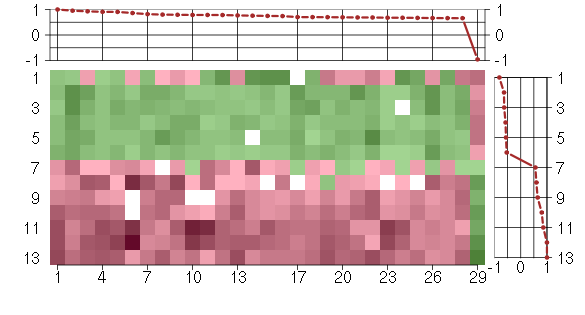

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

skeletal system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the skeleton over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The skeleton is the bony framework of the body in vertebrates (endoskeleton) or the hard outer envelope of insects (exoskeleton or dermoskeleton).
cell communication
Any process that mediates interactions between a cell and its surroundings. Encompasses interactions such as signaling or attachment between one cell and another cell, between a cell and an extracellular matrix, or between a cell and any other aspect of its environment.
cell-cell signaling
Any process that mediates the transfer of information from one cell to another.
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
tissue development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a tissue over time, from its formation to the mature structure.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
multicellular organismal process
Any biological process, occurring at the level of a multicellular organism, pertinent to its function.
developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an integrated living unit: an anatomical structure (which may be a subcellular structure, cell, tissue, or organ), or organism over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
organ development
Development of a tissue or tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Development pertains to the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a structure over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
anatomical structure development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an anatomical structure from an initial condition to its mature state. This process begins with the formation of the structure and ends with the mature structure, whatever form that may be including its natural destruction. An anatomical structure is any biological entity that occupies space and is distinguished from its surroundings. Anatomical structures can be macroscopic such as a carpel, or microscopic such as an acrosome.
cartilage development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the cartilage over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Cartilage is a connective tissue dominated by extracellular matrix containing collagen type II and large amounts of proteoglycan, particularly chondroitin sulfate.
all
This term is the most general term possible
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
organ development
Development of a tissue or tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Development pertains to the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a structure over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
tissue development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a tissue over time, from its formation to the mature structure.
cartilage development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the cartilage over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Cartilage is a connective tissue dominated by extracellular matrix containing collagen type II and large amounts of proteoglycan, particularly chondroitin sulfate.

extracellular region
The space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.
cellular_component
The part of a cell or its extracellular environment in which a gene product is located. A gene product may be located in one or more parts of a cell and its location may be as specific as a particular macromolecular complex, that is, a stable, persistent association of macromolecules that function together.
extracellular space
That part of a multicellular organism outside the cells proper, usually taken to be outside the plasma membranes, and occupied by fluid.
extracellular region part
Any constituent part of the extracellular region, the space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers constituent parts of the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.
all
This term is the most general term possible
extracellular region part
Any constituent part of the extracellular region, the space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers constituent parts of the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.

protein binding
Interacting selectively with any protein or protein complex (a complex of two or more proteins that may include other nonprotein molecules).
molecular_function
Elemental activities, such as catalysis or binding, describing the actions of a gene product at the molecular level. A given gene product may exhibit one or more molecular functions.
receptor binding
Interacting selectively with one or more specific sites on a receptor molecule, a macromolecule that undergoes combination with a hormone, neurotransmitter, drug or intracellular messenger to initiate a change in cell function.
cytokine activity
Functions to control the survival, growth, differentiation and effector function of tissues and cells.
binding
The selective, often stoichiometric, interaction of a molecule with one or more specific sites on another molecule.
growth factor activity
The function that stimulates a cell to grow or proliferate. Most growth factors have other actions besides the induction of cell growth or proliferation.
all
This term is the most general term possible
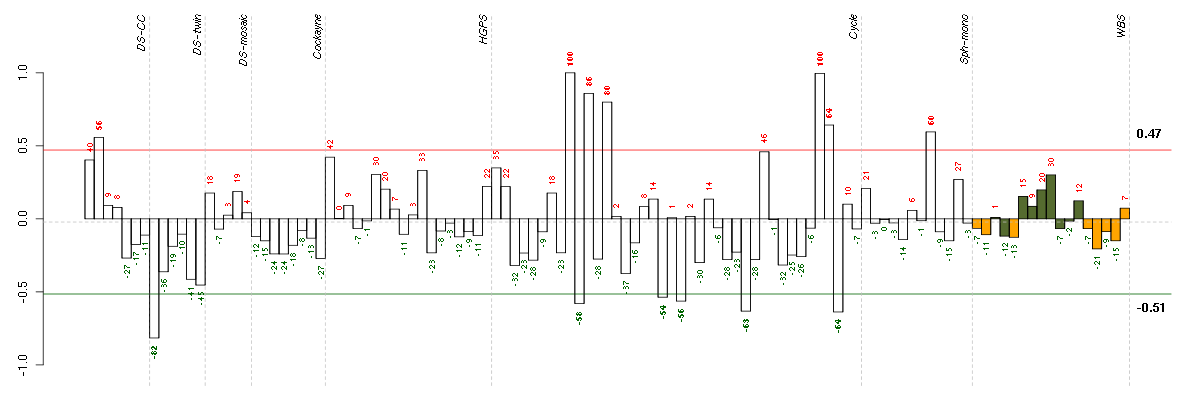
AHI1Abelson helper integration site 1 (221569_at), score: 0.66 AREGamphiregulin (205239_at), score: 0.86 BMP2bone morphogenetic protein 2 (205289_at), score: 0.79 BMP6bone morphogenetic protein 6 (206176_at), score: 1 CBLBCas-Br-M (murine) ecotropic retroviral transforming sequence b (209682_at), score: 0.7 CD55CD55 molecule, decay accelerating factor for complement (Cromer blood group) (201925_s_at), score: 0.7 COL5A3collagen, type V, alpha 3 (52255_s_at), score: 0.67 CXCL6chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 6 (granulocyte chemotactic protein 2) (206336_at), score: 0.82 DNAJB9DnaJ (Hsp40) homolog, subfamily B, member 9 (202843_at), score: 0.8 ENTPD7ectonucleoside triphosphate diphosphohydrolase 7 (220153_at), score: 0.68 ESM1endothelial cell-specific molecule 1 (208394_x_at), score: 0.69 FERMT1fermitin family homolog 1 (Drosophila) (218796_at), score: 0.7 FGF1fibroblast growth factor 1 (acidic) (205117_at), score: 0.75 FGF7fibroblast growth factor 7 (keratinocyte growth factor) (205782_at), score: 0.78 GKglycerol kinase (207387_s_at), score: 0.93 GK3Pglycerol kinase 3 pseudogene (215966_x_at), score: 0.77 GPR183G protein-coupled receptor 183 (205419_at), score: 0.79 GRB14growth factor receptor-bound protein 14 (206204_at), score: 0.69 HTR2A5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) receptor 2A (207135_at), score: 0.91 IL11interleukin 11 (206924_at), score: 0.74 IL1RL1interleukin 1 receptor-like 1 (207526_s_at), score: 0.76 IL33interleukin 33 (209821_at), score: 0.95 KAL1Kallmann syndrome 1 sequence (205206_at), score: 0.69 KLHL21kelch-like 21 (Drosophila) (203068_at), score: 0.67 MMP10matrix metallopeptidase 10 (stromelysin 2) (205680_at), score: 0.79 PIK3CDphosphoinositide-3-kinase, catalytic, delta polypeptide (203879_at), score: 0.68 PTHLHparathyroid hormone-like hormone (211756_at), score: 0.91 SERPINB2serpin peptidase inhibitor, clade B (ovalbumin), member 2 (204614_at), score: 0.66 TFDP2transcription factor Dp-2 (E2F dimerization partner 2) (203588_s_at), score: -0.96
| Id | sample | Experiment | ExpName | Array | Syndrome | Cell.line |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1Twin.CEL | 1 | 2 | DS-twin | hgu133plus2 | Down | DS-twin 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486391.cel | 38 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486191.cel | 28 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485831.cel | 10 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486051.cel | 21 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486011.cel | 19 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| ctrl b 08-03.CEL | 2 | 1 | DS-CC | hgu133a | none | DS-CC 2 |
| E-GEOD-4219-raw-cel-1311956418.cel | 13 | 7 | Sph-mono | hgu133plus2 | none | Sph-mon 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486371.cel | 37 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485891.cel | 13 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485851.cel | 11 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486351.cel | 36 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485811.cel | 9 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |