
Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

reproduction
The production by an organism of new individuals that contain some portion of their genetic material inherited from that organism.
M phase
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which a cell progresses through M phase, the part of the cell cycle comprising nuclear division.
cell cycle
The progression of biochemical and morphological phases and events that occur in a cell during successive cell replication or nuclear replication events. Canonically, the cell cycle comprises the replication and segregation of genetic material followed by the division of the cell, but in endocycles or syncytial cells nuclear replication or nuclear division may not be followed by cell division.
gamete generation
The generation and maintenance of gametes in a multicellular organism. A gamete is a haploid reproductive cell.
spermatogenesis
The process of formation of spermatozoa, including spermatocytogenesis and spermiogenesis.
single fertilization
The union of male and female gametes to form a zygote.
binding of sperm to zona pellucida
The process by which the sperm binds to the zona pellucida glycoprotein layer of the egg. The process begins with the attachment of the sperm plasma membrane to the zona pellucida and includes attachment of the acrosome inner membrane to the zona pellucida after the acrosomal reaction takes place.
cell recognition
The process by which a cell in a multicellular organism interprets its surroundings.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
fertilization
The union of gametes of opposite sexes during the process of sexual reproduction to form a zygote. It involves the fusion of the gametic nuclei (karyogamy) and cytoplasm (plasmogamy).
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
cell-cell recognition
Cell recognition between cells, usually involving the formation of specialized cell junctions.
sexual reproduction
The regular alternation, in the life cycle of haplontic, diplontic and diplohaplontic organisms, of meiosis and fertilization which provides for the production offspring. In diplontic organisms there is a life cycle in which the products of meiosis behave directly as gametes, fusing to form a zygote from which the diploid, or sexually reproductive polyploid, adult organism will develop. In diplohaplontic organisms a haploid phase (gametophyte) exists in the life cycle between meiosis and fertilization (e.g. higher plants, many algae and Fungi); the products of meiosis are spores that develop as haploid individuals from which haploid gametes develop to form a diploid zygote; diplohaplontic organisms show an alternation of haploid and diploid generations. In haplontic organisms meiosis occurs in the zygote, giving rise to four haploid cells (e.g. many algae and protozoa), only the zygote is diploid and this may form a resistant spore, tiding organisms over hard times.
cell cycle process
A cellular process that is involved in the progression of biochemical and morphological phases and events that occur in a cell during successive cell replication or nuclear replication events.
cell cycle phase
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which a cell progresses through one of the biochemical and morphological phases and events that occur during successive cell replication or nuclear replication events.
reproductive process
A biological process that directly contributes to the process of producing new individuals by one or two organisms. The new individuals inherit some proportion of their genetic material from the parent or parents.
multicellular organismal process
Any biological process, occurring at the level of a multicellular organism, pertinent to its function.
multicellular organism reproduction
The biological process by which new individuals are produced by one or two multicellular organisms. The new individuals inherit some proportion of their genetic material from the parent or parents.
sperm-egg recognition
The initial contact step made between the sperm plasma membrane and outer layer of the egg during fertilization.
male gamete generation
Generation of the male gamete; specialised haploid cells produced by meiosis and along with a female gamete takes part in sexual reproduction.
reproductive process in a multicellular organism
The process, occurring above the cellular level, that is pertinent to the reproductive function of a multicellular organism. This includes the integrated processes at the level of tissues and organs.
reproductive cellular process
A process, occurring at the cellular level, that is involved in the reproductive function of a multicellular or single-celled organism.
all
NA
reproductive process
A biological process that directly contributes to the process of producing new individuals by one or two organisms. The new individuals inherit some proportion of their genetic material from the parent or parents.
reproductive cellular process
A process, occurring at the cellular level, that is involved in the reproductive function of a multicellular or single-celled organism.
cell recognition
The process by which a cell in a multicellular organism interprets its surroundings.
multicellular organism reproduction
The biological process by which new individuals are produced by one or two multicellular organisms. The new individuals inherit some proportion of their genetic material from the parent or parents.
reproductive process in a multicellular organism
The process, occurring above the cellular level, that is pertinent to the reproductive function of a multicellular organism. This includes the integrated processes at the level of tissues and organs.
fertilization
The union of gametes of opposite sexes during the process of sexual reproduction to form a zygote. It involves the fusion of the gametic nuclei (karyogamy) and cytoplasm (plasmogamy).
reproductive process in a multicellular organism
The process, occurring above the cellular level, that is pertinent to the reproductive function of a multicellular organism. This includes the integrated processes at the level of tissues and organs.
cell cycle process
A cellular process that is involved in the progression of biochemical and morphological phases and events that occur in a cell during successive cell replication or nuclear replication events.
gamete generation
The generation and maintenance of gametes in a multicellular organism. A gamete is a haploid reproductive cell.
sperm-egg recognition
The initial contact step made between the sperm plasma membrane and outer layer of the egg during fertilization.
sperm-egg recognition
The initial contact step made between the sperm plasma membrane and outer layer of the egg during fertilization.

intracellular
The living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
cellular_component
The part of a cell or its extracellular environment in which a gene product is located. A gene product may be located in one or more parts of a cell and its location may be as specific as a particular macromolecular complex, that is, a stable, persistent association of macromolecules that function together.
cell
The basic structural and functional unit of all organisms. Includes the plasma membrane and any external encapsulating structures such as the cell wall and cell envelope.
cytoplasm
All of the contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures.
P granule
A small cytoplasmic, non-membranous RNA/protein complex aggregates in the primordial germ cells of many higher eukaryotes.
organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, and prokaryotic structures such as anammoxosomes and pirellulosomes. Excludes the plasma membrane.
non-membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, not bounded by a lipid bilayer membrane. Includes ribosomes, the cytoskeleton and chromosomes.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular non-membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, not bounded by a lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes ribosomes, the cytoskeleton and chromosomes.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
cytoplasmic part
Any constituent part of the cytoplasm, all of the contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures.
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
pole plasm
Differentiated cytoplasm associated with a pole (animal, vegetal, anterior, or posterior) of an oocyte, egg or early embryo.
germ plasm
Differentiated cytoplasm associated with a pole of an oocyte, egg or early embryo that will be inherited by the cells that will give rise to the germ line.
all
NA
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
intracellular non-membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, not bounded by a lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes ribosomes, the cytoskeleton and chromosomes.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
cytoplasmic part
Any constituent part of the cytoplasm, all of the contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures.
P granule
A small cytoplasmic, non-membranous RNA/protein complex aggregates in the primordial germ cells of many higher eukaryotes.
P granule
A small cytoplasmic, non-membranous RNA/protein complex aggregates in the primordial germ cells of many higher eukaryotes.

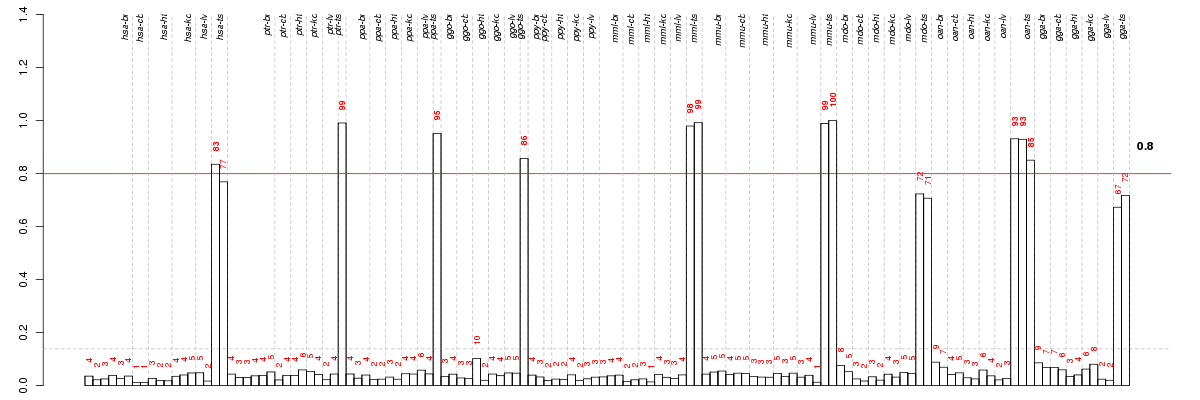
ADAD1adenosine deaminase domain containing 1 (testis-specific) (ENSG00000164113), score: 0.9 AK7adenylate kinase 7 (ENSG00000140057), score: 0.85 ARMC4armadillo repeat containing 4 (ENSG00000169126), score: 0.86 BOLLbol, boule-like (Drosophila) (ENSG00000152430), score: 0.87 C10orf96chromosome 10 open reading frame 96 (ENSG00000182645), score: 1 C7orf62chromosome 7 open reading frame 62 (ENSG00000164645), score: 0.85 CCDC83coiled-coil domain containing 83 (ENSG00000150676), score: 0.89 DDX4DEAD (Asp-Glu-Ala-Asp) box polypeptide 4 (ENSG00000152670), score: 0.86 DNAH8dynein, axonemal, heavy chain 8 (ENSG00000124721), score: 0.9 DNAJC5BDnaJ (Hsp40) homolog, subfamily C, member 5 beta (ENSG00000147570), score: 0.91 DTLdenticleless homolog (Drosophila) (ENSG00000143476), score: 0.9 FAM194Afamily with sequence similarity 194, member A (ENSG00000163645), score: 0.85 HSF2BPheat shock transcription factor 2 binding protein (ENSG00000160207), score: 0.85 KIF11kinesin family member 11 (ENSG00000138160), score: 0.86 LRRC18leucine rich repeat containing 18 (ENSG00000165383), score: 0.86 LRRC52leucine rich repeat containing 52 (ENSG00000162763), score: 0.85 PIWIL1piwi-like 1 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000125207), score: 0.85 SPACA1sperm acrosome associated 1 (ENSG00000118434), score: 0.88 SYCP1synaptonemal complex protein 1 (ENSG00000198765), score: 0.89 TTC29tetratricopeptide repeat domain 29 (ENSG00000137473), score: 0.85 TTKTTK protein kinase (ENSG00000112742), score: 0.87 ZPBPzona pellucida binding protein (ENSG00000042813), score: 0.88 ZPBP2zona pellucida binding protein 2 (ENSG00000186075), score: 0.85
| Id | species | tissue | sex | individual |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| hsa_ts_m2_ca1 | hsa | ts | m | 2 |
| oan_ts_m2_ca1 | oan | ts | m | 2 |
| ggo_ts_m_ca1 | ggo | ts | m | _ |
| oan_ts_m1_ca1 | oan | ts | m | 1 |
| oan_ts_m3_ca1 | oan | ts | m | 3 |
| ppa_ts_m_ca1 | ppa | ts | m | _ |
| mml_ts_m1_ca1 | mml | ts | m | 1 |
| mmu_ts_m1_ca1 | mmu | ts | m | 1 |
| ptr_ts_m_ca1 | ptr | ts | m | _ |
| mml_ts_m2_ca1 | mml | ts | m | 2 |
| mmu_ts_m2_ca1 | mmu | ts | m | 2 |