
Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways, including anabolism and catabolism, by which living organisms transform chemical substances. Metabolic processes typically transform small molecules, but also include macromolecular processes such as DNA repair and replication, and protein synthesis and degradation.
xenobiotic metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving a xenobiotic compound, a compound foreign to living organisms. Used of chemical compounds, e.g. a xenobiotic chemical, such as a pesticide.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
response to xenobiotic stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a xenobiotic compound stimulus. Xenobiotic compounds are compounds foreign to living organisms.
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
response to chemical stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a chemical stimulus.
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
response to stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
all
This term is the most general term possible
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
xenobiotic metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving a xenobiotic compound, a compound foreign to living organisms. Used of chemical compounds, e.g. a xenobiotic chemical, such as a pesticide.


molecular_function
Elemental activities, such as catalysis or binding, describing the actions of a gene product at the molecular level. A given gene product may exhibit one or more molecular functions.
ATPase activity, coupled
Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + H2O = ADP + phosphate to directly drive some other reaction, for example ion transport across a membrane.
catalytic activity
Catalysis of a biochemical reaction at physiological temperatures. In biologically catalyzed reactions, the reactants are known as substrates, and the catalysts are naturally occurring macromolecular substances known as enzymes. Enzymes possess specific binding sites for substrates, and are usually composed wholly or largely of protein, but RNA that has catalytic activity (ribozyme) is often also regarded as enzymatic.
ATPase activity, coupled to transmembrane movement of substances
Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + H2O = ADP + phosphate to directly drive the active transport of a substance across a membrane.
nucleoside-triphosphatase activity
Catalysis of the reaction: a nucleoside triphosphate + H2O = nucleoside diphosphate + phosphate.
transporter activity
Enables the directed movement of substances (such as macromolecules, small molecules, ions) into, out of, within or between cells.
transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a substance from one side of a membrane to the other.
UDP-glycosyltransferase activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a glycosyl group from a UDP-sugar to a small hydrophobic molecule.
xenobiotic-transporting ATPase activity
Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + H2O + xenobiotic(in) = ADP + phosphate + xenobiotic(out).
ATPase activity
Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + H2O = ADP + phosphate. May or may not be coupled to another reaction.
glucuronosyltransferase activity
Catalysis of the reaction: UDP-glucuronate + acceptor = UDP + acceptor beta-D-glucuronoside.
drug transporter activity
Enables the directed movement of a drug into, out of, within or between cells. A drug is any naturally occurring or synthetic substance, other than a nutrient, that, when administered or applied to an organism, affects the structure or functioning of the organism; in particular, any such substance used in the diagnosis, prevention, or treatment of disease.
multidrug transporter activity
Enables the directed movement of drugs across a membrane into, out of, within or between cells.
primary active transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a solute from one side of the membrane to the other, up the solute's concentration gradient, by binding the solute and undergoing a series of conformational changes. Transport works equally well in either direction and is powered by a primary energy source. Primary energy sources known to be coupled to transport are chemical, electrical and solar sources.
P-P-bond-hydrolysis-driven transmembrane transporter activity
Primary active transport of a solute across a membrane, driven by the hydrolysis of the diphosphate bond of inorganic pyrophosphate, ATP, or another nucleoside triphosphate. The transport protein may or may not be transiently phosphorylated, but the substrate is not phosphorylated. Primary active transport is catalysis of the transport of a solute across a membrane, up the solute's concentration gradient, by binding the solute and undergoing a series of conformational changes. Transport works equally well in either direction and is driven by a primary energy source.
pyrophosphatase activity
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of a pyrophosphate bond between two phosphate groups, leaving one phosphate on each of the two fragments.
transferase activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a group, e.g. a methyl group, glycosyl group, acyl group, phosphorus-containing, or other groups, from one compound (generally regarded as the donor) to another compound (generally regarded as the acceptor). Transferase is the systematic name for any enzyme of EC class 2.
transferase activity, transferring glycosyl groups
Catalysis of the transfer of a glycosyl group from one compound (donor) to another (acceptor).
transferase activity, transferring hexosyl groups
Catalysis of the transfer of a hexosyl group from one compound (donor) to another (acceptor).
hydrolase activity
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of various bonds, e.g. C-O, C-N, C-C, phosphoric anhydride bonds, etc. Hydrolase is the systematic name for any enzyme of EC class 3.
hydrolase activity, acting on acid anhydrides
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of any acid anhydride.
hydrolase activity, acting on acid anhydrides, in phosphorus-containing anhydrides
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of any acid anhydride which contains phosphorus.
hydrolase activity, acting on acid anhydrides, catalyzing transmembrane movement of substances
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of an acid anhydride to directly drive the transport of a substance across a membrane.
active transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a specific substance or related group of substances from one side of a membrane to the other, up the solute's concentration gradient. The transporter binds the solute and undergoes a series of conformational changes. Transport works equally well in either direction.
xenobiotic transporter activity
Enables the directed movement of a xenobiotic, a compound foreign to living organisms, into, out of, within or between cells.
ATPase activity, coupled to movement of substances
Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + H2O = ADP + phosphate to directly drive the transport of a substance.
all
This term is the most general term possible
multidrug transporter activity
Enables the directed movement of drugs across a membrane into, out of, within or between cells.
hydrolase activity, acting on acid anhydrides, catalyzing transmembrane movement of substances
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of an acid anhydride to directly drive the transport of a substance across a membrane.
xenobiotic-transporting ATPase activity
Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + H2O + xenobiotic(in) = ADP + phosphate + xenobiotic(out).
glucuronosyltransferase activity
Catalysis of the reaction: UDP-glucuronate + acceptor = UDP + acceptor beta-D-glucuronoside.
xenobiotic-transporting ATPase activity
Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + H2O + xenobiotic(in) = ADP + phosphate + xenobiotic(out).
ATPase activity, coupled to transmembrane movement of substances
Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + H2O = ADP + phosphate to directly drive the active transport of a substance across a membrane.
ATPase activity, coupled to transmembrane movement of substances
Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + H2O = ADP + phosphate to directly drive the active transport of a substance across a membrane.
| Id | Pvalue | ExpCount | Count | Size | Term |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 00040 | 3.466e-03 | 0.06676 | 3 | 13 | Pentose and glucuronate interconversions |
| 00150 | 1.223e-02 | 0.1079 | 3 | 21 | Androgen and estrogen metabolism |
| 00830 | 1.509e-02 | 0.1181 | 3 | 23 | Retinol metabolism |
| 00500 | 1.655e-02 | 0.1233 | 3 | 24 | Starch and sucrose metabolism |
| 00860 | 1.655e-02 | 0.1233 | 3 | 24 | Porphyrin and chlorophyll metabolism |
| 00983 | 2.499e-02 | 0.1489 | 3 | 29 | Drug metabolism - other enzymes |
| 00982 | 4.112e-02 | 0.1849 | 3 | 36 | Drug metabolism - cytochrome P450 |
| 00980 | 4.365e-02 | 0.19 | 3 | 37 | Metabolism of xenobiotics by cytochrome P450 |
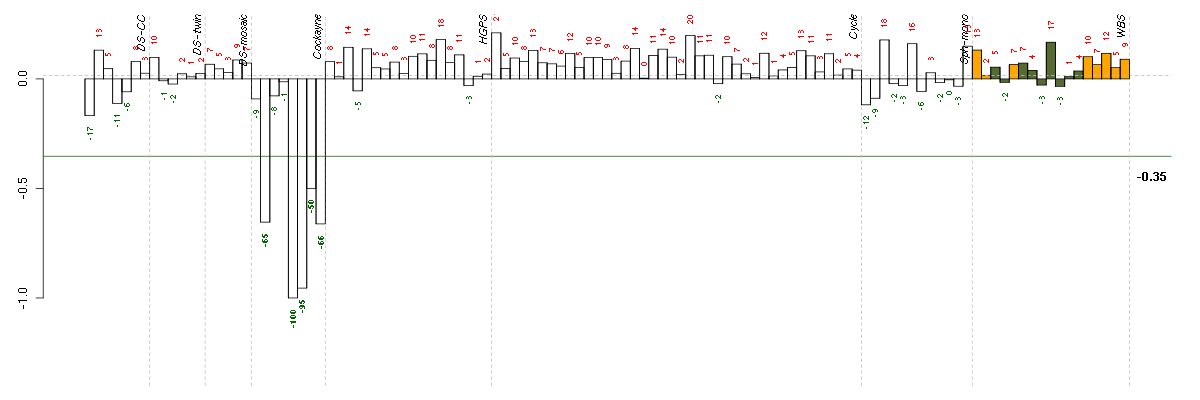
ABCB1ATP-binding cassette, sub-family B (MDR/TAP), member 1 (209993_at), score: -1 ABCB4ATP-binding cassette, sub-family B (MDR/TAP), member 4 (207819_s_at), score: -0.64 AIM2absent in melanoma 2 (206513_at), score: -0.62 ATP6V1B2ATPase, H+ transporting, lysosomal 56/58kDa, V1 subunit B2 (201089_at), score: -0.59 C5orf30chromosome 5 open reading frame 30 (221823_at), score: 0.52 CA3carbonic anhydrase III, muscle specific (204865_at), score: -0.61 CDR2Lcerebellar degeneration-related protein 2-like (213230_at), score: 0.54 CRTAPcartilage associated protein (201380_at), score: 0.57 DDX17DEAD (Asp-Glu-Ala-Asp) box polypeptide 17 (208151_x_at), score: -0.67 DIO2deiodinase, iodothyronine, type II (203699_s_at), score: -0.8 EPHB2EPH receptor B2 (209589_s_at), score: -0.66 FAM169Afamily with sequence similarity 169, member A (213954_at), score: -0.62 FAT1FAT tumor suppressor homolog 1 (Drosophila) (201579_at), score: 0.53 FKBP9FK506 binding protein 9, 63 kDa (212169_at), score: 0.6 GAGE4G antigen 4 (207086_x_at), score: -0.95 GAGE6G antigen 6 (208155_x_at), score: -0.9 GATA3GATA binding protein 3 (209604_s_at), score: -0.77 HERC5hect domain and RLD 5 (219863_at), score: -0.67 HGSNATheparan-alpha-glucosaminide N-acetyltransferase (218017_s_at), score: 0.59 HSPB7heat shock 27kDa protein family, member 7 (cardiovascular) (218934_s_at), score: 0.54 IRS2insulin receptor substrate 2 (209185_s_at), score: 0.55 LRRC2leucine rich repeat containing 2 (219949_at), score: 0.51 MAN2A1mannosidase, alpha, class 2A, member 1 (205105_at), score: 0.51 MARK1MAP/microtubule affinity-regulating kinase 1 (221047_s_at), score: -0.76 MFAP5microfibrillar associated protein 5 (213764_s_at), score: 0.52 MYO1Cmyosin IC (214656_x_at), score: 0.61 NEFLneurofilament, light polypeptide (221805_at), score: -0.71 NRGNneurogranin (protein kinase C substrate, RC3) (204081_at), score: -0.63 OASL2'-5'-oligoadenylate synthetase-like (210797_s_at), score: -0.96 PILRBpaired immunoglobin-like type 2 receptor beta (220954_s_at), score: -0.6 PTGER3prostaglandin E receptor 3 (subtype EP3) (213933_at), score: 0.51 RABGAP1LRAB GTPase activating protein 1-like (213982_s_at), score: 0.53 SNCAsynuclein, alpha (non A4 component of amyloid precursor) (204466_s_at), score: -0.7 TCEAL2transcription elongation factor A (SII)-like 2 (211276_at), score: -0.78 TIMP2TIMP metallopeptidase inhibitor 2 (203167_at), score: 0.5 TMEM47transmembrane protein 47 (209656_s_at), score: 0.51 TMOD1tropomodulin 1 (203661_s_at), score: -0.61 UBL3ubiquitin-like 3 (201535_at), score: 0.55 UGT1A1UDP glucuronosyltransferase 1 family, polypeptide A1 (207126_x_at), score: -0.88 UGT1A6UDP glucuronosyltransferase 1 family, polypeptide A6 (206094_x_at), score: -0.89 UGT1A9UDP glucuronosyltransferase 1 family, polypeptide A9 (204532_x_at), score: -0.87 WT1Wilms tumor 1 (206067_s_at), score: -0.64
| Id | sample | Experiment | ExpName | Array | Syndrome | Cell.line |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E-GEOD-3407-raw-cel-1437949721.cel | 5 | 4 | Cockayne | hgu133a | CS | CSB |
| E-GEOD-3407-raw-cel-1437949750.cel | 6 | 4 | Cockayne | hgu133a | CS | CSB |
| E-GEOD-3407-raw-cel-1437949938.cel | 8 | 4 | Cockayne | hgu133a | none | CSB |
| E-GEOD-3407-raw-cel-1437949579.cel | 2 | 4 | Cockayne | hgu133a | none | CSB |
| E-GEOD-3407-raw-cel-1437949854.cel | 7 | 4 | Cockayne | hgu133a | CS | eGFP |