

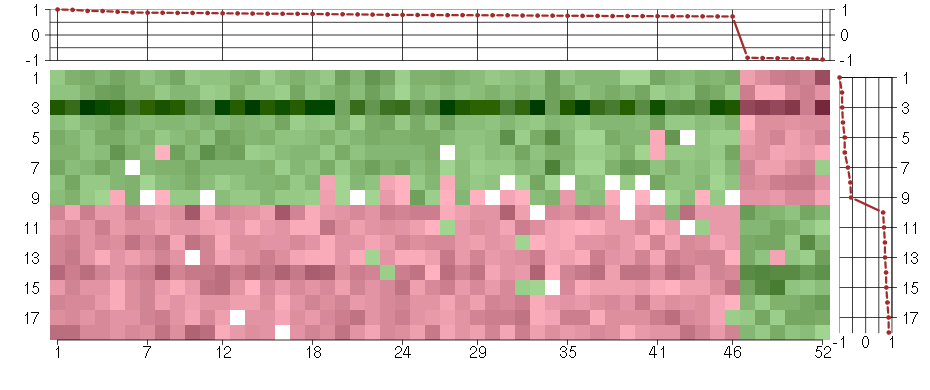

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

MAPKKK cascade
Cascade of at least three protein kinase activities culminating in the phosphorylation and activation of a MAP kinase. MAPKKK cascades lie downstream of numerous signaling pathways.
activation of MAPK activity
The initiation of the activity of the inactive enzyme MAP kinase by phosphorylation by a MAPKK.
metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways, including anabolism and catabolism, by which living organisms transform chemical substances. Metabolic processes typically transform small molecules, but also include macromolecular processes such as DNA repair and replication, and protein synthesis and degradation.
signal transduction
The cascade of processes by which a signal interacts with a receptor, causing a change in the level or activity of a second messenger or other downstream target, and ultimately effecting a change in the functioning of the cell.
protein modification process
The covalent alteration of one or more amino acids occurring in proteins, peptides and nascent polypeptides (co-translational, post-translational modifications). Includes the modification of charged tRNAs that are destined to occur in a protein (pre-translation modification).
protein amino acid phosphorylation
The process of introducing a phosphate group on to a protein.
phosphorus metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving the nonmetallic element phosphorus or compounds that contain phosphorus, usually in the form of a phosphate group (PO4).
phosphate metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving the phosphate group, the anion or salt of any phosphoric acid.
response to stress
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a disturbance in organismal or cellular homeostasis, usually, but not necessarily, exogenous (e.g. temperature, humidity, ionizing radiation).
cell communication
Any process that mediates interactions between a cell and its surroundings. Encompasses interactions such as signaling or attachment between one cell and another cell, between a cell and an extracellular matrix, or between a cell and any other aspect of its environment.
intracellular signaling cascade
A series of reactions within the cell that occur as a result of a single trigger reaction or compound.
protein kinase cascade
A series of reactions, mediated by protein kinases, which occurs as a result of a single trigger reaction or compound.
JNK cascade
A cascade of protein kinase activities, culminating in the phosphorylation and activation of a member of the JUN kinase subfamily of stress-activated protein kinases, which in turn are a subfamily of mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinases that is activated primarily by cytokines and exposure to environmental stress.
activation of JUN kinase activity
The initiation of the activity of the inactive enzyme JUN kinase by phosphorylation by a JUN kinase kinase (JNKK).
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
phosphorylation
The process of introducing a phosphate group into a molecule, usually with the formation of a phosphoric ester, a phosphoric anhydride or a phosphoric amide.
protein metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving a specific protein, rather than of proteins in general. Includes protein modification.
stress-activated protein kinase signaling pathway
A series of molecular signals in which a stress-activated protein kinase (SAPK) cascade relays one or more of the signals.
cellular response to stress
A change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus indicating the organism is under stress. The stress is usually, but not necessarily, exogenous (e.g. temperature, humidity, ionizing radiation).
positive regulation of kinase activity
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of kinase activity, the catalysis of the transfer of a phosphate group, usually from ATP, to a substrate molecule.
cellular biopolymer metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature, such as polysaccharides and proteins, as carried out by individual cells.
positive regulation of catalytic activity
Any process that activates or increases the activity of an enzyme.
macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
biopolymer metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature, such as polysaccharides and proteins.
regulation of MAP kinase activity
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of MAP kinase activity.
positive regulation of MAP kinase activity
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of MAP kinase activity.
biopolymer modification
The covalent alteration of one or more monomeric units in a polypeptide, polynucleotide, polysaccharide, or other biological polymer, resulting in a change in its properties.
regulation of JUN kinase activity
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of JUN kinase activity.
positive regulation of JUN kinase activity
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of JUN kinase activity.
regulation of kinase activity
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of kinase activity, the catalysis of the transfer of a phosphate group, usually from ATP, to a substrate molecule.
post-translational protein modification
The covalent alteration of one or more amino acids occurring in a protein after the protein has been completely translated and released from the ribosome.
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
primary metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving those compounds which are formed as a part of the normal anabolic and catabolic processes. These processes take place in most, if not all, cells of the organism.
cellular macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular protein metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving a specific protein, rather than of proteins in general, occurring at the level of an individual cell. Includes protein modification.
regulation of protein kinase activity
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of protein kinase activity.
positive regulation of protein kinase activity
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of protein kinase activity.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of catalytic activity
Any process that modulates the activity of an enzyme.
regulation of cellular process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
response to stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
regulation of transferase activity
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of transferase activity, the catalysis of the transfer of a group, e.g. a methyl group, glycosyl group, acyl group, phosphorus-containing, or other groups, from one compound (generally regarded as the donor) to another compound (generally regarded as the acceptor). Transferase is the systematic name for any enzyme of EC class 2.
positive regulation of transferase activity
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of transferase activity, the catalysis of the transfer of a group, e.g. a methyl group, glycosyl group, acyl group, phosphorus-containing, or other groups, from a donor compound to an acceptor.
cellular response to stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
biological regulation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of any biological process, quality or function.
regulation of molecular function
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of molecular functions. Molecular functions are elemental biological activities occurring at the molecular level, such as catalysis or binding.
all
This term is the most general term possible
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
regulation of cellular process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
cellular response to stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
cellular macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, as carried out by individual cells.
signal transduction
The cascade of processes by which a signal interacts with a receptor, causing a change in the level or activity of a second messenger or other downstream target, and ultimately effecting a change in the functioning of the cell.
cellular response to stress
A change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus indicating the organism is under stress. The stress is usually, but not necessarily, exogenous (e.g. temperature, humidity, ionizing radiation).
protein metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving a specific protein, rather than of proteins in general. Includes protein modification.
cellular biopolymer metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature, such as polysaccharides and proteins, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular protein metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving a specific protein, rather than of proteins in general, occurring at the level of an individual cell. Includes protein modification.
protein modification process
The covalent alteration of one or more amino acids occurring in proteins, peptides and nascent polypeptides (co-translational, post-translational modifications). Includes the modification of charged tRNAs that are destined to occur in a protein (pre-translation modification).
stress-activated protein kinase signaling pathway
A series of molecular signals in which a stress-activated protein kinase (SAPK) cascade relays one or more of the signals.
positive regulation of transferase activity
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of transferase activity, the catalysis of the transfer of a group, e.g. a methyl group, glycosyl group, acyl group, phosphorus-containing, or other groups, from a donor compound to an acceptor.
positive regulation of kinase activity
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of kinase activity, the catalysis of the transfer of a phosphate group, usually from ATP, to a substrate molecule.
protein amino acid phosphorylation
The process of introducing a phosphate group on to a protein.
activation of MAPK activity
The initiation of the activity of the inactive enzyme MAP kinase by phosphorylation by a MAPKK.
JNK cascade
A cascade of protein kinase activities, culminating in the phosphorylation and activation of a member of the JUN kinase subfamily of stress-activated protein kinases, which in turn are a subfamily of mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinases that is activated primarily by cytokines and exposure to environmental stress.
positive regulation of protein kinase activity
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of protein kinase activity.
activation of JUN kinase activity
The initiation of the activity of the inactive enzyme JUN kinase by phosphorylation by a JUN kinase kinase (JNKK).
positive regulation of MAP kinase activity
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of MAP kinase activity.
activation of MAPK activity
The initiation of the activity of the inactive enzyme MAP kinase by phosphorylation by a MAPKK.
positive regulation of JUN kinase activity
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of JUN kinase activity.
activation of JUN kinase activity
The initiation of the activity of the inactive enzyme JUN kinase by phosphorylation by a JUN kinase kinase (JNKK).


ABCD1ATP-binding cassette, sub-family D (ALD), member 1 (205142_x_at), score: 0.73 AGRNagrin (217419_x_at), score: 0.84 ARSAarylsulfatase A (204443_at), score: 0.84 BAP1BRCA1 associated protein-1 (ubiquitin carboxy-terminal hydrolase) (201419_at), score: 0.75 BAT2HLA-B associated transcript 2 (212081_x_at), score: 0.87 BAT2LHLA-B associated transcript 2-like (212068_s_at), score: 0.85 CDC42BPBCDC42 binding protein kinase beta (DMPK-like) (217849_s_at), score: 0.79 CIZ1CDKN1A interacting zinc finger protein 1 (205516_x_at), score: 0.74 COL18A1collagen, type XVIII, alpha 1 (209081_s_at), score: 0.79 CRTC3CREB regulated transcription coactivator 3 (218648_at), score: 0.76 DOK4docking protein 4 (209691_s_at), score: 0.73 FHOD1formin homology 2 domain containing 1 (218530_at), score: 0.87 FOXC2forkhead box C2 (MFH-1, mesenchyme forkhead 1) (214520_at), score: 0.74 FOXK2forkhead box K2 (203064_s_at), score: 0.91 FURINfurin (paired basic amino acid cleaving enzyme) (201945_at), score: 0.73 GTPBP1GTP binding protein 1 (219357_at), score: 0.74 HAB1B1 for mucin (215778_x_at), score: -0.9 HSF1heat shock transcription factor 1 (202344_at), score: 0.83 IDUAiduronidase, alpha-L- (205059_s_at), score: 0.88 JUPjunction plakoglobin (201015_s_at), score: 0.82 LEPREL2leprecan-like 2 (204854_at), score: 0.78 MAGOH2mago-nashi homolog 2, proliferation-associated (Drosophila) (217693_x_at), score: -0.89 MAP1Smicrotubule-associated protein 1S (218522_s_at), score: 1 MAP3K6mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 6 (219278_at), score: 0.79 MUL1mitochondrial E3 ubiquitin ligase 1 (218246_at), score: 0.78 NCDNneurochondrin (209556_at), score: 0.73 NCKAP1NCK-associated protein 1 (217465_at), score: -0.96 NINJ1ninjurin 1 (203045_at), score: 0.76 PARVBparvin, beta (204629_at), score: 0.77 PCDHG@protocadherin gamma cluster (215836_s_at), score: 0.78 PHF7PHD finger protein 7 (215622_x_at), score: -0.91 PIP5K1Cphosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate 5-kinase, type I, gamma (212518_at), score: 0.94 PKN1protein kinase N1 (202161_at), score: 0.83 PRKCDprotein kinase C, delta (202545_at), score: 0.87 RPS17P5ribosomal protein S17 pseudogene 5 (216348_at), score: -0.92 SBNO2strawberry notch homolog 2 (Drosophila) (204166_at), score: 0.77 SCAMP4secretory carrier membrane protein 4 (213244_at), score: 0.94 SIN3BSIN3 homolog B, transcription regulator (yeast) (209352_s_at), score: 0.83 SLC9A1solute carrier family 9 (sodium/hydrogen exchanger), member 1 (209453_at), score: 0.75 SMG6Smg-6 homolog, nonsense mediated mRNA decay factor (C. elegans) (214940_s_at), score: 0.81 SOLHsmall optic lobes homolog (Drosophila) (204275_at), score: 0.81 SPRY4sprouty homolog 4 (Drosophila) (221489_s_at), score: 0.75 SSBP3single stranded DNA binding protein 3 (217991_x_at), score: 0.78 TAPBPTAP binding protein (tapasin) (208829_at), score: 0.87 TERF2telomeric repeat binding factor 2 (203611_at), score: 0.74 TUBA4Btubulin, alpha 4b (pseudogene) (207490_at), score: -0.92 UBTD1ubiquitin domain containing 1 (219172_at), score: 0.86 USF2upstream transcription factor 2, c-fos interacting (202152_x_at), score: 0.73 VEGFBvascular endothelial growth factor B (203683_s_at), score: 0.99 VPS37Bvacuolar protein sorting 37 homolog B (S. cerevisiae) (221704_s_at), score: 0.85 WDR42AWD repeat domain 42A (202249_s_at), score: 0.76 WDR6WD repeat domain 6 (217734_s_at), score: 0.8
| Id | sample | Experiment | ExpName | Array | Syndrome | Cell.line |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485751.cel | 6 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485771.cel | 7 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-GEOD-3407-raw-cel-1437949557.cel | 1 | 4 | Cockayne | hgu133a | CS | eGFP |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486091.cel | 23 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486371.cel | 37 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486431.cel | 40 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485891.cel | 13 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| 2Twin.CEL | 2 | 2 | DS-twin | hgu133plus2 | none | DS-twin 2 |
| 5CTwin.CEL | 5 | 2 | DS-twin | hgu133plus2 | Down | DS-twin 5 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486031.cel | 20 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485871.cel | 12 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486071.cel | 22 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485991.cel | 18 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| 46A.CEL | 1 | 3 | DS-mosaic | hgu133plus2 | none | DS-mosaic 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485711.cel | 4 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486211.cel | 29 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485691.cel | 3 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486411.cel | 39 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
