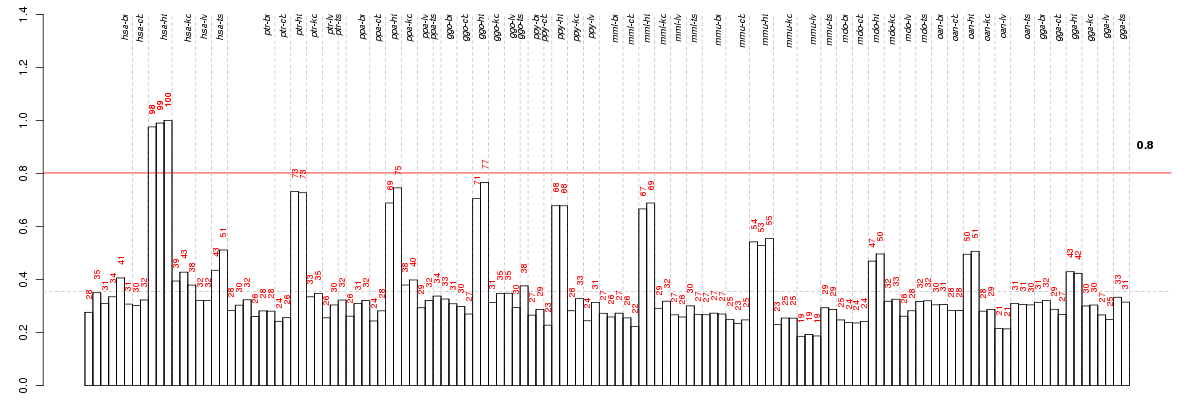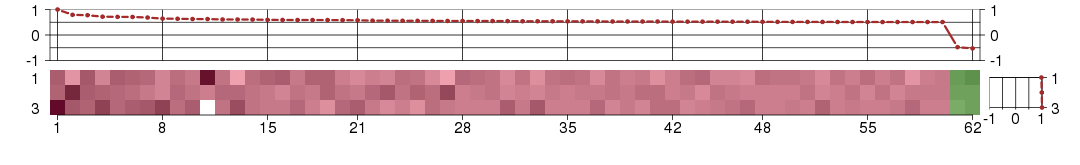

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways, including anabolism and catabolism, by which living organisms transform chemical substances. Metabolic processes typically transform small molecules, but also include macromolecular processes such as DNA repair and replication, and protein synthesis and degradation.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances; typically the energy-requiring part of metabolism in which simpler substances are transformed into more complex ones.
macromolecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
regulation of biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances.
negative regulation of biosynthetic process
Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the rate of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances.
negative regulation of metabolic process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism.
regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the rate, frequency or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
negative regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic process
Any process that decreases the rate, frequency or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
negative regulation of macromolecule metabolic process
Any process that decreases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
regulation of collagen metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the metabolism of collagen, any of a group of fibrous proteins of very high tensile strength that form the main component of connective tissue in animals.
negative regulation of collagen metabolic process
Any process that decreases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the metabolism of collagen, any of a group of fibrous proteins of very high tensile strength that form the main component of connective tissue in animals.
regulation of metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism.
multicellular organismal process
Any biological process, occurring at the level of a multicellular organism, pertinent to its function.
collagen metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving collagen, any of a group of fibrous proteins of very high tensile strength that form the main component of connective tissue in animals. Collagen is highly enriched in glycine (some regions are 33% glycine) and proline, occurring predominantly as 3-hydroxyproline (about 20%).
collagen biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of collagen, any of a group of fibrous proteins of very high tensile strength that form the main component of connective tissue in animals. Collagen is highly enriched in glycine (some regions are 33% glycine) and proline, occurring predominantly as 3-hydroxyproline (about 20%).
regulation of collagen biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of collagen, any of a group of fibrous proteins of very high tensile strength that form the main component of connective tissue in animals.
negative regulation of collagen biosynthetic process
Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of collagen, any of a group of fibrous proteins of very high tensile strength that form the main component of connective tissue in animals.
macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
multicellular organismal metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways in multicellular organisms that occur at the tissue, organ, or organismal level. These processes, unlike cellular metabolism, can include transport of substances between cells when that transport is required.
regulation of multicellular organismal metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of chemical reactions and pathways in multicellular organisms that occur at the tissue, organ, or organismal level.
negative regulation of multicellular organismal metabolic process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces frequency, rate or extent of chemical reactions and pathways in multicellular organisms that occur at the tissue, organ, or organismal level.
multicellular organismal macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, large molecules including proteins, nucleic acids and carbohydrates, in multicellular organisms occurring at the tissue, organ, or organismal level.
negative regulation of biological process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of multicellular organismal process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a multicellular organismal process, the processes pertinent to the function of a multicellular organism above the cellular level; includes the integrated processes of tissues and organs.
negative regulation of multicellular organismal process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of an organismal process, the processes pertinent to the function of an organism above the cellular level; includes the integrated processes of tissues and organs.
regulation of macromolecule metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
biological regulation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of any biological process, quality or function.
all
NA
multicellular organismal metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways in multicellular organisms that occur at the tissue, organ, or organismal level. These processes, unlike cellular metabolism, can include transport of substances between cells when that transport is required.
negative regulation of metabolic process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism.
negative regulation of multicellular organismal process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of an organismal process, the processes pertinent to the function of an organism above the cellular level; includes the integrated processes of tissues and organs.
regulation of metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism.
negative regulation of biological process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of multicellular organismal process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a multicellular organismal process, the processes pertinent to the function of a multicellular organism above the cellular level; includes the integrated processes of tissues and organs.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
negative regulation of biosynthetic process
Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the rate of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances.
regulation of biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances.
negative regulation of metabolic process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism.
macromolecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
negative regulation of macromolecule metabolic process
Any process that decreases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
regulation of macromolecule metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
regulation of multicellular organismal metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of chemical reactions and pathways in multicellular organisms that occur at the tissue, organ, or organismal level.
negative regulation of multicellular organismal metabolic process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces frequency, rate or extent of chemical reactions and pathways in multicellular organisms that occur at the tissue, organ, or organismal level.
multicellular organismal macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, large molecules including proteins, nucleic acids and carbohydrates, in multicellular organisms occurring at the tissue, organ, or organismal level.
regulation of multicellular organismal metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of chemical reactions and pathways in multicellular organisms that occur at the tissue, organ, or organismal level.
negative regulation of multicellular organismal process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of an organismal process, the processes pertinent to the function of an organism above the cellular level; includes the integrated processes of tissues and organs.
negative regulation of multicellular organismal metabolic process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces frequency, rate or extent of chemical reactions and pathways in multicellular organisms that occur at the tissue, organ, or organismal level.
negative regulation of biosynthetic process
Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the rate of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances.
regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the rate, frequency or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
negative regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic process
Any process that decreases the rate, frequency or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
negative regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic process
Any process that decreases the rate, frequency or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
negative regulation of collagen metabolic process
Any process that decreases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the metabolism of collagen, any of a group of fibrous proteins of very high tensile strength that form the main component of connective tissue in animals.
negative regulation of multicellular organismal metabolic process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces frequency, rate or extent of chemical reactions and pathways in multicellular organisms that occur at the tissue, organ, or organismal level.
regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the rate, frequency or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
negative regulation of macromolecule metabolic process
Any process that decreases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
regulation of collagen metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the metabolism of collagen, any of a group of fibrous proteins of very high tensile strength that form the main component of connective tissue in animals.
negative regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic process
Any process that decreases the rate, frequency or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
regulation of collagen biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of collagen, any of a group of fibrous proteins of very high tensile strength that form the main component of connective tissue in animals.
negative regulation of collagen biosynthetic process
Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of collagen, any of a group of fibrous proteins of very high tensile strength that form the main component of connective tissue in animals.
negative regulation of collagen biosynthetic process
Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of collagen, any of a group of fibrous proteins of very high tensile strength that form the main component of connective tissue in animals.
negative regulation of collagen metabolic process
Any process that decreases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the metabolism of collagen, any of a group of fibrous proteins of very high tensile strength that form the main component of connective tissue in animals.
regulation of collagen biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of collagen, any of a group of fibrous proteins of very high tensile strength that form the main component of connective tissue in animals.
regulation of collagen metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the metabolism of collagen, any of a group of fibrous proteins of very high tensile strength that form the main component of connective tissue in animals.
negative regulation of collagen metabolic process
Any process that decreases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the metabolism of collagen, any of a group of fibrous proteins of very high tensile strength that form the main component of connective tissue in animals.
collagen biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of collagen, any of a group of fibrous proteins of very high tensile strength that form the main component of connective tissue in animals. Collagen is highly enriched in glycine (some regions are 33% glycine) and proline, occurring predominantly as 3-hydroxyproline (about 20%).
negative regulation of collagen biosynthetic process
Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of collagen, any of a group of fibrous proteins of very high tensile strength that form the main component of connective tissue in animals.


AFTPHaftiphilin (ENSG00000119844), score: -0.48 ANAPC16anaphase promoting complex subunit 16 (ENSG00000166295), score: 0.56 ANKRD2ankyrin repeat domain 2 (stretch responsive muscle) (ENSG00000165887), score: 0.64 ANO2anoctamin 2 (ENSG00000047617), score: 0.51 ASB11ankyrin repeat and SOCS box-containing 11 (ENSG00000165192), score: 0.55 C15orf41chromosome 15 open reading frame 41 (ENSG00000186073), score: 0.71 CALHM2calcium homeostasis modulator 2 (ENSG00000138172), score: 0.59 CBLBCas-Br-M (murine) ecotropic retroviral transforming sequence b (ENSG00000114423), score: 0.53 CD151CD151 molecule (Raph blood group) (ENSG00000177697), score: 0.51 CD79BCD79b molecule, immunoglobulin-associated beta (ENSG00000007312), score: 0.54 CDH19cadherin 19, type 2 (ENSG00000071991), score: 0.55 CIITAclass II, major histocompatibility complex, transactivator (ENSG00000179583), score: 0.51 COL23A1collagen, type XXIII, alpha 1 (ENSG00000050767), score: 0.58 COL6A2collagen, type VI, alpha 2 (ENSG00000142173), score: 0.51 CREB3L1cAMP responsive element binding protein 3-like 1 (ENSG00000157613), score: 0.61 DUSP27dual specificity phosphatase 27 (putative) (ENSG00000198842), score: 0.54 EYA4eyes absent homolog 4 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000112319), score: 0.56 F2RL3coagulation factor II (thrombin) receptor-like 3 (ENSG00000127533), score: 0.64 FAM129Afamily with sequence similarity 129, member A (ENSG00000135842), score: 0.59 FAM179Afamily with sequence similarity 179, member A (ENSG00000189350), score: 0.59 FBLN2fibulin 2 (ENSG00000163520), score: 0.51 FGF18fibroblast growth factor 18 (ENSG00000156427), score: 0.51 FIGFc-fos induced growth factor (vascular endothelial growth factor D) (ENSG00000165197), score: 0.72 GJA3gap junction protein, alpha 3, 46kDa (ENSG00000121743), score: 0.55 GLP1Rglucagon-like peptide 1 receptor (ENSG00000112164), score: 0.62 GPR133G protein-coupled receptor 133 (ENSG00000111452), score: 0.71 GRK5G protein-coupled receptor kinase 5 (ENSG00000198873), score: 0.52 GRXCR2glutaredoxin, cysteine rich 2 (ENSG00000204928), score: 0.59 HAPLN3hyaluronan and proteoglycan link protein 3 (ENSG00000140511), score: 0.53 HEY2hairy/enhancer-of-split related with YRPW motif 2 (ENSG00000135547), score: 0.52 IL18R1interleukin 18 receptor 1 (ENSG00000115604), score: 0.61 IL6interleukin 6 (interferon, beta 2) (ENSG00000136244), score: 0.55 KBTBD10kelch repeat and BTB (POZ) domain containing 10 (ENSG00000239474), score: 0.51 KBTBD10kelch repeat and BTB (POZ) domain containing 10 (ENSG00000163093), score: 0.52 KLHL31kelch-like 31 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000124743), score: 0.52 LMOD3leiomodin 3 (fetal) (ENSG00000163380), score: 0.78 MAPKAPK3mitogen-activated protein kinase-activated protein kinase 3 (ENSG00000114738), score: 0.56 MARK3MAP/microtubule affinity-regulating kinase 3 (ENSG00000075413), score: 0.54 METTL6methyltransferase like 6 (ENSG00000206562), score: -0.53 MYBPC3myosin binding protein C, cardiac (ENSG00000134571), score: 0.51 MYOM3myomesin family, member 3 (ENSG00000142661), score: 0.61 MYPNmyopalladin (ENSG00000138347), score: 0.54 NEURL1Bneuralized homolog 1B (Drosophila) (ENSG00000214357), score: 0.52 PBX3pre-B-cell leukemia homeobox 3 (ENSG00000167081), score: 0.55 PPP1R3Aprotein phosphatase 1, regulatory (inhibitor) subunit 3A (ENSG00000154415), score: 0.51 PTPN12protein tyrosine phosphatase, non-receptor type 12 (ENSG00000127947), score: 0.51 PTX3pentraxin 3, long (ENSG00000163661), score: 0.79 RPUSD4RNA pseudouridylate synthase domain containing 4 (ENSG00000165526), score: 0.56 RRADRas-related associated with diabetes (ENSG00000166592), score: 0.51 RSPO1R-spondin homolog (Xenopus laevis) (ENSG00000169218), score: 0.68 SCUBE3signal peptide, CUB domain, EGF-like 3 (ENSG00000146197), score: 0.52 SLC41A1solute carrier family 41, member 1 (ENSG00000133065), score: 0.53 TBC1D8TBC1 domain family, member 8 (with GRAM domain) (ENSG00000204634), score: 0.52 TECRLtrans-2,3-enoyl-CoA reductase-like (ENSG00000205678), score: 0.53 TPM1tropomyosin 1 (alpha) (ENSG00000140416), score: 0.51 TPOthyroid peroxidase (ENSG00000115705), score: 1 TUBB6tubulin, beta 6 (ENSG00000176014), score: 0.54 TYRP1tyrosinase-related protein 1 (ENSG00000107165), score: 0.6 VIPR2vasoactive intestinal peptide receptor 2 (ENSG00000106018), score: 0.53 VITvitrin (ENSG00000205221), score: 0.63 WISP2WNT1 inducible signaling pathway protein 2 (ENSG00000064205), score: 0.53 ZNF330zinc finger protein 330 (ENSG00000109445), score: 0.58
| Id | species | tissue | sex | individual |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| hsa_ht_m1_ca1 | hsa | ht | m | 1 |
| hsa_ht_m2_ca1 | hsa | ht | m | 2 |
| hsa_ht_f_ca1 | hsa | ht | f | _ |