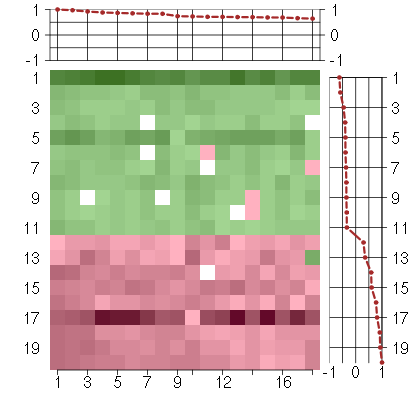

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways, including anabolism and catabolism, by which living organisms transform chemical substances. Metabolic processes typically transform small molecules, but also include macromolecular processes such as DNA repair and replication, and protein synthesis and degradation.
translation
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a protein. This is a ribosome-mediated process in which the information in messenger RNA (mRNA) is used to specify the sequence of amino acids in the protein.
translational elongation
The successive addition of amino acid residues to a nascent polypeptide chain during protein biosynthesis.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances; typically the energy-requiring part of metabolism in which simpler substances are transformed into more complex ones.
macromolecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
gene expression
The process by which a gene's coding sequence is converted into a mature gene product or products (proteins or RNA). This includes the production of an RNA transcript as well as any processing to produce a mature RNA product or an mRNA (for protein-coding genes) and the translation of that mRNA into protein. Some protein processing events may be included when they are required to form an active form of a product from an inactive precursor form.
protein metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving a specific protein, rather than of proteins in general. Includes protein modification.
cellular macromolecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, carried out by individual cells.
cellular biopolymer metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature, such as polysaccharides and proteins, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular biopolymer biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature, such as polysaccharides and proteins, as carried out by individual cells.
macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
biopolymer metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature, such as polysaccharides and proteins.
biopolymer biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature e.g. polysaccharides and proteins.
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
primary metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving those compounds which are formed as a part of the normal anabolic and catabolic processes. These processes take place in most, if not all, cells of the organism.
cellular biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
cellular macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular protein metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving a specific protein, rather than of proteins in general, occurring at the level of an individual cell. Includes protein modification.
all
This term is the most general term possible
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
macromolecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
cellular biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
cellular macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular macromolecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, carried out by individual cells.
protein metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving a specific protein, rather than of proteins in general. Includes protein modification.
biopolymer biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature e.g. polysaccharides and proteins.
cellular macromolecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, carried out by individual cells.
cellular biopolymer metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature, such as polysaccharides and proteins, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular biopolymer biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature, such as polysaccharides and proteins, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular biopolymer biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature, such as polysaccharides and proteins, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular protein metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving a specific protein, rather than of proteins in general, occurring at the level of an individual cell. Includes protein modification.
translation
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a protein. This is a ribosome-mediated process in which the information in messenger RNA (mRNA) is used to specify the sequence of amino acids in the protein.
translation
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a protein. This is a ribosome-mediated process in which the information in messenger RNA (mRNA) is used to specify the sequence of amino acids in the protein.
translational elongation
The successive addition of amino acid residues to a nascent polypeptide chain during protein biosynthesis.

cytosolic large ribosomal subunit
The large subunit of the ribosome that is found in the cytosol of the cell. The cytosol is that part of the cytoplasm that does not contain membranous or particulate subcellular components.
cytosolic small ribosomal subunit
The small subunit of the ribosome that is found in the cytosol of the cell. The cytosol is that part of the cytoplasm that does not contain membranous or particulate subcellular components.
intracellular
The living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
ribonucleoprotein complex
A macromolecular complex containing both protein and RNA molecules.
cytosol
That part of the cytoplasm that does not contain membranous or particulate subcellular components.
ribosome
An intracellular organelle, about 200 A in diameter, consisting of RNA and protein. It is the site of protein biosynthesis resulting from translation of messenger RNA (mRNA). It consists of two subunits, one large and one small, each containing only protein and RNA. Both the ribosome and its subunits are characterized by their sedimentation coefficients, expressed in Svedberg units (symbol: S). Hence, the prokaryotic ribosome (70S) comprises a large (50S) subunit and a small (30S) subunit, while the eukaryotic ribosome (80S) comprises a large (60S) subunit and a small (40S) subunit. Two sites on the ribosomal large subunit are involved in translation, namely the aminoacyl site (A site) and peptidyl site (P site). Ribosomes from prokaryotes, eukaryotes, mitochondria, and chloroplasts have characteristically distinct ribosomal proteins.
cellular_component
The part of a cell or its extracellular environment in which a gene product is located. A gene product may be located in one or more parts of a cell and its location may be as specific as a particular macromolecular complex, that is, a stable, persistent association of macromolecules that function together.
cell
The basic structural and functional unit of all organisms. Includes the plasma membrane and any external encapsulating structures such as the cell wall and cell envelope.
cytoplasm
All of the contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures.
large ribosomal subunit
The larger of the two subunits of a ribosome. Two sites on the ribosomal large subunit are involved in translation, namely the aminoacyl site (A site) and peptidyl site (P site).
small ribosomal subunit
The smaller of the two subunits of a ribosome.
cytosolic ribosome
A ribosome that is found in the cytosol of the cell. The cytosol is that part of the cytoplasm that does not contain membranous or particulate subcellular components.
macromolecular complex
A stable assembly of two or more macromolecules, i.e. proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates or lipids, in which the constituent parts function together.
ribosomal subunit
Either of the two ribonucleoprotein complexes that associate to form a ribosome.
organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
non-membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, not bounded by a lipid bilayer membrane. Includes ribosomes, the cytoskeleton and chromosomes.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular non-membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, not bounded by a lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes ribosomes, the cytoskeleton and chromosomes.
organelle part
Any constituent part of an organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, but excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
cytoplasmic part
Any constituent part of the cytoplasm, all of the contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures.
cytosolic part
Any constituent part of cytosol, that part of the cytoplasm that does not contain membranous or particulate subcellular components.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
all
This term is the most general term possible
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
organelle part
Any constituent part of an organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, but excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular non-membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, not bounded by a lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes ribosomes, the cytoskeleton and chromosomes.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
ribosomal subunit
Either of the two ribonucleoprotein complexes that associate to form a ribosome.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
ribonucleoprotein complex
A macromolecular complex containing both protein and RNA molecules.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
ribosomal subunit
Either of the two ribonucleoprotein complexes that associate to form a ribosome.
ribosome
An intracellular organelle, about 200 A in diameter, consisting of RNA and protein. It is the site of protein biosynthesis resulting from translation of messenger RNA (mRNA). It consists of two subunits, one large and one small, each containing only protein and RNA. Both the ribosome and its subunits are characterized by their sedimentation coefficients, expressed in Svedberg units (symbol: S). Hence, the prokaryotic ribosome (70S) comprises a large (50S) subunit and a small (30S) subunit, while the eukaryotic ribosome (80S) comprises a large (60S) subunit and a small (40S) subunit. Two sites on the ribosomal large subunit are involved in translation, namely the aminoacyl site (A site) and peptidyl site (P site). Ribosomes from prokaryotes, eukaryotes, mitochondria, and chloroplasts have characteristically distinct ribosomal proteins.
cytoplasmic part
Any constituent part of the cytoplasm, all of the contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures.
ribosome
An intracellular organelle, about 200 A in diameter, consisting of RNA and protein. It is the site of protein biosynthesis resulting from translation of messenger RNA (mRNA). It consists of two subunits, one large and one small, each containing only protein and RNA. Both the ribosome and its subunits are characterized by their sedimentation coefficients, expressed in Svedberg units (symbol: S). Hence, the prokaryotic ribosome (70S) comprises a large (50S) subunit and a small (30S) subunit, while the eukaryotic ribosome (80S) comprises a large (60S) subunit and a small (40S) subunit. Two sites on the ribosomal large subunit are involved in translation, namely the aminoacyl site (A site) and peptidyl site (P site). Ribosomes from prokaryotes, eukaryotes, mitochondria, and chloroplasts have characteristically distinct ribosomal proteins.
ribosomal subunit
Either of the two ribonucleoprotein complexes that associate to form a ribosome.
cytosolic large ribosomal subunit
The large subunit of the ribosome that is found in the cytosol of the cell. The cytosol is that part of the cytoplasm that does not contain membranous or particulate subcellular components.
cytosolic small ribosomal subunit
The small subunit of the ribosome that is found in the cytosol of the cell. The cytosol is that part of the cytoplasm that does not contain membranous or particulate subcellular components.
cytosolic part
Any constituent part of cytosol, that part of the cytoplasm that does not contain membranous or particulate subcellular components.
cytosolic large ribosomal subunit
The large subunit of the ribosome that is found in the cytosol of the cell. The cytosol is that part of the cytoplasm that does not contain membranous or particulate subcellular components.
cytosolic small ribosomal subunit
The small subunit of the ribosome that is found in the cytosol of the cell. The cytosol is that part of the cytoplasm that does not contain membranous or particulate subcellular components.
cytosolic ribosome
A ribosome that is found in the cytosol of the cell. The cytosol is that part of the cytoplasm that does not contain membranous or particulate subcellular components.

molecular_function
Elemental activities, such as catalysis or binding, describing the actions of a gene product at the molecular level. A given gene product may exhibit one or more molecular functions.
nucleic acid binding
Interacting selectively with any nucleic acid.
RNA binding
Interacting selectively with an RNA molecule or a portion thereof.
structural constituent of ribosome
The action of a molecule that contributes to the structural integrity of the ribosome.
structural molecule activity
The action of a molecule that contributes to the structural integrity of a complex or assembly within or outside a cell.
binding
The selective, often stoichiometric, interaction of a molecule with one or more specific sites on another molecule.
all
This term is the most general term possible
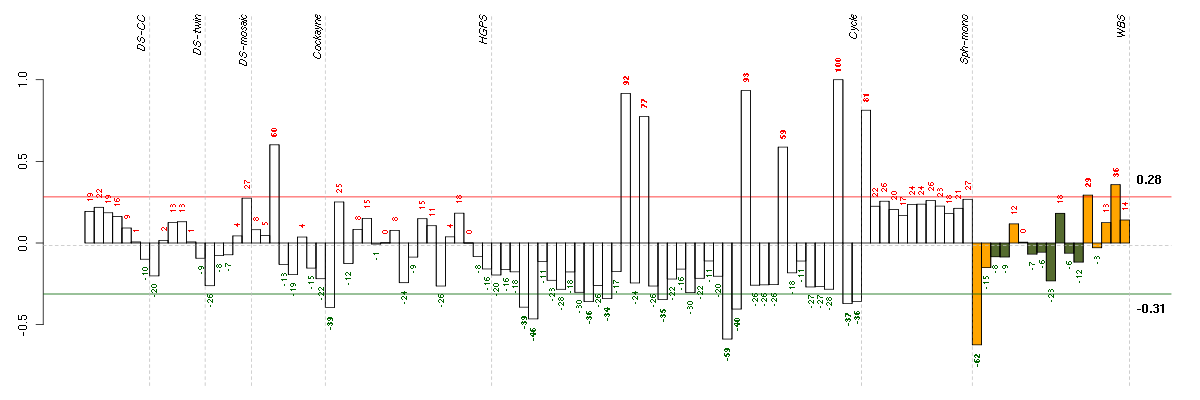
ATP6V0E1ATPase, H+ transporting, lysosomal 9kDa, V0 subunit e1 (214244_s_at), score: 0.92 B4GALT1UDP-Gal:betaGlcNAc beta 1,4- galactosyltransferase, polypeptide 1 (201883_s_at), score: 0.74 CDC42SE1CDC42 small effector 1 (218157_x_at), score: 0.64 COX5Bcytochrome c oxidase subunit Vb (213736_at), score: 0.7 EEF1Deukaryotic translation elongation factor 1 delta (guanine nucleotide exchange protein) (214395_x_at), score: 0.69 MRPL52mitochondrial ribosomal protein L52 (221997_s_at), score: 0.71 NDUFA2NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) 1 alpha subcomplex, 2, 8kDa (213550_s_at), score: 0.73 RHEBRas homolog enriched in brain (213409_s_at), score: 0.66 RPL14ribosomal protein L14 (219138_at), score: 0.88 RPL27Aribosomal protein L27a (212044_s_at), score: 0.97 RPL37Aribosomal protein L37a (214041_x_at), score: 0.69 RPL38ribosomal protein L38 (202028_s_at), score: 0.83 RPLP2ribosomal protein, large, P2 (200908_s_at), score: 0.87 RPS10ribosomal protein S10 (214001_x_at), score: 0.83 RPS11ribosomal protein S11 (213350_at), score: 1 RPS19ribosomal protein S19 (202648_at), score: 0.85 SNRPEsmall nuclear ribonucleoprotein polypeptide E (215450_at), score: 0.71 TXNthioredoxin (216609_at), score: 0.7
| Id | sample | Experiment | ExpName | Array | Syndrome | Cell.line |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10358_WBS.CEL | 1 | 8 | WBS | hgu133plus2 | WBS | WBS 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486151.cel | 26 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485731.cel | 5 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486171.cel | 27 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-GEOD-3860-raw-cel-1561690199.cel | 1 | 5 | HGPS | hgu133a | none | GM0316B |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485711.cel | 4 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486411.cel | 39 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485851.cel | 11 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486431.cel | 40 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486011.cel | 19 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485891.cel | 13 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| D890_WBS.CEL | 13 | 8 | WBS | hgu133plus2 | WBS | WBS 1 |
| F348_WBS.CEL | 16 | 8 | WBS | hgu133plus2 | WBS | WBS 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486271.cel | 32 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-GEOD-3407-raw-cel-1437949655.cel | 3 | 4 | Cockayne | hgu133a | none | CSB |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485971.cel | 17 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-GEOD-4219-raw-cel-1311956083.cel | 2 | 7 | Sph-mono | hgu133plus2 | none | Sph-mon 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485931.cel | 15 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486191.cel | 28 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486391.cel | 38 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |