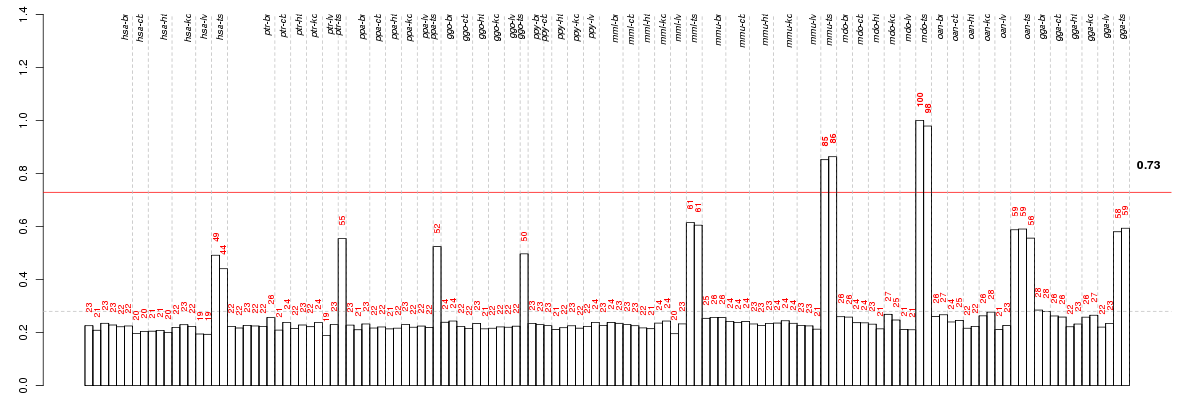

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways, including anabolism and catabolism, by which living organisms transform chemical substances. Metabolic processes typically transform small molecules, but also include macromolecular processes such as DNA repair and replication, and protein synthesis and degradation.
carbohydrate metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving carbohydrates, any of a group of organic compounds based of the general formula Cx(H2O)y. Includes the formation of carbohydrate derivatives by the addition of a carbohydrate residue to another molecule.
monosaccharide metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving monosaccharides, the simplest carbohydrates. They are polyhydric alcohols containing either an aldehyde or a keto group and between three to ten or more carbon atoms. They form the constitutional repeating units of oligo- and polysaccharides.
glucose metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving glucose, the aldohexose gluco-hexose. D-glucose is dextrorotatory and is sometimes known as dextrose; it is an important source of energy for living organisms and is found free as well as combined in homo- and hetero-oligosaccharides and polysaccharides.
glucose catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of glucose, the aldohexose gluco-hexose.
alcohol metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving alcohols, any of a class of compounds containing one or more hydroxyl groups attached to a saturated carbon atom.
generation of precursor metabolites and energy
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of precursor metabolites, substances from which energy is derived, and any process involved in the liberation of energy from these substances.
glycolysis
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of a monosaccharide (generally glucose) into pyruvate, with the concomitant production of a small amount of ATP. Pyruvate may be converted to ethanol, lactate, or other small molecules, or fed into the TCA cycle.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of substances, including the breakdown of carbon compounds with the liberation of energy for use by the cell or organism.
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
carbohydrate catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of carbohydrates, any of a group of organic compounds based of the general formula Cx(H2O)y.
hexose metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving a hexose, any monosaccharide with a chain of six carbon atoms in the molecule.
hexose catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of hexose, any monosaccharide with a chain of six carbon atoms in the molecule.
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
primary metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving those compounds which are formed as a part of the normal anabolic and catabolic processes. These processes take place in most, if not all, cells of the organism.
cellular carbohydrate metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving carbohydrates, any of a group of organic compounds based of the general formula Cx(H2O)y, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular carbohydrate catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of carbohydrates, any of a group of organic compounds based of the general formula Cx(H2O)y, as carried out by individual cells.
small molecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving small molecules, any monomeric molecule of small relative molecular mass.
small molecule catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of small molecules, any monomeric molecule of small relative molecular mass.
alcohol catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of alcohols, any of a class of compounds containing one or more hydroxyl groups attached to a saturated carbon atom.
monosaccharide catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of monosaccharides, polyhydric alcohols containing either an aldehyde or a keto group and between three to ten or more carbon atoms.
all
NA
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
small molecule catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of small molecules, any monomeric molecule of small relative molecular mass.
cellular carbohydrate catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of carbohydrates, any of a group of organic compounds based of the general formula Cx(H2O)y, as carried out by individual cells.
carbohydrate catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of carbohydrates, any of a group of organic compounds based of the general formula Cx(H2O)y.
cellular carbohydrate metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving carbohydrates, any of a group of organic compounds based of the general formula Cx(H2O)y, as carried out by individual cells.
monosaccharide metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving monosaccharides, the simplest carbohydrates. They are polyhydric alcohols containing either an aldehyde or a keto group and between three to ten or more carbon atoms. They form the constitutional repeating units of oligo- and polysaccharides.
alcohol catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of alcohols, any of a class of compounds containing one or more hydroxyl groups attached to a saturated carbon atom.
monosaccharide catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of monosaccharides, polyhydric alcohols containing either an aldehyde or a keto group and between three to ten or more carbon atoms.
monosaccharide catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of monosaccharides, polyhydric alcohols containing either an aldehyde or a keto group and between three to ten or more carbon atoms.
hexose catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of hexose, any monosaccharide with a chain of six carbon atoms in the molecule.
glucose catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of glucose, the aldohexose gluco-hexose.
glycolysis
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of a monosaccharide (generally glucose) into pyruvate, with the concomitant production of a small amount of ATP. Pyruvate may be converted to ethanol, lactate, or other small molecules, or fed into the TCA cycle.

intracellular
The living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
cellular_component
The part of a cell or its extracellular environment in which a gene product is located. A gene product may be located in one or more parts of a cell and its location may be as specific as a particular macromolecular complex, that is, a stable, persistent association of macromolecules that function together.
cell
The basic structural and functional unit of all organisms. Includes the plasma membrane and any external encapsulating structures such as the cell wall and cell envelope.
nucleus
A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent.
organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, and prokaryotic structures such as anammoxosomes and pirellulosomes. Excludes the plasma membrane.
membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
all
NA
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
intracellular membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.

APTXaprataxin (ENSG00000137074), score: 0.99 BPGM2,3-bisphosphoglycerate mutase (ENSG00000172331), score: 0.79 C11orf82chromosome 11 open reading frame 82 (ENSG00000165490), score: 0.86 C12orf48chromosome 12 open reading frame 48 (ENSG00000185480), score: 0.83 C14orf166Bchromosome 14 open reading frame 166B (ENSG00000100565), score: 0.84 C15orf26chromosome 15 open reading frame 26 (ENSG00000156206), score: 0.79 C6orf204chromosome 6 open reading frame 204 (ENSG00000111860), score: 0.8 C7orf45chromosome 7 open reading frame 45 (ENSG00000165120), score: 0.83 CCDC37coiled-coil domain containing 37 (ENSG00000163885), score: 0.8 CCDC41coiled-coil domain containing 41 (ENSG00000173588), score: 0.83 CCDC67coiled-coil domain containing 67 (ENSG00000165325), score: 0.82 ECDecdysoneless homolog (Drosophila) (ENSG00000122882), score: 0.93 ENO4enolase family member 4 (ENSG00000188316), score: 0.86 FAM118Bfamily with sequence similarity 118, member B (ENSG00000197798), score: 0.79 FAM161Afamily with sequence similarity 161, member A (ENSG00000170264), score: 0.98 FAM54Afamily with sequence similarity 54, member A (ENSG00000146410), score: 0.81 FOXN1forkhead box N1 (ENSG00000109101), score: 0.82 GDPD4glycerophosphodiester phosphodiesterase domain containing 4 (ENSG00000178795), score: 0.97 GEMIN5gem (nuclear organelle) associated protein 5 (ENSG00000082516), score: 1 HOXB13homeobox B13 (ENSG00000159184), score: 0.78 KIAA1609KIAA1609 (ENSG00000140950), score: 0.78 KIF14kinesin family member 14 (ENSG00000118193), score: 0.83 KIF18Bkinesin family member 18B (ENSG00000186185), score: 0.9 KIF27kinesin family member 27 (ENSG00000165115), score: 0.85 MAKmale germ cell-associated kinase (ENSG00000111837), score: 0.79 NUP153nucleoporin 153kDa (ENSG00000124789), score: 0.97 NUP205nucleoporin 205kDa (ENSG00000155561), score: 0.82 PRKCQprotein kinase C, theta (ENSG00000065675), score: 0.85 PRSSL1protease, serine-like 1 (ENSG00000185198), score: 1 PUS3pseudouridylate synthase 3 (ENSG00000110060), score: 0.82 RGP1RGP1 retrograde golgi transport homolog (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000107185), score: 0.83 SMC1Bstructural maintenance of chromosomes 1B (ENSG00000077935), score: 0.88 SPO11SPO11 meiotic protein covalently bound to DSB homolog (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000054796), score: 0.95 SRMSsrc-related kinase lacking C-terminal regulatory tyrosine and N-terminal myristylation sites (ENSG00000125508), score: 0.86 STILSCL/TAL1 interrupting locus (ENSG00000123473), score: 0.92 SUFUsuppressor of fused homolog (Drosophila) (ENSG00000107882), score: 0.82 TDRD5tudor domain containing 5 (ENSG00000162782), score: 0.8 TERTtelomerase reverse transcriptase (ENSG00000164362), score: 0.78 UHRF1ubiquitin-like with PHD and ring finger domains 1 (ENSG00000034063), score: 0.92 VWA5B1von Willebrand factor A domain containing 5B1 (ENSG00000158816), score: 0.92 WDR48WD repeat domain 48 (ENSG00000114742), score: 0.97 WDR64WD repeat domain 64 (ENSG00000162843), score: 0.95 XPO4exportin 4 (ENSG00000132953), score: 0.8 ZPBP2zona pellucida binding protein 2 (ENSG00000186075), score: 0.78
| Id | species | tissue | sex | individual |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| mmu_ts_m1_ca1 | mmu | ts | m | 1 |
| mmu_ts_m2_ca1 | mmu | ts | m | 2 |
| mdo_ts_m1_ca1 | mdo | ts | m | 1 |
| mdo_ts_m2_ca1 | mdo | ts | m | 2 |