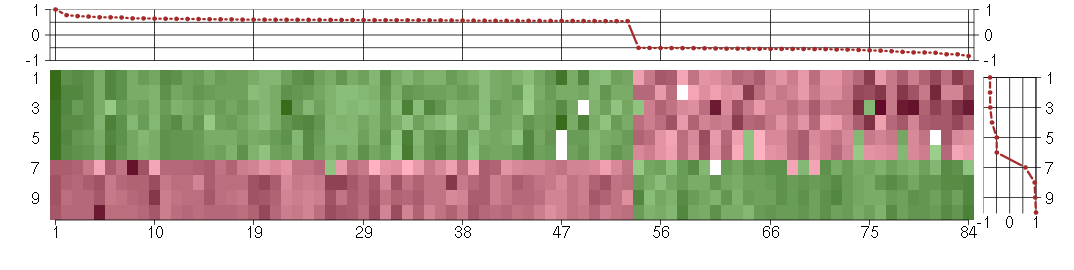

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

immune system process
Any process involved in the development or functioning of the immune system, an organismal system for calibrated responses to potential internal or invasive threats.
regulation of immune system process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of an immune system process.
negative regulation of immune system process
Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate, or extent of an immune system process.
immune response
Any immune system process that functions in the calibrated response of an organism to a potential internal or invasive threat.
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
nervous system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of nervous tissue over time, from its formation to its mature state.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
neurogenesis
Generation of cells within the nervous system.
cell differentiation
The process whereby relatively unspecialized cells, e.g. embryonic or regenerative cells, acquire specialized structural and/or functional features that characterize the cells, tissues, or organs of the mature organism or some other relatively stable phase of the organism's life history. Differentiation includes the processes involved in commitment of a cell to a specific fate.
neuron differentiation
The process whereby a relatively unspecialized cell acquires specialized features of a neuron.
multicellular organismal process
Any biological process, occurring at the level of a multicellular organism, pertinent to its function.
developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an integrated living unit: an anatomical structure (which may be a subcellular structure, cell, tissue, or organ), or organism over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
regulation of cell differentiation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell differentiation, the process whereby relatively unspecialized cells acquire specialized structural and functional features.
negative regulation of cell differentiation
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of cell differentiation.
regulation of neuron differentiation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of neuron differentiation.
negative regulation of neuron differentiation
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of neuron differentiation.
cell development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the cell over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Cell development does not include the steps involved in committing a cell to a specific fate.
negative regulation of biological process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
negative regulation of cellular process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
regulation of response to stimulus
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a response to a stimulus. Response to stimulus is a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
negative regulation of response to stimulus
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of a response to a stimulus. Response to stimulus is a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
generation of neurons
The process by which nerve cells are generated. This includes the production of neuroblasts and their differentiation into neurons.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
anatomical structure development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an anatomical structure from an initial condition to its mature state. This process begins with the formation of the structure and ends with the mature structure, whatever form that may be including its natural destruction. An anatomical structure is any biological entity that occupies space and is distinguished from its surroundings. Anatomical structures can be macroscopic such as a carpel, or microscopic such as an acrosome.
cellular developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a cell over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
regulation of neurogenesis
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of neurogenesis, the origin and formation of neurons.
regulation of immune response
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the immune response, the immunological reaction of an organism to an immunogenic stimulus.
negative regulation of immune response
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the immune response, the immunological reaction of an organism to an immunogenic stimulus.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of developmental process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of development, the biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote, or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
regulation of cellular process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
response to stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
negative regulation of developmental process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the rate or extent of development, the biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote, or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
regulation of multicellular organismal process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a multicellular organismal process, the processes pertinent to the function of a multicellular organism above the cellular level; includes the integrated processes of tissues and organs.
regulation of nervous system development
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of nervous system development, the origin and formation of nervous tissue.
regulation of cell development
Any process that modulates the rate, frequency or extent of the progression of the cell over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Cell development does not include the steps involved in committing a cell to a specific fate.
biological regulation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of any biological process, quality or function.
all
This term is the most general term possible
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
cellular developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a cell over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
negative regulation of immune system process
Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate, or extent of an immune system process.
negative regulation of cellular process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
negative regulation of developmental process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the rate or extent of development, the biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote, or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
regulation of immune system process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of an immune system process.
negative regulation of biological process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of developmental process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of development, the biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote, or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
regulation of cellular process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
regulation of multicellular organismal process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a multicellular organismal process, the processes pertinent to the function of a multicellular organism above the cellular level; includes the integrated processes of tissues and organs.
immune response
Any immune system process that functions in the calibrated response of an organism to a potential internal or invasive threat.
regulation of response to stimulus
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a response to a stimulus. Response to stimulus is a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
negative regulation of response to stimulus
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of a response to a stimulus. Response to stimulus is a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
negative regulation of immune system process
Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate, or extent of an immune system process.
regulation of immune response
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the immune response, the immunological reaction of an organism to an immunogenic stimulus.
negative regulation of immune response
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the immune response, the immunological reaction of an organism to an immunogenic stimulus.
negative regulation of cellular process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
regulation of cell differentiation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell differentiation, the process whereby relatively unspecialized cells acquire specialized structural and functional features.
negative regulation of developmental process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the rate or extent of development, the biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote, or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
regulation of nervous system development
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of nervous system development, the origin and formation of nervous tissue.
negative regulation of cell differentiation
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of cell differentiation.
negative regulation of immune response
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the immune response, the immunological reaction of an organism to an immunogenic stimulus.
negative regulation of response to stimulus
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of a response to a stimulus. Response to stimulus is a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
regulation of immune response
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the immune response, the immunological reaction of an organism to an immunogenic stimulus.
negative regulation of immune response
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the immune response, the immunological reaction of an organism to an immunogenic stimulus.
regulation of neurogenesis
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of neurogenesis, the origin and formation of neurons.
regulation of cell differentiation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell differentiation, the process whereby relatively unspecialized cells acquire specialized structural and functional features.
negative regulation of cell differentiation
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of cell differentiation.
cell development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the cell over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Cell development does not include the steps involved in committing a cell to a specific fate.
negative regulation of cell differentiation
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of cell differentiation.
regulation of cell development
Any process that modulates the rate, frequency or extent of the progression of the cell over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Cell development does not include the steps involved in committing a cell to a specific fate.
regulation of neurogenesis
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of neurogenesis, the origin and formation of neurons.
neuron differentiation
The process whereby a relatively unspecialized cell acquires specialized features of a neuron.
regulation of neurogenesis
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of neurogenesis, the origin and formation of neurons.
regulation of neuron differentiation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of neuron differentiation.
negative regulation of neuron differentiation
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of neuron differentiation.
neurogenesis
Generation of cells within the nervous system.
regulation of nervous system development
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of nervous system development, the origin and formation of nervous tissue.
negative regulation of neuron differentiation
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of neuron differentiation.


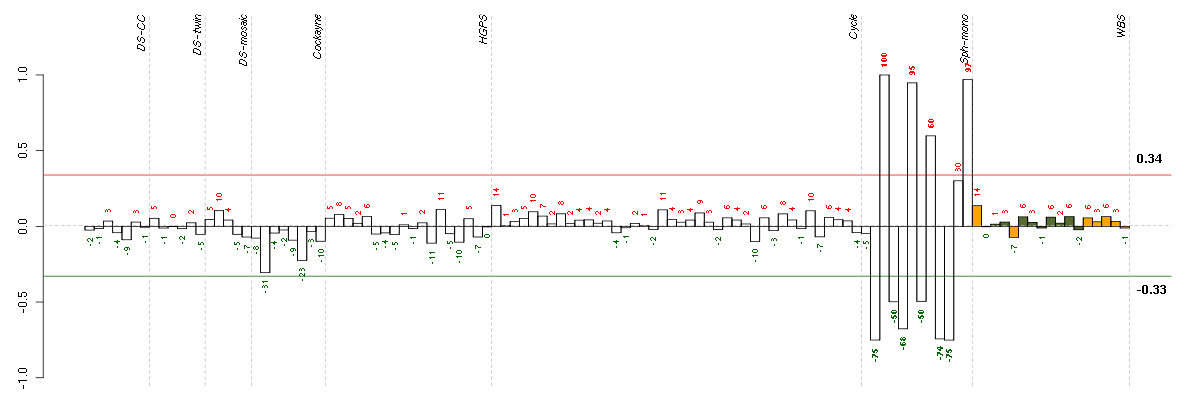
AEBP1AE binding protein 1 (201792_at), score: 0.56 AKAP2A kinase (PRKA) anchor protein 2 (202759_s_at), score: 0.6 AKR1B10aldo-keto reductase family 1, member B10 (aldose reductase) (206561_s_at), score: -0.66 ARMCX1armadillo repeat containing, X-linked 1 (218694_at), score: 0.63 BMP7bone morphogenetic protein 7 (209590_at), score: -0.53 C14orf169chromosome 14 open reading frame 169 (219526_at), score: 0.72 CAND2cullin-associated and neddylation-dissociated 2 (putative) (213547_at), score: 0.58 CD24CD24 molecule (209771_x_at), score: -0.54 CDH6cadherin 6, type 2, K-cadherin (fetal kidney) (205532_s_at), score: -0.51 CELSR1cadherin, EGF LAG seven-pass G-type receptor 1 (flamingo homolog, Drosophila) (41660_at), score: -0.59 CELSR3cadherin, EGF LAG seven-pass G-type receptor 3 (flamingo homolog, Drosophila) (40020_at), score: -0.76 CHMP1Achromatin modifying protein 1A (201933_at), score: -0.51 CLEC11AC-type lectin domain family 11, member A (211709_s_at), score: 0.55 CLEC2BC-type lectin domain family 2, member B (209732_at), score: -0.55 COL3A1collagen, type III, alpha 1 (215076_s_at), score: 0.64 CYB561cytochrome b-561 (209163_at), score: -0.51 DGKDdiacylglycerol kinase, delta 130kDa (208072_s_at), score: -0.64 ENOSF1enolase superfamily member 1 (204142_at), score: 0.56 ENPP2ectonucleotide pyrophosphatase/phosphodiesterase 2 (209392_at), score: 0.55 EPB41L1erythrocyte membrane protein band 4.1-like 1 (212339_at), score: -0.52 EPHX1epoxide hydrolase 1, microsomal (xenobiotic) (202017_at), score: -0.54 FAM174Bfamily with sequence similarity 174, member B (51158_at), score: 0.69 FAM65Bfamily with sequence similarity 65, member B (209829_at), score: 0.58 FCGR2AFc fragment of IgG, low affinity IIa, receptor (CD32) (203561_at), score: -0.61 FLT1fms-related tyrosine kinase 1 (vascular endothelial growth factor/vascular permeability factor receptor) (222033_s_at), score: 0.6 FOXG1forkhead box G1 (206018_at), score: -0.57 GAL3ST4galactose-3-O-sulfotransferase 4 (219815_at), score: 0.56 GALCgalactosylceramidase (204417_at), score: 0.63 GPRC5BG protein-coupled receptor, family C, group 5, member B (203632_s_at), score: -0.54 GREM1gremlin 1, cysteine knot superfamily, homolog (Xenopus laevis) (218469_at), score: 1 HEY1hairy/enhancer-of-split related with YRPW motif 1 (44783_s_at), score: -0.55 HSD17B12hydroxysteroid (17-beta) dehydrogenase 12 (217869_at), score: 0.58 IGSF3immunoglobulin superfamily, member 3 (202421_at), score: -0.76 IL23Ainterleukin 23, alpha subunit p19 (211796_s_at), score: 0.6 IPWimprinted in Prader-Willi syndrome (non-protein coding) (221974_at), score: 0.61 ISL1ISL LIM homeobox 1 (206104_at), score: 0.62 KYNUkynureninase (L-kynurenine hydrolase) (217388_s_at), score: -0.83 LAPTM5lysosomal multispanning membrane protein 5 (201721_s_at), score: -0.54 LEF1lymphoid enhancer-binding factor 1 (221558_s_at), score: -0.68 LPPR4plasticity related gene 1 (213496_at), score: 0.59 LUMlumican (201744_s_at), score: 0.74 MLF1myeloid leukemia factor 1 (204784_s_at), score: -0.54 MLLT3myeloid/lymphoid or mixed-lineage leukemia (trithorax homolog, Drosophila); translocated to, 3 (204918_s_at), score: 0.59 MOXD1monooxygenase, DBH-like 1 (209708_at), score: 0.55 MPPED2metallophosphoesterase domain containing 2 (205413_at), score: -0.7 MYO1Bmyosin IB (212364_at), score: 0.78 NESnestin (218678_at), score: 0.55 NETO2neuropilin (NRP) and tolloid (TLL)-like 2 (218888_s_at), score: 0.56 NPTX1neuronal pentraxin I (204684_at), score: -0.55 NRN1neuritin 1 (218625_at), score: -0.55 NT5E5'-nucleotidase, ecto (CD73) (203939_at), score: 0.58 PCLOpiccolo (presynaptic cytomatrix protein) (213558_at), score: -0.6 PDGFRAplatelet-derived growth factor receptor, alpha polypeptide (203131_at), score: 0.69 PDLIM4PDZ and LIM domain 4 (214175_x_at), score: 0.58 PEX5peroxisomal biogenesis factor 5 (203244_at), score: -0.57 PSMD5proteasome (prosome, macropain) 26S subunit, non-ATPase, 5 (203447_at), score: 0.56 PSTPIP2proline-serine-threonine phosphatase interacting protein 2 (219938_s_at), score: 0.65 PTPRDprotein tyrosine phosphatase, receptor type, D (214043_at), score: 0.65 RECKreversion-inducing-cysteine-rich protein with kazal motifs (205407_at), score: 0.54 RIPK4receptor-interacting serine-threonine kinase 4 (221215_s_at), score: -0.69 RND3Rho family GTPase 3 (212724_at), score: 0.55 S100A4S100 calcium binding protein A4 (203186_s_at), score: 0.57 SCRIBscribbled homolog (Drosophila) (212556_at), score: 0.55 SERPINB9serpin peptidase inhibitor, clade B (ovalbumin), member 9 (209723_at), score: 0.58 SIM1single-minded homolog 1 (Drosophila) (206876_at), score: 0.54 SLC38A4solute carrier family 38, member 4 (220786_s_at), score: 0.59 SMA5glucuronidase, beta pseudogene (215043_s_at), score: -0.5 SPANXCSPANX family, member C (220217_x_at), score: -0.54 STAT6signal transducer and activator of transcription 6, interleukin-4 induced (201331_s_at), score: 0.57 SULF1sulfatase 1 (212353_at), score: 0.56 SYNGR1synaptogyrin 1 (210613_s_at), score: 0.6 TBXA2Rthromboxane A2 receptor (336_at), score: 0.64 TCF7L2transcription factor 7-like 2 (T-cell specific, HMG-box) (212761_at), score: 0.6 TEStestis derived transcript (3 LIM domains) (202720_at), score: 0.69 TGFB2transforming growth factor, beta 2 (220407_s_at), score: -0.51 THBS2thrombospondin 2 (203083_at), score: 0.63 TMEM111transmembrane protein 111 (217882_at), score: -0.51 TNS1tensin 1 (221748_s_at), score: 0.59 TPBGtrophoblast glycoprotein (203476_at), score: 0.6 TSPYL5TSPY-like 5 (213122_at), score: 0.62 TUBB6tubulin, beta 6 (209191_at), score: 0.58 ULK2unc-51-like kinase 2 (C. elegans) (204062_s_at), score: 0.6 ZNF215zinc finger protein 215 (220214_at), score: 0.57 ZNF518Azinc finger protein 518A (204291_at), score: 0.56
| Id | sample | Experiment | ExpName | Array | Syndrome | Cell.line |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E-GEOD-4219-raw-cel-1311956614.cel | 18 | 7 | Sph-mono | hgu133plus2 | none | Sph-mon 1 |
| E-GEOD-4219-raw-cel-1311956138.cel | 4 | 7 | Sph-mono | hgu133plus2 | none | Sph-mon 1 |
| E-GEOD-4219-raw-cel-1311956457.cel | 14 | 7 | Sph-mono | hgu133plus2 | none | Sph-mon 1 |
| E-GEOD-4219-raw-cel-1311956321.cel | 9 | 7 | Sph-mono | hgu133plus2 | none | Sph-mon 1 |
| E-GEOD-4219-raw-cel-1311956275.cel | 8 | 7 | Sph-mono | hgu133plus2 | none | Sph-mon 1 |
| E-GEOD-4219-raw-cel-1311956398.cel | 12 | 7 | Sph-mono | hgu133plus2 | none | Sph-mon 1 |
| E-GEOD-4219-raw-cel-1311956418.cel | 13 | 7 | Sph-mono | hgu133plus2 | none | Sph-mon 1 |
| E-GEOD-4219-raw-cel-1311956358.cel | 10 | 7 | Sph-mono | hgu133plus2 | none | Sph-mon 1 |
| E-GEOD-4219-raw-cel-1311956824.cel | 24 | 7 | Sph-mono | hgu133plus2 | none | Sph-mon 1 |
| E-GEOD-4219-raw-cel-1311956178.cel | 6 | 7 | Sph-mono | hgu133plus2 | none | Sph-mon 1 |