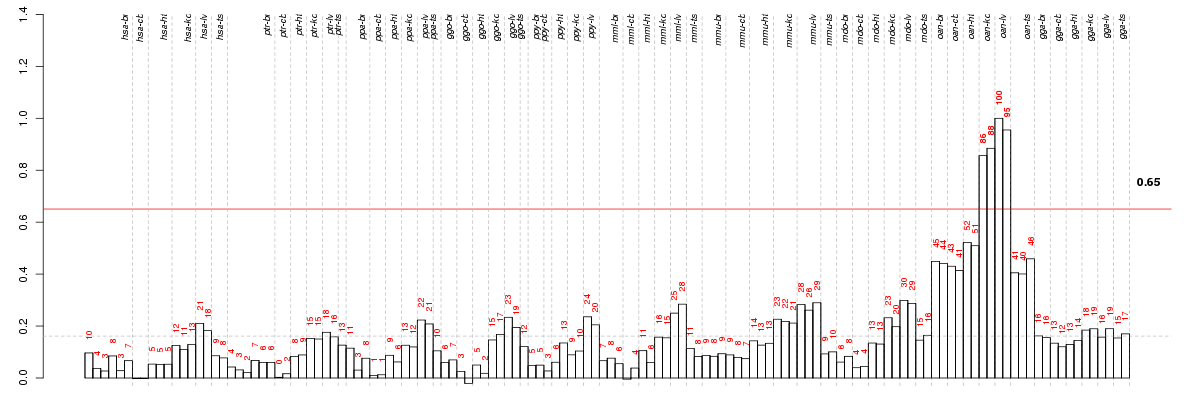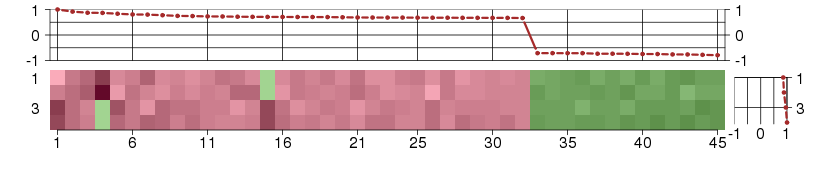

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

reproduction
The production by an organism of new individuals that contain some portion of their genetic material inherited from that organism.
urea cycle
A cyclic metabolic pathway that converts waste nitrogen in the form of ammonium to urea.
metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways, including anabolism and catabolism, by which living organisms transform chemical substances. Metabolic processes typically transform small molecules, but also include macromolecular processes such as DNA repair and replication, and protein synthesis and degradation.
reproductive developmental process
A developmental process by which a progressive change in the state of some part of an organism specifically contributes to its ability to form offspring.
nitrogen compound metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving various organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds; includes nitrogen fixation, nitrification, denitrification, assimilatory/dissimilatory nitrate reduction and the interconversion of nitrogenous organic matter and ammonium.
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
sex differentiation
The establishment of the sex of an organism by physical differentiation.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
cell proliferation
The multiplication or reproduction of cells, resulting in the expansion of a cell population.
gonad development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the gonad over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The gonad is an animal organ that produces gametes; in some species it also produces hormones.
male gonad development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the male gonad over time, from its formation to the mature structure.
biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances; typically the energy-requiring part of metabolism in which simpler substances are transformed into more complex ones.
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
urea metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving urea, the water soluble compound O=C-(NH2)2, produced in the liver by the ornithine cycle. It is the main nitrogen-containing excretion product in ureotelic animals.
reproductive process
A biological process that directly contributes to the process of producing new individuals by one or two organisms. The new individuals inherit some proportion of their genetic material from the parent or parents.
multicellular organismal process
Any biological process, occurring at the level of a multicellular organism, pertinent to its function.
developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an integrated living unit: an anatomical structure (which may be a subcellular structure, cell, tissue, or organ), or organism over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
cellular nitrogen compound metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving various organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular amide metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving an amide, any derivative of an oxoacid in which an acidic hydroxy group has been replaced by an amino or substituted amino group, as carried out by individual cells.
amide biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of an amide, any derivative of an oxoacid in which an acidic hydroxy group has been replaced by an amino or substituted amino group.
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
cellular biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
cellular nitrogen compound biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds.
small molecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving small molecules, any monomeric molecule of small relative molecular mass.
development of primary sexual characteristics
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the primary sexual characteristics over time, from their formation to the mature structures. The primary sexual characteristics are the testes in males and the ovaries in females and they develop in response to sex hormone secretion.
development of primary male sexual characteristics
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the primary male sexual characteristics over time, from their formation to the mature structures. The primary male sexual characteristics are the testes, and they develop in response to sex hormone secretion.
male sex differentiation
The establishment of the sex of a male organism by physical differentiation.
organ development
Development of a tissue or tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Development pertains to the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a structure over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
reproductive structure development
The reproductive developmental process whose specific outcome is the progression of structures that will be used in the process of creating new individuals from one or more parents, from their formation to the mature structures.
reproductive cellular process
A process, occurring at the cellular level, that is involved in the reproductive function of a multicellular or single-celled organism.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
anatomical structure development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an anatomical structure from an initial condition to its mature state. This process begins with the formation of the structure and ends with the mature structure, whatever form that may be including its natural destruction. An anatomical structure is any biological entity that occupies space and is distinguished from its surroundings. Anatomical structures can be macroscopic such as a carpel, or microscopic such as an acrosome.
Sertoli cell proliferation
The multiplication or reproduction of Sertoli cells, resulting in the expansion of the Sertoli cell population. A Sertoli cell is a supporting cell projecting inward from the basement membrane of seminiferous tubules.
all
NA
reproductive process
A biological process that directly contributes to the process of producing new individuals by one or two organisms. The new individuals inherit some proportion of their genetic material from the parent or parents.
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
reproductive cellular process
A process, occurring at the cellular level, that is involved in the reproductive function of a multicellular or single-celled organism.
reproductive developmental process
A developmental process by which a progressive change in the state of some part of an organism specifically contributes to its ability to form offspring.
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
cellular nitrogen compound metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving various organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
Sertoli cell proliferation
The multiplication or reproduction of Sertoli cells, resulting in the expansion of the Sertoli cell population. A Sertoli cell is a supporting cell projecting inward from the basement membrane of seminiferous tubules.
development of primary sexual characteristics
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the primary sexual characteristics over time, from their formation to the mature structures. The primary sexual characteristics are the testes in males and the ovaries in females and they develop in response to sex hormone secretion.
reproductive structure development
The reproductive developmental process whose specific outcome is the progression of structures that will be used in the process of creating new individuals from one or more parents, from their formation to the mature structures.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
cellular nitrogen compound biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds.
development of primary sexual characteristics
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the primary sexual characteristics over time, from their formation to the mature structures. The primary sexual characteristics are the testes in males and the ovaries in females and they develop in response to sex hormone secretion.
male sex differentiation
The establishment of the sex of a male organism by physical differentiation.
gonad development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the gonad over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The gonad is an animal organ that produces gametes; in some species it also produces hormones.
development of primary male sexual characteristics
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the primary male sexual characteristics over time, from their formation to the mature structures. The primary male sexual characteristics are the testes, and they develop in response to sex hormone secretion.
organ development
Development of a tissue or tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Development pertains to the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a structure over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
gonad development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the gonad over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The gonad is an animal organ that produces gametes; in some species it also produces hormones.
urea metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving urea, the water soluble compound O=C-(NH2)2, produced in the liver by the ornithine cycle. It is the main nitrogen-containing excretion product in ureotelic animals.
amide biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of an amide, any derivative of an oxoacid in which an acidic hydroxy group has been replaced by an amino or substituted amino group.
male gonad development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the male gonad over time, from its formation to the mature structure.
urea cycle
A cyclic metabolic pathway that converts waste nitrogen in the form of ammonium to urea.
Sertoli cell proliferation
The multiplication or reproduction of Sertoli cells, resulting in the expansion of the Sertoli cell population. A Sertoli cell is a supporting cell projecting inward from the basement membrane of seminiferous tubules.


ACER3alkaline ceramidase 3 (ENSG00000078124), score: 0.73 ACVR2Aactivin A receptor, type IIA (ENSG00000121989), score: 0.74 AVPR1Aarginine vasopressin receptor 1A (ENSG00000166148), score: 0.67 BDKRB1bradykinin receptor B1 (ENSG00000100739), score: 0.8 C6orf62chromosome 6 open reading frame 62 (ENSG00000112308), score: 0.68 CD86CD86 molecule (ENSG00000114013), score: 0.67 CDKN2AIPCDKN2A interacting protein (ENSG00000168564), score: -0.73 CLPXClpX caseinolytic peptidase X homolog (E. coli) (ENSG00000166855), score: 0.67 COPAcoatomer protein complex, subunit alpha (ENSG00000122218), score: -0.76 DIRC2disrupted in renal carcinoma 2 (ENSG00000138463), score: 0.71 EDEM3ER degradation enhancer, mannosidase alpha-like 3 (ENSG00000116406), score: 0.68 FSHBfollicle stimulating hormone, beta polypeptide (ENSG00000131808), score: 0.87 GPN1GPN-loop GTPase 1 (ENSG00000198522), score: 0.71 HTThuntingtin (ENSG00000197386), score: -0.73 ITGA4integrin, alpha 4 (antigen CD49D, alpha 4 subunit of VLA-4 receptor) (ENSG00000115232), score: 0.68 KLHL8kelch-like 8 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000145332), score: 0.69 LRIG3leucine-rich repeats and immunoglobulin-like domains 3 (ENSG00000139263), score: 0.69 LRRC15leucine rich repeat containing 15 (ENSG00000172061), score: 0.71 LRRC31leucine rich repeat containing 31 (ENSG00000114248), score: 0.83 MAP2K5mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 5 (ENSG00000137764), score: -0.75 MBNL2muscleblind-like 2 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000139793), score: -0.79 MYNNmyoneurin (ENSG00000085274), score: 0.68 NT5E5'-nucleotidase, ecto (CD73) (ENSG00000135318), score: 0.81 OTCornithine carbamoyltransferase (ENSG00000036473), score: 0.67 PARP6poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase family, member 6 (ENSG00000137817), score: -0.75 PEX11Aperoxisomal biogenesis factor 11 alpha (ENSG00000166821), score: 0.68 PGM3phosphoglucomutase 3 (ENSG00000013375), score: 0.87 QPCTglutaminyl-peptide cyclotransferase (ENSG00000115828), score: 0.71 RAB11ARAB11A, member RAS oncogene family (ENSG00000103769), score: 0.72 RECKreversion-inducing-cysteine-rich protein with kazal motifs (ENSG00000122707), score: 0.71 SETD5SET domain containing 5 (ENSG00000168137), score: -0.76 SLC17A5solute carrier family 17 (anion/sugar transporter), member 5 (ENSG00000119899), score: 0.73 SLC39A9solute carrier family 39 (zinc transporter), member 9 (ENSG00000029364), score: 0.92 SRSF5serine/arginine-rich splicing factor 5 (ENSG00000100650), score: -0.71 STOML2stomatin (EPB72)-like 2 (ENSG00000165283), score: -0.71 TARSL2threonyl-tRNA synthetase-like 2 (ENSG00000185418), score: -0.71 TMEM33transmembrane protein 33 (ENSG00000109133), score: 0.67 UBL3ubiquitin-like 3 (ENSG00000122042), score: 0.68 USP20ubiquitin specific peptidase 20 (ENSG00000136878), score: -0.78 VGLL1vestigial like 1 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000102243), score: 0.7 XKR9XK, Kell blood group complex subunit-related family, member 9 (ENSG00000221947), score: 0.78 ZBTB49zinc finger and BTB domain containing 49 (ENSG00000168826), score: -0.71 ZC3H12Dzinc finger CCCH-type containing 12D (ENSG00000178199), score: 1 ZNF326zinc finger protein 326 (ENSG00000162664), score: 0.75 ZNHIT6zinc finger, HIT type 6 (ENSG00000117174), score: -0.74
| Id | species | tissue | sex | individual |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| oan_kd_m_ca1 | oan | kd | m | _ |
| oan_kd_f_ca1 | oan | kd | f | _ |
| oan_lv_f_ca1 | oan | lv | f | _ |
| oan_lv_m_ca1 | oan | lv | m | _ |