
Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways, including anabolism and catabolism, by which living organisms transform chemical substances. Metabolic processes typically transform small molecules, but also include macromolecular processes such as DNA repair and replication, and protein synthesis and degradation.
organic acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving organic acids, any acidic compound containing carbon in covalent linkage.
cellular amino acid and derivative metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving amino acids, organic acids containing one or more amino substituents, and compounds derived from amino acids, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular amino acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving amino acids, organic acids containing one or more amino substituents.
lipid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving lipids, compounds soluble in an organic solvent but not, or sparingly, in an aqueous solvent. Includes fatty acids; neutral fats, other fatty-acid esters, and soaps; long-chain (fatty) alcohols and waxes; sphingoids and other long-chain bases; glycolipids, phospholipids and sphingolipids; and carotenes, polyprenols, sterols, terpenes and other isoprenoids.
steroid catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of steroids, compounds with a 1,2,cyclopentanoperhydrophenanthrene nucleus.
nitrogen compound metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving various organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds; includes nitrogen fixation, nitrification, denitrification, assimilatory/dissimilatory nitrate reduction and the interconversion of nitrogenous organic matter and ammonium.
transport
The directed movement of substances (such as macromolecules, small molecules, ions) into, out of, within or between cells, or within a multicellular organism by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
amino acid transport
The directed movement of amino acids, organic acids containing one or more amino substituents, into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
steroid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving steroids, compounds with a 1,2,cyclopentanoperhydrophenanthrene nucleus.
bile acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving bile acids, any of a group of steroid carboxylic acids occurring in bile, where they are present as the sodium salts of their amides with glycine or taurine.
catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of substances, including the breakdown of carbon compounds with the liberation of energy for use by the cell or organism.
cellular amino acid catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of amino acids, organic acids containing one or more amino substituents.
amine metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving any organic compound that is weakly basic in character and contains an amino or a substituted amino group, as carried out by individual cells. Amines are called primary, secondary, or tertiary according to whether one, two, or three carbon atoms are attached to the nitrogen atom.
amine catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of any organic compound that is weakly basic in character and contains an amino or a substituted amino group. Amines are called primary, secondary, or tertiary according to whether one, two, or three carbon atoms are attached to the nitrogen atom.
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
amine transport
The directed movement of amines, including polyamines, organic compounds containing one or more amino groups, into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
organic acid transport
The directed movement of organic acids, any acidic compound containing carbon in covalent linkage, into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
lipid catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of lipids, compounds soluble in an organic solvent but not, or sparingly, in an aqueous solvent.
organic acid catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of organic acids, any acidic compound containing carbon in covalent linkage.
carboxylic acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving carboxylic acids, any organic acid containing one or more carboxyl (COOH) groups or anions (COO-).
bile acid catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of bile acids, any of a group of steroid carboxylic acids occurring in bile.
monocarboxylic acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving monocarboxylic acids, any organic acid containing one carboxyl (COOH) group or anion (COO-).
cellular nitrogen compound metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving various organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular ketone metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving any of a class of organic compounds that contain the carbonyl group, CO, and in which the carbonyl group is bonded only to carbon atoms, as carried out by individual cells. The general formula for a ketone is RCOR, where R and R are alkyl or aryl groups.
oxoacid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving any oxoacid; an oxoacid is a compound which contains oxygen, at least one other element, and at least one hydrogen bound to oxygen, and which produces a conjugate base by loss of positive hydrogen ion(s) (hydrons).
cellular amine metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving any organic compound that is weakly basic in character and contains an amino or a substituted amino group, as carried out by individual cells. Amines are called primary, secondary, or tertiary according to whether one, two, or three carbon atoms are attached to the nitrogen atom.
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
primary metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving those compounds which are formed as a part of the normal anabolic and catabolic processes. These processes take place in most, if not all, cells of the organism.
cellular catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of substances, carried out by individual cells.
small molecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving small molecules, any monomeric molecule of small relative molecular mass.
small molecule catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of small molecules, any monomeric molecule of small relative molecular mass.
carboxylic acid catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of carboxylic acids, any organic acid containing one or more carboxyl (-COOH) groups.
carboxylic acid transport
The directed movement of carboxylic acids into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore. Carboxylic acids are organic acids containing one or more carboxyl (COOH) groups or anions (COO-).
localization
Any process by which a cell, a substance, or a cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, is transported to, and/or maintained in a specific location.
establishment of localization
The directed movement of a cell, substance or cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, to a specific location.
all
NA
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
establishment of localization
The directed movement of a cell, substance or cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, to a specific location.
cellular nitrogen compound metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving various organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of substances, carried out by individual cells.
cellular amino acid and derivative metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving amino acids, organic acids containing one or more amino substituents, and compounds derived from amino acids, as carried out by individual cells.
organic acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving organic acids, any acidic compound containing carbon in covalent linkage.
