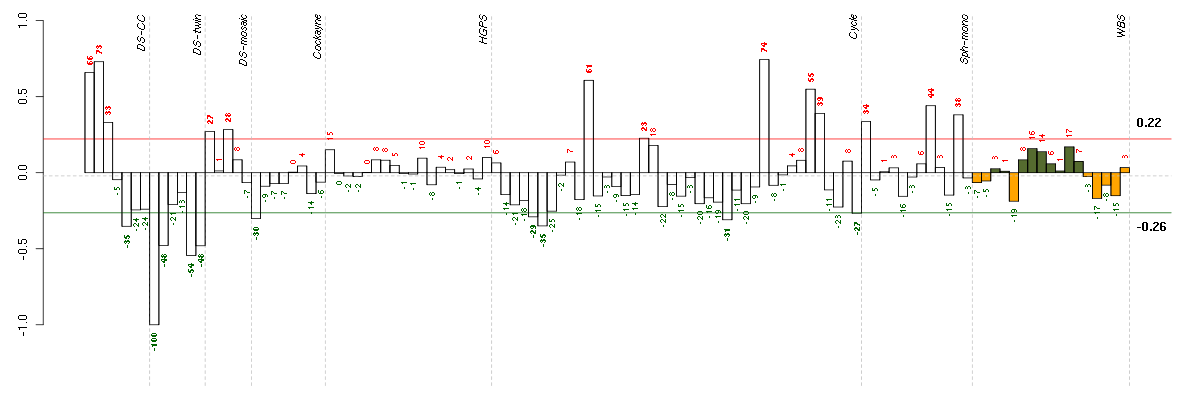

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways, including anabolism and catabolism, by which living organisms transform chemical substances. Metabolic processes typically transform small molecules, but also include macromolecular processes such as DNA repair and replication, and protein synthesis and degradation.
regulation of protein amino acid phosphorylation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of addition of phosphate groups into an amino acid in a protein.
positive regulation of protein amino acid phosphorylation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of addition of phosphate groups to amino acids within a protein.
response to molecule of bacterial origin
A change in state or activity of an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus by molecules of bacterial origin such as peptides derived from bacterial flagellin.
immune system process
Any process involved in the development or functioning of the immune system, an organismal system for calibrated responses to potential internal or invasive threats.
regulation of immune system process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of an immune system process.
positive regulation of immune system process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of an immune system process.
regulation of leukocyte migration
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of leukocyte migration.
positive regulation of leukocyte migration
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of leukocyte migration.
generation of a signal involved in cell-cell signaling
The cellular process by which a physical entity or change in state, a signal, is created that originates in one cell and is used to transfer information to another cell. This process begins with the initial formation of the signal and ends with the mature form and placement of the signal.
defense response
Reactions, triggered in response to the presence of a foreign body or the occurrence of an injury, which result in restriction of damage to the organism attacked or prevention/recovery from the infection caused by the attack.
secretion
The controlled release of a substance by a cell, a group of cells, or a tissue.
signal transduction
The cascade of processes by which a signal interacts with a receptor, causing a change in the level or activity of a second messenger or other downstream target, and ultimately effecting a change in the functioning of the cell.
nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
transcription
The synthesis of either RNA on a template of DNA or DNA on a template of RNA.
transcription, DNA-dependent
The synthesis of RNA on a template of DNA.
regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of DNA-dependent transcription.
regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of transcription from an RNA polymerase II promoter.
transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter
The synthesis of RNA from a DNA template by RNA polymerase II (Pol II), originating at a Pol II-specific promoter. Includes transcription of messenger RNA (mRNA) and certain small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs).
protein modification process
The covalent alteration of one or more amino acids occurring in proteins, peptides and nascent polypeptides (co-translational, post-translational modifications). Includes the modification of charged tRNAs that are destined to occur in a protein (pre-translation modification).
protein amino acid phosphorylation
The process of introducing a phosphate group on to a protein.
phosphorus metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving the nonmetallic element phosphorus or compounds that contain phosphorus, usually in the form of a phosphate group (PO4).
phosphate metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving the phosphate group, the anion or salt of any phosphoric acid.
transport
The directed movement of substances (such as macromolecules, small molecules, ions) into, out of, within or between cells, or within a multicellular organism.
cell motion
Any process involved in the controlled movement of a cell.
chemotaxis
The directed movement of a motile cell or organism, or the directed growth of a cell guided by a specific chemical concentration gradient. Movement may be towards a higher concentration (positive chemotaxis) or towards a lower concentration (negative chemotaxis).
response to stress
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a disturbance in organismal or cellular homeostasis, usually, but not necessarily, exogenous (e.g. temperature, humidity, ionizing radiation).
inflammatory response
The immediate defensive reaction (by vertebrate tissue) to infection or injury caused by chemical or physical agents. The process is characterized by local vasodilation, extravasation of plasma into intercellular spaces and accumulation of white blood cells and macrophages.
immune response
Any immune system process that functions in the calibrated response of an organism to a potential internal or invasive threat.
cell communication
Any process that mediates interactions between a cell and its surroundings. Encompasses interactions such as signaling or attachment between one cell and another cell, between a cell and an extracellular matrix, or between a cell and any other aspect of its environment.
cell-cell signaling
Any process that mediates the transfer of information from one cell to another.
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
anatomical structure morphogenesis
The process by which anatomical structures are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
organ morphogenesis
Morphogenesis of an organ. An organ is defined as a tissue or set of tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Morphogenesis is the process by which anatomical structures are generated and organized. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
behavior
The specific actions or reactions of an organism in response to external or internal stimuli. Patterned activity of a whole organism in a manner dependent upon some combination of that organism's internal state and external conditions.
locomotory behavior
The specific movement from place to place of an organism in response to external or internal stimuli. Locomotion of a whole organism in a manner dependent upon some combination of that organism's internal state and external conditions.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
cell proliferation
The multiplication or reproduction of cells, resulting in the expansion of a cell population.
positive regulation of cell proliferation
Any process that activates or increases the rate or extent of cell proliferation.
biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances; typically the energy-requiring part of metabolism in which simpler substances are transformed into more complex ones.
macromolecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
response to external stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an external stimulus.
response to biotic stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a biotic stimulus, a stimulus caused or produced by a living organism.
response to wounding
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus indicating damage to the organism.
response to other organism
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus from another living organism.
response to bacterium
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus from a bacterium.
regulation of biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances.
positive regulation of biosynthetic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances.
positive regulation of metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism.
hormone transport
The directed movement of hormones into, out of, within or between cells.
regulation of signal transduction
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of signal transduction.
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
gene expression
The process by which a gene's coding sequence is converted into a mature gene product or products (proteins or RNA). This includes the production of an RNA transcript as well as any processing to produce a mature RNA product or an mRNA (for protein-coding genes) and the translation of that mRNA into protein. Some protein processing events may be included when they are required to form an active form of a product from an inactive precursor form.
regulation of gene expression
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of gene expression. Gene expression is the process in which a gene's coding sequence is converted into a mature gene product or products (proteins or RNA). This includes the production of an RNA transcript as well as any processing to produce a mature RNA product or an mRNA (for protein-coding genes) and the translation of that mRNA into protein. Some protein processing events may be included when they are required to form an active form of a product from an inactive precursor form.
regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the rate, frequency or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
positive regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic process
Any process that increases the rate, frequency or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
positive regulation of phosphorus metabolic process
Any process that increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving phosphorus or compounds containing phosphorus.
positive regulation of macromolecule metabolic process
Any process that increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
positive regulation of gene expression
Any process that increases the frequency, rate or extent of gene expression. Gene expression is the process in which a gene's coding sequence is converted into a mature gene product or products (proteins or RNA). This includes the production of an RNA transcript as well as any processing to produce a mature RNA product or an mRNA (for protein-coding genes) and the translation of that mRNA into protein. Some protein processing events may be included when they are required to form an active form of a product from an inactive precursor form.
regulation of cell communication
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell communication. Cell communication is the process that mediates interactions between a cell and its surroundings. Encompasses interactions such as signaling or attachment between one cell and another cell, between a cell and an extracellular matrix, or between a cell and any other aspect of its environment.
regulation of hormone levels
Any process that modulates the levels of hormone within an organism or a tissue. A hormone is any substance formed in very small amounts in one specialized organ or group of cells and carried (sometimes in the bloodstream) to another organ or group of cells in the same organism, upon which it has a specific regulatory action.
RNA metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving RNA, ribonucleic acid, one of the two main type of nucleic acid, consisting of a long, unbranched macromolecule formed from ribonucleotides joined in 3',5'-phosphodiester linkage.
positive regulation of nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
phosphorylation
The process of introducing a phosphate group into a molecule, usually with the formation of a phosphoric ester, a phosphoric anhydride or a phosphoric amide.
cell migration
The orderly movement of cells from one site to another, often during the development of a multicellular organism or multicellular structure.
peptidyl-serine phosphorylation
The posttranslational phosphorylation of peptidyl-serine to form peptidyl-O-phospho-L-serine.
peptidyl-amino acid modification
The alteration of an amino acid residue in a peptide.
peptidyl-serine modification
The modification of peptidyl-serine.
regulation of nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
regulation of phosphate metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving phosphates.
regulation of metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism.
protein metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving a specific protein, rather than of proteins in general. Includes protein modification.
cell differentiation
The process whereby relatively unspecialized cells, e.g. embryonic or regenerative cells, acquire specialized structural and/or functional features that characterize the cells, tissues, or organs of the mature organism or some other relatively stable phase of the organism's life history. Differentiation includes the processes involved in commitment of a cell to a specific fate.
regulation of cell migration
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell migration.
positive regulation of cell migration
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cell migration.
regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
positive regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
regulation of cellular biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
positive regulation of cellular biosynthetic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
regulation of protein modification process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the covalent alteration of one or more amino acid residues within a protein.
positive regulation of protein modification process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the covalent alteration of one or more amino acid residues within a protein.
regulation of cellular protein metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving a protein, occurring at the level of an individual cell.
positive regulation of cellular protein metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving a protein, occurring at the level of an individual cell.
multicellular organismal process
Any biological process, occurring at the level of a multicellular organism, pertinent to its function.
developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an integrated living unit: an anatomical structure (which may be a subcellular structure, cell, tissue, or organ), or organism over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
RNA biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of RNA, ribonucleic acid, one of the two main type of nucleic acid, consisting of a long, unbranched macromolecule formed from ribonucleotides joined in 3',5'-phosphodiester linkage. Includes polymerization of ribonucleotide monomers.
regulation of localization
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of any process by which a cell, a substance, or a cellular entity is transported to, or maintained in, a specific location.
regulation of peptidyl-serine phosphorylation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the phosphorylation of peptidyl-serine.
positive regulation of peptidyl-serine phosphorylation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the phosphorylation of peptidyl-serine.
cellular macromolecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, carried out by individual cells.
cellular biopolymer metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature, such as polysaccharides and proteins, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular biopolymer biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature, such as polysaccharides and proteins, as carried out by individual cells.
locomotion
Self-propelled movement of a cell or organism from one location to another.
regulation of locomotion
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of locomotion of a cell or organism.
wound healing
The series of events that restore integrity to a damaged tissue, following an injury.
regulation of cell proliferation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell proliferation.
response to chemical stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a chemical stimulus.
regulation of phosphorylation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of addition of phosphate groups into a molecule.
positive regulation of phosphorylation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of addition of phosphate groups to a molecule.
taxis
The directed movement of a motile cell or organism in response to an external stimulus.
macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
biopolymer metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature, such as polysaccharides and proteins.
biopolymer biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature e.g. polysaccharides and proteins.
biopolymer modification
The covalent alteration of one or more monomeric units in a polypeptide, polynucleotide, polysaccharide, or other biological polymer, resulting in a change in its properties.
post-translational protein modification
The covalent alteration of one or more amino acids occurring in a protein after the protein has been completely translated and released from the ribosome.
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
primary metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving those compounds which are formed as a part of the normal anabolic and catabolic processes. These processes take place in most, if not all, cells of the organism.
cellular biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
cellular macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular protein metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving a specific protein, rather than of proteins in general, occurring at the level of an individual cell. Includes protein modification.
regulation of transcription
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the synthesis of either RNA on a template of DNA or DNA on a template of RNA.
regulation of cell differentiation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell differentiation, the process whereby relatively unspecialized cells acquire specialized structural and functional features.
positive regulation of cell differentiation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cell differentiation.
positive regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of DNA-dependent transcription.
positive regulation of phosphate metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving phosphates.
positive regulation of transcription
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of transcription.
positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of transcription from the RNA polymerase II promoter.
hormone secretion
The regulated release of hormones, substances with a specific regulatory effect on a particular organ or group of cells.
organ development
Development of a tissue or tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Development pertains to the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a structure over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
positive regulation of biological process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
negative regulation of biological process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
positive regulation of cellular process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
negative regulation of cellular process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
anatomical structure formation
The process pertaining to the initial formation of an anatomical structure from unspecified parts. This process begins with the specific processes that contribute to the appearance of the discrete structure and ends when the structural rudiment is recognizable. An anatomical structure is any biological entity that occupies space and is distinguished from its surroundings. Anatomical structures can be macroscopic such as a carpel, or microscopic such as an acrosome.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
anatomical structure development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an anatomical structure from an initial condition to its mature state. This process begins with the formation of the structure and ends with the mature structure, whatever form that may be including its natural destruction. An anatomical structure is any biological entity that occupies space and is distinguished from its surroundings. Anatomical structures can be macroscopic such as a carpel, or microscopic such as an acrosome.
cellular developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a cell over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
cell motility
Any process involved in the controlled movement of a cell that results in translocation of the cell from one place to another.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of developmental process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of development, the biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote, or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
regulation of cellular process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
response to stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
leukocyte migration
The movement of leukocytes within or between different tissues and organs of the body.
positive regulation of developmental process
Any process that activates or increases the rate or extent of development, the biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote, or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
regulation of phosphorus metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving phosphorus or compounds containing phosphorus.
localization
Any process by which a cell, a substance, or a cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, is transported to, and/or maintained in a specific location.
establishment of localization
The directed movement of a cell, substance or cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, to a specific location.
regulation of multicellular organismal process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a multicellular organismal process, the processes pertinent to the function of a multicellular organism above the cellular level; includes the integrated processes of tissues and organs.
regulation of protein metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving a protein.
positive regulation of protein metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving a protein.
regulation of RNA metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving RNA.
positive regulation of RNA metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving RNA.
regulation of cell motion
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the movement of a cell.
positive regulation of cell motion
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the movement of a cell.
localization of cell
Any process by which a cell is transported to, and/or maintained in, a specific location.
multi-organism process
Any process by which an organism has an effect on another organism of the same or different species.
regulation of macromolecule metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
biological regulation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of any biological process, quality or function.
regulation of biological quality
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological quality. A biological quality is a measurable attribute of an organism or part of an organism, such as size, mass, shape, color, etc.
all
This term is the most general term possible
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
cellular developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a cell over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
positive regulation of immune system process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of an immune system process.
positive regulation of metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism.
positive regulation of cellular process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
positive regulation of developmental process
Any process that activates or increases the rate or extent of development, the biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote, or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
negative regulation of cellular process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
regulation of immune system process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of an immune system process.
regulation of metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism.
regulation of locomotion
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of locomotion of a cell or organism.
positive regulation of biological process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
negative regulation of biological process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of developmental process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of development, the biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote, or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
regulation of cellular process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
regulation of multicellular organismal process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a multicellular organismal process, the processes pertinent to the function of a multicellular organism above the cellular level; includes the integrated processes of tissues and organs.
immune response
Any immune system process that functions in the calibrated response of an organism to a potential internal or invasive threat.
regulation of localization
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of any process by which a cell, a substance, or a cellular entity is transported to, or maintained in, a specific location.
establishment of localization
The directed movement of a cell, substance or cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, to a specific location.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
positive regulation of biosynthetic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances.
regulation of biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances.
positive regulation of metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism.
macromolecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
positive regulation of macromolecule metabolic process
Any process that increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
regulation of macromolecule metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
positive regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
cellular biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
cellular macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, as carried out by individual cells.
nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
positive regulation of immune system process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of an immune system process.
regulation of leukocyte migration
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of leukocyte migration.
positive regulation of leukocyte migration
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of leukocyte migration.
cell motility
Any process involved in the controlled movement of a cell that results in translocation of the cell from one place to another.
positive regulation of cell proliferation
Any process that activates or increases the rate or extent of cell proliferation.
positive regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
positive regulation of cell motion
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the movement of a cell.
signal transduction
The cascade of processes by which a signal interacts with a receptor, causing a change in the level or activity of a second messenger or other downstream target, and ultimately effecting a change in the functioning of the cell.
regulation of cell communication
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell communication. Cell communication is the process that mediates interactions between a cell and its surroundings. Encompasses interactions such as signaling or attachment between one cell and another cell, between a cell and an extracellular matrix, or between a cell and any other aspect of its environment.
regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
regulation of cell proliferation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell proliferation.
positive regulation of cellular process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
negative regulation of cellular process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
regulation of cell motion
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the movement of a cell.
anatomical structure formation
The process pertaining to the initial formation of an anatomical structure from unspecified parts. This process begins with the specific processes that contribute to the appearance of the discrete structure and ends when the structural rudiment is recognizable. An anatomical structure is any biological entity that occupies space and is distinguished from its surroundings. Anatomical structures can be macroscopic such as a carpel, or microscopic such as an acrosome.
anatomical structure morphogenesis
The process by which anatomical structures are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
regulation of cell differentiation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell differentiation, the process whereby relatively unspecialized cells acquire specialized structural and functional features.
positive regulation of developmental process
Any process that activates or increases the rate or extent of development, the biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote, or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
positive regulation of cell differentiation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cell differentiation.
regulation of cell motion
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the movement of a cell.
response to wounding
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus indicating damage to the organism.
taxis
The directed movement of a motile cell or organism in response to an external stimulus.
response to other organism
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus from another living organism.
response to molecule of bacterial origin
A change in state or activity of an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus by molecules of bacterial origin such as peptides derived from bacterial flagellin.
chemotaxis
The directed movement of a motile cell or organism, or the directed growth of a cell guided by a specific chemical concentration gradient. Movement may be towards a higher concentration (positive chemotaxis) or towards a lower concentration (negative chemotaxis).
cell motion
Any process involved in the controlled movement of a cell.
positive regulation of biosynthetic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances.
regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the rate, frequency or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
positive regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic process
Any process that increases the rate, frequency or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
regulation of cellular biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
positive regulation of cellular biosynthetic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
cellular macromolecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, carried out by individual cells.
positive regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic process
Any process that increases the rate, frequency or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
positive regulation of cellular biosynthetic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
positive regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
regulation of cellular biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the rate, frequency or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
positive regulation of macromolecule metabolic process
Any process that increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
regulation of gene expression
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of gene expression. Gene expression is the process in which a gene's coding sequence is converted into a mature gene product or products (proteins or RNA). This includes the production of an RNA transcript as well as any processing to produce a mature RNA product or an mRNA (for protein-coding genes) and the translation of that mRNA into protein. Some protein processing events may be included when they are required to form an active form of a product from an inactive precursor form.
positive regulation of gene expression
Any process that increases the frequency, rate or extent of gene expression. Gene expression is the process in which a gene's coding sequence is converted into a mature gene product or products (proteins or RNA). This includes the production of an RNA transcript as well as any processing to produce a mature RNA product or an mRNA (for protein-coding genes) and the translation of that mRNA into protein. Some protein processing events may be included when they are required to form an active form of a product from an inactive precursor form.
protein metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving a specific protein, rather than of proteins in general. Includes protein modification.
biopolymer biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature e.g. polysaccharides and proteins.
cellular macromolecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, carried out by individual cells.
cellular biopolymer metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature, such as polysaccharides and proteins, as carried out by individual cells.
transcription
The synthesis of either RNA on a template of DNA or DNA on a template of RNA.
positive regulation of nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
regulation of nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
positive regulation of phosphorus metabolic process
Any process that increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving phosphorus or compounds containing phosphorus.
regulation of phosphorus metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving phosphorus or compounds containing phosphorus.
regulation of protein metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving a protein.
positive regulation of protein metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving a protein.
positive regulation of leukocyte migration
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of leukocyte migration.
regulation of cell migration
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell migration.
positive regulation of cell motion
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the movement of a cell.
generation of a signal involved in cell-cell signaling
The cellular process by which a physical entity or change in state, a signal, is created that originates in one cell and is used to transfer information to another cell. This process begins with the initial formation of the signal and ends with the mature form and placement of the signal.
regulation of signal transduction
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of signal transduction.
positive regulation of cell proliferation
Any process that activates or increases the rate or extent of cell proliferation.
regulation of cell differentiation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell differentiation, the process whereby relatively unspecialized cells acquire specialized structural and functional features.
positive regulation of cell differentiation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cell differentiation.
positive regulation of cell differentiation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cell differentiation.
organ development
Development of a tissue or tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Development pertains to the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a structure over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
organ morphogenesis
Morphogenesis of an organ. An organ is defined as a tissue or set of tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Morphogenesis is the process by which anatomical structures are generated and organized. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
regulation of leukocyte migration
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of leukocyte migration.
positive regulation of cell migration
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cell migration.
regulation of cell migration
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell migration.
positive regulation of cell migration
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cell migration.
leukocyte migration
The movement of leukocytes within or between different tissues and organs of the body.
inflammatory response
The immediate defensive reaction (by vertebrate tissue) to infection or injury caused by chemical or physical agents. The process is characterized by local vasodilation, extravasation of plasma into intercellular spaces and accumulation of white blood cells and macrophages.
taxis
The directed movement of a motile cell or organism in response to an external stimulus.
hormone secretion
The regulated release of hormones, substances with a specific regulatory effect on a particular organ or group of cells.
hormone secretion
The regulated release of hormones, substances with a specific regulatory effect on a particular organ or group of cells.
response to molecule of bacterial origin
A change in state or activity of an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus by molecules of bacterial origin such as peptides derived from bacterial flagellin.
hormone transport
The directed movement of hormones into, out of, within or between cells.
positive regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic process
Any process that increases the rate, frequency or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
cellular biopolymer biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature, such as polysaccharides and proteins, as carried out by individual cells.
positive regulation of cellular biosynthetic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
regulation of transcription
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the synthesis of either RNA on a template of DNA or DNA on a template of RNA.
positive regulation of transcription
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of transcription.
positive regulation of transcription
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of transcription.
positive regulation of cellular protein metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving a protein, occurring at the level of an individual cell.
positive regulation of transcription
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of transcription.
positive regulation of RNA metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving RNA.
positive regulation of nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
regulation of transcription
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the synthesis of either RNA on a template of DNA or DNA on a template of RNA.
regulation of RNA metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving RNA.
positive regulation of cellular protein metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving a protein, occurring at the level of an individual cell.
positive regulation of phosphorus metabolic process
Any process that increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving phosphorus or compounds containing phosphorus.
positive regulation of gene expression
Any process that increases the frequency, rate or extent of gene expression. Gene expression is the process in which a gene's coding sequence is converted into a mature gene product or products (proteins or RNA). This includes the production of an RNA transcript as well as any processing to produce a mature RNA product or an mRNA (for protein-coding genes) and the translation of that mRNA into protein. Some protein processing events may be included when they are required to form an active form of a product from an inactive precursor form.
regulation of transcription
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the synthesis of either RNA on a template of DNA or DNA on a template of RNA.
regulation of cellular protein metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving a protein, occurring at the level of an individual cell.
positive regulation of protein metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving a protein.
positive regulation of RNA metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving RNA.
transcription, DNA-dependent
The synthesis of RNA on a template of DNA.
regulation of transcription
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the synthesis of either RNA on a template of DNA or DNA on a template of RNA.
positive regulation of transcription
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of transcription.
