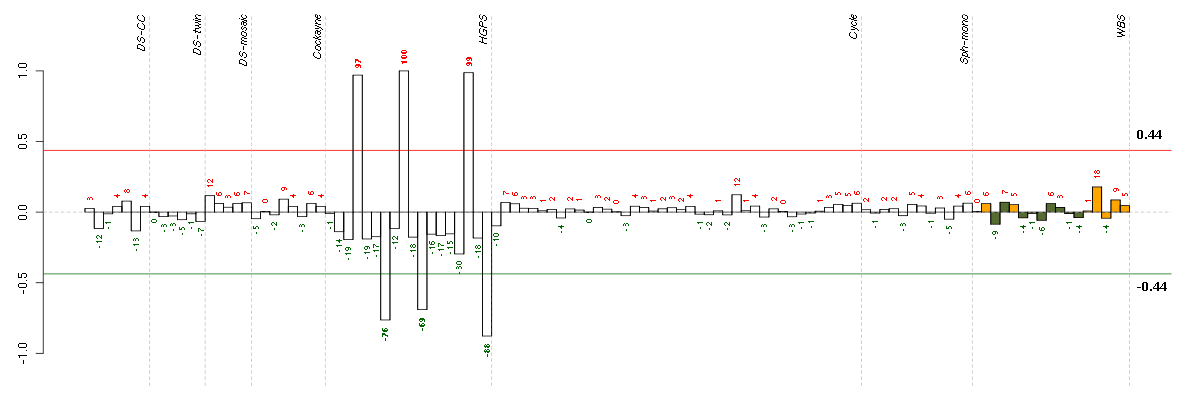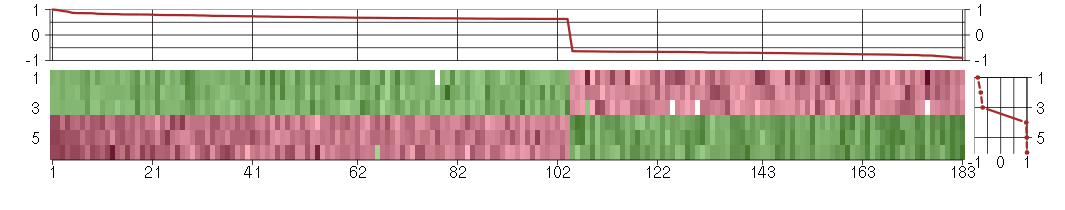

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

angiogenesis
Blood vessel formation when new vessels emerge from the proliferation of pre-existing blood vessels.
blood vessel development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the blood vessel over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The blood vessel is the vasculature carrying blood.
vasculature development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the vasculature over time, from its formation to the mature structure.
system process
A multicellular organismal process carried out by any of the organs or tissues in an organ system. An organ system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a biological objective.
muscle system process
A organ system process carried out at the level of a muscle. Muscle tissue is composed of contractile cells or fibers.
muscle contraction
A process whereby force is generated within muscle tissue, resulting in a change in muscle geometry. Force generation involves a chemo-mechanical energy conversion step that is carried out by the actin/myosin complex activity, which generates force through ATP hydrolysis.
signal transduction
The cascade of processes by which a signal interacts with a receptor, causing a change in the level or activity of a second messenger or other downstream target, and ultimately effecting a change in the functioning of the cell.
regulation of muscle contraction
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of muscle contraction.
smooth muscle contraction
A process whereby force is generated within smooth muscle tissue, resulting in a change in muscle geometry. Force generation involves a chemo-mechanical energy conversion step that is carried out by the actin/myosin complex activity, which generates force through ATP hydrolysis. Smooth muscle differs from striated muscle in the much higher actin/myosin ratio, the absence of conspicuous sarcomeres and the ability to contract to a much smaller fraction of its resting length.
regulation of smooth muscle contraction
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of smooth muscle contraction.
response to stress
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a disturbance in organismal or cellular homeostasis, usually, but not necessarily, exogenous (e.g. temperature, humidity, ionizing radiation).
cell communication
Any process that mediates interactions between a cell and its surroundings. Encompasses interactions such as signaling or attachment between one cell and another cell, between a cell and an extracellular matrix, or between a cell and any other aspect of its environment.
cell surface receptor linked signal transduction
Any series of molecular signals initiated by the binding of an extracellular ligand to a receptor on the surface of the target cell.
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
anatomical structure morphogenesis
The process by which anatomical structures are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
organ morphogenesis
Morphogenesis of an organ. An organ is defined as a tissue or set of tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Morphogenesis is the process by which anatomical structures are generated and organized. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
response to external stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an external stimulus.
response to wounding
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus indicating damage to the organism.
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
multicellular organismal process
Any biological process, occurring at the level of a multicellular organism, pertinent to its function.
developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an integrated living unit: an anatomical structure (which may be a subcellular structure, cell, tissue, or organ), or organism over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
regulation of system process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a system process, a multicellular organismal process carried out by any of the organs or tissues in an organ system.
organ development
Development of a tissue or tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Development pertains to the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a structure over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
blood vessel morphogenesis
The process by which the anatomical structures of blood vessels are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form. The blood vessel is the vasculature carrying blood.
anatomical structure formation
The process pertaining to the initial formation of an anatomical structure from unspecified parts. This process begins with the specific processes that contribute to the appearance of the discrete structure and ends when the structural rudiment is recognizable. An anatomical structure is any biological entity that occupies space and is distinguished from its surroundings. Anatomical structures can be macroscopic such as a carpel, or microscopic such as an acrosome.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
anatomical structure development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an anatomical structure from an initial condition to its mature state. This process begins with the formation of the structure and ends with the mature structure, whatever form that may be including its natural destruction. An anatomical structure is any biological entity that occupies space and is distinguished from its surroundings. Anatomical structures can be macroscopic such as a carpel, or microscopic such as an acrosome.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of cellular process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
response to stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
regulation of multicellular organismal process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a multicellular organismal process, the processes pertinent to the function of a multicellular organism above the cellular level; includes the integrated processes of tissues and organs.
biological regulation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of any biological process, quality or function.
all
This term is the most general term possible
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
regulation of cellular process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
regulation of multicellular organismal process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a multicellular organismal process, the processes pertinent to the function of a multicellular organism above the cellular level; includes the integrated processes of tissues and organs.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
signal transduction
The cascade of processes by which a signal interacts with a receptor, causing a change in the level or activity of a second messenger or other downstream target, and ultimately effecting a change in the functioning of the cell.
regulation of system process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a system process, a multicellular organismal process carried out by any of the organs or tissues in an organ system.
anatomical structure formation
The process pertaining to the initial formation of an anatomical structure from unspecified parts. This process begins with the specific processes that contribute to the appearance of the discrete structure and ends when the structural rudiment is recognizable. An anatomical structure is any biological entity that occupies space and is distinguished from its surroundings. Anatomical structures can be macroscopic such as a carpel, or microscopic such as an acrosome.
anatomical structure morphogenesis
The process by which anatomical structures are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
response to wounding
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus indicating damage to the organism.
organ development
Development of a tissue or tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Development pertains to the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a structure over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
organ morphogenesis
Morphogenesis of an organ. An organ is defined as a tissue or set of tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Morphogenesis is the process by which anatomical structures are generated and organized. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
regulation of muscle contraction
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of muscle contraction.
angiogenesis
Blood vessel formation when new vessels emerge from the proliferation of pre-existing blood vessels.
regulation of smooth muscle contraction
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of smooth muscle contraction.
blood vessel morphogenesis
The process by which the anatomical structures of blood vessels are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form. The blood vessel is the vasculature carrying blood.

intracellular
The living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
extracellular region
The space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.
cellular_component
The part of a cell or its extracellular environment in which a gene product is located. A gene product may be located in one or more parts of a cell and its location may be as specific as a particular macromolecular complex, that is, a stable, persistent association of macromolecules that function together.
extracellular space
That part of a multicellular organism outside the cells proper, usually taken to be outside the plasma membranes, and occupied by fluid.
cell
The basic structural and functional unit of all organisms. Includes the plasma membrane and any external encapsulating structures such as the cell wall and cell envelope.
cytoskeleton
Any of the various filamentous elements that form the internal framework of cells, and typically remain after treatment of the cells with mild detergent to remove membrane constituents and soluble components of the cytoplasm. The term embraces intermediate filaments, microfilaments, microtubules, the microtrabecular lattice, and other structures characterized by a polymeric filamentous nature and long-range order within the cell. The various elements of the cytoskeleton not only serve in the maintenance of cellular shape but also have roles in other cellular functions, including cellular movement, cell division, endocytosis, and movement of organelles.
extracellular matrix
A structure lying external to one or more cells, which provides structural support for cells or tissues; may be completely external to the cell (as in animals) or be part of the cell (as in plants).
organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
non-membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, not bounded by a lipid bilayer membrane. Includes ribosomes, the cytoskeleton and chromosomes.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular non-membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, not bounded by a lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes ribosomes, the cytoskeleton and chromosomes.
extracellular region part
Any constituent part of the extracellular region, the space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers constituent parts of the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
intermediate filament cytoskeleton
Cytoskeletal structure made from intermediate filaments, typically organized in the cytosol as an extended system that stretches from the nuclear envelope to the plasma membrane. Some intermediate filaments run parallel to the cell surface, while others traverse the cytosol; together they form an internal framework that helps support the shape and resilience of the cell.
neurofilament cytoskeleton
Intermediate filament cytoskeletal structure that is made up of neurofilaments. Neurofilaments are specialized intermediate filaments found in neurons.
all
This term is the most general term possible
extracellular region part
Any constituent part of the extracellular region, the space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers constituent parts of the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
intracellular non-membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, not bounded by a lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes ribosomes, the cytoskeleton and chromosomes.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.

calcium ion binding
Interacting selectively with calcium ions (Ca2+).
molecular_function
Elemental activities, such as catalysis or binding, describing the actions of a gene product at the molecular level. A given gene product may exhibit one or more molecular functions.
binding
The selective, often stoichiometric, interaction of a molecule with one or more specific sites on another molecule.
metal ion binding
Interacting selectively with any metal ion.
ion binding
Interacting selectively with ions, charged atoms or groups of atoms.
cation binding
Interacting selectively with cations, charged atoms or groups of atoms with a net positive charge.
all
This term is the most general term possible
calcium ion binding
Interacting selectively with calcium ions (Ca2+).
ABCA8ATP-binding cassette, sub-family A (ABC1), member 8 (204719_at), score: -0.72 ABCG2ATP-binding cassette, sub-family G (WHITE), member 2 (209735_at), score: 0.81 ACANaggrecan (205679_x_at), score: 0.64 ACTG2actin, gamma 2, smooth muscle, enteric (202274_at), score: 0.65 ADAM23ADAM metallopeptidase domain 23 (206046_at), score: 0.65 ADAMTSL3ADAMTS-like 3 (213974_at), score: -0.69 AGTR1angiotensin II receptor, type 1 (205357_s_at), score: 0.7 AKR1C3aldo-keto reductase family 1, member C3 (3-alpha hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase, type II) (209160_at), score: -0.67 ANK3ankyrin 3, node of Ranvier (ankyrin G) (206385_s_at), score: 0.78 ANKRD6ankyrin repeat domain 6 (204671_s_at), score: 0.78 ANO3anoctamin 3 (215241_at), score: 0.69 ANXA3annexin A3 (209369_at), score: -0.71 APOLD1apolipoprotein L domain containing 1 (221031_s_at), score: 0.65 AQP1aquaporin 1 (Colton blood group) (209047_at), score: 0.7 ARHGAP29Rho GTPase activating protein 29 (203910_at), score: -0.8 ARHGEF10LRho guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) 10-like (221656_s_at), score: 0.63 ATF3activating transcription factor 3 (202672_s_at), score: 0.77 BNC2basonuclin 2 (220272_at), score: -0.78 C16orf45chromosome 16 open reading frame 45 (212736_at), score: 0.65 C8orf84chromosome 8 open reading frame 84 (214725_at), score: -0.69 C9orf95chromosome 9 open reading frame 95 (219147_s_at), score: 0.63 CARHSP1calcium regulated heat stable protein 1, 24kDa (218384_at), score: -0.75 CCDC81coiled-coil domain containing 81 (220389_at), score: 0.75 CCDC92coiled-coil domain containing 92 (218175_at), score: 0.69 CCND2cyclin D2 (200953_s_at), score: 0.66 CD200CD200 molecule (209583_s_at), score: -0.73 CD34CD34 molecule (209543_s_at), score: -0.66 CD55CD55 molecule, decay accelerating factor for complement (Cromer blood group) (201925_s_at), score: -0.88 CDK5R1cyclin-dependent kinase 5, regulatory subunit 1 (p35) (204995_at), score: 0.63 CENPQcentromere protein Q (219294_at), score: -0.66 CFHcomplement factor H (213800_at), score: -0.7 CFHR1complement factor H-related 1 (215388_s_at), score: -0.71 CHRDL1chordin-like 1 (209763_at), score: -0.74 CMAHcytidine monophosphate-N-acetylneuraminic acid hydroxylase (CMP-N-acetylneuraminate monooxygenase) pseudogene (205518_s_at), score: -0.66 CORINcorin, serine peptidase (220356_at), score: 0.82 CUGBP2CUG triplet repeat, RNA binding protein 2 (202158_s_at), score: -0.76 CXCL1chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 1 (melanoma growth stimulating activity, alpha) (204470_at), score: -0.72 CYB5Acytochrome b5 type A (microsomal) (215726_s_at), score: -0.73 CYFIP2cytoplasmic FMR1 interacting protein 2 (215785_s_at), score: 0.8 CYTIPcytohesin 1 interacting protein (209606_at), score: 0.65 DAAM2dishevelled associated activator of morphogenesis 2 (212793_at), score: 0.75 DLEU1deleted in lymphocytic leukemia 1 (non-protein coding) (205677_s_at), score: -0.66 DPYSL3dihydropyrimidinase-like 3 (201430_s_at), score: -0.81 DSG2desmoglein 2 (217901_at), score: -0.78 EDN1endothelin 1 (218995_s_at), score: -0.69 EFHD1EF-hand domain family, member D1 (209343_at), score: 0.83 EHD3EH-domain containing 3 (218935_at), score: 0.63 EMP1epithelial membrane protein 1 (201325_s_at), score: -0.67 EN1engrailed homeobox 1 (220559_at), score: 0.78 ENPEPglutamyl aminopeptidase (aminopeptidase A) (204844_at), score: 0.77 EREGepiregulin (205767_at), score: 0.69 ERGv-ets erythroblastosis virus E26 oncogene homolog (avian) (213541_s_at), score: -0.65 FBLN1fibulin 1 (202995_s_at), score: -0.7 FBLN2fibulin 2 (203886_s_at), score: 0.79 FGL2fibrinogen-like 2 (204834_at), score: -0.8 FOXE1forkhead box E1 (thyroid transcription factor 2) (206912_at), score: 0.73 FOXO1forkhead box O1 (202724_s_at), score: -0.71 FUT8fucosyltransferase 8 (alpha (1,6) fucosyltransferase) (203988_s_at), score: -0.77 GALNT12UDP-N-acetyl-alpha-D-galactosamine:polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase 12 (GalNAc-T12) (218885_s_at), score: -0.65 GALNT3UDP-N-acetyl-alpha-D-galactosamine:polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase 3 (GalNAc-T3) (203397_s_at), score: 0.67 GPR116G protein-coupled receptor 116 (212950_at), score: 1 GPR126G protein-coupled receptor 126 (213094_at), score: -0.73 GPR4G protein-coupled receptor 4 (206236_at), score: -0.76 GPRC5AG protein-coupled receptor, family C, group 5, member A (203108_at), score: -0.66 GPRC5BG protein-coupled receptor, family C, group 5, member B (203632_s_at), score: -0.7 GPX3glutathione peroxidase 3 (plasma) (214091_s_at), score: 0.64 GRIK2glutamate receptor, ionotropic, kainate 2 (213845_at), score: 0.63 HCLS1hematopoietic cell-specific Lyn substrate 1 (202957_at), score: 0.76 HNMThistamine N-methyltransferase (204112_s_at), score: 0.7 HOXB7homeobox B7 (204779_s_at), score: -0.71 HRH1histamine receptor H1 (205579_at), score: -0.74 HSPB8heat shock 22kDa protein 8 (221667_s_at), score: 0.77 ID1inhibitor of DNA binding 1, dominant negative helix-loop-helix protein (208937_s_at), score: -0.7 IFI27interferon, alpha-inducible protein 27 (202411_at), score: -0.69 IL18interleukin 18 (interferon-gamma-inducing factor) (206295_at), score: -0.66 IL1Ainterleukin 1, alpha (210118_s_at), score: -0.64 INAinternexin neuronal intermediate filament protein, alpha (204465_s_at), score: 0.68 IRF1interferon regulatory factor 1 (202531_at), score: 0.67 ITGA7integrin, alpha 7 (216331_at), score: 0.74 ITGA8integrin, alpha 8 (214265_at), score: 0.94 IVNS1ABPinfluenza virus NS1A binding protein (206245_s_at), score: -0.64 KANK2KN motif and ankyrin repeat domains 2 (218418_s_at), score: 0.63 KCND2potassium voltage-gated channel, Shal-related subfamily, member 2 (207103_at), score: 0.8 KCNE4potassium voltage-gated channel, Isk-related family, member 4 (222379_at), score: 0.68 KCTD12potassium channel tetramerisation domain containing 12 (212192_at), score: -0.84 KIAA0247KIAA0247 (202181_at), score: -0.65 KLF5Kruppel-like factor 5 (intestinal) (209212_s_at), score: -0.77 LAMA4laminin, alpha 4 (202202_s_at), score: -0.9 LAMC2laminin, gamma 2 (202267_at), score: -0.73 LGR5leucine-rich repeat-containing G protein-coupled receptor 5 (213880_at), score: 0.86 LIMCH1LIM and calponin homology domains 1 (212327_at), score: -0.72 LIPGlipase, endothelial (219181_at), score: -0.76 LMOD1leiomodin 1 (smooth muscle) (203766_s_at), score: 0.67 LPPR4plasticity related gene 1 (213496_at), score: 0.81 LTBP2latent transforming growth factor beta binding protein 2 (204682_at), score: -0.67 MAPRE2microtubule-associated protein, RP/EB family, member 2 (202501_at), score: 0.66 MATN3matrilin 3 (206091_at), score: -0.66 MFGE8milk fat globule-EGF factor 8 protein (210605_s_at), score: 0.65 MMDmonocyte to macrophage differentiation-associated (203414_at), score: -0.66 MMP2matrix metallopeptidase 2 (gelatinase A, 72kDa gelatinase, 72kDa type IV collagenase) (201069_at), score: -0.77 MRASmuscle RAS oncogene homolog (206538_at), score: -0.64 MYH10myosin, heavy chain 10, non-muscle (212372_at), score: -0.88 MYLKmyosin light chain kinase (202555_s_at), score: 0.72 MYO1Emyosin IE (203072_at), score: 0.63 NAAAN-acylethanolamine acid amidase (214765_s_at), score: 0.68 NAGLUN-acetylglucosaminidase, alpha- (204360_s_at), score: 0.63 NAP1L3nucleosome assembly protein 1-like 3 (204749_at), score: -0.71 NBEAneurobeachin (221207_s_at), score: 0.64 NEFMneurofilament, medium polypeptide (205113_at), score: 0.81 NESnestin (218678_at), score: 0.66 NFIBnuclear factor I/B (209289_at), score: -0.73 NMUneuromedin U (206023_at), score: 0.66 NOTCH1Notch homolog 1, translocation-associated (Drosophila) (218902_at), score: 0.63 NOX4NADPH oxidase 4 (219773_at), score: -0.79 NQO2NAD(P)H dehydrogenase, quinone 2 (203814_s_at), score: -0.66 NUDT2nudix (nucleoside diphosphate linked moiety X)-type motif 2 (218609_s_at), score: -0.67 OSBPL1Aoxysterol binding protein-like 1A (209485_s_at), score: 0.67 PARP3poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase family, member 3 (209940_at), score: 0.8 PDGFAplatelet-derived growth factor alpha polypeptide (205463_s_at), score: 0.66 PDLIM3PDZ and LIM domain 3 (209621_s_at), score: 0.78 PHF11PHD finger protein 11 (221816_s_at), score: 0.69 PIK3R1phosphoinositide-3-kinase, regulatory subunit 1 (alpha) (212240_s_at), score: 0.66 PKIAprotein kinase (cAMP-dependent, catalytic) inhibitor alpha (204612_at), score: -0.66 PLCE1phospholipase C, epsilon 1 (205112_at), score: -0.67 PLK2polo-like kinase 2 (Drosophila) (201939_at), score: -0.74 PLXDC1plexin domain containing 1 (219700_at), score: 0.64 PLXNA2plexin A2 (213030_s_at), score: -0.83 PORCNporcupine homolog (Drosophila) (219483_s_at), score: 0.82 PPAP2Aphosphatidic acid phosphatase type 2A (209147_s_at), score: 0.7 PPP1R13Lprotein phosphatase 1, regulatory (inhibitor) subunit 13 like (218849_s_at), score: -0.78 PRNPprion protein (201300_s_at), score: -0.64 PROCRprotein C receptor, endothelial (EPCR) (203650_at), score: 0.65 PRSS1protease, serine, 1 (trypsin 1) (216470_x_at), score: 0.75 PRSS2protease, serine, 2 (trypsin 2) (205402_x_at), score: 0.75 PRSS3protease, serine, 3 (207463_x_at), score: 0.85 PTGESprostaglandin E synthase (210367_s_at), score: -0.66 PTPRZ1protein tyrosine phosphatase, receptor-type, Z polypeptide 1 (204469_at), score: 0.98 RAC2ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate 2 (rho family, small GTP binding protein Rac2) (213603_s_at), score: 0.66 RHBDL2rhomboid, veinlet-like 2 (Drosophila) (219489_s_at), score: -0.76 RPP25ribonuclease P/MRP 25kDa subunit (219143_s_at), score: 0.86 RTN1reticulon 1 (203485_at), score: 0.92 SCN3Asodium channel, voltage-gated, type III, alpha subunit (210432_s_at), score: 0.78 SCRN1secernin 1 (201462_at), score: 0.63 SEPT6septin 6 (212414_s_at), score: -0.7 SERPINF1serpin peptidase inhibitor, clade F (alpha-2 antiplasmin, pigment epithelium derived factor), member 1 (202283_at), score: -0.65 SIGLEC15sialic acid binding Ig-like lectin 15 (215856_at), score: 0.73 SIM2single-minded homolog 2 (Drosophila) (206558_at), score: 0.86 SIX2SIX homeobox 2 (206510_at), score: 0.71 SLC17A9solute carrier family 17, member 9 (219559_at), score: 0.73 SLC24A3solute carrier family 24 (sodium/potassium/calcium exchanger), member 3 (57588_at), score: 0.87 SLC39A8solute carrier family 39 (zinc transporter), member 8 (209267_s_at), score: -0.66 SLC7A5solute carrier family 7 (cationic amino acid transporter, y+ system), member 5 (201195_s_at), score: -0.75 SMAD6SMAD family member 6 (207069_s_at), score: -0.7 SORBS2sorbin and SH3 domain containing 2 (204288_s_at), score: 0.71 SOX17SRY (sex determining region Y)-box 17 (219993_at), score: -0.75 SPINT2serine peptidase inhibitor, Kunitz type, 2 (210715_s_at), score: 0.64 SPP1secreted phosphoprotein 1 (209875_s_at), score: 0.78 STARD7StAR-related lipid transfer (START) domain containing 7 (200028_s_at), score: 0.67 STAT6signal transducer and activator of transcription 6, interleukin-4 induced (201331_s_at), score: 0.63 STBD1starch binding domain 1 (203986_at), score: 0.71 STXBP2syntaxin binding protein 2 (209367_at), score: 0.63 STYK1serine/threonine/tyrosine kinase 1 (221696_s_at), score: 0.66 SYNMsynemin, intermediate filament protein (212730_at), score: 0.72 TBXA2Rthromboxane A2 receptor (336_at), score: 0.8 TEAD3TEA domain family member 3 (209454_s_at), score: 0.74 TIMP3TIMP metallopeptidase inhibitor 3 (201149_s_at), score: 0.71 TMEM35transmembrane protein 35 (219685_at), score: 0.64 TPK1thiamin pyrophosphokinase 1 (221218_s_at), score: -0.66 TRIM34tripartite motif-containing 34 (221044_s_at), score: 0.74 TRPV2transient receptor potential cation channel, subfamily V, member 2 (219282_s_at), score: 0.73 TRY6trypsinogen C (215395_x_at), score: 0.82 TSPAN12tetraspanin 12 (219274_at), score: 0.68 TSPYL5TSPY-like 5 (213122_at), score: -0.79 UAP1UDP-N-acteylglucosamine pyrophosphorylase 1 (209340_at), score: -0.63 UAP1L1UDP-N-acteylglucosamine pyrophosphorylase 1-like 1 (214755_at), score: 0.74 VAMP8vesicle-associated membrane protein 8 (endobrevin) (202546_at), score: 0.83 WNT10Bwingless-type MMTV integration site family, member 10B (206213_at), score: 0.65 ZDHHC7zinc finger, DHHC-type containing 7 (218606_at), score: 0.64 ZEB2zinc finger E-box binding homeobox 2 (203603_s_at), score: 0.69 ZFHX4zinc finger homeobox 4 (219779_at), score: -0.85 ZFP36zinc finger protein 36, C3H type, homolog (mouse) (201531_at), score: 0.67 ZFPM2zinc finger protein, multitype 2 (219778_at), score: -0.7 ZNF365zinc finger protein 365 (206448_at), score: -0.69
| Id | sample | Experiment | ExpName | Array | Syndrome | Cell.line |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E-GEOD-3860-raw-cel-1561690480.cel | 18 | 5 | HGPS | hgu133a | HGPS | AG11498 |
| E-GEOD-3860-raw-cel-1561690272.cel | 7 | 5 | HGPS | hgu133a | HGPS | AG11498 |
| E-GEOD-3860-raw-cel-1561690352.cel | 11 | 5 | HGPS | hgu133a | HGPS | AG11498 |
| E-GEOD-3860-raw-cel-1561690231.cel | 4 | 5 | HGPS | hgu133a | HGPS | AG10750 |
| E-GEOD-3860-raw-cel-1561690432.cel | 16 | 5 | HGPS | hgu133a | HGPS | AG10750 |
| E-GEOD-3860-raw-cel-1561690336.cel | 9 | 5 | HGPS | hgu133a | HGPS | AG10750 |