cellular amino acid and derivative metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving amino acids, organic acids containing one or more amino substituents, and compounds derived from amino acids, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular ketone metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving any of a class of organic compounds that contain the carbonyl group, CO, and in which the carbonyl group is bonded only to carbon atoms, as carried out by individual cells. The general formula for a ketone is RCOR, where R and R are alkyl or aryl groups.
small molecule catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of small molecules, any monomeric molecule of small relative molecular mass.
cellular amine metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving any organic compound that is weakly basic in character and contains an amino or a substituted amino group, as carried out by individual cells. Amines are called primary, secondary, or tertiary according to whether one, two, or three carbon atoms are attached to the nitrogen atom.
organic acid catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of organic acids, any acidic compound containing carbon in covalent linkage.
organic acid catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of organic acids, any acidic compound containing carbon in covalent linkage.
oxoacid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving any oxoacid; an oxoacid is a compound which contains oxygen, at least one other element, and at least one hydrogen bound to oxygen, and which produces a conjugate base by loss of positive hydrogen ion(s) (hydrons).
lipid catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of lipids, compounds soluble in an organic solvent but not, or sparingly, in an aqueous solvent.
cellular amino acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving amino acids, organic acids containing one or more amino substituents.
cellular amino acid catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of amino acids, organic acids containing one or more amino substituents.
steroid catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of steroids, compounds with a 1,2,cyclopentanoperhydrophenanthrene nucleus.
amino acid transport
The directed movement of amino acids, organic acids containing one or more amino substituents, into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
cellular amino acid catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of amino acids, organic acids containing one or more amino substituents.
bile acid catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of bile acids, any of a group of steroid carboxylic acids occurring in bile.
cellular amino acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving amino acids, organic acids containing one or more amino substituents.
carboxylic acid catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of carboxylic acids, any organic acid containing one or more carboxyl (-COOH) groups.
bile acid catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of bile acids, any of a group of steroid carboxylic acids occurring in bile.
bile acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving bile acids, any of a group of steroid carboxylic acids occurring in bile, where they are present as the sodium salts of their amides with glycine or taurine.


molecular_function
Elemental activities, such as catalysis or binding, describing the actions of a gene product at the molecular level. A given gene product may exhibit one or more molecular functions.
enzyme inhibitor activity
Stops, prevents or reduces the activity of an enzyme.
endopeptidase inhibitor activity
Stops, prevents or reduces the activity of an endopeptidase, any enzyme that hydrolyzes nonterminal peptide bonds in polypeptides.
transporter activity
Enables the directed movement of substances (such as macromolecules, small molecules, ions) into, out of, within or between cells.
transmembrane transporter activity
Enables the transfer of a substance from one side of a membrane to the other.
organic acid transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of organic acids, any acidic compound containing carbon in covalent linkage, from one side of the membrane to the other.
binding
The selective, non-covalent, often stoichiometric, interaction of a molecule with one or more specific sites on another molecule.
endopeptidase regulator activity
Modulates the activity of a peptidase, any enzyme that hydrolyzes nonterminal peptide bonds in polypeptides.
amino acid binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with an amino acid, organic acids containing one or more amino substituents.
peptidase inhibitor activity
Stops, prevents or reduces the activity of a peptidase, any enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis peptide bonds.
substrate-specific transmembrane transporter activity
Enables the transfer of a specific substance or group of related substances from one side of a membrane to the other.
substrate-specific transporter activity
Enables the directed movement of a specific substance or group of related substances (such as macromolecules, small molecules, ions) into, out of, within or between cells.
enzyme regulator activity
Modulates the activity of an enzyme.
carboxylic acid binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with a carboxylic acid, any organic acid containing one or more carboxyl (COOH) groups or anions (COO-).
amine binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with any organic compound that is weakly basic in character and contains an amino or a substituted amino group.
carboxylic acid transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of carboxylic acids from one side of the membrane to the other. Carboxylic acids are organic acids containing one or more carboxyl (COOH) groups or anions (COO-).
peptidase regulator activity
Modulates the activity of a peptidase, any enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis peptide bonds.
all
NA
substrate-specific transmembrane transporter activity
Enables the transfer of a specific substance or group of related substances from one side of a membrane to the other.
amino acid binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with an amino acid, organic acids containing one or more amino substituents.
peptidase inhibitor activity
Stops, prevents or reduces the activity of a peptidase, any enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis peptide bonds.
endopeptidase inhibitor activity
Stops, prevents or reduces the activity of an endopeptidase, any enzyme that hydrolyzes nonterminal peptide bonds in polypeptides.
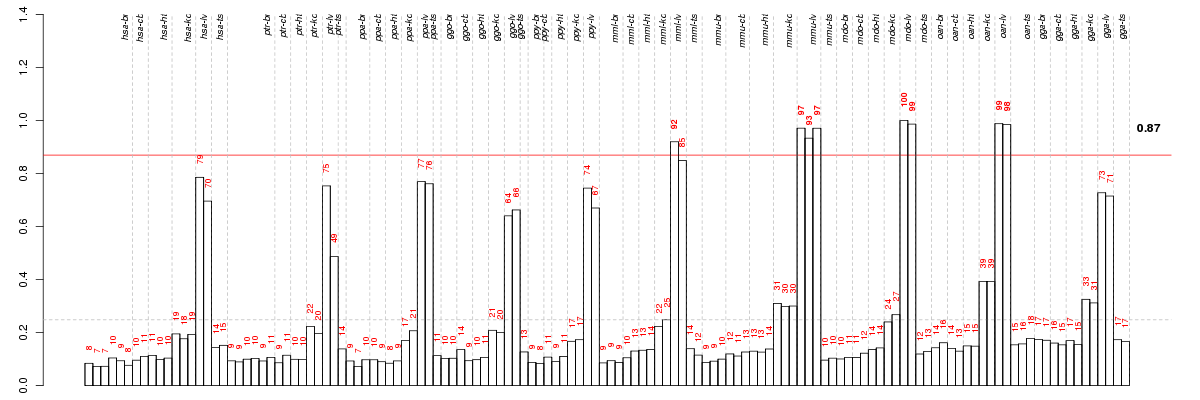
ABCB11ATP-binding cassette, sub-family B (MDR/TAP), member 11 (ENSG00000073734), score: 0.81 ABCD3ATP-binding cassette, sub-family D (ALD), member 3 (ENSG00000117528), score: 0.82 ACOT12acyl-CoA thioesterase 12 (ENSG00000172497), score: 0.84 AKR1D1aldo-keto reductase family 1, member D1 (delta 4-3-ketosteroid-5-beta-reductase) (ENSG00000122787), score: 0.8 AMDHD1amidohydrolase domain containing 1 (ENSG00000139344), score: 0.79 AVPR1Aarginine vasopressin receptor 1A (ENSG00000166148), score: 0.86 C5complement component 5 (ENSG00000106804), score: 0.82 CNR2cannabinoid receptor 2 (macrophage) (ENSG00000188822), score: 0.86 CYP39A1cytochrome P450, family 39, subfamily A, polypeptide 1 (ENSG00000146233), score: 0.82 EGFRepidermal growth factor receptor (ENSG00000146648), score: 0.79 FETUBfetuin B (ENSG00000090512), score: 0.98 GNMTglycine N-methyltransferase (ENSG00000124713), score: 0.86 GPLD1glycosylphosphatidylinositol specific phospholipase D1 (ENSG00000112293), score: 0.87 HALhistidine ammonia-lyase (ENSG00000084110), score: 0.95 IYDiodotyrosine deiodinase (ENSG00000009765), score: 0.86 LECT2leukocyte cell-derived chemotaxin 2 (ENSG00000145826), score: 0.98 MAT1Amethionine adenosyltransferase I, alpha (ENSG00000151224), score: 0.83 ONECUT1one cut homeobox 1 (ENSG00000169856), score: 0.84 OTCornithine carbamoyltransferase (ENSG00000036473), score: 1 PM20D1peptidase M20 domain containing 1 (ENSG00000162877), score: 0.8 SERPINC1serpin peptidase inhibitor, clade C (antithrombin), member 1 (ENSG00000117601), score: 0.79 SLC16A10solute carrier family 16, member 10 (aromatic amino acid transporter) (ENSG00000112394), score: 0.79 SLC25A47solute carrier family 25, member 47 (ENSG00000140107), score: 0.82 SLC38A4solute carrier family 38, member 4 (ENSG00000139209), score: 0.88 SLC46A1solute carrier family 46 (folate transporter), member 1 (ENSG00000076351), score: 0.79 SLC7A2solute carrier family 7 (cationic amino acid transporter, y+ system), member 2 (ENSG00000003989), score: 0.83 SLC7A6solute carrier family 7 (cationic amino acid transporter, y+ system), member 6 (ENSG00000103064), score: -0.93 SPP2secreted phosphoprotein 2, 24kDa (ENSG00000072080), score: 0.79 STARD5StAR-related lipid transfer (START) domain containing 5 (ENSG00000172345), score: 0.93 TATtyrosine aminotransferase (ENSG00000198650), score: 0.87 TDO2tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase (ENSG00000151790), score: 0.84 TTPAtocopherol (alpha) transfer protein (ENSG00000137561), score: 0.87 XKR9XK, Kell blood group complex subunit-related family, member 9 (ENSG00000221947), score: 1
| Id | species | tissue | sex | individual |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| mml_lv_m_ca1 | mml | lv | m | _ |
| mmu_lv_m1_ca1 | mmu | lv | m | 1 |
| mmu_lv_f_ca1 | mmu | lv | f | _ |
| mmu_lv_m2_ca1 | mmu | lv | m | 2 |
| oan_lv_f_ca1 | oan | lv | f | _ |
| mdo_lv_f_ca1 | mdo | lv | f | _ |
| oan_lv_m_ca1 | oan | lv | m | _ |
| mdo_lv_m_ca1 | mdo | lv | m | _ |