groups to amino acids within a protein.
regulation of protein amino acid phosphorylation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of addition of phosphate groups into an amino acid in a protein.
positive regulation of phosphorylation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of addition of phosphate groups to a molecule.
protein amino acid phosphorylation
The process of introducing a phosphate group on to a protein.
regulation of protein amino acid phosphorylation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of addition of phosphate groups into an amino acid in a protein.
positive regulation of protein amino acid phosphorylation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of addition of phosphate groups to amino acids within a protein.
positive regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the phosphorylation of peptidyl-tyrosine.
peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation
The posttranslational phosphorylation of peptidyl-tyrosine to form peptidyl-O4'-phospho-L-tyrosine.
regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the phosphorylation of peptidyl-tyrosine.
positive regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the phosphorylation of peptidyl-tyrosine.


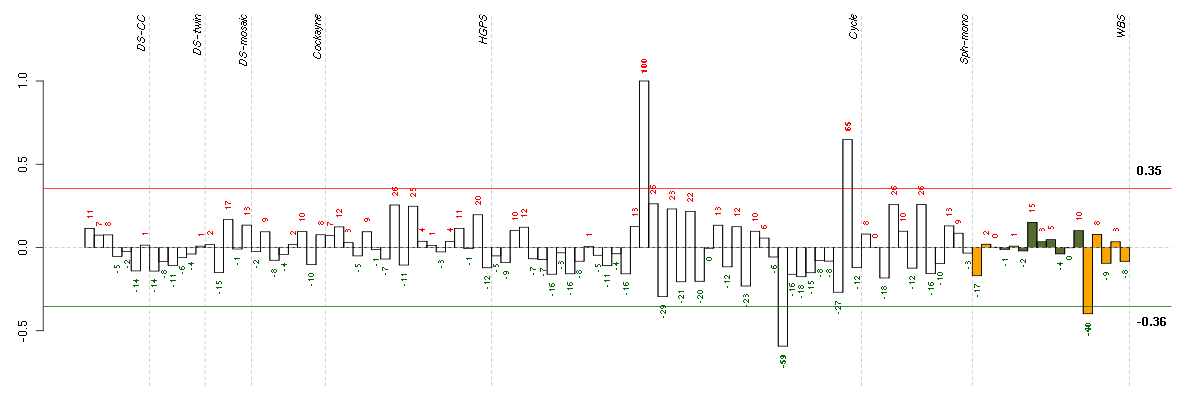
BAIAP2BAI1-associated protein 2 (209502_s_at), score: 0.78 BAZ2Bbromodomain adjacent to zinc finger domain, 2B (203080_s_at), score: -0.76 C16orf57chromosome 16 open reading frame 57 (218060_s_at), score: 0.91 CCNE1cyclin E1 (213523_at), score: 0.78 CDCA4cell division cycle associated 4 (218399_s_at), score: 0.82 CLCF1cardiotrophin-like cytokine factor 1 (219500_at), score: 0.78 CYTH1cytohesin 1 (202880_s_at), score: 0.8 FAM131Bfamily with sequence similarity 131, member B (205368_at), score: -0.8 FCER1AFc fragment of IgE, high affinity I, receptor for; alpha polypeptide (211734_s_at), score: -0.81 GIT1G protein-coupled receptor kinase interacting ArfGAP 1 (218030_at), score: 1 IPPKinositol 1,3,4,5,6-pentakisphosphate 2-kinase (219092_s_at), score: 0.93 KRTAP1-1keratin associated protein 1-1 (220976_s_at), score: 0.83 NEDD4Lneural precursor cell expressed, developmentally down-regulated 4-like (212445_s_at), score: 0.86 PHTF1putative homeodomain transcription factor 1 (215285_s_at), score: 0.79 RAB36RAB36, member RAS oncogene family (211471_s_at), score: 0.88 RHOBTB1Rho-related BTB domain containing 1 (212651_at), score: -0.85 RIPK1receptor (TNFRSF)-interacting serine-threonine kinase 1 (209941_at), score: 0.77 RPS6KA5ribosomal protein S6 kinase, 90kDa, polypeptide 5 (204633_s_at), score: 0.99 SHROOM2shroom family member 2 (204967_at), score: 0.8 SLC25A17solute carrier family 25 (mitochondrial carrier; peroxisomal membrane protein, 34kDa), member 17 (211754_s_at), score: 0.78 TNK2tyrosine kinase, non-receptor, 2 (203839_s_at), score: 0.76 ZFHX4zinc finger homeobox 4 (219779_at), score: -0.82 ZFYVE26zinc finger, FYVE domain containing 26 (37943_at), score: -1
| Id | sample | Experiment | ExpName | Array | Syndrome | Cell.line |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486271.cel | 32 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| D890_WBS.CEL | 13 | 8 | WBS | hgu133plus2 | WBS | WBS 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486411.cel | 39 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485971.cel | 17 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |