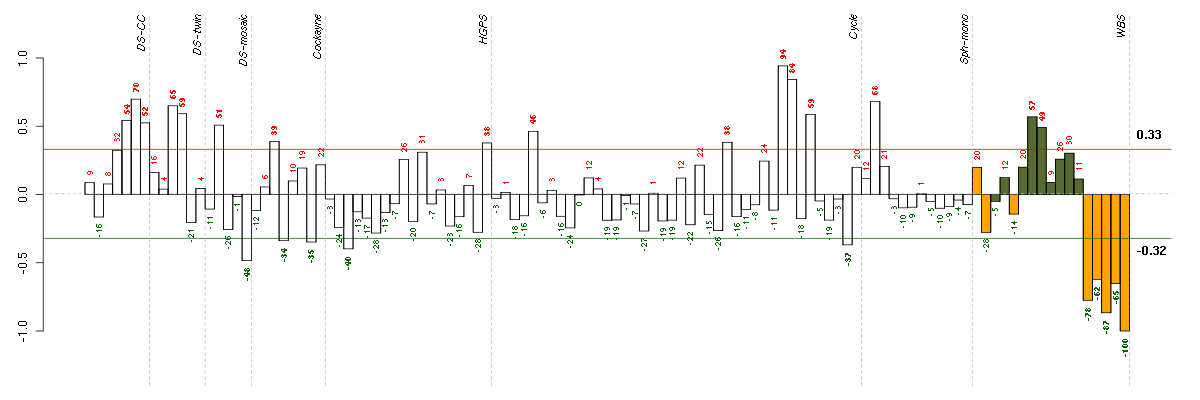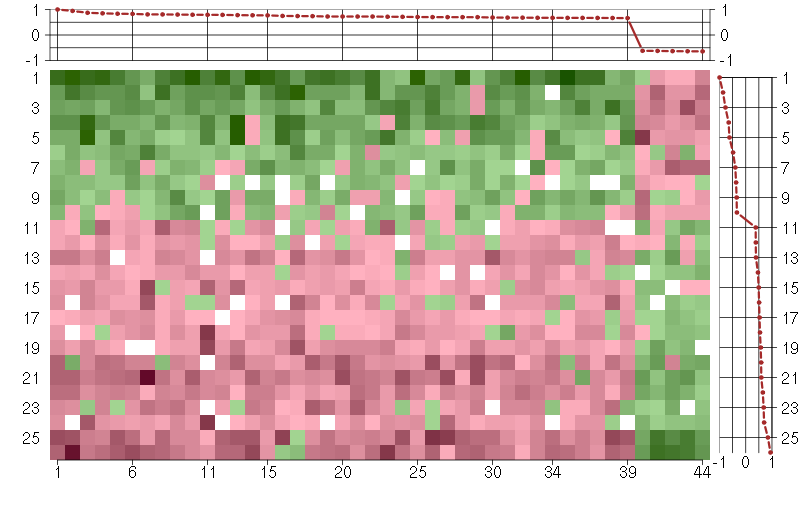

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

sulfur amino acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving amino acids containing sulfur, comprising cysteine, homocysteine, methionine and selenocysteine.
sulfur amino acid biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of amino acids containing sulfur, comprising cysteine, methionine and selenocysteine.
sulfur metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving the nonmetallic element sulfur or compounds that contain sulfur, such as the amino acids methionine and cysteine or the tripeptide glutathione.
metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways, including anabolism and catabolism, by which living organisms transform chemical substances. Metabolic processes typically transform small molecules, but also include macromolecular processes such as DNA repair and replication, and protein synthesis and degradation.
organic acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving organic acids, any acidic compound containing carbon in covalent linkage.
cellular amino acid and derivative metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving amino acids, organic acids containing one or more amino substituents, and compounds derived from amino acids, as carried out by individual cells.
amino acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving amino acids, organic acids containing one or more amino substituents.
cysteine metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving cysteine, 2-amino-3-mercaptopropanoic acid.
nitrogen compound metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving various organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds; includes nitrogen fixation, nitrification, denitrification, assimilatory/dissimilatory nitrate reduction and the interconversion of nitrogenous organic matter and ammonium.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
amino acid biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of amino acids, organic acids containing one or more amino substituents.
biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances; typically the energy-requiring part of metabolism in which simpler substances are transformed into more complex ones.
serine family amino acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving amino acids of the serine family, comprising cysteine, glycine, homoserine, selenocysteine and serine.
serine family amino acid biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of amino acids of the serine family, comprising cysteine, glycine, homoserine, selenocysteine and serine.
cellular amine metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving any organic compound that is weakly basic in character and contains an amino or a substituted amino group, as carried out by individual cells. Amines are called primary, secondary, or tertiary according to whether one, two, or three carbon atoms are attached to the nitrogen atom.
amine biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of any organic compound that is weakly basic in character and contains an amino or a substituted amino group. Amines are called primary, secondary, or tertiary according to whether one, two, or three carbon atoms are attached to the nitrogen atom.
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
cysteine biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of cysteine, 2-amino-3-mercaptopropanoic acid.
carboxylic acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving carboxylic acids, any organic acid containing one or more carboxyl (COOH) groups or anions (COO-).
cellular nitrogen compound metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving various organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
primary metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving those compounds which are formed as a part of the normal anabolic and catabolic processes. These processes take place in most, if not all, cells of the organism.
cellular biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
nitrogen compound biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds.
sulfur compound biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of compounds that contain sulfur, such as the amino acids methionine and cysteine or the tripeptide glutathione.
all
This term is the most general term possible
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
cellular nitrogen compound metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving various organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
cellular amino acid and derivative metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving amino acids, organic acids containing one or more amino substituents, and compounds derived from amino acids, as carried out by individual cells.
nitrogen compound biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds.
sulfur compound biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of compounds that contain sulfur, such as the amino acids methionine and cysteine or the tripeptide glutathione.
amino acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving amino acids, organic acids containing one or more amino substituents.
amine biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of any organic compound that is weakly basic in character and contains an amino or a substituted amino group. Amines are called primary, secondary, or tertiary according to whether one, two, or three carbon atoms are attached to the nitrogen atom.
sulfur amino acid biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of amino acids containing sulfur, comprising cysteine, methionine and selenocysteine.
amino acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving amino acids, organic acids containing one or more amino substituents.
sulfur amino acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving amino acids containing sulfur, comprising cysteine, homocysteine, methionine and selenocysteine.
amino acid biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of amino acids, organic acids containing one or more amino substituents.
cysteine biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of cysteine, 2-amino-3-mercaptopropanoic acid.
sulfur amino acid biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of amino acids containing sulfur, comprising cysteine, methionine and selenocysteine.
cysteine metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving cysteine, 2-amino-3-mercaptopropanoic acid.
serine family amino acid biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of amino acids of the serine family, comprising cysteine, glycine, homoserine, selenocysteine and serine.
cysteine biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of cysteine, 2-amino-3-mercaptopropanoic acid.


molecular_function
Elemental activities, such as catalysis or binding, describing the actions of a gene product at the molecular level. A given gene product may exhibit one or more molecular functions.
catalytic activity
Catalysis of a biochemical reaction at physiological temperatures. In biologically catalyzed reactions, the reactants are known as substrates, and the catalysts are naturally occurring macromolecular substances known as enzymes. Enzymes possess specific binding sites for substrates, and are usually composed wholly or largely of protein, but RNA that has catalytic activity (ribozyme) is often also regarded as enzymatic.
binding
The selective, often stoichiometric, interaction of a molecule with one or more specific sites on another molecule.
steroid binding
Interacting selectively with a steroid, any of a large group of substances that have in common a ring system based on 1,2-cyclopentanoperhydrophenanthrene.
lipid binding
Interacting selectively with a lipid.
lyase activity
Catalysis of the cleavage of C-C, C-O, C-N and other bonds by other means than by hydrolysis or oxidation, or conversely adding a group to a double bond. They differ from other enzymes in that two substrates are involved in one reaction direction, but only one in the other direction. When acting on the single substrate, a molecule is eliminated and this generates either a new double bond or a new ring.
vitamin binding
Interacting selectively with a vitamin, one of a number of unrelated organic substances that occur in many foods in small amounts and that are necessary in trace amounts for the normal metabolic functioning of the body.
pyridoxal phosphate binding
Interacting selectively with pyridoxal 5' phosphate, 3-hydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)-2-methyl4-pyridine carboxaldehyde 5' phosphate, the biologically active form of vitamin B6.
cofactor binding
Interacting selectively with a cofactor, a substance that is required for the activity of an enzyme or other protein. Cofactors may be inorganic, such as the metal atoms zinc, iron, and copper in certain forms, or organic, in which case they are referred to as coenzymes. Cofactors may either be bound tightly to active sites or bind loosely with the substrate.
vitamin B6 binding
Interacting selectively with any of the vitamin B6 compounds: pyridoxal, pyridoxamine and pyridoxine and the active form, pyridoxal phosphate.
all
This term is the most general term possible
vitamin B6 binding
Interacting selectively with any of the vitamin B6 compounds: pyridoxal, pyridoxamine and pyridoxine and the active form, pyridoxal phosphate.
pyridoxal phosphate binding
Interacting selectively with pyridoxal 5' phosphate, 3-hydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)-2-methyl4-pyridine carboxaldehyde 5' phosphate, the biologically active form of vitamin B6.
| Id | Pvalue | ExpCount | Count | Size | Term |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 00260 | 2.017e-03 | 0.1651 | 4 | 25 | Glycine, serine and threonine metabolism |
APOL6apolipoprotein L, 6 (219716_at), score: 0.67 ARHGAP26Rho GTPase activating protein 26 (205068_s_at), score: 0.7 ARHGEF2rho/rac guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) 2 (209435_s_at), score: 0.77 ARNTL2aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator-like 2 (220658_s_at), score: -0.62 ASNSasparagine synthetase (205047_s_at), score: 0.8 ATF4activating transcription factor 4 (tax-responsive enhancer element B67) (200779_at), score: 0.83 C9orf91chromosome 9 open reading frame 91 (221865_at), score: 0.72 CBScystathionine-beta-synthase (212816_s_at), score: 0.7 CEBPGCCAAT/enhancer binding protein (C/EBP), gamma (204203_at), score: 0.85 CHAC1ChaC, cation transport regulator homolog 1 (E. coli) (219270_at), score: 0.67 CSTAcystatin A (stefin A) (204971_at), score: 0.69 CTHcystathionase (cystathionine gamma-lyase) (217127_at), score: 0.74 DAPK1death-associated protein kinase 1 (203139_at), score: 0.7 DDIT3DNA-damage-inducible transcript 3 (209383_at), score: 0.94 DDIT4DNA-damage-inducible transcript 4 (202887_s_at), score: 0.81 DOCK10dedicator of cytokinesis 10 (219279_at), score: -0.64 EGFL6EGF-like-domain, multiple 6 (219454_at), score: 0.75 EIF4EBP1eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E binding protein 1 (221539_at), score: 0.71 ENPP1ectonucleotide pyrophosphatase/phosphodiesterase 1 (205066_s_at), score: -0.64 FAM129Afamily with sequence similarity 129, member A (217966_s_at), score: 0.73 FGF5fibroblast growth factor 5 (210310_s_at), score: -0.62 FGF9fibroblast growth factor 9 (glia-activating factor) (206404_at), score: 0.78 FLGfilaggrin (215704_at), score: 0.79 FMODfibromodulin (202709_at), score: 0.71 GDF15growth differentiation factor 15 (221577_x_at), score: 0.83 GOLSYNGolgi-localized protein (218692_at), score: 0.87 GOT1glutamic-oxaloacetic transaminase 1, soluble (aspartate aminotransferase 