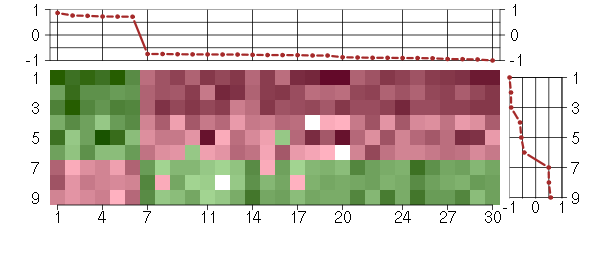

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

cytoskeleton organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the formation, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of cytoskeletal structures.
organelle organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the formation, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of an organelle within a cell. An organelle is an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
cellular component organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the formation, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of a cellular component.
cellular component assembly
A cellular process that results in the assembly of a part of the cell.
intermediate filament-based process
Any cellular process that depends upon or alters the intermediate filament cytoskeleton, that part of the cytoskeleton comprising intermediate filaments and their associated proteins.
intermediate filament cytoskeleton organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the formation, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of cytoskeletal structures comprising intermediate filaments and their associated proteins.
intermediate filament organization
Control of the spatial distribution of intermediate filaments; includes organizing filaments into meshworks, bundles, or other structures, as by cross-linking.
intermediate filament bundle assembly
The formation of the bundles of intermediate filaments, known as tonofilaments. Intermediate filament-associated proteins (IFAPs) cross-link intermediate filaments with one another, forming a bundle or a network, and with other cell structures, including the plasma membrane. The organization of intermediate filaments and their supportive function in various cells types depends in large part on their linkage to other cell structures via IFAPs.
neurofilament cytoskeleton organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the formation, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of cytoskeletal structures comprising neurofilaments and their associated proteins.
all
This term is the most general term possible
intermediate filament cytoskeleton organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the formation, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of cytoskeletal structures comprising intermediate filaments and their associated proteins.
intermediate filament bundle assembly
The formation of the bundles of intermediate filaments, known as tonofilaments. Intermediate filament-associated proteins (IFAPs) cross-link intermediate filaments with one another, forming a bundle or a network, and with other cell structures, including the plasma membrane. The organization of intermediate filaments and their supportive function in various cells types depends in large part on their linkage to other cell structures via IFAPs.

intracellular
The living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
intermediate filament
A cytoskeletal structure that forms a distinct elongated structure, characteristically 10 nm in diameter, that occurs in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells. Intermediate filaments form a fibrous system, composed of chemically heterogeneous subunits and involved in mechanically integrating the various components of the cytoplasmic space. Intermediate filaments may be divided into five chemically distinct classes: Type I, acidic keratins; Type II, basic keratins; Type III, including desmin, vimentin and others; Type IV, neurofilaments and related filaments; and Type V, lamins.
cellular_component
The part of a cell or its extracellular environment in which a gene product is located. A gene product may be located in one or more parts of a cell and its location may be as specific as a particular macromolecular complex, that is, a stable, persistent association of macromolecules that function together.
cell
The basic structural and functional unit of all organisms. Includes the plasma membrane and any external encapsulating structures such as the cell wall and cell envelope.
cytoskeleton
Any of the various filamentous elements that form the internal framework of cells, and typically remain after treatment of the cells with mild detergent to remove membrane constituents and soluble components of the cytoplasm. The term embraces intermediate filaments, microfilaments, microtubules, the microtrabecular lattice, and other structures characterized by a polymeric filamentous nature and long-range order within the cell. The various elements of the cytoskeleton not only serve in the maintenance of cellular shape but also have roles in other cellular functions, including cellular movement, cell division, endocytosis, and movement of organelles.
neurofilament
A type of intermediate filament found in the core of neuronal axons. Neurofilaments are heteropolymers composed of three type IV polypeptides: NF-L, NF-M, and NF-H (for low, middle, and high molecular weight). Neurofilaments are responsible for the radial growth of an axon and determine axonal diameter.
organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
non-membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, not bounded by a lipid bilayer membrane. Includes ribosomes, the cytoskeleton and chromosomes.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular non-membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, not bounded by a lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes ribosomes, the cytoskeleton and chromosomes.
organelle part
Any constituent part of an organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, but excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
cytoskeletal part
Any constituent part of the cytoskeleton, a cellular scaffolding or skeleton that maintains cell shape, enables some cell motion (using structures such as flagella and cilia), and plays important roles in both intra-cellular transport (e.g. the movement of vesicles and organelles) and cellular division. Includes constituent parts of intermediate filaments, microfilaments, microtubules, and the microtrabecular lattice.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
intermediate filament cytoskeleton
Cytoskeletal structure made from intermediate filaments, typically organized in the cytosol as an extended system that stretches from the nuclear envelope to the plasma membrane. Some intermediate filaments run parallel to the cell surface, while others traverse the cytosol; together they form an internal framework that helps support the shape and resilience of the cell.
neurofilament cytoskeleton
Intermediate filament cytoskeletal structure that is made up of neurofilaments. Neurofilaments are specialized intermediate filaments found in neurons.
all
This term is the most general term possible
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
organelle part
Any constituent part of an organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, but excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular non-membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, not bounded by a lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes ribosomes, the cytoskeleton and chromosomes.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
cytoskeletal part
Any constituent part of the cytoskeleton, a cellular scaffolding or skeleton that maintains cell shape, enables some cell motion (using structures such as flagella and cilia), and plays important roles in both intra-cellular transport (e.g. the movement of vesicles and organelles) and cellular division. Includes constituent parts of intermediate filaments, microfilaments, microtubules, and the microtrabecular lattice.
intermediate filament
A cytoskeletal structure that forms a distinct elongated structure, characteristically 10 nm in diameter, that occurs in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells. Intermediate filaments form a fibrous system, composed of chemically heterogeneous subunits and involved in mechanically integrating the various components of the cytoplasmic space. Intermediate filaments may be divided into five chemically distinct classes: Type I, acidic keratins; Type II, basic keratins; Type III, including desmin, vimentin and others; Type IV, neurofilaments and related filaments; and Type V, lamins.
neurofilament
A type of intermediate filament found in the core of neuronal axons. Neurofilaments are heteropolymers composed of three type IV polypeptides: NF-L, NF-M, and NF-H (for low, middle, and high molecular weight). Neurofilaments are responsible for the radial growth of an axon and determine axonal diameter.

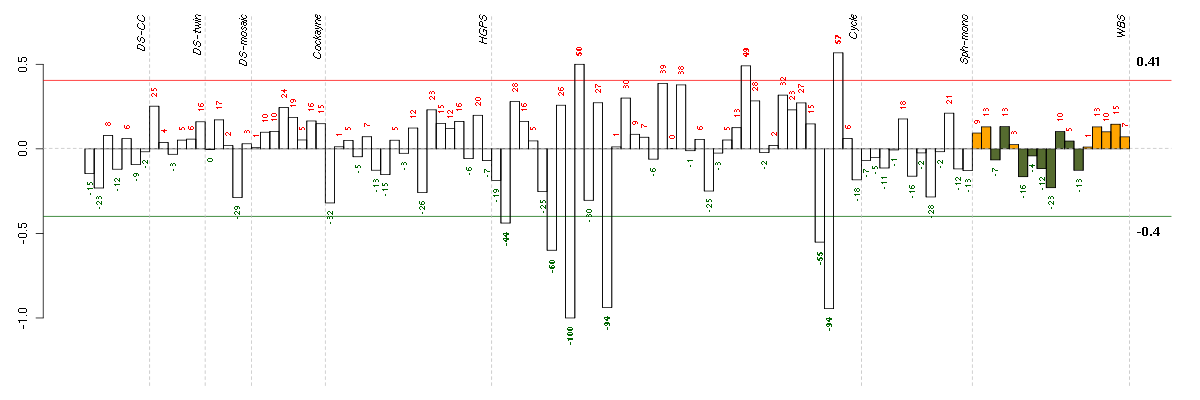
ADORA2Badenosine A2b receptor (205891_at), score: 0.75 AHI1Abelson helper integration site 1 (221569_at), score: -0.91 ANXA10annexin A10 (210143_at), score: -0.88 BMP6bone morphogenetic protein 6 (206176_at), score: -0.87 CRTC3CREB regulated transcription coactivator 3 (218648_at), score: 0.76 DNAJB9DnaJ (Hsp40) homolog, subfamily B, member 9 (202843_at), score: -0.94 EAF2ELL associated factor 2 (219551_at), score: -0.79 ESM1endothelial cell-specific molecule 1 (208394_x_at), score: -0.89 FERMT1fermitin family homolog 1 (Drosophila) (218796_at), score: -0.8 GHRgrowth hormone receptor (205498_at), score: -0.77 GKglycerol kinase (207387_s_at), score: -0.95 GK3Pglycerol kinase 3 pseudogene (215966_x_at), score: -0.96 GMCL1germ cell-less homolog 1 (Drosophila) (218458_at), score: -0.76 GPR177G protein-coupled receptor 177 (221958_s_at), score: -0.75 IL33interleukin 33 (209821_at), score: -0.9 KAL1Kallmann syndrome 1 sequence (205206_at), score: -1 MFAP3Lmicrofibrillar-associated protein 3-like (205442_at), score: -0.75 NCALDneurocalcin delta (211685_s_at), score: -0.81 NEFLneurofilament, light polypeptide (221805_at), score: -0.78 NEFMneurofilament, medium polypeptide (205113_at), score: -0.89 NPTX1neuronal pentraxin I (204684_at), score: -0.77 OPCMLopioid binding protein/cell adhesion molecule-like (214111_at), score: -0.79 PCDH9protocadherin 9 (219737_s_at), score: -0.9 RFX5regulatory factor X, 5 (influences HLA class II expression) (202963_at), score: 0.72 SLC33A1solute carrier family 33 (acetyl-CoA transporter), member 1 (203165_s_at), score: -0.79 SLC4A7solute carrier family 4, sodium bicarbonate cotransporter, member 7 (209884_s_at), score: -0.75 SMAD3SMAD family member 3 (218284_at), score: 0.72 TFDP2transcription factor Dp-2 (E2F dimerization partner 2) (203588_s_at), score: 0.86 TGDSTDP-glucose 4,6-dehydratase (208249_s_at), score: -0.76 WDR6WD repeat domain 6 (217734_s_at), score: 0.72
| Id | sample | Experiment | ExpName | Array | Syndrome | Cell.line |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485811.cel | 9 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486371.cel | 37 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485891.cel | 13 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485771.cel | 7 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486351.cel | 36 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485671.cel | 2 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486191.cel | 28 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485831.cel | 10 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486391.cel | 38 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |