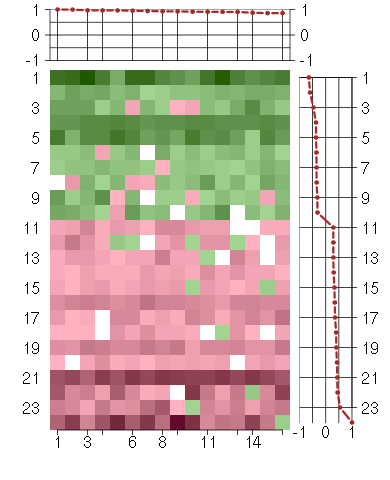

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

eye development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the eye over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The eye is the organ of sight.
eye photoreceptor cell differentiation
The process whereby a relatively unspecialized cell acquires the specialized features of a photoreceptor cell, as found in the eye, the primary visual organ of most organisms.
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
anatomical structure morphogenesis
The process by which anatomical structures are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
organ morphogenesis
Morphogenesis of an organ. An organ is defined as a tissue or set of tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Morphogenesis is the process by which anatomical structures are generated and organized. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
nervous system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of nervous tissue over time, from its formation to its mature state.
sensory organ development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of sensory organs over time, from its formation to the mature structure.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
neurogenesis
Generation of cells within the nervous system.
cell differentiation
The process whereby relatively unspecialized cells, e.g. embryonic or regenerative cells, acquire specialized structural and/or functional features that characterize the cells, tissues, or organs of the mature organism or some other relatively stable phase of the organism's life history. Differentiation includes the processes involved in commitment of a cell to a specific fate.
neuron differentiation
The process whereby a relatively unspecialized cell acquires specialized features of a neuron.
multicellular organismal process
Any biological process, occurring at the level of a multicellular organism, pertinent to its function.
developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an integrated living unit: an anatomical structure (which may be a subcellular structure, cell, tissue, or organ), or organism over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
photoreceptor cell development
Development of a photoreceptor, a cell that responds to incident electromagnetic radiation, particularly visible light.
eye photoreceptor cell development
Development of a photoreceptor, a sensory cell in the eye that reacts to the presence of light. They usually contain a pigment that undergoes a chemical change when light is absorbed, thus stimulating a nerve.
photoreceptor cell differentiation
The specialization of organization of a photoreceptor, a cell that responds to incident electromagnetic radiation, particularly visible light.
cell development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the cell over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Cell development does not include the steps involved in committing a cell to a specific fate.
organ development
Development of a tissue or tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Development pertains to the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a structure over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
eye morphogenesis
The process by which the anatomical structures of the eye are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
neuron development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a neuron over time, from initial commitment of the cell to a specific fate, to the fully functional differentiated cell.
generation of neurons
The process by which nerve cells are generated. This includes the production of neuroblasts and their differentiation into neurons.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
anatomical structure development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an anatomical structure from an initial condition to its mature state. This process begins with the formation of the structure and ends with the mature structure, whatever form that may be including its natural destruction. An anatomical structure is any biological entity that occupies space and is distinguished from its surroundings. Anatomical structures can be macroscopic such as a carpel, or microscopic such as an acrosome.
cellular developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a cell over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
all
This term is the most general term possible
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
cellular developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a cell over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
anatomical structure morphogenesis
The process by which anatomical structures are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
cell development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the cell over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Cell development does not include the steps involved in committing a cell to a specific fate.
organ development
Development of a tissue or tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Development pertains to the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a structure over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
organ morphogenesis
Morphogenesis of an organ. An organ is defined as a tissue or set of tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Morphogenesis is the process by which anatomical structures are generated and organized. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
neuron differentiation
The process whereby a relatively unspecialized cell acquires specialized features of a neuron.
neuron development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a neuron over time, from initial commitment of the cell to a specific fate, to the fully functional differentiated cell.
neurogenesis
Generation of cells within the nervous system.
eye photoreceptor cell differentiation
The process whereby a relatively unspecialized cell acquires the specialized features of a photoreceptor cell, as found in the eye, the primary visual organ of most organisms.
photoreceptor cell development
Development of a photoreceptor, a cell that responds to incident electromagnetic radiation, particularly visible light.
eye photoreceptor cell development
Development of a photoreceptor, a sensory cell in the eye that reacts to the presence of light. They usually contain a pigment that undergoes a chemical change when light is absorbed, thus stimulating a nerve.
eye morphogenesis
The process by which the anatomical structures of the eye are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.


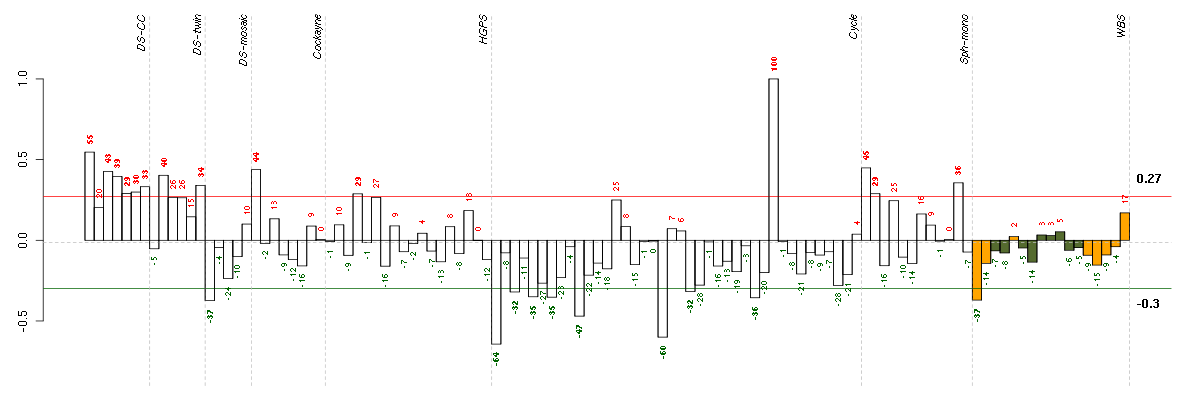
AFF2AF4/FMR2 family, member 2 (206105_at), score: 0.87 CA1carbonic anhydrase I (205949_at), score: 0.93 CD53CD53 molecule (203416_at), score: 0.95 CLDN10claudin 10 (205328_at), score: 0.93 CNKSR2connector enhancer of kinase suppressor of Ras 2 (206731_at), score: 1 DNM3dynamin 3 (209839_at), score: 0.86 GRHL2grainyhead-like 2 (Drosophila) (219388_at), score: 1 KCNJ16potassium inwardly-rectifying channel, subfamily J, member 16 (219564_at), score: 0.86 KRT2keratin 2 (207908_at), score: 0.96 MSTP9macrophage stimulating, pseudogene 9 (213382_at), score: 0.9 NTRK2neurotrophic tyrosine kinase, receptor, type 2 (207152_at), score: 0.91 POU4F2POU class 4 homeobox 2 (207725_at), score: 0.91 RPGRIP1retinitis pigmentosa GTPase regulator interacting protein 1 (206608_s_at), score: 0.94 SIRPB1signal-regulatory protein beta 1 (206934_at), score: 0.96 TAAR2trace amine associated receptor 2 (221394_at), score: 0.91 TP63tumor protein p63 (209863_s_at), score: 0.97
| Id | sample | Experiment | ExpName | Array | Syndrome | Cell.line |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485651.cel | 1 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486011.cel | 19 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485831.cel | 10 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| 46A.CEL | 1 | 3 | DS-mosaic | hgu133plus2 | none | DS-mosaic 1 |
| 10358_WBS.CEL | 1 | 8 | WBS | hgu133plus2 | WBS | WBS 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486211.cel | 29 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485771.cel | 7 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485731.cel | 5 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485691.cel | 3 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486071.cel | 22 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-GEOD-3860-raw-cel-1561690231.cel | 4 | 5 | HGPS | hgu133a | HGPS | AG10750 |
| E-GEOD-4219-raw-cel-1311956138.cel | 4 | 7 | Sph-mono | hgu133plus2 | none | Sph-mon 1 |
| t21b 08-03.CEL | 5 | 1 | DS-CC | hgu133a | Down | DS-CC 5 |
| t21c 08-03.CEL | 6 | 1 | DS-CC | hgu133a | Down | DS-CC 6 |
| t21d 08-03.CEL | 7 | 1 | DS-CC | hgu133a | Down | DS-CC 7 |
| 6Twin.CEL | 6 | 2 | DS-twin | hgu133plus2 | none | DS-twin 6 |
| E-GEOD-4219-raw-cel-1311956634.cel | 19 | 7 | Sph-mono | hgu133plus2 | none | Sph-mon 1 |
| t21a 08-03.CEL | 4 | 1 | DS-CC | hgu133a | Down | DS-CC 4 |
| 2Twin.CEL | 2 | 2 | DS-twin | hgu133plus2 | none | DS-twin 2 |
| ctrl c 08-03.CEL | 3 | 1 | DS-CC | hgu133a | none | DS-CC 3 |
| E-GEOD-3407-raw-cel-1437949557.cel | 1 | 4 | Cockayne | hgu133a | CS | eGFP |
| E-GEOD-4219-raw-cel-1311956083.cel | 2 | 7 | Sph-mono | hgu133plus2 | none | Sph-mon 1 |
| ctrl a 08-03.CEL | 1 | 1 | DS-CC | hgu133a | none | DS-CC 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486251.cel | 31 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |