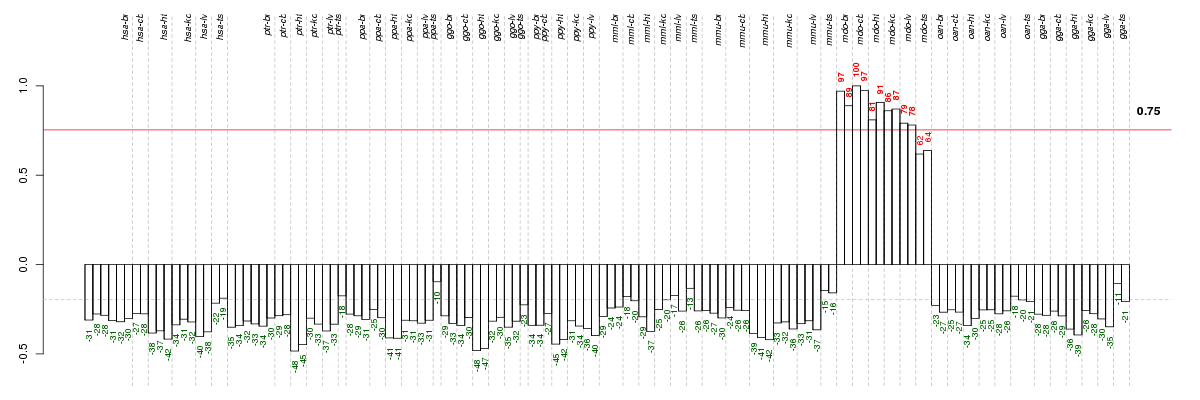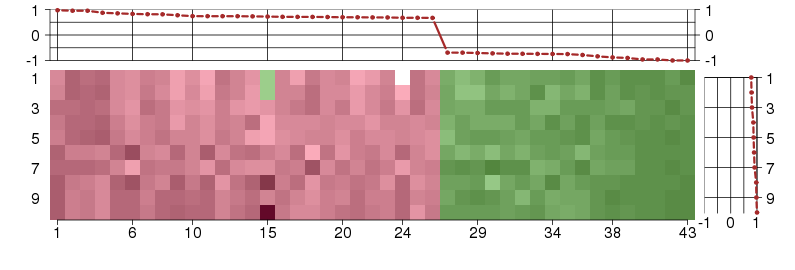

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways, including anabolism and catabolism, by which living organisms transform chemical substances. Metabolic processes typically transform small molecules, but also include macromolecular processes such as DNA repair and replication, and protein synthesis and degradation.
protein modification process
The covalent alteration of one or more amino acids occurring in proteins, peptides and nascent polypeptides (co-translational, post-translational modifications). Includes the modification of charged tRNAs that are destined to occur in a protein (pre-translation modification).
protein amino acid lipidation
The covalent or non-covalent attachment of lipid moieties to an amino acid in a protein.
GPI anchor metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving glycosylphosphatidylinositol anchors, molecular mechanisms for attaching membrane proteins to the lipid bilayer of cell membranes. Structurally they consist of a molecule of phosphatidylinositol to which is linked, via the C-6 hydroxyl of the inositol, a carbohydrate chain. This chain is in turn linked to the protein through an ethanolamine phosphate moiety, the amino group of which is in amide linkage with the C-terminal carboxyl of the protein chain, the phosphate group being esterified to the C-6 hydroxyl of the terminal mannose of the core carbohydrate chain.
GPI anchor biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI) anchor that attaches some membrane proteins to the lipid bilayer of the cell membrane. The phosphatidylinositol moiety is linked via the C-6 hydroxyl residue of inositol to a carbohydrate chain which is itself linked to the protein via an ethanolamine phosphate moiety, its amino group forming an amide linkage with the C-terminal carboxyl of the protein. Some GPI anchors have variants on this canonical linkage.
lipid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving lipids, compounds soluble in an organic solvent but not, or sparingly, in an aqueous solvent. Includes fatty acids; neutral fats, other fatty-acid esters, and soaps; long-chain (fatty) alcohols and waxes; sphingoids and other long-chain bases; glycolipids, phospholipids and sphingolipids; and carotenes, polyprenols, sterols, terpenes and other isoprenoids.
phospholipid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving phospholipids, any lipid containing phosphoric acid as a mono- or diester.
glycerophospholipid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving glycerophospholipids, any derivative of glycerophosphate that contains at least one O-acyl, O-alkyl, or O-alkenyl group attached to the glycerol residue.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
lipid biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of lipids, compounds soluble in an organic solvent but not, or sparingly, in an aqueous solvent.
phospholipid biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of phospholipids, any lipid containing phosphoric acid as a mono- or diester.
biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances; typically the energy-requiring part of metabolism in which simpler substances are transformed into more complex ones.
macromolecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
protein metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving a specific protein, rather than of proteins in general. Includes protein modification.
organophosphate metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving organophosphates, any phosphate-containing organic compound.
phosphoinositide metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving phosphoinositides, any of a class of glycerophospholipids in which the phosphatidyl group is esterified to the hydroxyl group of inositol. They are important constituents of cell membranes.
cellular macromolecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, carried out by individual cells.
lipoprotein metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving any conjugated, water-soluble protein in which the nonprotein moiety consists of a lipid or lipids.
lipoprotein biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of any conjugated, water-soluble protein in which the nonprotein moiety consists of a lipid or lipids.
macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
macromolecule modification
The covalent alteration of one or more monomeric units in a polypeptide, polynucleotide, polysaccharide, or other biological macromolecule, resulting in a change in its properties.
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
primary metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving those compounds which are formed as a part of the normal anabolic and catabolic processes. These processes take place in most, if not all, cells of the organism.
cellular biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
cellular lipid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving lipids, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular protein metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving a specific protein, rather than of proteins in general, occurring at the level of an individual cell. Includes protein modification.
glycerolipid biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of glycerolipids, any lipid with a glycerol backbone.
glycerophospholipid biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of glycerophospholipids, any derivative of glycerophosphate that contains at least one O-acyl, O-alkyl, or O-alkenyl group attached to the glycerol residue.
glycerolipid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving glycerolipids, any lipid with a glycerol backbone. Diacylglycerol and phosphatidate are key lipid intermediates of glycerolipid biosynthesis.
phosphoinositide biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of phosphoinositides, any of a class of glycerophospholipids in which the phosphatidyl group is esterified to the hydroxyl group of inositol.
all
NA
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
macromolecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
cellular biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
cellular macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, as carried out by individual cells.
protein metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving a specific protein, rather than of proteins in general. Includes protein modification.
phospholipid biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of phospholipids, any lipid containing phosphoric acid as a mono- or diester.
cellular macromolecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, carried out by individual cells.
glycerolipid biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of glycerolipids, any lipid with a glycerol backbone.
phospholipid biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of phospholipids, any lipid containing phosphoric acid as a mono- or diester.
cellular macromolecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, carried out by individual cells.
cellular protein metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving a specific protein, rather than of proteins in general, occurring at the level of an individual cell. Includes protein modification.
phospholipid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving phospholipids, any lipid containing phosphoric acid as a mono- or diester.
lipid biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of lipids, compounds soluble in an organic solvent but not, or sparingly, in an aqueous solvent.
cellular lipid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving lipids, as carried out by individual cells.
glycerophospholipid biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of glycerophospholipids, any derivative of glycerophosphate that contains at least one O-acyl, O-alkyl, or O-alkenyl group attached to the glycerol residue.
glycerophospholipid biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of glycerophospholipids, any derivative of glycerophosphate that contains at least one O-acyl, O-alkyl, or O-alkenyl group attached to the glycerol residue.
protein modification process
The covalent alteration of one or more amino acids occurring in proteins, peptides and nascent polypeptides (co-translational, post-translational modifications). Includes the modification of charged tRNAs that are destined to occur in a protein (pre-translation modification).
lipoprotein biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of any conjugated, water-soluble protein in which the nonprotein moiety consists of a lipid or lipids.
glycerophospholipid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving glycerophospholipids, any derivative of glycerophosphate that contains at least one O-acyl, O-alkyl, or O-alkenyl group attached to the glycerol residue.
glycerolipid biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of glycerolipids, any lipid with a glycerol backbone.
protein amino acid lipidation
The covalent or non-covalent attachment of lipid moieties to an amino acid in a protein.
phosphoinositide biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of phosphoinositides, any of a class of glycerophospholipids in which the phosphatidyl group is esterified to the hydroxyl group of inositol.
GPI anchor biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI) anchor that attaches some membrane proteins to the lipid bilayer of the cell membrane. The phosphatidylinositol moiety is linked via the C-6 hydroxyl residue of inositol to a carbohydrate chain which is itself linked to the protein via an ethanolamine phosphate moiety, its amino group forming an amide linkage with the C-terminal carboxyl of the protein. Some GPI anchors have variants on this canonical linkage.
GPI anchor biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI) anchor that attaches some membrane proteins to the lipid bilayer of the cell membrane. The phosphatidylinositol moiety is linked via the C-6 hydroxyl residue of inositol to a carbohydrate chain which is itself linked to the protein via an ethanolamine phosphate moiety, its amino group forming an amide linkage with the C-terminal carboxyl of the protein. Some GPI anchors have variants on this canonical linkage.

intracellular
The living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
membrane
Double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
integral to membrane
Penetrating at least one phospholipid bilayer of a membrane. May also refer to the state of being buried in the bilayer with no exposure outside the bilayer. When used to describe a protein, indicates that all or part of the peptide sequence is embedded in the membrane.
endoplasmic reticulum
The irregular network of unit membranes, visible only by electron microscopy, that occurs in the cytoplasm of many eukaryotic cells. The membranes form a complex meshwork of tubular channels, which are often expanded into slitlike cavities called cisternae. The ER takes two forms, rough (or granular), with ribosomes adhering to the outer surface, and smooth (with no ribosomes attached).
cellular_component
The part of a cell or its extracellular environment in which a gene product is located. A gene product may be located in one or more parts of a cell and its location may be as specific as a particular macromolecular complex, that is, a stable, persistent association of macromolecules that function together.
cell
The basic structural and functional unit of all organisms. Includes the plasma membrane and any external encapsulating structures such as the cell wall and cell envelope.
cytoplasm
All of the contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures.
endoplasmic reticulum membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding the endoplasmic reticulum.
endomembrane system
A collection of membranous structures involved in transport within the cell. The main components of the endomembrane system are endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi bodies, vesicles, cell membrane and nuclear envelope. Members of the endomembrane system pass materials through each other or though the use of vesicles.
integral to endoplasmic reticulum membrane
Penetrating at least one phospholipid bilayer of an endoplasmic reticulum membrane. May also refer to the state of being buried in the bilayer with no exposure outside the bilayer.
organelle membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding an organelle.
intrinsic to membrane
Located in a membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
intrinsic to endoplasmic reticulum membrane
Located in the endoplasmic reticulum membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
intrinsic to organelle membrane
Located in an organelle membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
integral to organelle membrane
Penetrating at least one phospholipid bilayer of an organelle membrane. May also refer to the state of being buried in the bilayer with no exposure outside the bilayer.
macromolecular complex
A stable assembly of two or more macromolecules, i.e. proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates or lipids, in which the constituent parts function together.
nuclear membrane-endoplasmic reticulum network
The continuous network of membranes encompassing the outer nuclear membrane and the endoplasmic reticulum.
GPI-anchor transamidase complex
An enzyme complex which in humans and yeast consists of at least five proteins; for example, the complex contains GAA1, GPI8, PIG-S, PIG-U, and PIG-T in human, and Gaa1p, Gab1p, Gpi8p, Gpi16p, and Gpi17p in yeast. Catalyzes the posttranslational attachment of the carboxyl-terminus of a precursor protein to a GPI-anchor.
organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, and prokaryotic structures such as anammoxosomes and pirellulosomes. Excludes the plasma membrane.
membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
protein complex
Any macromolecular complex composed of two or more polypeptide subunits, which may or may not be identical. Protein complexes may have other associated non-protein prosthetic groups, such as nucleotides, metal ions or other small molecules.
organelle part
Any constituent part of an organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, but excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
membrane part
Any constituent part of a membrane, a double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
endoplasmic reticulum part
Any constituent part of the endoplasmic reticulum, the irregular network of unit membranes, visible only by electron microscopy, that occurs in the cytoplasm of many eukaryotic cells. The membranes form a complex meshwork of tubular channels, which are often expanded into slitlike cavities called cisternae.
cytoplasmic part
Any constituent part of the cytoplasm, all of the contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
subsynaptic reticulum
An elaborate tubulolamellar membrane system that underlies the postsynaptic cell membrane.
all
NA
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
organelle part
Any constituent part of an organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, but excludes the plasma membrane.
organelle membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding an organelle.
intracellular membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
intrinsic to organelle membrane
Located in an organelle membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
organelle membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding an organelle.
membrane part
Any constituent part of a membrane, a double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
nuclear membrane-endoplasmic reticulum network
The continuous network of membranes encompassing the outer nuclear membrane and the endoplasmic reticulum.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
endoplasmic reticulum membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding the endoplasmic reticulum.
nuclear membrane-endoplasmic reticulum network
The continuous network of membranes encompassing the outer nuclear membrane and the endoplasmic reticulum.
GPI-anchor transamidase complex
An enzyme complex which in humans and yeast consists of at least five proteins; for example, the complex contains GAA1, GPI8, PIG-S, PIG-U, and PIG-T in human, and Gaa1p, Gab1p, Gpi8p, Gpi16p, and Gpi17p in yeast. Catalyzes the posttranslational attachment of the carboxyl-terminus of a precursor protein to a GPI-anchor.
intrinsic to endoplasmic reticulum membrane
Located in the endoplasmic reticulum membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
endoplasmic reticulum membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding the endoplasmic reticulum.
intrinsic to endoplasmic reticulum membrane
Located in the endoplasmic reticulum membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
GPI-anchor transamidase complex
An enzyme complex which in humans and yeast consists of at least five proteins; for example, the complex contains GAA1, GPI8, PIG-S, PIG-U, and PIG-T in human, and Gaa1p, Gab1p, Gpi8p, Gpi16p, and Gpi17p in yeast. Catalyzes the posttranslational attachment of the carboxyl-terminus of a precursor protein to a GPI-anchor.
endoplasmic reticulum membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding the endoplasmic reticulum.
cytoplasmic part
Any constituent part of the cytoplasm, all of the contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures.
endoplasmic reticulum
The irregular network of unit membranes, visible only by electron microscopy, that occurs in the cytoplasm of many eukaryotic cells. The membranes form a complex meshwork of tubular channels, which are often expanded into slitlike cavities called cisternae. The ER takes two forms, rough (or granular), with ribosomes adhering to the outer surface, and smooth (with no ribosomes attached).
endoplasmic reticulum part
Any constituent part of the endoplasmic reticulum, the irregular network of unit membranes, visible only by electron microscopy, that occurs in the cytoplasm of many eukaryotic cells. The membranes form a complex meshwork of tubular channels, which are often expanded into slitlike cavities called cisternae.
subsynaptic reticulum
An elaborate tubulolamellar membrane system that underlies the postsynaptic cell membrane.
intrinsic to organelle membrane
Located in an organelle membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
endoplasmic reticulum part
Any constituent part of the endoplasmic reticulum, the irregular network of unit membranes, visible only by electron microscopy, that occurs in the cytoplasm of many eukaryotic cells. The membranes form a complex meshwork of tubular channels, which are often expanded into slitlike cavities called cisternae.
endoplasmic reticulum part
Any constituent part of the endoplasmic reticulum, the irregular network of unit membranes, visible only by electron microscopy, that occurs in the cytoplasm of many eukaryotic cells. The membranes form a complex meshwork of tubular channels, which are often expanded into slitlike cavities called cisternae.
integral to endoplasmic reticulum membrane
Penetrating at least one phospholipid bilayer of an endoplasmic reticulum membrane. May also refer to the state of being buried in the bilayer with no exposure outside the bilayer.
integral to organelle membrane
Penetrating at least one phospholipid bilayer of an organelle membrane. May also refer to the state of being buried in the bilayer with no exposure outside the bilayer.
GPI-anchor transamidase complex
An enzyme complex which in humans and yeast consists of at least five proteins; for example, the complex contains GAA1, GPI8, PIG-S, PIG-U, and PIG-T in human, and Gaa1p, Gab1p, Gpi8p, Gpi16p, and Gpi17p in yeast. Catalyzes the posttranslational attachment of the carboxyl-terminus of a precursor protein to a GPI-anchor.

molecular_function
Elemental activities, such as catalysis or binding, describing the actions of a gene product at the molecular level. A given gene product may exhibit one or more molecular functions.
catalytic activity
Catalysis of a biochemical reaction at physiological temperatures. In biologically catalyzed reactions, the reactants are known as substrates, and the catalysts are naturally occurring macromolecular substances known as enzymes. Enzymes possess specific binding sites for substrates, and are usually composed wholly or largely of protein, but RNA that has catalytic activity (ribozyme) is often also regarded as enzymatic.
GPI-anchor transamidase activity
Catalysis of the formation of the linkage between a protein and a glycosylphosphatidylinositol anchor. The reaction probably occurs by subjecting a peptide bond to nucleophilic attack by the amino group of ethanolamine-GPI, transferring the protein from a signal peptide to the GPI anchor.
hydrolase activity
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of various bonds, e.g. C-O, C-N, C-C, phosphoric anhydride bonds, etc. Hydrolase is the systematic name for any enzyme of EC class 3.
all
NA
| Id | Pvalue | ExpCount | Count | Size | Term |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 05012 | 2.216e-03 | 0.1954 | 4 | 27 | Parkinson's disease |
| 00563 | 3.590e-03 | 0.07961 | 3 | 11 | Glycosylphosphatidylinositol(GPI)-anchor biosynthesis |
| 00190 | 3.924e-02 | 0.2171 | 3 | 30 | Oxidative phosphorylation |
ACYP2acylphosphatase 2, muscle type (ENSG00000170634), score: -0.9 ADCK1aarF domain containing kinase 1 (ENSG00000063761), score: -0.74 ALKBH2alkB, alkylation repair homolog 2 (E. coli) (ENSG00000189046), score: 0.73 AMBRA1autophagy/beclin-1 regulator 1 (ENSG00000110497), score: 0.71 ASB1ankyrin repeat and SOCS box-containing 1 (ENSG00000065802), score: 0.69 ATP2B4ATPase, Ca++ transporting, plasma membrane 4 (ENSG00000058668), score: -0.84 C13orf31chromosome 13 open reading frame 31 (ENSG00000179630), score: 0.83 C1orf123chromosome 1 open reading frame 123 (ENSG00000162384), score: 0.7 C20orf43chromosome 20 open reading frame 43 (ENSG00000022277), score: -0.72 C3orf39chromosome 3 open reading frame 39 (ENSG00000144647), score: 0.69 CDC123cell division cycle 123 homolog (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000151465), score: -0.78 CDCA3cell division cycle associated 3 (ENSG00000111665), score: 0.81 COX1cytochrome c oxidase subunit I (ENSG00000198804), score: -0.88 CYTBcytochrome b (ENSG00000198727), score: -1 ERCC6excision repair cross-complementing rodent repair deficiency, complementation group 6 (ENSG00000225830), score: -0.74 FUT10fucosyltransferase 10 (alpha (1,3) fucosyltransferase) (ENSG00000172728), score: 0.81 GPR107G protein-coupled receptor 107 (ENSG00000148358), score: -0.69 IKIK cytokine, down-regulator of HLA II (ENSG00000113141), score: -0.75 IPPintracisternal A particle-promoted polypeptide (ENSG00000197429), score: 0.97 LYSMD4LysM, putative peptidoglycan-binding, domain containing 4 (ENSG00000183060), score: -0.69 N4BP1NEDD4 binding protein 1 (ENSG00000102921), score: 0.67 ND2MTND2 (ENSG00000198763), score: -0.96 NIF3L1NIF3 NGG1 interacting factor 3-like 1 (S. pombe) (ENSG00000196290), score: 0.74 NOXO1NADPH oxidase organizer 1 (ENSG00000196408), score: 0.95 NSUN2NOP2/Sun domain family, member 2 (ENSG00000037474), score: -0.74 OTOL1otolin 1 homolog (zebrafish) (ENSG00000182447), score: 0.72 PGRprogesterone receptor (ENSG00000082175), score: 0.68 PIGKphosphatidylinositol glycan anchor biosynthesis, class K (ENSG00000142892), score: 0.74 PIGLphosphatidylinositol glycan anchor biosynthesis, class L (ENSG00000108474), score: 0.74 PIGSphosphatidylinositol glycan anchor biosynthesis, class S (ENSG00000087111), score: 0.77 RIC8Bresistance to inhibitors of cholinesterase 8 homolog B (C. elegans) (ENSG00000111785), score: 0.85 RPS6KA6ribosomal protein S6 kinase, 90kDa, polypeptide 6 (ENSG00000072133), score: 0.69 SAP30LSAP30-like (ENSG00000164576), score: 0.71 SFRS8splicing factor, arginine/serine-rich 8 (suppressor-of-white-apricot homolog, Drosophila) (ENSG00000061936), score: 0.71 SLC38A8solute carrier family 38, member 8 (ENSG00000166558), score: 0.95 THYN1thymocyte nuclear protein 1 (ENSG00000151500), score: -0.73 TMEM18transmembrane protein 18 (ENSG00000151353), score: -0.71 TMEM184Ctransmembrane protein 184C (ENSG00000164168), score: 0.87 TOE1target of EGR1, member 1 (nuclear) (ENSG00000132773), score: 0.67 UBE2G1ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2G 1 (UBC7 homolog, yeast) (ENSG00000132388), score: -0.96 ZC3H15zinc finger CCCH-type containing 15 (ENSG00000065548), score: -1 ZNF512zinc finger protein 512 (ENSG00000243943), score: 0.74 ZWILCHZwilch, kinetochore associated, homolog (Drosophila) (ENSG00000174442), score: 0.7
| Id | species | tissue | sex | individual |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| mdo_lv_f_ca1 | mdo | lv | f | _ |
| mdo_lv_m_ca1 | mdo | lv | m | _ |
| mdo_ht_m_ca1 | mdo | ht | m | _ |
| mdo_kd_m_ca1 | mdo | kd | m | _ |
| mdo_kd_f_ca1 | mdo | kd | f | _ |
| mdo_br_f_ca1 | mdo | br | f | _ |
| mdo_ht_f_ca1 | mdo | ht | f | _ |
| mdo_br_m_ca1 | mdo | br | m | _ |
| mdo_cb_f_ca1 | mdo | cb | f | _ |
| mdo_cb_m_ca1 | mdo | cb | m | _ |