1) (208813_at), score: 0.68 HERPUD1homocysteine-inducible, endoplasmic reticulum stress-inducible, ubiquitin-like domain member 1 (217168_s_at), score: 0.72 INHBEinhibin, beta E (210587_at), score: 0.81 LOC100132540similar to LOC339047 protein (214870_x_at), score: 0.66 MOCOSmolybdenum cofactor sulfurase (219959_at), score: 0.67 MTHFD2methylenetetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase (NADP+ dependent) 2, methenyltetrahydrofolate cyclohydrolase (201761_at), score: 0.77 NET1neuroepithelial cell transforming 1 (201830_s_at), score: -0.63 PALMparalemmin (203859_s_at), score: 0.7 PAPPA2pappalysin 2 (213332_at), score: 0.74 PCK2phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase 2 (mitochondrial) (202847_at), score: 0.79 PGPEP1pyroglutamyl-peptidase I (219891_at), score: 0.72 PSAT1phosphoserine aminotransferase 1 (220892_s_at), score: 0.67 SLC1A4solute carrier family 1 (glutamate/neutral amino acid transporter), member 4 (209610_s_at), score: 0.68 SLC3A2solute carrier family 3 (activators of dibasic and neutral amino acid transport), member 2 (200924_s_at), score: 0.79 STACSH3 and cysteine rich domain (205743_at), score: 0.72 TARSthreonyl-tRNA synthetase (201263_at), score: 0.67 TRIB3tribbles homolog 3 (Drosophila) (218145_at), score: 1 XPOTexportin, tRNA (nuclear export receptor for tRNAs) (212160_at), score: 0.68
| Id | sample | Experiment | ExpName | Array | Syndrome | Cell.line |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H652_WBS.CEL | 17 | 8 | WBS | hgu133plus2 | WBS | WBS 1 |
| F223_WBS.CEL | 15 | 8 | WBS | hgu133plus2 | WBS | WBS 1 |
| D890_WBS.CEL | 13 | 8 | WBS | hgu133plus2 | WBS | WBS 1 |
| F348_WBS.CEL | 16 | 8 | WBS | hgu133plus2 | WBS | WBS 1 |
| F055_WBS.CEL | 14 | 8 | WBS | hgu133plus2 | WBS | WBS 1 |
| 47C.CEL | 5 | 3 | DS-mosaic | hgu133plus2 | Down mosaic | DS-mosaic 5 |
| E-GEOD-3860-raw-cel-1561690223.cel | 3 | 5 | HGPS | hgu133a | none | GM00038C |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486411.cel | 39 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-GEOD-3407-raw-cel-1437949854.cel | 7 | 4 | Cockayne | hgu133a | CS | eGFP |
| E-GEOD-3407-raw-cel-1437949704.cel | 4 | 4 | Cockayne | hgu133a | CS | eGFP |
| E-GEOD-3860-raw-cel-1561690480.cel | 18 | 5 | HGPS | hgu133a | HGPS | AG11498 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486151.cel | 26 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-GEOD-3407-raw-cel-1437949655.cel | 3 | 4 | Cockayne | hgu133a | none | CSB |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485731.cel | 5 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| 5850_CNTL.CEL | 8 | 8 | WBS | hgu133plus2 | none | WBS 1 |
| 46B.CEL | 2 | 3 | DS-mosaic | hgu133plus2 | none | DS-mosaic 2 |
| t21d 08-03.CEL | 7 | 1 | DS-CC | hgu133a | Down | DS-CC 7 |
| t21b 08-03.CEL | 5 | 1 | DS-CC | hgu133a | Down | DS-CC 5 |
| 5290_CNTL.CEL | 7 | 8 | WBS | hgu133plus2 | none | WBS 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486331.cel | 35 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| 4Twin.CEL | 4 | 2 | DS-twin | hgu133plus2 | none | DS-twin 4 |
| 3Twin.CEL | 3 | 2 | DS-twin | hgu133plus2 | Down | DS-twin 3 |
| E-GEOD-4219-raw-cel-1311956138.cel | 4 | 7 | Sph-mono | hgu133plus2 | none | Sph-mon 1 |
| t21c 08-03.CEL | 6 | 1 | DS-CC | hgu133a | Down | DS-CC 6 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486291.cel | 33 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486271.cel | 32 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |