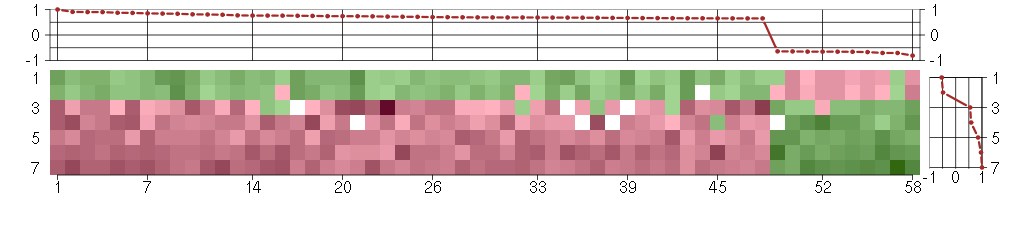

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways, including anabolism and catabolism, by which living organisms transform chemical substances. Metabolic processes typically transform small molecules, but also include macromolecular processes such as DNA repair and replication, and protein synthesis and degradation.
nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
regulation of nucleotide metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleotides.
cAMP biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of the nucleotide cAMP (cyclic AMP, adenosine 3',5'-cyclophosphate).
nucleoside phosphate metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving any phosphorylated nucleoside.
activation of adenylate cyclase activity
Any process that initiates the activity of the inactive enzyme adenylate cyclase.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
cAMP metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving the nucleotide cAMP (cyclic AMP, adenosine 3',5'-cyclophosphate).
biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances; typically the energy-requiring part of metabolism in which simpler substances are transformed into more complex ones.
nucleotide metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving a nucleotide, a nucleoside that is esterified with (ortho)phosphate or an oligophosphate at any hydroxyl group on the glycose moiety; may be mono-, di- or triphosphate; this definition includes cyclic nucleotides (nucleoside cyclic phosphates).
nucleotide biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of nucleotides, any nucleoside that is esterified with (ortho)phosphate or an oligophosphate at any hydroxyl group on the glycose moiety; may be mono-, di- or triphosphate; this definition includes cyclic-nucleotides (nucleoside cyclic phosphates).
cyclic nucleotide metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving a cyclic nucleotide, a nucleotide in which the phosphate group is in diester linkage to two positions on the sugar residue.
cyclic nucleotide biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a cyclic nucleotide, a nucleotide in which the phosphate group is in diester linkage to two positions on the sugar residue.
regulation of biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances.
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
regulation of nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
regulation of metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism.
regulation of cyclic nucleotide metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving cyclic nucleotides.
regulation of cyclic nucleotide biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of cyclic nucleotides.
regulation of nucleotide biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of nucleotides.
regulation of cAMP metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving the nucleotide cAMP (cyclic AMP, adenosine 3',5'-cyclophosphate).
regulation of cAMP biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of the nucleotide cAMP (cyclic AMP, adenosine 3',5'-cyclophosphate).
regulation of cyclase activity
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cyclase activity.
positive regulation of cyclase activity
Any process that activates or increases the activity of a cyclase.
regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
regulation of cellular biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
positive regulation of catalytic activity
Any process that activates or increases the activity of an enzyme.
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
primary metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving those compounds which are formed as a part of the normal anabolic and catabolic processes. These processes take place in most, if not all, cells of the organism.
cellular biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
regulation of adenylate cyclase activity
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of adenylate cyclase activity.
positive regulation of adenylate cyclase activity
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of adenylate cyclase activity.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of catalytic activity
Any process that modulates the activity of an enzyme.
regulation of cellular process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
regulation of lyase activity
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of lyase activity, the catalysis of the cleavage of C-C, C-O, C-N and other bonds by other means than by hydrolysis or oxidation, or conversely adding a group to a double bond. They differ from other enzymes in that two substrates are involved in one reaction direction, but only one in the other direction. When acting on the single substrate, a molecule is eliminated and this generates either a new double bond or a new ring.
positive regulation of lyase activity
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of lyase activity, the catalysis of the cleavage of C-C, C-O, C-N and other bonds by other means than by hydrolysis or oxidation, or conversely adding a group to a double bond.
nucleobase, nucleoside and nucleotide metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleobases, nucleosides and nucleotides.
biological regulation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of any biological process, quality or function.
regulation of molecular function
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of molecular functions. Molecular functions are elemental biological activities occurring at the molecular level, such as catalysis or binding.
all
This term is the most general term possible
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
regulation of metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism.
regulation of cellular process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances.
regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
cellular biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
regulation of cellular biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
regulation of cellular biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
regulation of nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
positive regulation of cyclase activity
Any process that activates or increases the activity of a cyclase.
regulation of adenylate cyclase activity
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of adenylate cyclase activity.
positive regulation of lyase activity
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of lyase activity, the catalysis of the cleavage of C-C, C-O, C-N and other bonds by other means than by hydrolysis or oxidation, or conversely adding a group to a double bond.
regulation of nucleotide biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of nucleotides.
positive regulation of adenylate cyclase activity
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of adenylate cyclase activity.
positive regulation of adenylate cyclase activity
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of adenylate cyclase activity.
regulation of cyclase activity
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cyclase activity.
regulation of cyclic nucleotide biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of cyclic nucleotides.
regulation of nucleotide metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleotides.
regulation of adenylate cyclase activity
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of adenylate cyclase activity.
regulation of cAMP biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of the nucleotide cAMP (cyclic AMP, adenosine 3',5'-cyclophosphate).
regulation of nucleotide biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of nucleotides.
cyclic nucleotide biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a cyclic nucleotide, a nucleotide in which the phosphate group is in diester linkage to two positions on the sugar residue.
regulation of cyclic nucleotide metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving cyclic nucleotides.
regulation of cyclic nucleotide biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of cyclic nucleotides.
cAMP biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of the nucleotide cAMP (cyclic AMP, adenosine 3',5'-cyclophosphate).
regulation of cAMP metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving the nucleotide cAMP (cyclic AMP, adenosine 3',5'-cyclophosphate).
regulation of cAMP biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of the nucleotide cAMP (cyclic AMP, adenosine 3',5'-cyclophosphate).

extracellular region
The space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.
cellular_component
The part of a cell or its extracellular environment in which a gene product is located. A gene product may be located in one or more parts of a cell and its location may be as specific as a particular macromolecular complex, that is, a stable, persistent association of macromolecules that function together.
extracellular space
That part of a multicellular organism outside the cells proper, usually taken to be outside the plasma membranes, and occupied by fluid.
extracellular region part
Any constituent part of the extracellular region, the space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers constituent parts of the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.
all
This term is the most general term possible
extracellular region part
Any constituent part of the extracellular region, the space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers constituent parts of the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.

ACSL4acyl-CoA synthetase long-chain family member 4 (202422_s_at), score: 0.72 ADORA2Badenosine A2b receptor (205891_at), score: -0.67 AHI1Abelson helper integration site 1 (221569_at), score: 0.9 ANXA10annexin A10 (210143_at), score: 0.76 BMP6bone morphogenetic protein 6 (206176_at), score: 0.91 C4orf43chromosome 4 open reading frame 43 (218513_at), score: 0.67 CD55CD55 molecule, decay accelerating factor for complement (Cromer blood group) (201925_s_at), score: 0.67 CDH13cadherin 13, H-cadherin (heart) (204726_at), score: 0.65 COL5A3collagen, type V, alpha 3 (52255_s_at), score: 0.66 CRTC3CREB regulated transcription coactivator 3 (218648_at), score: -0.7 CSGALNACT2chondroitin sulfate N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase 2 (222235_s_at), score: 0.71 CTAGE5CTAGE family, member 5 (215930_s_at), score: 0.7 CXCL6chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 6 (granulocyte chemotactic protein 2) (206336_at), score: 0.81 DNAJB9DnaJ (Hsp40) homolog, subfamily B, member 9 (202843_at), score: 0.9 EAF2ELL associated factor 2 (219551_at), score: 0.69 EDNRAendothelin receptor type A (204464_s_at), score: 0.65 ESM1endothelial cell-specific molecule 1 (208394_x_at), score: 0.84 FERMT1fermitin family homolog 1 (Drosophila) (218796_at), score: 0.76 GHRgrowth hormone receptor (205498_at), score: 0.66 GKglycerol kinase (207387_s_at), score: 1 GK3Pglycerol kinase 3 pseudogene (215966_x_at), score: 0.87 GMCL1germ cell-less homolog 1 (Drosophila) (218458_at), score: 0.74 GPM6Bglycoprotein M6B (209170_s_at), score: 0.74 GPR177G protein-coupled receptor 177 (221958_s_at), score: 0.68 GRB14growth factor receptor-bound protein 14 (206204_at), score: 0.69 H1FXH1 histone family, member X (204805_s_at), score: -0.66 HTR2A5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) receptor 2A (207135_at), score: 0.75 IL24interleukin 24 (206569_at), score: 0.72 IL33interleukin 33 (209821_at), score: 0.83 KAL1Kallmann syndrome 1 sequence (205206_at), score: 0.85 MAP7microtubule-associated protein 7 (202890_at), score: 0.65 MFAP3Lmicrofibrillar-associated protein 3-like (205442_at), score: 0.69 MMP10matrix metallopeptidase 10 (stromelysin 2) (205680_at), score: 0.74 NCALDneurocalcin delta (211685_s_at), score: 0.79 NCAPD2non-SMC condensin I complex, subunit D2 (201774_s_at), score: -0.65 NEFMneurofilament, medium polypeptide (205113_at), score: 0.69 NOX4NADPH oxidase 4 (219773_at), score: 0.73 NPTX1neuronal pentraxin I (204684_at), score: 0.69 NRXN3neurexin 3 (205795_at), score: 0.66 PCDH9protocadherin 9 (219737_s_at), score: 0.76 PCTK2PCTAIRE protein kinase 2 (221918_at), score: 0.7 PID1phosphotyrosine interaction domain containing 1 (219093_at), score: 0.77 PIONpigeon homolog (Drosophila) (222150_s_at), score: 0.68 PTHLHparathyroid hormone-like hormone (211756_at), score: 0.87 PTTG3pituitary tumor-transforming 3 (208511_at), score: -0.64 RAB6CRAB6C, member RAS oncogene family (210406_s_at), score: 0.66 RFX5regulatory factor X, 5 (influences HLA class II expression) (202963_at), score: -0.65 SLC33A1solute carrier family 33 (acetyl-CoA transporter), member 1 (203165_s_at), score: 0.8 SLC4A7solute carrier family 4, sodium bicarbonate cotransporter, member 7 (209884_s_at), score: 0.69 SLMO2slowmo homolog 2 (Drosophila) (217851_s_at), score: 0.68 SMAD3SMAD family member 3 (218284_at), score: -0.65 SNNstannin (218032_at), score: -0.71 TFDP2transcription factor Dp-2 (E2F dimerization partner 2) (203588_s_at), score: -0.81 TGDSTDP-glucose 4,6-dehydratase (208249_s_at), score: 0.68 TMEM2transmembrane protein 2 (218113_at), score: 0.66 URB1URB1 ribosome biogenesis 1 homolog (S. cerevisiae) (212996_s_at), score: 0.76 ZBTB6zinc finger and BTB domain containing 6 (206098_at), score: 0.65 ZDHHC7zinc finger, DHHC-type containing 7 (218606_at), score: -0.64
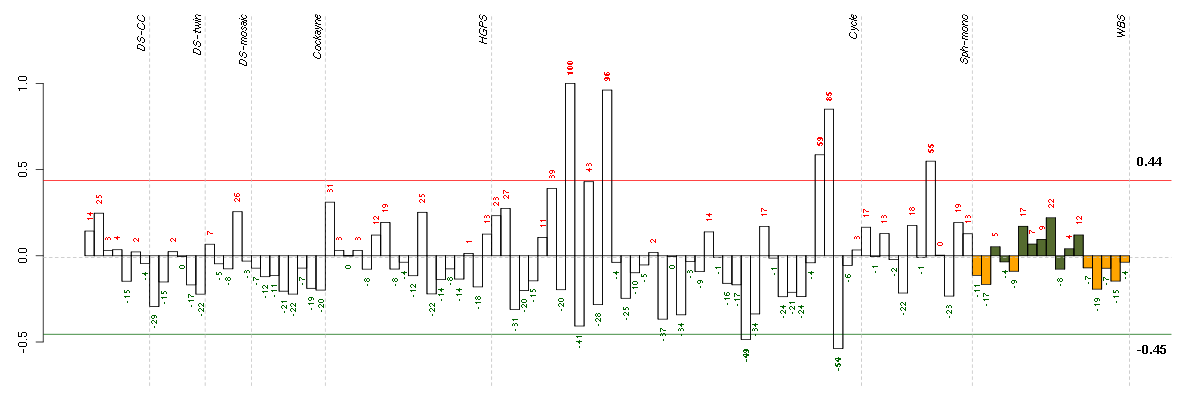
| Id | sample | Experiment | ExpName | Array | Syndrome | Cell.line |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486391.cel | 38 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486191.cel | 28 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-GEOD-4219-raw-cel-1311956418.cel | 13 | 7 | Sph-mono | hgu133plus2 | none | Sph-mon 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486351.cel | 36 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486371.cel | 37 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485891.cel | 13 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485811.cel | 9 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |