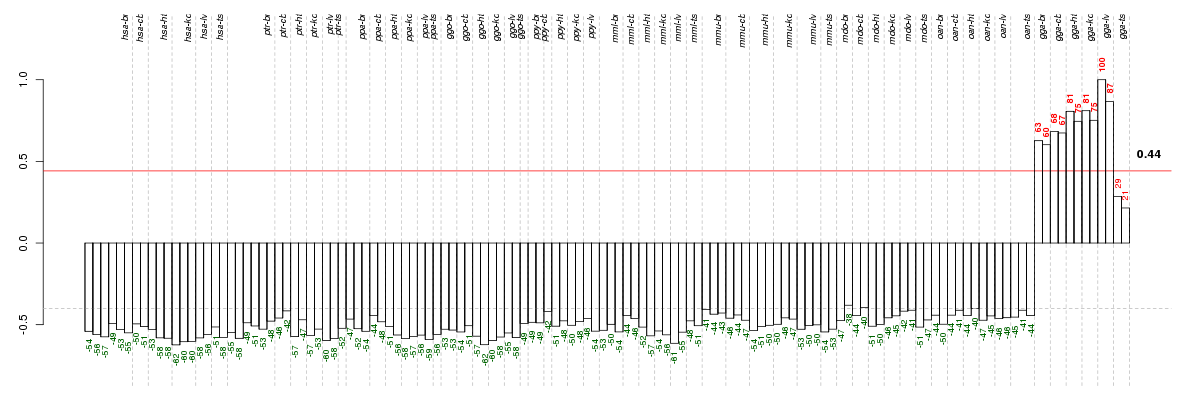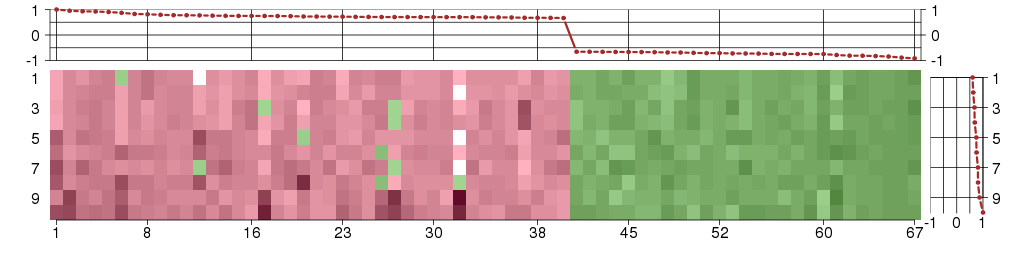

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways, including anabolism and catabolism, by which living organisms transform chemical substances. Metabolic processes typically transform small molecules, but also include macromolecular processes such as DNA repair and replication, and protein synthesis and degradation.
cytokine production
The appearance of a cytokine due to biosynthesis or secretion following a cellular stimulus, resulting in an increase in its intracellular or extracellular levels.
regulation of cytokine production
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of production of a cytokine.
nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
Any cellular metabolic process involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
DNA metabolic process
Any cellular metabolic process involving deoxyribonucleic acid. This is one of the two main types of nucleic acid, consisting of a long, unbranched macromolecule formed from one, or more commonly, two, strands of linked deoxyribonucleotides.
nitrogen compound metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving various organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds; includes nitrogen fixation, nitrification, denitrification, assimilatory/dissimilatory nitrate reduction and the interconversion of nitrogenous organic matter and ammonium.
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
nervous system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of nervous tissue over time, from its formation to its mature state.
central nervous system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the central nervous system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The central nervous system is the core nervous system that serves an integrating and coordinating function. In vertebrates it consists of the brain, spinal cord and spinal nerves. In those invertebrates with a central nervous system it typically consists of a brain, cerebral ganglia and a nerve cord.
brain development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the brain over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Brain development begins with patterning events in the neural tube and ends with the mature structure that is the center of thought and emotion. The brain is responsible for the coordination and control of bodily activities and the interpretation of information from the senses (sight, hearing, smell, etc.).
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
generation of neurons in the forebrain
The process by which nerve cells are generated in the forebrain. This includes the production of neuroblasts from and their differentiation into neurons.
forebrain neuron differentiation
The process whereby a relatively unspecialized cell acquires specialized features of a neuron that will reside in the forebrain.
forebrain neuron development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a neuron that resides in the forebrain, from its initial commitment to its fate, to the fully functional differentiated cell.
central nervous system neuron differentiation
The process whereby a relatively unspecialized cell acquires specialized features of a neuron whose cell body resides in the central nervous system.
central nervous system neuron development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a neuron whose cell body is located in the central nervous system, from initial commitment of the cell to a neuronal fate, to the fully functional differentiated neuron.
neurogenesis
Generation of cells within the nervous system.
cell differentiation
The process whereby relatively unspecialized cells, e.g. embryonic or regenerative cells, acquire specialized structural and/or functional features that characterize the cells, tissues, or organs of the mature organism or some other relatively stable phase of the organism's life history. Differentiation includes the processes involved in commitment of a cell to a specific fate and its subsequent development to the mature state.
neuron differentiation
The process whereby a relatively unspecialized cell acquires specialized features of a neuron.
forebrain development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the forebrain over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The forebrain is the anterior of the three primary divisions of the developing chordate brain or the corresponding part of the adult brain (in vertebrates, includes especially the cerebral hemispheres, the thalamus, and the hypothalamus and especially in higher vertebrates is the main control center for sensory and associative information processing, visceral functions, and voluntary motor functions).
multicellular organismal process
Any biological process, occurring at the level of a multicellular organism, pertinent to its function.
developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an integrated living unit: an anatomical structure (which may be a subcellular structure, cell, tissue, or organ), or organism over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
interleukin-12 production
The appearance of interleukin-12 due to biosynthesis or secretion following a cellular stimulus, resulting in an increase in its intracellular or extracellular levels.
regulation of interleukin-12 production
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of interleukin-12 production.
cellular nitrogen compound metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving various organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds, as carried out by individual cells.
macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
primary metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving those compounds which are formed as a part of the normal anabolic and catabolic processes. These processes take place in most, if not all, cells of the organism.
cellular macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, as carried out by individual cells.
cell development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the cell over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Cell development does not include the steps involved in committing a cell to a specific fate.
organ development
Development of a tissue or tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Development pertains to the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a structure over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
neuron development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a neuron over time, from initial commitment of the cell to a specific fate, to the fully functional differentiated cell.
generation of neurons
The process by which nerve cells are generated. This includes the production of neuroblasts and their differentiation into neurons.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
anatomical structure development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an anatomical structure from an initial condition to its mature state. This process begins with the formation of the structure and ends with the mature structure, whatever form that may be including its natural destruction. An anatomical structure is any biological entity that occupies space and is distinguished from its surroundings. Anatomical structures can be macroscopic such as a carpel, or microscopic such as an acrosome.
cellular developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a cell over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of multicellular organismal process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a multicellular organismal process, the processes pertinent to the function of a multicellular organism above the cellular level; includes the integrated processes of tissues and organs.
biological regulation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of any biological process, quality or function.
nucleic acid metabolic process
Any cellular metabolic process involving nucleic acids.
all
NA
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
cellular developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a cell over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
regulation of multicellular organismal process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a multicellular organismal process, the processes pertinent to the function of a multicellular organism above the cellular level; includes the integrated processes of tissues and organs.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
cellular nitrogen compound metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving various organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, as carried out by individual cells.
regulation of cytokine production
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of production of a cytokine.
cell development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the cell over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Cell development does not include the steps involved in committing a cell to a specific fate.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
Any cellular metabolic process involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
cell development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the cell over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Cell development does not include the steps involved in committing a cell to a specific fate.
regulation of interleukin-12 production
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of interleukin-12 production.
organ development
Development of a tissue or tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Development pertains to the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a structure over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
DNA metabolic process
Any cellular metabolic process involving deoxyribonucleic acid. This is one of the two main types of nucleic acid, consisting of a long, unbranched macromolecule formed from one, or more commonly, two, strands of linked deoxyribonucleotides.
neuron development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a neuron over time, from initial commitment of the cell to a specific fate, to the fully functional differentiated cell.
central nervous system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the central nervous system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The central nervous system is the core nervous system that serves an integrating and coordinating function. In vertebrates it consists of the brain, spinal cord and spinal nerves. In those invertebrates with a central nervous system it typically consists of a brain, cerebral ganglia and a nerve cord.
neurogenesis
Generation of cells within the nervous system.
brain development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the brain over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Brain development begins with patterning events in the neural tube and ends with the mature structure that is the center of thought and emotion. The brain is responsible for the coordination and control of bodily activities and the interpretation of information from the senses (sight, hearing, smell, etc.).
central nervous system neuron differentiation
The process whereby a relatively unspecialized cell acquires specialized features of a neuron whose cell body resides in the central nervous system.
forebrain development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the forebrain over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The forebrain is the anterior of the three primary divisions of the developing chordate brain or the corresponding part of the adult brain (in vertebrates, includes especially the cerebral hemispheres, the thalamus, and the hypothalamus and especially in higher vertebrates is the main control center for sensory and associative information processing, visceral functions, and voluntary motor functions).
generation of neurons in the forebrain
The process by which nerve cells are generated in the forebrain. This includes the production of neuroblasts from and their differentiation into neurons.
neuron differentiation
The process whereby a relatively unspecialized cell acquires specialized features of a neuron.
forebrain neuron differentiation
The process whereby a relatively unspecialized cell acquires specialized features of a neuron that will reside in the forebrain.
central nervous system neuron development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a neuron whose cell body is located in the central nervous system, from initial commitment of the cell to a neuronal fate, to the fully functional differentiated neuron.
forebrain neuron development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a neuron that resides in the forebrain, from its initial commitment to its fate, to the fully functional differentiated cell.

intracellular
The living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
cellular_component
The part of a cell or its extracellular environment in which a gene product is located. A gene product may be located in one or more parts of a cell and its location may be as specific as a particular macromolecular complex, that is, a stable, persistent association of macromolecules that function together.
cell
The basic structural and functional unit of all organisms. Includes the plasma membrane and any external encapsulating structures such as the cell wall and cell envelope.
nucleus
A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent.
organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, and prokaryotic structures such as anammoxosomes and pirellulosomes. Excludes the plasma membrane.
membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
all
NA
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
intracellular membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.

ADAT1adenosine deaminase, tRNA-specific 1 (ENSG00000065457), score: 0.67 ARPC5Lactin related protein 2/3 complex, subunit 5-like (ENSG00000136950), score: -0.74 ATP7AATPase, Cu++ transporting, alpha polypeptide (ENSG00000165240), score: 0.7 BLKB lymphoid tyrosine kinase (ENSG00000136573), score: 0.68 BRWD3bromodomain and WD repeat domain containing 3 (ENSG00000165288), score: 0.69 C13orf39chromosome 13 open reading frame 39 (ENSG00000139780), score: 0.93 C18orf22chromosome 18 open reading frame 22 (ENSG00000101546), score: -0.67 CCDC45coiled-coil domain containing 45 (ENSG00000141325), score: -0.69 CD40LGCD40 ligand (ENSG00000102245), score: 0.77 CDCP2CUB domain containing protein 2 (ENSG00000157211), score: 1 CELF1CUGBP, Elav-like family member 1 (ENSG00000149187), score: -0.66 CHRNA5cholinergic receptor, nicotinic, alpha 5 (ENSG00000169684), score: 0.79 CIB3calcium and integrin binding family member 3 (ENSG00000141977), score: 0.77 DBR1debranching enzyme homolog 1 (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000138231), score: 0.7 DFFBDNA fragmentation factor, 40kDa, beta polypeptide (caspase-activated DNase) (ENSG00000169598), score: 0.75 DHX32DEAH (Asp-Glu-Ala-His) box polypeptide 32 (ENSG00000089876), score: -0.84 DNMT3ADNA (cytosine-5-)-methyltransferase 3 alpha (ENSG00000119772), score: 0.7 FAM109Bfamily with sequence similarity 109, member B (ENSG00000177096), score: 0.75 FAM166Afamily with sequence similarity 166, member A (ENSG00000188163), score: -0.71 FANCAFanconi anemia, complementation group A (ENSG00000187741), score: -0.67 FBXL18F-box and leucine-rich repeat protein 18 (ENSG00000155034), score: 0.9 FBXL20F-box and leucine-rich repeat protein 20 (ENSG00000108306), score: 0.69 FNBP4formin binding protein 4 (ENSG00000109920), score: 0.7 HNRNPA0heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A0 (ENSG00000177733), score: -0.72 HPGDShematopoietic prostaglandin D synthase (ENSG00000163106), score: 0.87 ICOSinducible T-cell co-stimulator (ENSG00000163600), score: 0.73 IL22RA2interleukin 22 receptor, alpha 2 (ENSG00000164485), score: 0.7 IMPG2interphotoreceptor matrix proteoglycan 2 (ENSG00000081148), score: 0.74 INPPL1inositol polyphosphate phosphatase-like 1 (ENSG00000165458), score: -0.7 IRF8interferon regulatory factor 8 (ENSG00000140968), score: 0.7 KIAA0368KIAA0368 (ENSG00000136813), score: -0.67 LHX8LIM homeobox 8 (ENSG00000162624), score: 0.7 LRRC41leucine rich repeat containing 41 (ENSG00000132128), score: -0.73 LSM4LSM4 homolog, U6 small nuclear RNA associated (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000130520), score: -0.74 MST4serine/threonine protein kinase MST4 (ENSG00000134602), score: 0.69 MUTYHmutY homolog (E. coli) (ENSG00000132781), score: 0.7 NAT10N-acetyltransferase 10 (GCN5-related) (ENSG00000135372), score: -0.66 NUSAP1nucleolar and spindle associated protein 1 (ENSG00000137804), score: 0.75 OLFML2Aolfactomedin-like 2A (ENSG00000185585), score: 0.74 ORC5Lorigin recognition complex, subunit 5-like (yeast) (ENSG00000164815), score: -0.74 PANX3pannexin 3 (ENSG00000154143), score: 0.92 PAPOLGpoly(A) polymerase gamma (ENSG00000115421), score: -0.89 PATZ1POZ (BTB) and AT hook containing zinc finger 1 (ENSG00000100105), score: -0.69 PIK3CGphosphoinositide-3-kinase, catalytic, gamma polypeptide (ENSG00000105851), score: 0.81 POLE2polymerase (DNA directed), epsilon 2 (p59 subunit) (ENSG00000100479), score: 0.78 PRKAG3protein kinase, AMP-activated, gamma 3 non-catalytic subunit (ENSG00000115592), score: 0.72 RBP1retinol binding protein 1, cellular (ENSG00000114115), score: -0.66 RELv-rel reticuloendotheliosis viral oncogene homolog (avian) (ENSG00000162924), score: 0.67 SDF4stromal cell derived factor 4 (ENSG00000078808), score: -0.66 SEPT2septin 2 (ENSG00000168385), score: -0.73 SLBPstem-loop binding protein (ENSG00000163950), score: -0.92 SLC26A5solute carrier family 26, member 5 (prestin) (ENSG00000170615), score: 0.95 SPINK4serine peptidase inhibitor, Kazal type 4 (ENSG00000122711), score: 0.75 SSNA1Sjogren syndrome nuclear autoantigen 1 (ENSG00000176101), score: -0.74 SYPL1synaptophysin-like 1 (ENSG00000008282), score: -0.75 TAF3TAF3 RNA polymerase II, TATA box binding protein (TBP)-associated factor, 140kDa (ENSG00000165632), score: 0.76 TAF5TAF5 RNA polymerase II, TATA box binding protein (TBP)-associated factor, 100kDa (ENSG00000148835), score: 0.72 TMEM41Atransmembrane protein 41A (ENSG00000163900), score: 0.71 TMX1thioredoxin-related transmembrane protein 1 (ENSG00000139921), score: -0.83 TNFRSF11Atumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily, member 11a, NFKB activator (ENSG00000141655), score: 0.72 UBAP1ubiquitin associated protein 1 (ENSG00000165006), score: -0.81 UBE2Zubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2Z (ENSG00000159202), score: -0.71 WDR41WD repeat domain 41 (ENSG00000164253), score: -0.78 ZBTB37zinc finger and BTB domain containing 37 (ENSG00000185278), score: 0.71 ZBTB8Bzinc finger and BTB domain containing 8B (ENSG00000215897), score: 0.83 ZNF828zinc finger protein 828 (ENSG00000198824), score: 0.68
| Id | species | tissue | sex | individual |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| gga_br_f_ca1 | gga | br | f | _ |
| gga_br_m_ca1 | gga | br | m | _ |
| gga_cb_f_ca1 | gga | cb | f | _ |
| gga_cb_m_ca1 | gga | cb | m | _ |
| gga_ht_f_ca1 | gga | ht | f | _ |
| gga_kd_f_ca1 | gga | kd | f | _ |
| gga_ht_m_ca1 | gga | ht | m | _ |
| gga_kd_m_ca1 | gga | kd | m | _ |
| gga_lv_f_ca1 | gga | lv | f | _ |
| gga_lv_m_ca1 | gga | lv | m | _ |