

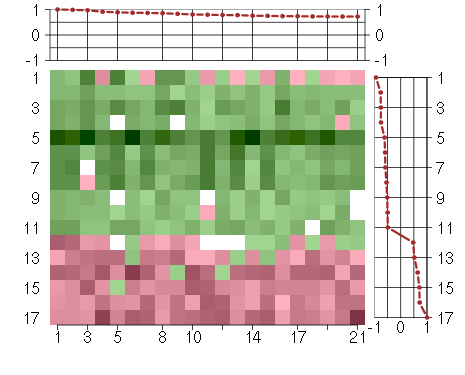

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

immune system process
Any process involved in the development or functioning of the immune system, an organismal system for calibrated responses to potential internal or invasive threats.
acute inflammatory response
Inflammation which comprises a rapid, short-lived, relatively uniform response to acute injury or antigenic challenge and is characterized by accumulations of fluid, plasma proteins, and granulocytic leukocytes. An acute inflammatory response occurs within a matter of minutes or hours, and either resolves within a few days or becomes a chronic inflammatory response.
monocyte chemotaxis
The movement of a monocyte in response to an external stimulus.
defense response
Reactions, triggered in response to the presence of a foreign body or the occurrence of an injury, which result in restriction of damage to the organism attacked or prevention/recovery from the infection caused by the attack.
cell motion
Any process involved in the controlled movement of a cell.
chemotaxis
The directed movement of a motile cell or organism, or the directed growth of a cell guided by a specific chemical concentration gradient. Movement may be towards a higher concentration (positive chemotaxis) or towards a lower concentration (negative chemotaxis).
response to stress
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a disturbance in organismal or cellular homeostasis, usually, but not necessarily, exogenous (e.g. temperature, humidity, ionizing radiation).
inflammatory response
The immediate defensive reaction (by vertebrate tissue) to infection or injury caused by chemical or physical agents. The process is characterized by local vasodilation, extravasation of plasma into intercellular spaces and accumulation of white blood cells and macrophages.
immune response
Any immune system process that functions in the calibrated response of an organism to a potential internal or invasive threat.
humoral immune response
An immune response mediated through a body fluid.
behavior
The specific actions or reactions of an organism in response to external or internal stimuli. Patterned activity of a whole organism in a manner dependent upon some combination of that organism's internal state and external conditions.
locomotory behavior
The specific movement from place to place of an organism in response to external or internal stimuli. Locomotion of a whole organism in a manner dependent upon some combination of that organism's internal state and external conditions.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
response to external stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an external stimulus.
response to wounding
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus indicating damage to the organism.
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
cell migration
The orderly movement of cells from one site to another, often during the development of a multicellular organism or multicellular structure.
leukocyte chemotaxis
The movement of a leukocyte in response to an external stimulus.
locomotion
Self-propelled movement of a cell or organism from one location to another.
response to chemical stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a chemical stimulus.
taxis
The directed movement of a motile cell or organism in response to an external stimulus.
positive regulation of biological process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of response to stimulus
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a response to a stimulus. Response to stimulus is a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
positive regulation of response to stimulus
Any process that activates, maintains or increases the rate of a response to a stimulus. Response to stimulus is a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
cell motility
Any process involved in the controlled movement of a cell that results in translocation of the cell from one place to another.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
response to stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
leukocyte migration
The movement of leukocytes within or between different tissues and organs of the body.
localization
Any process by which a cell, a substance, or a cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, is transported to, and/or maintained in a specific location.
localization of cell
Any process by which a cell is transported to, and/or maintained in, a specific location.
cell chemotaxis
The directed movement of a motile cell guided by a specific chemical concentration gradient. Movement may be towards a higher concentration (positive chemotaxis) or towards a lower concentration (negative chemotaxis).
biological regulation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of any biological process, quality or function.
all
This term is the most general term possible
positive regulation of biological process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
immune response
Any immune system process that functions in the calibrated response of an organism to a potential internal or invasive threat.
regulation of response to stimulus
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a response to a stimulus. Response to stimulus is a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
positive regulation of response to stimulus
Any process that activates, maintains or increases the rate of a response to a stimulus. Response to stimulus is a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
cell motility
Any process involved in the controlled movement of a cell that results in translocation of the cell from one place to another.
positive regulation of response to stimulus
Any process that activates, maintains or increases the rate of a response to a stimulus. Response to stimulus is a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
response to wounding
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus indicating damage to the organism.
taxis
The directed movement of a motile cell or organism in response to an external stimulus.
chemotaxis
The directed movement of a motile cell or organism, or the directed growth of a cell guided by a specific chemical concentration gradient. Movement may be towards a higher concentration (positive chemotaxis) or towards a lower concentration (negative chemotaxis).
cell motion
Any process involved in the controlled movement of a cell.
cell chemotaxis
The directed movement of a motile cell guided by a specific chemical concentration gradient. Movement may be towards a higher concentration (positive chemotaxis) or towards a lower concentration (negative chemotaxis).
leukocyte migration
The movement of leukocytes within or between different tissues and organs of the body.
leukocyte chemotaxis
The movement of a leukocyte in response to an external stimulus.
inflammatory response
The immediate defensive reaction (by vertebrate tissue) to infection or injury caused by chemical or physical agents. The process is characterized by local vasodilation, extravasation of plasma into intercellular spaces and accumulation of white blood cells and macrophages.
taxis
The directed movement of a motile cell or organism in response to an external stimulus.

extracellular region
The space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.
cellular_component
The part of a cell or its extracellular environment in which a gene product is located. A gene product may be located in one or more parts of a cell and its location may be as specific as a particular macromolecular complex, that is, a stable, persistent association of macromolecules that function together.
extracellular space
That part of a multicellular organism outside the cells proper, usually taken to be outside the plasma membranes, and occupied by fluid.
extracellular region part
Any constituent part of the extracellular region, the space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers constituent parts of the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.
all
This term is the most general term possible
extracellular region part
Any constituent part of the extracellular region, the space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers constituent parts of the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.

CADPS2Ca++-dependent secretion activator 2 (219572_at), score: 0.81 CCL2chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 2 (216598_s_at), score: 0.89 CD200CD200 molecule (209583_s_at), score: 0.72 CFHcomplement factor H (213800_at), score: 0.91 CFHR1complement factor H-related 1 (215388_s_at), score: 0.87 COL15A1collagen, type XV, alpha 1 (203477_at), score: 0.97 CREG1cellular repressor of E1A-stimulated genes 1 (201200_at), score: 0.74 DDX3YDEAD (Asp-Glu-Ala-Asp) box polypeptide 3, Y-linked (205000_at), score: 0.99 EIF1AYeukaryotic translation initiation factor 1A, Y-linked (204409_s_at), score: 0.74 IL6interleukin 6 (interferon, beta 2) (205207_at), score: 0.85 IL8interleukin 8 (202859_x_at), score: 0.83 JARID1Djumonji, AT rich interactive domain 1D (206700_s_at), score: 0.72 KIAA0247KIAA0247 (202181_at), score: 0.73 LGALS3BPlectin, galactoside-binding, soluble, 3 binding protein (200923_at), score: 0.78 LIPGlipase, endothelial (219181_at), score: 0.8 LYPD1LY6/PLAUR domain containing 1 (212909_at), score: 0.75 MTSS1metastasis suppressor 1 (203037_s_at), score: 0.76 PKP2plakophilin 2 (207717_s_at), score: 0.87 RPS4Y1ribosomal protein S4, Y-linked 1 (201909_at), score: 1 SLC39A8solute carrier family 39 (zinc transporter), member 8 (209267_s_at), score: 0.78 TNFAIP8tumor necrosis factor, alpha-induced protein 8 (210260_s_at), score: 0.72
| Id | sample | Experiment | ExpName | Array | Syndrome | Cell.line |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1Twin.CEL | 1 | 2 | DS-twin | hgu133plus2 | Down | DS-twin 1 |
| 5CTwin.CEL | 5 | 2 | DS-twin | hgu133plus2 | Down | DS-twin 5 |
| 2Twin.CEL | 2 | 2 | DS-twin | hgu133plus2 | none | DS-twin 2 |
| 6Twin.CEL | 6 | 2 | DS-twin | hgu133plus2 | none | DS-twin 6 |
| E-GEOD-3407-raw-cel-1437949557.cel | 1 | 4 | Cockayne | hgu133a | CS | eGFP |
| E-GEOD-3860-raw-cel-1561690472.cel | 17 | 5 | HGPS | hgu133a | none | GM00038C |
| E-GEOD-3860-raw-cel-1561690223.cel | 3 | 5 | HGPS | hgu133a | none | GM00038C |
| E-GEOD-3860-raw-cel-1561690344.cel | 10 | 5 | HGPS | hgu133a | none | GM00038C |
| t21b 08-03.CEL | 5 | 1 | DS-CC | hgu133a | Down | DS-CC 5 |
| t21d 08-03.CEL | 7 | 1 | DS-CC | hgu133a | Down | DS-CC 7 |
| E-GEOD-3860-raw-cel-1561690215.cel | 2 | 5 | HGPS | hgu133a | HGPS | AG11513 |
| ctrl c 08-03.CEL | 3 | 1 | DS-CC | hgu133a | none | DS-CC 3 |
| E-GEOD-4219-raw-cel-1311956418.cel | 13 | 7 | Sph-mono | hgu133plus2 | none | Sph-mon 1 |
| 46A.CEL | 1 | 3 | DS-mosaic | hgu133plus2 | none | DS-mosaic 1 |
| E-GEOD-3860-raw-cel-1561690352.cel | 11 | 5 | HGPS | hgu133a | HGPS | AG11498 |
| E-GEOD-3860-raw-cel-1561690272.cel | 7 | 5 | HGPS | hgu133a | HGPS | AG11498 |
| E-GEOD-3860-raw-cel-1561690480.cel | 18 | 5 | HGPS | hgu133a | HGPS | AG11498 |