RNA metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving RNA, ribonucleic acid, one of the two main type of nucleic acid, consisting of a long, unbranched macromolecule formed from ribonucleotides joined in 3',5'-phosphodiester linkage.
cellular biopolymer biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature, such as polysaccharides and proteins, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular protein metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving a specific protein, rather than of proteins in general, occurring at the level of an individual cell. Includes protein modification.
RNA biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of RNA, ribonucleic acid, one of the two main type of nucleic acid, consisting of a long, unbranched macromolecule formed from ribonucleotides joined in 3',5'-phosphodiester linkage. Includes polymerization of ribonucleotide monomers.
regulation of RNA metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving RNA.
positive regulation of RNA metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving RNA.
regulation of phosphate metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving phosphates.
positive regulation of phosphate metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving phosphates.
protein modification process
The covalent alteration of one or more amino acids occurring in proteins, peptides and nascent polypeptides (co-translational, post-translational modifications). Includes the modification of charged tRNAs that are destined to occur in a protein (pre-translation modification).
regulation of cellular protein metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving a protein, occurring at the level of an individual cell.
positive regulation of cellular protein metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving a protein, occurring at the level of an individual cell.
positive regulation of leukocyte migration
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of leukocyte migration.
regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of DNA-dependent transcription.
positive regulation of transcription
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of transcription.
positive regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of DNA-dependent transcription.
transcription
The synthesis of either RNA on a template of DNA or DNA on a template of RNA.
regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of DNA-dependent transcription.
positive regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of DNA-dependent transcription.
positive regulation of protein modification process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the covalent alteration of one or more amino acid residues within a protein.
positive regulation of phosphate metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving phosphates.
positive regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of DNA-dependent transcription.
regulation of protein modification process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the covalent alteration of one or more amino acid residues within a protein.
positive regulation of protein modification process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the covalent alteration of one or more amino acid residues within a protein.
regulation of phosphorylation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of addition of phosphate groups into a molecule.
positive regulation of phosphorylation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of addition of phosphate groups to a molecule.
regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of transcription from an RNA polymerase II promoter.
positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of transcription from the RNA polymerase II promoter.
positive regulation of protein amino acid phosphorylation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of addition of phosphate groups to amino acids within a protein.
positive regulation of protein amino acid phosphorylation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of addition of phosphate groups to amino acids within a protein.
regulation of protein amino acid phosphorylation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of addition of phosphate groups into an amino acid in a protein.
positive regulation of phosphorylation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of addition of phosphate groups to a molecule.
positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of transcription from the RNA polymerase II promoter.
protein amino acid phosphorylation
The process of introducing a phosphate group on to a protein.
regulation of protein amino acid phosphorylation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of addition of phosphate groups into an amino acid in a protein.
positive regulation of protein amino acid phosphorylation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of addition of phosphate groups to amino acids within a protein.
positive regulation of peptidyl-serine phosphorylation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the phosphorylation of peptidyl-serine.
peptidyl-serine phosphorylation
The posttranslational phosphorylation of peptidyl-serine to form peptidyl-O-phospho-L-serine.
regulation of peptidyl-serine phosphorylation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the phosphorylation of peptidyl-serine.
positive regulation of peptidyl-serine phosphorylation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the phosphorylation of peptidyl-serine.

extracellular region
The space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.
cellular_component
The part of a cell or its extracellular environment in which a gene product is located. A gene product may be located in one or more parts of a cell and its location may be as specific as a particular macromolecular complex, that is, a stable, persistent association of macromolecules that function together.
extracellular space
That part of a multicellular organism outside the cells proper, usually taken to be outside the plasma membranes, and occupied by fluid.
extracellular region part
Any constituent part of the extracellular region, the space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers constituent parts of the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.
all
This term is the most general term possible
extracellular region part
Any constituent part of the extracellular region, the space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers constituent parts of the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.

protein binding
Interacting selectively with any protein or protein complex (a complex of two or more proteins that may include other nonprotein molecules).
G-protein-coupled receptor binding
Interacting selectively with a G-protein-coupled receptor.
molecular_function
Elemental activities, such as catalysis or binding, describing the actions of a gene product at the molecular level. A given gene product may exhibit one or more molecular functions.
receptor binding
Interacting selectively with one or more specific sites on a receptor molecule, a macromolecule that undergoes combination with a hormone, neurotransmitter, drug or intracellular messenger to initiate a change in cell function.
cytokine activity
Functions to control the survival, growth, differentiation and effector function of tissues and cells.
binding
The selective, often stoichiometric, interaction of a molecule with one or more specific sites on another molecule.
chemokine activity
The function of a family of chemotactic pro-inflammatory activation-inducible cytokines acting primarily upon hemopoietic cells in immunoregulatory processes; all chemokines possess a number of conserved cysteine residues involved in intramolecular disulfide bond formation.
growth factor activity
The function that stimulates a cell to grow or proliferate. Most growth factors have other actions besides the induction of cell growth or proliferation.
chemokine receptor binding
Interacting selectively with any chemokine receptor.
all
This term is the most general term possible
chemokine activity
The function of a family of chemotactic pro-inflammatory activation-inducible cytokines acting primarily upon hemopoietic cells in immunoregulatory processes; all chemokines possess a number of conserved cysteine residues involved in intramolecular disulfide bond formation.
| Id | Pvalue | ExpCount | Count | Size | Term |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 04060 | 6.614e-07 | 1.656 | 13 | 122 | Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction |
| 04630 | 1.213e-02 | 1.194 | 7 | 88 | Jak-STAT signaling pathway |
ANGPTL4angiopoietin-like 4 (221009_s_at), score: 0.89 APODapolipoprotein D (201525_at), score: 0.58 BMP2bone morphogenetic protein 2 (205289_at), score: 0.81 CCL2chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 2 (216598_s_at), score: 0.56 CCL7chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 7 (208075_s_at), score: 0.58 CD302CD302 molecule (203799_at), score: 0.6 CHST2carbohydrate (N-acetylglucosamine-6-O) sulfotransferase 2 (203921_at), score: 0.63 COL15A1collagen, type XV, alpha 1 (203477_at), score: 0.71 CXCL1chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 1 (melanoma growth stimulating activity, alpha) (204470_at), score: 0.62 CXCL2chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 2 (209774_x_at), score: 0.68 CXCL3chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 3 (207850_at), score: 0.87 CXCR7chemokine (C-X-C motif) receptor 7 (212977_at), score: 0.55 DKK2dickkopf homolog 2 (Xenopus laevis) (219908_at), score: 0.74 DUSP5dual specificity phosphatase 5 (209457_at), score: 0.54 EGR2early growth response 2 (Krox-20 homolog, Drosophila) (205249_at), score: 0.78 EGR3early growth response 3 (206115_at), score: 0.78 F3coagulation factor III (thromboplastin, tissue factor) (204363_at), score: 0.57 FBXW7F-box and WD repeat domain containing 7 (218751_s_at), score: 0.57 FOSBFBJ murine osteosarcoma viral oncogene homolog B (202768_at), score: 1 GCH1GTP cyclohydrolase 1 (204224_s_at), score: 0.7 GEMGTP binding protein overexpressed in skeletal muscle (204472_at), score: 0.79 GFPT2glutamine-fructose-6-phosphate transaminase 2 (205100_at), score: 0.56 GPNMBglycoprotein (transmembrane) nmb (201141_at), score: 0.59 HBEGFheparin-binding EGF-like growth factor (203821_at), score: 0.75 HIVEP1human immunodeficiency virus type I enhancer binding protein 1 (204512_at), score: 0.64 HIVEP2human immunodeficiency virus type I enhancer binding protein 2 (212642_s_at), score: 0.69 HK2hexokinase 2 (202934_at), score: 0.56 ICAM1intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (202638_s_at), score: 0.72 IL11interleukin 11 (206924_at), score: 0.72 IL1RAPinterleukin 1 receptor accessory protein (205227_at), score: 0.7 IL1RL1interleukin 1 receptor-like 1 (207526_s_at), score: 0.6 IL6interleukin 6 (interferon, beta 2) (205207_at), score: 0.84 IL8interleukin 8 (202859_x_at), score: 0.82 INSIG1insulin induced gene 1 (201627_s_at), score: 0.65 JARID2jumonji, AT rich interactive domain 2 (203297_s_at), score: 0.7 JHDM1Djumonji C domain containing histone demethylase 1 homolog D (S. cerevisiae) (221778_at), score: 0.84 JMJD3jumonji domain containing 3, histone lysine demethylase (213146_at), score: 0.98 JUNDjun D proto-oncogene (203751_x_at), score: 0.57 KIAA0247KIAA0247 (202181_at), score: 0.65 KIAA1024KIAA1024 (215081_at), score: 0.56 LIFleukemia inhibitory factor (cholinergic differentiation factor) (205266_at), score: 0.88 LMCD1LIM and cysteine-rich domains 1 (218574_s_at), score: 0.65 LOH3CR2Aloss of heterozygosity, 3, chromosomal region 2, gene A (220244_at), score: 0.59 LRIG1leucine-rich repeats and immunoglobulin-like domains 1 (211596_s_at), score: 0.7 MAN1C1mannosidase, alpha, class 1C, member 1 (218918_at), score: 0.59 MTSS1metastasis suppressor 1 (203037_s_at), score: 0.65 NAMPTnicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase (217738_at), score: 0.68 NFATC1nuclear factor of activated T-cells, cytoplasmic, calcineurin-dependent 1 (210162_s_at), score: 0.78 NFKB1nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells 1 (209239_at), score: 0.56 NINJ1ninjurin 1 (203045_at), score: 0.57 NR4A3nuclear receptor subfamily 4, group A, member 3 (209959_at), score: 0.94 PDGFAplatelet-derived growth factor alpha polypeptide (205463_s_at), score: 0.56 PIK3CDphosphoinositide-3-kinase, catalytic, delta polypeptide (203879_at), score: 0.61 PMEPA1prostate transmembrane protein, androgen induced 1 (217875_s_at), score: 0.88 PPLperiplakin (203407_at), score: 0.58 PTPREprotein tyrosine phosphatase, receptor type, E (221840_at), score: 0.61 RGS2regulator of G-protein signaling 2, 24kDa (202388_at), score: 0.63 RRADRas-related associated with diabetes (204803_s_at), score: 0.88 RUNX1runt-related transcription factor 1 (209360_s_at), score: 0.69 SLC19A2solute carrier family 19 (thiamine transporter), member 2 (209681_at), score: 0.84 SMOXspermine oxidase (210357_s_at), score: 0.84 SOD2superoxide dismutase 2, mitochondrial (221477_s_at), score: 0.62 SOX4SRY (sex determining region Y)-box 4 (201417_at), score: 0.67 SOX9SRY (sex determining region Y)-box 9 (202935_s_at), score: 0.57 SPRED2sprouty-related, EVH1 domain containing 2 (212458_at), score: 0.86 SPRY2sprouty homolog 2 (Drosophila) (204011_at), score: 0.78 SPRY4sprouty homolog 4 (Drosophila) (221489_s_at), score: 0.69 SPSB1splA/ryanodine receptor domain and SOCS box containing 1 (219677_at), score: 0.63 SRFserum response factor (c-fos serum response element-binding transcription factor) (202401_s_at), score: 0.58 ST3GAL1ST3 beta-galactoside alpha-2,3-sialyltransferase 1 (208322_s_at), score: 0.55 STK38Lserine/threonine kinase 38 like (212572_at), score: 0.77 TBX3T-box 3 (219682_s_at), score: 0.69 THBDthrombomodulin (203887_s_at), score: 0.84 TNFAIP3tumor necrosis factor, alpha-induced protein 3 (202644_s_at), score: 0.57 TRIB1tribbles homolog 1 (Drosophila) (202241_at), score: 0.72 VEGFAvascular endothelial growth factor A (211527_x_at), score: 0.67 YRDCyrdC domain containing (E. coli) (218647_s_at), score: 0.55 ZNF35zinc finger protein 35 (206096_at), score: 0.61
| Id | sample | Experiment | ExpName | Array | Syndrome | Cell.line |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1Twin.CEL | 1 | 2 | DS-twin | hgu133plus2 | Down | DS-twin 1 |
| 5CTwin.CEL | 5 | 2 | DS-twin | hgu133plus2 | Down | DS-twin 5 |
| 6Twin.CEL | 6 | 2 | DS-twin | hgu133plus2 | none | DS-twin 6 |
| 2Twin.CEL | 2 | 2 | DS-twin | hgu133plus2 | none | DS-twin 2 |
| t21b 08-03.CEL | 5 | 1 | DS-CC | hgu133a | Down | DS-CC 5 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485751.cel | 6 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486151.cel | 26 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-GEOD-3407-raw-cel-1437949557.cel | 1 | 4 | Cockayne | hgu133a | CS | eGFP |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485731.cel | 5 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486431.cel | 40 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485971.cel | 17 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| 46A.CEL | 1 | 3 | DS-mosaic | hgu133plus2 | none | DS-mosaic 1 |
| 46C.CEL | 3 | 3 | DS-mosaic | hgu133plus2 | none | DS-mosaic 3 |
| ctrl c 08-03.CEL | 3 | 1 | DS-CC | hgu133a | none | DS-CC 3 |
| E-GEOD-4219-raw-cel-1311956083.cel | 2 | 7 | Sph-mono | hgu133plus2 | none | Sph-mon 1 |
| E-GEOD-4219-raw-cel-1311956634.cel | 19 | 7 | Sph-mono | hgu133plus2 | none | Sph-mon 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486351.cel | 36 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-GEOD-4219-raw-cel-1311956418.cel | 13 | 7 | Sph-mono | hgu133plus2 | none | Sph-mon 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486331.cel | 35 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485851.cel | 11 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| ctrl a 08-03.CEL | 1 | 1 | DS-CC | hgu133a | none | DS-CC 1 |
| ctrl b 08-03.CEL | 2 | 1 | DS-CC | hgu133a | none | DS-CC 2 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486231.cel | 30 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |