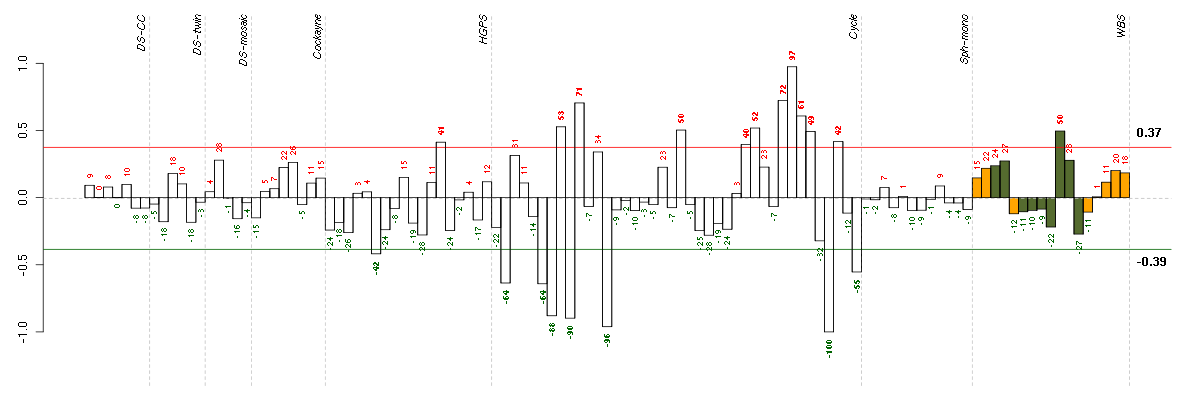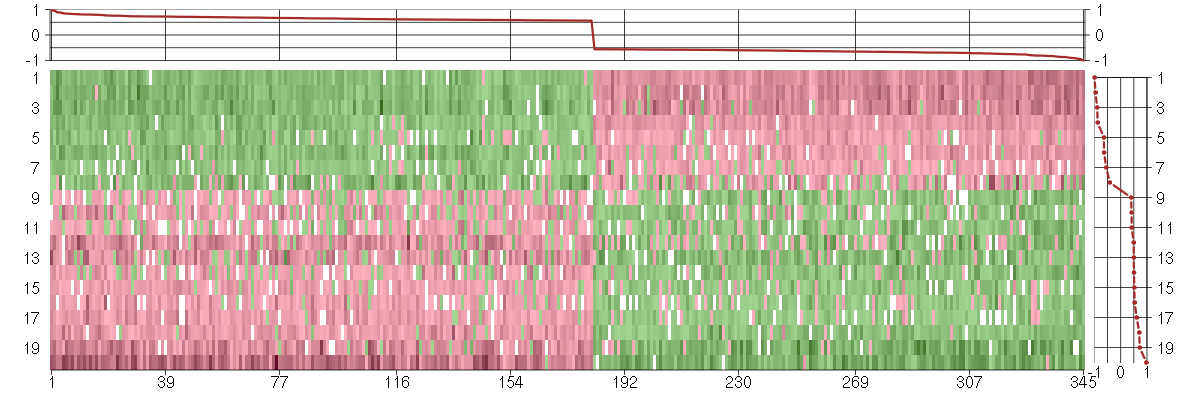

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

reproduction
The production by an organism of new individuals that contain some portion of their genetic material inherited from that organism.
metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways, including anabolism and catabolism, by which living organisms transform chemical substances. Metabolic processes typically transform small molecules, but also include macromolecular processes such as DNA repair and replication, and protein synthesis and degradation.
immune system process
Any process involved in the development or functioning of the immune system, an organismal system for calibrated responses to potential internal or invasive threats.
immune system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system whose objective is to provide calibrated responses by an organism to a potential internal or invasive threat, over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
leukocyte differentiation
The process whereby a relatively unspecialized hemopoietic precursor cell acquires the specialized features of a plasmacytoid dendritic cell or any cell of the myeloid leukocyte or lymphocyte lineages.
myeloid leukocyte differentiation
The process whereby a relatively unspecialized myeloid precursor cell acquires the specialized features of any cell of the myeloid leukocyte lineage.
regulation of immune system process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of an immune system process.
regulation of myeloid leukocyte differentiation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of myeloid leukocyte differentiation.
negative regulation of myeloid leukocyte differentiation
Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate, or extent of myeloid leukocyte differentiation.
defense response
Reactions, triggered in response to the presence of a foreign body or the occurrence of an injury, which result in restriction of damage to the organism attacked or prevention/recovery from the infection caused by the attack.
nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
response to stress
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a disturbance in organismal or cellular homeostasis, usually, but not necessarily, exogenous (e.g. temperature, humidity, ionizing radiation).
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
viral genome replication
Any process involved directly in viral genome replication, including viral nucleotide metabolism.
viral reproduction
The process by which a virus reproduces. Usually, this is by infection of a host cell, replication of the viral genome, and assembly of progeny virus particles. In some cases the viral genetic material may integrate into the host genome and only subsequently, under particular circumstances, 'complete' its life cycle.
RNA modification
The covalent alteration of one or more nucleotides within an RNA molecule to produce an RNA molecule with a sequence that differs from that coded genetically.
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
foam cell differentiation
The process whereby a relatively unspecialized monocyte acquires the specialized features of a foam cell. A foam cell is a macrophage containing lipid in small vacuoles.
regulation of foam cell differentiation
Any process that modulates the rate, frequency or extent of foam cell differentiation. Foam cell differentiation is the process whereby a relatively unspecialized monocyte acquires the specialized features of a foam cell. A foam cell is a macrophage containing lipid in small vacuoles.
negative regulation of foam cell differentiation
Any process that decreases the rate, frequency or extent of foam cell differentiation. Foam cell differentiation is the process whereby a relatively unspecialized monocyte acquires the specialized features of a foam cell. A foam cell is a macrophage containing lipid in small vacuoles.
RNA metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving RNA, ribonucleic acid, one of the two main type of nucleic acid, consisting of a long, unbranched macromolecule formed from ribonucleotides joined in 3',5'-phosphodiester linkage.
base conversion or substitution editing
Any base modification or substitution events that result in alterations in the coding potential or structural properties of RNAs as a result of changes in the base-pairing properties of the modified ribonucleoside(s).
viral infectious cycle
A set of processes which all viruses follow to ensure survival; includes attachment and entry of the virus particle, decoding of genome information, translation of viral mRNA by host ribosomes, genome replication, and assembly and release of viral particles containing the genome.
reproductive process
A biological process that directly contributes to the process of producing new individuals by one or two organisms. The new individuals inherit some proportion of their genetic material from the parent or parents.
viral reproductive process
A reproductive process involved in viral reproduction. Usually, this is by infection of a host cell, replication of the viral genome, and assembly of progeny virus particles. In some cases the viral genetic material may integrate into the host genome and only subsequently, under particular circumstances, 'complete' its life cycle.
hemopoiesis
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the myeloid and lymphoid derived organ/tissue systems of the blood and other parts of the body over time, from formation to the mature structure. The site of hemopoiesis is variable during development, but occurs primarily in bone marrow or kidney in many adult vertebrates.
myeloid cell differentiation
The process whereby a relatively unspecialized myeloid precursor cell acquires the specialized features of any cell of the myeloid leukocyte, megakaryocyte, thrombocyte, or erythrocyte lineages.
cell differentiation
The process whereby relatively unspecialized cells, e.g. embryonic or regenerative cells, acquire specialized structural and/or functional features that characterize the cells, tissues, or organs of the mature organism or some other relatively stable phase of the organism's life history. Differentiation includes the processes involved in commitment of a cell to a specific fate.
macrophage differentiation
The process whereby a relatively unspecialized monocyte acquires the specialized features of a macrophage.
multicellular organismal process
Any biological process, occurring at the level of a multicellular organism, pertinent to its function.
developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an integrated living unit: an anatomical structure (which may be a subcellular structure, cell, tissue, or organ), or organism over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
cellular biopolymer metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature, such as polysaccharides and proteins, as carried out by individual cells.
response to chemical stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a chemical stimulus.
macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
biopolymer metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature, such as polysaccharides and proteins.
response to dsRNA
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a double-stranded RNA stimulus.
biopolymer modification
The covalent alteration of one or more monomeric units in a polypeptide, polynucleotide, polysaccharide, or other biological polymer, resulting in a change in its properties.
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
primary metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving those compounds which are formed as a part of the normal anabolic and catabolic processes. These processes take place in most, if not all, cells of the organism.
cellular macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, as carried out by individual cells.
regulation of viral genome replication
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of viral genome replication.
negative regulation of viral genome replication
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of viral genome replication.
regulation of cell differentiation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell differentiation, the process whereby relatively unspecialized cells acquire specialized structural and functional features.
negative regulation of cell differentiation
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of cell differentiation.
regulation of myeloid cell differentiation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of myeloid cell differentiation.
negative regulation of myeloid cell differentiation
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of myeloid cell differentiation.
regulation of macrophage differentiation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of macrophage differentiation.
negative regulation of macrophage differentiation
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of macrophage differentiation.
organ development
Development of a tissue or tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Development pertains to the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a structure over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
negative regulation of biological process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
negative regulation of cellular process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
negative regulation of viral reproduction
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the viral life cycle, the set of processes by which a virus reproduces and spreads among hosts.
hemopoietic or lymphoid organ development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of any organ involved in hemopoiesis or lymphoid cell activation over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Such development includes differentiation of resident cell types (stromal cells) and of migratory cell types dependent on the unique microenvironment afforded by the organ for their proper differentiation.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
anatomical structure development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an anatomical structure from an initial condition to its mature state. This process begins with the formation of the structure and ends with the mature structure, whatever form that may be including its natural destruction. An anatomical structure is any biological entity that occupies space and is distinguished from its surroundings. Anatomical structures can be macroscopic such as a carpel, or microscopic such as an acrosome.
cellular developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a cell over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of viral reproduction
Any process that modulates the rate or extent of the viral life cycle, the set of processes by which a virus reproduces and spreads among hosts.
regulation of developmental process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of development, the biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote, or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
regulation of cellular process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
response to stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
negative regulation of developmental process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the rate or extent of development, the biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote, or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
regulation of multicellular organismal process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a multicellular organismal process, the processes pertinent to the function of a multicellular organism above the cellular level; includes the integrated processes of tissues and organs.
biological regulation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of any biological process, quality or function.
all
This term is the most general term possible
reproductive process
A biological process that directly contributes to the process of producing new individuals by one or two organisms. The new individuals inherit some proportion of their genetic material from the parent or parents.
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
viral reproductive process
A reproductive process involved in viral reproduction. Usually, this is by infection of a host cell, replication of the viral genome, and assembly of progeny virus particles. In some cases the viral genetic material may integrate into the host genome and only subsequently, under particular circumstances, 'complete' its life cycle.
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
cellular developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a cell over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
negative regulation of cellular process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
negative regulation of viral reproduction
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the viral life cycle, the set of processes by which a virus reproduces and spreads among hosts.
negative regulation of developmental process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the rate or extent of development, the biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote, or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
regulation of immune system process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of an immune system process.
negative regulation of biological process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of viral reproduction
Any process that modulates the rate or extent of the viral life cycle, the set of processes by which a virus reproduces and spreads among hosts.
regulation of developmental process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of development, the biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote, or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
regulation of cellular process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
regulation of multicellular organismal process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a multicellular organismal process, the processes pertinent to the function of a multicellular organism above the cellular level; includes the integrated processes of tissues and organs.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
cellular macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, as carried out by individual cells.
nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
negative regulation of viral reproduction
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the viral life cycle, the set of processes by which a virus reproduces and spreads among hosts.
negative regulation of cellular process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
regulation of myeloid cell differentiation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of myeloid cell differentiation.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
regulation of cell differentiation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell differentiation, the process whereby relatively unspecialized cells acquire specialized structural and functional features.
negative regulation of developmental process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the rate or extent of development, the biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote, or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
negative regulation of cell differentiation
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of cell differentiation.
cellular biopolymer metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature, such as polysaccharides and proteins, as carried out by individual cells.
regulation of viral genome replication
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of viral genome replication.
negative regulation of viral genome replication
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of viral genome replication.
viral genome replication
Any process involved directly in viral genome replication, including viral nucleotide metabolism.
negative regulation of viral genome replication
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of viral genome replication.
negative regulation of myeloid cell differentiation
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of myeloid cell differentiation.
regulation of cell differentiation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell differentiation, the process whereby relatively unspecialized cells acquire specialized structural and functional features.
negative regulation of cell differentiation
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of cell differentiation.
negative regulation of cell differentiation
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of cell differentiation.
regulation of myeloid cell differentiation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of myeloid cell differentiation.
immune system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system whose objective is to provide calibrated responses by an organism to a potential internal or invasive threat, over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
organ development
Development of a tissue or tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Development pertains to the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a structure over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
hemopoietic or lymphoid organ development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of any organ involved in hemopoiesis or lymphoid cell activation over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Such development includes differentiation of resident cell types (stromal cells) and of migratory cell types dependent on the unique microenvironment afforded by the organ for their proper differentiation.
RNA metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving RNA, ribonucleic acid, one of the two main type of nucleic acid, consisting of a long, unbranched macromolecule formed from ribonucleotides joined in 3',5'-phosphodiester linkage.
RNA modification
The covalent alteration of one or more nucleotides within an RNA molecule to produce an RNA molecule with a sequence that differs from that coded genetically.
leukocyte differentiation
The process whereby a relatively unspecialized hemopoietic precursor cell acquires the specialized features of a plasmacytoid dendritic cell or any cell of the myeloid leukocyte or lymphocyte lineages.
myeloid cell differentiation
The process whereby a relatively unspecialized myeloid precursor cell acquires the specialized features of any cell of the myeloid leukocyte, megakaryocyte, thrombocyte, or erythrocyte lineages.
negative regulation of myeloid leukocyte differentiation
Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate, or extent of myeloid leukocyte differentiation.
myeloid leukocyte differentiation
The process whereby a relatively unspecialized myeloid precursor cell acquires the specialized features of any cell of the myeloid leukocyte lineage.
regulation of myeloid cell differentiation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of myeloid cell differentiation.
negative regulation of myeloid cell differentiation
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of myeloid cell differentiation.
negative regulation of macrophage differentiation
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of macrophage differentiation.
regulation of myeloid leukocyte differentiation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of myeloid leukocyte differentiation.
negative regulation of myeloid leukocyte differentiation
Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate, or extent of myeloid leukocyte differentiation.
negative regulation of foam cell differentiation
Any process that decreases the rate, frequency or extent of foam cell differentiation. Foam cell differentiation is the process whereby a relatively unspecialized monocyte acquires the specialized features of a foam cell. A foam cell is a macrophage containing lipid in small vacuoles.
regulation of macrophage differentiation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of macrophage differentiation.
negative regulation of macrophage differentiation
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of macrophage differentiation.
regulation of foam cell differentiation
Any process that modulates the rate, frequency or extent of foam cell differentiation. Foam cell differentiation is the process whereby a relatively unspecialized monocyte acquires the specialized features of a foam cell. A foam cell is a macrophage containing lipid in small vacuoles.
negative regulation of foam cell differentiation
Any process that decreases the rate, frequency or extent of foam cell differentiation. Foam cell differentiation is the process whereby a relatively unspecialized monocyte acquires the specialized features of a foam cell. A foam cell is a macrophage containing lipid in small vacuoles.


| Id | Pvalue | ExpCount | Count | Size | Term |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 04080 | 8.551e-03 | 3.349 | 12 | 83 | Neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction |
ABCA8ATP-binding cassette, sub-family A (ABC1), member 8 (204719_at), score: 0.64 ABHD3abhydrolase domain containing 3 (213017_at), score: -0.68 ABHD5abhydrolase domain containing 5 (218739_at), score: -0.6 ACSL4acyl-CoA synthetase long-chain family member 4 (202422_s_at), score: -0.69 ACTR3BARP3 actin-related protein 3 homolog B (yeast) (218868_at), score: -0.7 ADAM19ADAM metallopeptidase domain 19 (meltrin beta) (209765_at), score: -0.69 ADARadenosine deaminase, RNA-specific (201786_s_at), score: 0.71 ADH1Balcohol dehydrogenase 1B (class I), beta polypeptide (209612_s_at), score: 0.67 ADORA2Badenosine A2b receptor (205891_at), score: 0.82 AGBL5ATP/GTP binding protein-like 5 (218480_at), score: 0.64 AHI1Abelson helper integration site 1 (221569_at), score: -0.81 AIM1absent in melanoma 1 (212543_at), score: 0.74 AJAP1adherens junctions associated protein 1 (206460_at), score: -0.59 AKR1B10aldo-keto reductase family 1, member B10 (aldose reductase) (206561_s_at), score: 0.63 AKR1C3aldo-keto reductase family 1, member C3 (3-alpha hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase, type II) (209160_at), score: 0.65 ALDH3A2aldehyde dehydrogenase 3 family, member A2 (202053_s_at), score: 0.58 ANGPTL2angiopoietin-like 2 (213001_at), score: 0.83 ANXA10annexin A10 (210143_at), score: -0.9 AOX1aldehyde oxidase 1 (205083_at), score: 0.56 APAF1apoptotic peptidase activating factor 1 (204859_s_at), score: -0.61 APOBEC3Fapolipoprotein B mRNA editing enzyme, catalytic polypeptide-like 3F (214995_s_at), score: 0.6 APOBEC3Gapolipoprotein B mRNA editing enzyme, catalytic polypeptide-like 3G (204205_at), score: 0.6 APOL6apolipoprotein L, 6 (219716_at), score: 0.7 ARAP1ArfGAP with RhoGAP domain, ankyrin repeat and PH domain 1 (34206_at), score: 0.58 ARHGEF2rho/rac guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) 2 (209435_s_at), score: 0.7 ARHGEF3Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) 3 (218501_at), score: 0.65 ARL4CADP-ribosylation factor-like 4C (202207_at), score: 0.66 ARMC9armadillo repeat containing 9 (219637_at), score: 0.69 ASAP3ArfGAP with SH3 domain, ankyrin repeat and PH domain 3 (219103_at), score: 0.72 ATP2C1ATPase, Ca++ transporting, type 2C, member 1 (211137_s_at), score: -0.6 ATP6V0BATPase, H+ transporting, lysosomal 21kDa, V0 subunit b (200078_s_at), score: -0.64 B9D1B9 protein domain 1 (210534_s_at), score: 0.71 BDH23-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase, type 2 (218285_s_at), score: 0.57 BDKRB2bradykinin receptor B2 (205870_at), score: 0.71 BEX4brain expressed, X-linked 4 (215440_s_at), score: 0.63 BIN1bridging integrator 1 (210201_x_at), score: 0.68 BMP6bone morphogenetic protein 6 (206176_at), score: -0.68 BNIP3LBCL2/adenovirus E1B 19kDa interacting protein 3-like (221479_s_at), score: 0.56 BRIP1BRCA1 interacting protein C-terminal helicase 1 (221703_at), score: -0.72 BTBD2BTB (POZ) domain containing 2 (207722_s_at), score: 0.67 BTG2BTG family, member 2 (201236_s_at), score: 0.81 C13orf15chromosome 13 open reading frame 15 (218723_s_at), score: 0.76 C14orf159chromosome 14 open reading frame 159 (218298_s_at), score: 0.59 C1orf107chromosome 1 open reading frame 107 (214193_s_at), score: -0.58 C1orf109chromosome 1 open reading frame 109 (218712_at), score: -0.56 C1orf9chromosome 1 open reading frame 9 (203429_s_at), score: -0.61 C4orf15chromosome 4 open reading frame 15 (210054_at), score: -0.63 C4orf43chromosome 4 open reading frame 43 (218513_at), score: -0.66 CALB2calbindin 2 (205428_s_at), score: -0.73 CALCOCO1calcium binding and coiled-coil domain 1 (209002_s_at), score: 0.8 CAMLGcalcium modulating ligand (203538_at), score: 0.57 CASZ1castor zinc finger 1 (220015_at), score: -0.56 CCDC28Acoiled-coil domain containing 28A (209479_at), score: 0.7 CCNE2cyclin E2 (205034_at), score: -0.65 CCNG1cyclin G1 (208796_s_at), score: 0.72 CDC25Acell division cycle 25 homolog A (S. pombe) (204695_at), score: -0.57 CDC2L6cell division cycle 2-like 6 (CDK8-like) (212899_at), score: 0.59 CDC42EP2CDC42 effector protein (Rho GTPase binding) 2 (209850_s_at), score: 0.59 CDC6cell division cycle 6 homolog (S. cerevisiae) (203967_at), score: -0.56 CDCP1CUB domain containing protein 1 (218451_at), score: -0.66 CDH6cadherin 6, type 2, K-cadherin (fetal kidney) (205532_s_at), score: -0.61 CDKN1Ccyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1C (p57, Kip2) (213348_at), score: 0.68 CENPQcentromere protein Q (219294_at), score: -0.58 CEP68centrosomal protein 68kDa (212677_s_at), score: 0.58 CHRNA10cholinergic receptor, nicotinic, alpha 10 (220210_at), score: -0.59 CHUKconserved helix-loop-helix ubiquitous kinase (209666_s_at), score: -0.69 CLASP2cytoplasmic linker associated protein 2 (212306_at), score: -0.6 CLDN11claudin 11 (206908_s_at), score: 0.58 CLIP3CAP-GLY domain containing linker protein 3 (212358_at), score: 0.83 CMPK1cytidine monophosphate (UMP-CMP) kinase 1, cytosolic (217870_s_at), score: -0.63 CRBNcereblon (218142_s_at), score: 0.67 CRTC3CREB regulated transcription coactivator 3 (218648_at), score: 0.89 CSGALNACT2chondroitin sulfate N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase 2 (222235_s_at), score: -0.62 CTDSP2CTD (carboxy-terminal domain, RNA polymerase II, polypeptide A) small phosphatase 2 (203445_s_at), score: 0.71 CUL7cullin 7 (36084_at), score: 0.57 DAAM2dishevelled associated activator of morphogenesis 2 (212793_at), score: 0.62 DAPK1death-associated protein kinase 1 (203139_at), score: 0.71 DCKdeoxycytidine kinase (203302_at), score: -0.69 DCLK1doublecortin-like kinase 1 (205399_at), score: 0.7 DCP2DCP2 decapping enzyme homolog (S. cerevisiae) (212919_at), score: -0.63 DDAH2dimethylarginine dimethylaminohydrolase 2 (215537_x_at), score: 0.65 DDB2damage-specific DNA binding protein 2, 48kDa (203409_at), score: 0.65 DENND2ADENN/MADD domain containing 2A (53991_at), score: 0.65 DEPDC6DEP domain containing 6 (218858_at), score: 0.81 DHRS3dehydrogenase/reductase (SDR family) member 3 (202481_at), score: 0.76 DIRAS3DIRAS family, GTP-binding RAS-like 3 (215506_s_at), score: -0.86 DMPKdystrophia myotonica-protein kinase (37996_s_at), score: 0.68 DNAJB9DnaJ (Hsp40) homolog, subfamily B, member 9 (202843_at), score: -0.84 DNAJC1DnaJ (Hsp40) homolog, subfamily C, member 1 (218409_s_at), score: -0.56 DOCK10dedicator of cytokinesis 10 (219279_at), score: -0.7 DPH5DPH5 homolog (S. cerevisiae) (219590_x_at), score: 0.6 DRAMdamage-regulated autophagy modulator (218627_at), score: 0.62 DTX4deltex homolog 4 (Drosophila) (212611_at), score: 0.73 DUSP4dual specificity phosphatase 4 (204014_at), score: -0.74 DZIP3DAZ interacting protein 3, zinc finger (213186_at), score: 0.68 EAF2ELL associated factor 2 (219551_at), score: -0.56 EDEM1ER degradation enhancer, mannosidase alpha-like 1 (203279_at), score: -0.63 EFNA5ephrin-A5 (214036_at), score: 0.61 EGFepidermal growth factor (beta-urogastrone) (206254_at), score: -0.58 EIF4Eeukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E (201436_at), score: -0.72 EIF5Beukaryotic translation initiation factor 5B (214314_s_at), score: -0.57 ELTD1EGF, latrophilin and seven transmembrane domain containing 1 (219134_at), score: -0.61 ENOX1ecto-NOX disulfide-thiol exchanger 1 (219501_at), score: 0.65 EPHA4EPH receptor A4 (206114_at), score: -0.61 ESM1endothelial cell-specific molecule 1 (208394_x_at), score: -0.81 FAM29Afamily with sequence similarity 29, member A (218602_s_at), score: -0.6 FBXL7F-box and leucine-rich repeat protein 7 (213249_at), score: 0.56 FDXRferredoxin reductase (207813_s_at), score: 0.59 FERMT1fermitin family homolog 1 (Drosophila) (218796_at), score: -0.61 FGGYFGGY carbohydrate kinase domain containing (219718_at), score: 0.71 FICDFIC domain containing (219910_at), score: -0.66 FNBP1formin binding protein 1 (212288_at), score: 0.8 FNDC3Afibronectin type III domain containing 3A (202304_at), score: -0.57 FOLR3folate receptor 3 (gamma) (206371_at), score: -0.62 FSTL3follistatin-like 3 (secreted glycoprotein) (203592_s_at), score: -0.56 FYNFYN oncogene related to SRC, FGR, YES (210105_s_at), score: 0.61 GABBR2gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) B receptor, 2 (209990_s_at), score: -0.71 GALgalanin prepropeptide (214240_at), score: -0.68 GALNT12UDP-N-acetyl-alpha-D-galactosamine:polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase 12 (GalNAc-T12) (218885_s_at), score: 0.59 GDF15growth differentiation factor 15 (221577_x_at), score: 0.67 GDF5growth differentiation factor 5 (206614_at), score: 0.65 GDPD5glycerophosphodiester phosphodiesterase domain containing 5 (32502_at), score: 0.58 GFOD1glucose-fructose oxidoreductase domain containing 1 (219821_s_at), score: -0.79 GINS3GINS complex subunit 3 (Psf3 homolog) (45633_at), score: -0.58 GKglycerol kinase (207387_s_at), score: -0.86 GK3Pglycerol kinase 3 pseudogene (215966_x_at), score: -0.89 GLTSCR2glioma tumor suppressor candidate region gene 2 (217807_s_at), score: 0.7 GMCL1germ cell-less homolog 1 (Drosophila) (218458_at), score: -0.74 GMPRguanosine monophosphate reductase (204187_at), score: 0.67 GOLT1Bgolgi transport 1 homolog B (S. cerevisiae) (218193_s_at), score: -0.75 GPM6Bglycoprotein M6B (209170_s_at), score: -0.67 GPR177G protein-coupled receptor 177 (221958_s_at), score: -0.68 GRAMD1BGRAM domain containing 1B (212906_at), score: -0.58 GRSF1G-rich RNA sequence binding factor 1 (201501_s_at), score: -0.6 GTF2A1Lgeneral transcription factor IIA, 1-like (213413_at), score: 0.96 HDGFhepatoma-derived growth factor (high-mobility group protein 1-like) (200896_x_at), score: 0.6 HHIPL2HHIP-like 2 (220283_at), score: -0.58 HISPPD1histidine acid phosphatase domain containing 1 (203253_s_at), score: -0.66 HSD17B6hydroxysteroid (17-beta) dehydrogenase 6 homolog (mouse) (37512_at), score: -0.64 HSD17B7hydroxysteroid (17-beta) dehydrogenase 7 (220081_x_at), score: 0.59 HSPA12Aheat shock 70kDa protein 12A (214434_at), score: 0.7 HTR2A5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) receptor 2A (207135_at), score: -0.58 IFIH1interferon induced with helicase C domain 1 (219209_at), score: 0.73 IGBP1immunoglobulin (CD79A) binding protein 1 (202105_at), score: 0.58 IL13RA2interleukin 13 receptor, alpha 2 (206172_at), score: -0.72 IL33interleukin 33 (209821_at), score: -0.81 IRF1interferon regulatory factor 1 (202531_at), score: 0.71 ITGAVintegrin, alpha V (vitronectin receptor, alpha polypeptide, antigen CD51) (202351_at), score: -0.57 JUNDjun D proto-oncogene (203751_x_at), score: 0.6 JUPjunction plakoglobin (201015_s_at), score: 0.57 KAL1Kallmann syndrome 1 sequence (205206_at), score: -0.93 KCNJ8potassium inwardly-rectifying channel, subfamily J, member 8 (205303_at), score: -0.64 KIAA1305KIAA1305 (220911_s_at), score: 0.84 KIAA1462KIAA1462 (213316_at), score: 0.76 KLHDC2kelch domain containing 2 (217906_at), score: 0.62 KLHL23kelch-like 23 (Drosophila) (213610_s_at), score: -0.73 LARP4La ribonucleoprotein domain family, member 4 (214155_s_at), score: -0.67 LDLRlow density lipoprotein receptor (202068_s_at), score: 0.73 LEPREL1leprecan-like 1 (218717_s_at), score: -0.62 LIN7Blin-7 homolog B (C. elegans) (219760_at), score: -0.61 LOC100132540similar to LOC339047 protein (214870_x_at), score: 0.71 LOC100133105hypothetical protein LOC100133105 (214237_x_at), score: -0.56 LOC339047hypothetical protein LOC339047 (221501_x_at), score: 0.73 LOC399491LOC399491 protein (214035_x_at), score: 0.66 LOC440434hypothetical protein FLJ11822 (215090_x_at), score: 0.66 LRP8low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 8, apolipoprotein e receptor (205282_at), score: -0.91 LRRC40leucine rich repeat containing 40 (218577_at), score: -0.59 LYPD1LY6/PLAUR domain containing 1 (212909_at), score: -0.58 LYRM1LYR motif containing 1 (203897_at), score: 0.58 MAN1C1mannosidase, alpha, class 1C, member 1 (218918_at), score: 0.96 MAP2K5mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 5 (211370_s_at), score: 0.62 MBPmyelin basic protein (210136_at), score: 0.62 MC4Rmelanocortin 4 receptor (221467_at), score: -0.83 MFAP3Lmicrofibrillar-associated protein 3-like (205442_at), score: -0.59 MGC87042similar to Six transmembrane epithelial antigen of prostate (217553_at), score: -0.64 MIS12MIS12, MIND kinetochore complex component, homolog (yeast) (221559_s_at), score: -0.69 MKNK2MAP kinase interacting serine/threonine kinase 2 (218205_s_at), score: 0.61 MMP10matrix metallopeptidase 10 (stromelysin 2) (205680_at), score: -0.83 MMP16matrix metallopeptidase 16 (membrane-inserted) (207012_at), score: -0.81 MSTO1misato homolog 1 (Drosophila) (218296_x_at), score: -0.69 MT1Xmetallothionein 1X (204326_x_at), score: -0.56 MTAPmethylthioadenosine phosphorylase (211363_s_at), score: -0.57 MX2myxovirus (influenza virus) resistance 2 (mouse) (204994_at), score: 0.76 MXD4MAX dimerization protein 4 (210778_s_at), score: 0.6 MYL4myosin, light chain 4, alkali; atrial, embryonic (210088_x_at), score: -0.65 NAGPAN-acetylglucosamine-1-phosphodiester alpha-N-acetylglucosaminidase (205090_s_at), score: 0.64 NCALDneurocalcin delta (211685_s_at), score: -0.76 NDRG4NDRG family member 4 (209159_s_at), score: 0.6 NDUFA2NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) 1 alpha subcomplex, 2, 8kDa (213550_s_at), score: 0.6 NEDD4neural precursor cell expressed, developmentally down-regulated 4 (213012_at), score: -0.6 NEFLneurofilament, light polypeptide (221805_at), score: -0.63 NEFMneurofilament, medium polypeptide (205113_at), score: -1 NETO2neuropilin (NRP) and tolloid (TLL)-like 2 (218888_s_at), score: -0.6 NFKBIAnuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells inhibitor, alpha (201502_s_at), score: 0.63 NMIN-myc (and STAT) interactor (203964_at), score: 0.63 NOX4NADPH oxidase 4 (219773_at), score: -0.57 NPnucleoside phosphorylase (201695_s_at), score: -0.6 NPC2Niemann-Pick disease, type C2 (200701_at), score: 0.59 NPIPnuclear pore complex interacting protein (204538_x_at), score: 0.76 NPTX1neuronal pentraxin I (204684_at), score: -0.8 NR1H3nuclear receptor subfamily 1, group H, member 3 (203920_at), score: 0.68 NR5A2nuclear receptor subfamily 5, group A, member 2 (208343_s_at), score: -0.73 NTMneurotrimin (222020_s_at), score: -0.75 NUP160nucleoporin 160kDa (212709_at), score: -0.72 OAS22'-5'-oligoadenylate synthetase 2, 69/71kDa (204972_at), score: 0.73 OBFC2Aoligonucleotide/oligosaccharide-binding fold containing 2A (219334_s_at), score: -0.58 OPCMLopioid binding protein/cell adhesion molecule-like (214111_at), score: -0.82 ORAI3ORAI calcium release-activated calcium modulator 3 (221864_at), score: 0.84 ORC1Lorigin recognition complex, subunit 1-like (yeast) (205085_at), score: -0.57 OSTM1osteopetrosis associated transmembrane protein 1 (218196_at), score: -0.69 P2RX5purinergic receptor P2X, ligand-gated ion channel, 5 (210448_s_at), score: -0.7 P2RY5purinergic receptor P2Y, G-protein coupled, 5 (218589_at), score: 0.71 PAQR3progestin and adipoQ receptor family member III (213372_at), score: -0.66 PCDH9protocadherin 9 (219737_s_at), score: -0.86 PCYT2phosphate cytidylyltransferase 2, ethanolamine (209577_at), score: 0.67 PDCD1LG2programmed cell death 1 ligand 2 (220049_s_at), score: -0.69 PDE5Aphosphodiesterase 5A, cGMP-specific (206757_at), score: 0.72 PDGFRBplatelet-derived growth factor receptor, beta polypeptide (202273_at), score: 0.56 PDK2pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase, isozyme 2 (202590_s_at), score: 0.59 PDSS1prenyl (decaprenyl) diphosphate synthase, subunit 1 (220865_s_at), score: -0.63 PECRperoxisomal trans-2-enoyl-CoA reductase (221142_s_at), score: 0.61 PET112LPET112-like (yeast) (204300_at), score: 0.57 PIGLphosphatidylinositol glycan anchor biosynthesis, class L (213889_at), score: 0.73 PITX1paired-like homeodomain 1 (208502_s_at), score: 0.68 PKIAprotein kinase (cAMP-dependent, catalytic) inhibitor alpha (204612_at), score: -0.63 PLA2G4Cphospholipase A2, group IVC (cytosolic, calcium-independent) (209785_s_at), score: 0.6 PMAIP1phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate-induced protein 1 (204286_s_at), score: -0.64 PMP22peripheral myelin protein 22 (210139_s_at), score: 0.61 PNRC1proline-rich nuclear receptor coactivator 1 (209034_at), score: 0.62 PPARGperoxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (208510_s_at), score: 0.73 PPATphosphoribosyl pyrophosphate amidotransferase (209433_s_at), score: -0.76 PPLperiplakin (203407_at), score: 0.59 PPP2R1Bprotein phosphatase 2 (formerly 2A), regulatory subunit A, beta isoform (202884_s_at), score: -0.67 PPP3R1protein phosphatase 3 (formerly 2B), regulatory subunit B, alpha isoform (204507_s_at), score: -0.56 PRPS2phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate synthetase 2 (203401_at), score: -0.7 PRSS1protease, serine, 1 (trypsin 1) (216470_x_at), score: -0.59 PRSS2protease, serine, 2 (trypsin 2) (205402_x_at), score: -0.75 PRSS3protease, serine, 3 (207463_x_at), score: -0.67 PSMB8proteasome (prosome, macropain) subunit, beta type, 8 (large multifunctional peptidase 7) (209040_s_at), score: 0.62 PSMB9proteasome (prosome, macropain) subunit, beta type, 9 (large multifunctional peptidase 2) (204279_at), score: 0.57 PTGS1prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase 1 (prostaglandin G/H synthase and cyclooxygenase) (215813_s_at), score: -0.69 PTP4A1protein tyrosine phosphatase type IVA, member 1 (200730_s_at), score: -0.57 PYCARDPYD and CARD domain containing (221666_s_at), score: 0.58 PYGLphosphorylase, glycogen, liver (202990_at), score: 0.57 RAB1ARAB1A, member RAS oncogene family (213440_at), score: -0.6 RAB7ARAB7A, member RAS oncogene family (211960_s_at), score: -0.66 RANBP6RAN binding protein 6 (213019_at), score: -0.57 RASSF2Ras association (RalGDS/AF-6) domain family member 2 (203185_at), score: 0.65 RBL1retinoblastoma-like 1 (p107) (205296_at), score: -0.6 RBM4BRNA binding motif protein 4B (209497_s_at), score: 0.61 RCAN2regulator of calcineurin 2 (203498_at), score: 0.63 REEP1receptor accessory protein 1 (204364_s_at), score: -0.67 REREarginine-glutamic acid dipeptide (RE) repeats (200940_s_at), score: 0.69 RGNregucalcin (senescence marker protein-30) (210751_s_at), score: 0.58 RGS20regulator of G-protein signaling 20 (210138_at), score: -0.56 RHBDF1rhomboid 5 homolog 1 (Drosophila) (218686_s_at), score: 0.6 RNF138ring finger protein 138 (218738_s_at), score: -0.58 RNF44ring finger protein 44 (203286_at), score: 0.6 ROR1receptor tyrosine kinase-like orphan receptor 1 (205805_s_at), score: 0.59 ROR2receptor tyrosine kinase-like orphan receptor 2 (205578_at), score: 0.67 RP11-345P4.4similar to solute carrier family 35, member E2 (217122_s_at), score: 0.73 RP2retinitis pigmentosa 2 (X-linked recessive) (205191_at), score: -0.61 RPL13Aribosomal protein L13a (200715_x_at), score: 0.68 RPL21P68ribosomal protein L21 pseudogene 68 (217340_at), score: -0.65 RPL23ribosomal protein L23 (214744_s_at), score: -0.58 RPLP2P1ribosomal protein, large P2, pseudogene 1 (216490_x_at), score: -0.74 RPS17P5ribosomal protein S17 pseudogene 5 (216348_at), score: -0.56 S1PR1sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 (204642_at), score: -0.68 SAV1salvador homolog 1 (Drosophila) (218276_s_at), score: 0.69 SCAMP4secretory carrier membrane protein 4 (213244_at), score: 0.61 SDF2L1stromal cell-derived factor 2-like 1 (218681_s_at), score: -0.65 SDPRserum deprivation response (phosphatidylserine binding protein) (218711_s_at), score: 0.61 SECTM1secreted and transmembrane 1 (213716_s_at), score: 0.8 SELENBP1selenium binding protein 1 (214433_s_at), score: 0.74 SERPINB2serpin peptidase inhibitor, clade B (ovalbumin), member 2 (204614_at), score: -0.57 SESN1sestrin 1 (218346_s_at), score: 0.8 SGSHN-sulfoglucosamine sulfohydrolase (35626_at), score: 0.65 SIGIRRsingle immunoglobulin and toll-interleukin 1 receptor (TIR) domain (52940_at), score: 0.61 SIX2SIX homeobox 2 (206510_at), score: 0.61 SLC25A13solute carrier family 25, member 13 (citrin) (203775_at), score: -0.76 SLC2A6solute carrier family 2 (facilitated glucose transporter), member 6 (220091_at), score: 0.65 SLC4A4solute carrier family 4, sodium bicarbonate cotransporter, member 4 (203908_at), score: -0.59 SLC4A7solute carrier family 4, sodium bicarbonate cotransporter, member 7 (209884_s_at), score: -0.69 SLC8A1solute carrier family 8 (sodium/calcium exchanger), member 1 (207053_at), score: -0.61 SLMO2slowmo homolog 2 (Drosophila) (217851_s_at), score: -0.64 SMAD3SMAD family member 3 (218284_at), score: 0.69 SNNstannin (218032_at), score: 0.62 SPATA20spermatogenesis associated 20 (218164_at), score: 0.67 SSTR1somatostatin receptor 1 (208482_at), score: -0.66 ST5suppression of tumorigenicity 5 (202440_s_at), score: 0.71 STARD5StAR-related lipid transfer (START) domain containing 5 (213820_s_at), score: 0.61 STIM1stromal interaction molecule 1 (202764_at), score: 0.6 SV2Asynaptic vesicle glycoprotein 2A (203069_at), score: 0.57 SYNJ1synaptojanin 1 (212990_at), score: -0.65 SYNPOsynaptopodin (202796_at), score: 0.7 TBC1D2BTBC1 domain family, member 2B (212796_s_at), score: 0.73 TBC1D8TBC1 domain family, member 8 (with GRAM domain) (204526_s_at), score: 0.8 TCEB1transcription elongation factor B (SIII), polypeptide 1 (15kDa, elongin C) (202823_at), score: -0.57 TENC1tensin like C1 domain containing phosphatase (tensin 2) (212494_at), score: 0.79 TFDP2transcription factor Dp-2 (E2F dimerization partner 2) (203588_s_at), score: 0.57 TGDSTDP-glucose 4,6-dehydratase (208249_s_at), score: -0.57 THSD7Athrombospondin, type I, domain containing 7A (214920_at), score: 0.59 THYN1thymocyte nuclear protein 1 (218491_s_at), score: 0.57 TICAM2toll-like receptor adaptor molecule 2 (214658_at), score: -0.72 TLR3toll-like receptor 3 (206271_at), score: 0.77 TM4SF1transmembrane 4 L six family member 1 (209386_at), score: -0.62 TMEFF1transmembrane protein with EGF-like and two follistatin-like domains 1 (205122_at), score: -0.63 TMEM2transmembrane protein 2 (218113_at), score: -0.7 TMOD1tropomodulin 1 (203661_s_at), score: -0.59 TNFAIP2tumor necrosis factor, alpha-induced protein 2 (202510_s_at), score: 0.66 TNFAIP6tumor necrosis factor, alpha-induced protein 6 (206026_s_at), score: 0.64 TNFRSF10Ctumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily, member 10c, decoy without an intracellular domain (206222_at), score: 0.58 TNIP1TNFAIP3 interacting protein 1 (207196_s_at), score: 0.65 TNS3tensin 3 (217853_at), score: 0.75 TP53tumor protein p53 (201746_at), score: 0.89 TRIM21tripartite motif-containing 21 (204804_at), score: 0.72 TRIM24tripartite motif-containing 24 (213301_x_at), score: -0.65 TRMT2ATRM2 tRNA methyltransferase 2 homolog A (S. cerevisiae) (91617_at), score: -0.57 TRPC4transient receptor potential cation channel, subfamily C, member 4 (220817_at), score: -0.66 TSKUtsukushin (218245_at), score: 0.6 TSPAN13tetraspanin 13 (217979_at), score: -0.77 TUBA4Btubulin, alpha 4b (pseudogene) (207490_at), score: -0.65 UBA2ubiquitin-like modifier activating enzyme 2 (201177_s_at), score: -0.58 UBE2L6ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2L 6 (201649_at), score: 0.68 UBXN1UBX domain protein 1 (201871_s_at), score: 0.67 UHRF1BP1LUHRF1 binding protein 1-like (213118_at), score: -0.74 ULBP2UL16 binding protein 2 (221291_at), score: -0.95 USF2upstream transcription factor 2, c-fos interacting (202152_x_at), score: 0.58 VWA5Avon Willebrand factor A domain containing 5A (210102_at), score: 0.79 WBP2WW domain binding protein 2 (209117_at), score: 0.68 WDR4WD repeat domain 4 (221632_s_at), score: -0.66 WDR6WD repeat domain 6 (217734_s_at), score: 0.73 XPCxeroderma pigmentosum, complementation group C (209375_at), score: 0.61 XYLT1xylosyltransferase I (213725_x_at), score: -0.65 YDD19YDD19 protein (37079_at), score: -0.58 YEATS4YEATS domain containing 4 (218911_at), score: -0.58 YPEL5yippee-like 5 (Drosophila) (217783_s_at), score: 0.62 ZBTB20zinc finger and BTB domain containing 20 (205383_s_at), score: 0.57 ZBTB22zinc finger and BTB domain containing 22 (213081_at), score: 0.57 ZDHHC4zinc finger, DHHC-type containing 4 (220261_s_at), score: 0.61 ZDHHC7zinc finger, DHHC-type containing 7 (218606_at), score: 0.73 ZHX2zinc fingers and homeoboxes 2 (203556_at), score: 0.59 ZNF273zinc finger protein 273 (215239_x_at), score: -0.56 ZNF358zinc finger protein 358 (219379_x_at), score: 0.58 ZNF580zinc finger protein 580 (220748_s_at), score: 0.67
| Id | sample | Experiment | ExpName | Array | Syndrome | Cell.line |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486371.cel | 37 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485891.cel | 13 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485811.cel | 9 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485771.cel | 7 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485751.cel | 6 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485671.cel | 2 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486431.cel | 40 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-GEOD-3860-raw-cel-1561690256.cel | 6 | 5 | HGPS | hgu133a | none | GMO8398C |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486191.cel | 28 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-GEOD-3860-raw-cel-1561690376.cel | 13 | 5 | HGPS | hgu133a | HGPS | AG11513 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486391.cel | 38 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486331.cel | 35 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| 8495_CNTL.CEL | 10 | 8 | WBS | hgu133plus2 | none | WBS 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486051.cel | 21 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486211.cel | 29 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485791.cel | 8 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486311.cel | 34 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485831.cel | 10 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486271.cel | 32 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486291.cel | 33 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |