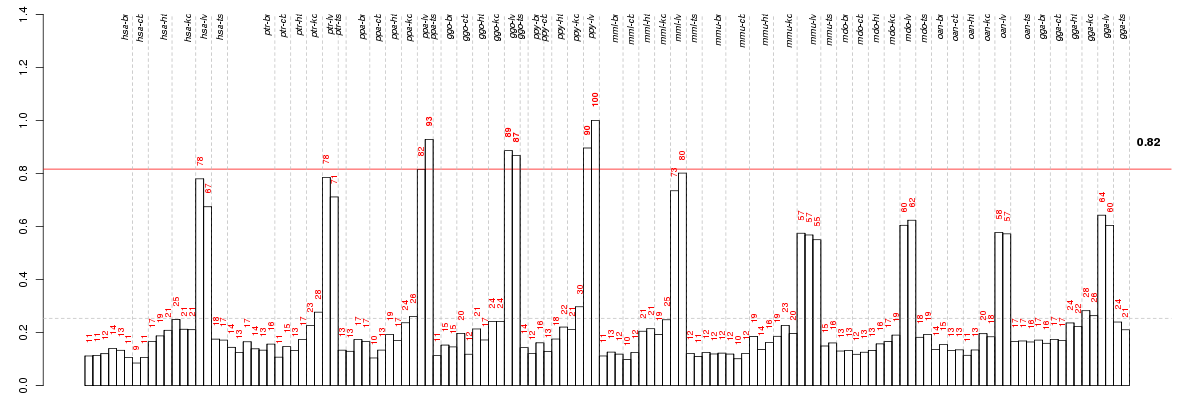

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways, including anabolism and catabolism, by which living organisms transform chemical substances. Metabolic processes typically transform small molecules, but also include macromolecular processes such as DNA repair and replication, and protein synthesis and degradation.
immune system process
Any process involved in the development or functioning of the immune system, an organismal system for calibrated responses to potential internal or invasive threats.
blood coagulation
The sequential process by which the multiple coagulation factors of the blood interact, ultimately resulting in the formation of an insoluble fibrin clot; it may be divided into three stages: stage 1, the formation of intrinsic and extrinsic prothrombin converting principle; stage 2, the formation of thrombin; stage 3, the formation of stable fibrin polymers.
organic acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving organic acids, any acidic compound containing carbon in covalent linkage.
cellular amino acid and derivative metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving amino acids, organic acids containing one or more amino substituents, and compounds derived from amino acids, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular amino acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving amino acids, organic acids containing one or more amino substituents.
histidine metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving histidine, 2-amino-3-(1H-imidazol-4-yl)propanoic acid.
nitrogen compound metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving various organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds; includes nitrogen fixation, nitrification, denitrification, assimilatory/dissimilatory nitrate reduction and the interconversion of nitrogenous organic matter and ammonium.
response to stress
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a disturbance in organismal or cellular homeostasis, usually, but not necessarily, exogenous (e.g. temperature, humidity, ionizing radiation).
immune response
Any immune system process that functions in the calibrated response of an organism to a potential internal or invasive threat.
hemostasis
The stopping of bleeding (loss of body fluid) or the arrest of the circulation to an organ or part.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
histidine family amino acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving amino acids of the histidine family.
amine metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving any organic compound that is weakly basic in character and contains an amino or a substituted amino group, as carried out by individual cells. Amines are called primary, secondary, or tertiary according to whether one, two, or three carbon atoms are attached to the nitrogen atom.
response to wounding
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus indicating damage to the organism.
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
carboxylic acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving carboxylic acids, any organic acid containing one or more carboxyl (COOH) groups or anions (COO-).
multicellular organismal process
Any biological process, occurring at the level of a multicellular organism, pertinent to its function.
cellular nitrogen compound metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving various organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds, as carried out by individual cells.
wound healing
The series of events that restore integrity to a damaged tissue, following an injury.
cellular ketone metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving any of a class of organic compounds that contain the carbonyl group, CO, and in which the carbonyl group is bonded only to carbon atoms, as carried out by individual cells. The general formula for a ketone is RCOR, where R and R are alkyl or aryl groups.
oxoacid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving any oxoacid; an oxoacid is a compound which contains oxygen, at least one other element, and at least one hydrogen bound to oxygen, and which produces a conjugate base by loss of positive hydrogen ion(s) (hydrons).
cellular amine metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving any organic compound that is weakly basic in character and contains an amino or a substituted amino group, as carried out by individual cells. Amines are called primary, secondary, or tertiary according to whether one, two, or three carbon atoms are attached to the nitrogen atom.
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
primary metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving those compounds which are formed as a part of the normal anabolic and catabolic processes. These processes take place in most, if not all, cells of the organism.
small molecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving small molecules, any monomeric molecule of small relative molecular mass.
heterocycle metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving heterocyclic compounds, those with a cyclic molecular structure and at least two different atoms in the ring (or rings).
coagulation
The process by which a fluid solution, or part of it, changes into a solid or semisolid mass.
regulation of body fluid levels
Any process that modulates the levels of body fluids.
response to stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
biological regulation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of any biological process, quality or function.
regulation of biological quality
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological quality. A biological quality is a measurable attribute of an organism or part of an organism, such as size, mass, shape, color, etc.
all
NA
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
immune response
Any immune system process that functions in the calibrated response of an organism to a potential internal or invasive threat.
cellular nitrogen compound metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving various organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular amino acid and derivative metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving amino acids, organic acids containing one or more amino substituents, and compounds derived from amino acids, as carried out by individual cells.
organic acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving organic acids, any acidic compound containing carbon in covalent linkage.
cellular amino acid and derivative metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving amino acids, organic acids containing one or more amino substituents, and compounds derived from amino acids, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular ketone metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving any of a class of organic compounds that contain the carbonyl group, CO, and in which the carbonyl group is bonded only to carbon atoms, as carried out by individual cells. The general formula for a ketone is RCOR, where R and R are alkyl or aryl groups.
regulation of body fluid levels
Any process that modulates the levels of body fluids.
cellular amine metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving any organic compound that is weakly basic in character and contains an amino or a substituted amino group, as carried out by individual cells. Amines are called primary, secondary, or tertiary according to whether one, two, or three carbon atoms are attached to the nitrogen atom.
oxoacid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving any oxoacid; an oxoacid is a compound which contains oxygen, at least one other element, and at least one hydrogen bound to oxygen, and which produces a conjugate base by loss of positive hydrogen ion(s) (hydrons).
blood coagulation
The sequential process by which the multiple coagulation factors of the blood interact, ultimately resulting in the formation of an insoluble fibrin clot; it may be divided into three stages: stage 1, the formation of intrinsic and extrinsic prothrombin converting principle; stage 2, the formation of thrombin; stage 3, the formation of stable fibrin polymers.
cellular amino acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving amino acids, organic acids containing one or more amino substituents.
blood coagulation
The sequential process by which the multiple coagulation factors of the blood interact, ultimately resulting in the formation of an insoluble fibrin clot; it may be divided into three stages: stage 1, the formation of intrinsic and extrinsic prothrombin converting principle; stage 2, the formation of thrombin; stage 3, the formation of stable fibrin polymers.
cellular amino acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving amino acids, organic acids containing one or more amino substituents.
histidine metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving histidine, 2-amino-3-(1H-imidazol-4-yl)propanoic acid.

plasma membrane
The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
intracellular
The living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
membrane
Double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
extracellular region
The space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.
cellular_component
The part of a cell or its extracellular environment in which a gene product is located. A gene product may be located in one or more parts of a cell and its location may be as specific as a particular macromolecular complex, that is, a stable, persistent association of macromolecules that function together.
extracellular space
That part of a multicellular organism outside the cells proper, usually taken to be outside the plasma membranes, and occupied by fluid.
cell
The basic structural and functional unit of all organisms. Includes the plasma membrane and any external encapsulating structures such as the cell wall and cell envelope.
cytoplasm
All of the contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures.
stored secretory granule
A small subcellular vesicle, surrounded by a membrane, that is formed from the Golgi apparatus and contains a highly concentrated protein destined for secretion. Secretory granules move towards the periphery of the cell and upon stimulation, their membranes fuse with the cell membrane, and their protein load is exteriorized. Processing of the contained protein may take place in secretory granules.
external side of plasma membrane
The side of the plasma membrane that is opposite to the side that faces the cytoplasm.
cell surface
The external part of the cell wall and/or plasma membrane.
cytoplasmic membrane-bounded vesicle
A membrane-bounded vesicle found in the cytoplasm of the cell.
platelet alpha granule
A secretory organelle found in blood platelets, which is unique in that it exhibits further compartmentalization and acquires its protein content via two distinct mechanisms: (1) biosynthesis predominantly at the megakaryocyte (MK) level (with some vestigial platelet synthesis) (e.g. platelet factor 4) and (2) endocytosis and pinocytosis at both the MK and circulating platelet levels (e.g. fibrinogen (Fg) and IgG).
platelet alpha granule lumen
The volume enclosed by the membrane of the platelet alpha granule.
cytoplasmic vesicle
A vesicle formed of membrane or protein, found in the cytoplasm of a cell.
membrane-enclosed lumen
The enclosed volume within a sealed membrane or between two sealed membranes. Encompasses the volume enclosed by the membranes of a particular organelle, e.g. endoplasmic reticulum lumen, or the space between the two lipid bilayers of a double membrane surrounding an organelle, e.g. nuclear envelope lumen.
vesicle
Any small, fluid-filled, spherical organelle enclosed by membrane or protein.
vesicle lumen
The volume enclosed by the membrane or protein that forms a vesicle.
membrane-bounded vesicle
Any small, fluid-filled, spherical organelle enclosed by a lipid bilayer.
organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, and prokaryotic structures such as anammoxosomes and pirellulosomes. Excludes the plasma membrane.
membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
organelle lumen
The internal volume enclosed by the membranes of a particular organelle; includes the volume enclosed by a single organelle membrane, e.g. endoplasmic reticulum lumen, or the volume enclosed by the innermost of the two lipid bilayers of an organelle envelope, e.g. nuclear lumen.
extracellular region part
Any constituent part of the extracellular region, the space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers constituent parts of the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.
organelle part
Any constituent part of an organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, but excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
membrane part
Any constituent part of a membrane, a double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
cytoplasmic vesicle part
Any constituent part of cytoplasmic vesicle, a vesicle formed of membrane or protein, found in the cytoplasm of a cell.
cytoplasmic part
Any constituent part of the cytoplasm, all of the contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
plasma membrane part
Any constituent part of the plasma membrane, the membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
cytoplasmic membrane-bounded vesicle lumen
The volume enclosed by the membrane of a cytoplasmic membrane-bounded vesicle.
all
NA
extracellular region part
Any constituent part of the extracellular region, the space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers constituent parts of the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
organelle part
Any constituent part of an organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, but excludes the plasma membrane.
organelle lumen
The internal volume enclosed by the membranes of a particular organelle; includes the volume enclosed by a single organelle membrane, e.g. endoplasmic reticulum lumen, or the volume enclosed by the innermost of the two lipid bilayers of an organelle envelope, e.g. nuclear lumen.
cytoplasmic vesicle
A vesicle formed of membrane or protein, found in the cytoplasm of a cell.
intracellular membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
membrane part
Any constituent part of a membrane, a double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
cytoplasmic vesicle part
Any constituent part of cytoplasmic vesicle, a vesicle formed of membrane or protein, found in the cytoplasm of a cell.
cytoplasmic membrane-bounded vesicle
A membrane-bounded vesicle found in the cytoplasm of the cell.
vesicle lumen
The volume enclosed by the membrane or protein that forms a vesicle.
cytoplasmic membrane-bounded vesicle
A membrane-bounded vesicle found in the cytoplasm of the cell.
cytoplasmic membrane-bounded vesicle lumen
The volume enclosed by the membrane of a cytoplasmic membrane-bounded vesicle.
plasma membrane part
Any constituent part of the plasma membrane, the membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
cytoplasmic part
Any constituent part of the cytoplasm, all of the contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures.
cytoplasmic vesicle
A vesicle formed of membrane or protein, found in the cytoplasm of a cell.
cytoplasmic vesicle part
Any constituent part of cytoplasmic vesicle, a vesicle formed of membrane or protein, found in the cytoplasm of a cell.
external side of plasma membrane
The side of the plasma membrane that is opposite to the side that faces the cytoplasm.
cytoplasmic membrane-bounded vesicle lumen
The volume enclosed by the membrane of a cytoplasmic membrane-bounded vesicle.
platelet alpha granule lumen
The volume enclosed by the membrane of the platelet alpha granule.

molecular_function
Elemental activities, such as catalysis or binding, describing the actions of a gene product at the molecular level. A given gene product may exhibit one or more molecular functions.
enzyme inhibitor activity
Stops, prevents or reduces the activity of an enzyme.
endopeptidase inhibitor activity
Stops, prevents or reduces the activity of an endopeptidase, any enzyme that hydrolyzes nonterminal peptide bonds in polypeptides.
serine-type endopeptidase inhibitor activity
Stops, prevents or reduces the activity of serine-type endopeptidases, enzymes that catalyze the hydrolysis of nonterminal peptide bonds in a polypeptide chain; a serine residue (and a histidine residue) are at the active center of the enzyme.
endopeptidase regulator activity
Modulates the activity of a peptidase, any enzyme that hydrolyzes nonterminal peptide bonds in polypeptides.
peptidase inhibitor activity
Stops, prevents or reduces the activity of a peptidase, any enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis peptide bonds.
enzyme regulator activity
Modulates the activity of an enzyme.
peptidase regulator activity
Modulates the activity of a peptidase, any enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis peptide bonds.
all
NA
peptidase inhibitor activity
Stops, prevents or reduces the activity of a peptidase, any enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis peptide bonds.
endopeptidase inhibitor activity
Stops, prevents or reduces the activity of an endopeptidase, any enzyme that hydrolyzes nonterminal peptide bonds in polypeptides.
| Id | Pvalue | ExpCount | Count | Size | Term |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 04610 | 3.055e-06 | 0.3293 | 7 | 21 | Complement and coagulation cascades |
| 04060 | 3.891e-02 | 1.239 | 6 | 79 | Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction |
ALPK1alpha-kinase 1 (ENSG00000073331), score: 0.52 AMBPalpha-1-microglobulin/bikunin precursor (ENSG00000106927), score: 0.54 BMP10bone morphogenetic protein 10 (ENSG00000163217), score: 0.55 BMPERBMP binding endothelial regulator (ENSG00000164619), score: 0.54 C8Bcomplement component 8, beta polypeptide (ENSG00000021852), score: 0.58 CCNL1cyclin L1 (ENSG00000163660), score: 0.57 CLDN14claudin 14 (ENSG00000159261), score: 0.61 COLEC10collectin sub-family member 10 (C-type lectin) (ENSG00000184374), score: 0.59 CPB2carboxypeptidase B2 (plasma) (ENSG00000080618), score: 0.58 CSF3Rcolony stimulating factor 3 receptor (granulocyte) (ENSG00000119535), score: 0.56 CYTIPcytohesin 1 interacting protein (ENSG00000115165), score: 0.52 DBHdopamine beta-hydroxylase (dopamine beta-monooxygenase) (ENSG00000123454), score: 0.58 DHODHdihydroorotate dehydrogenase (ENSG00000102967), score: 0.71 F9coagulation factor IX (ENSG00000101981), score: 0.52 FAM83Afamily with sequence similarity 83, member A (ENSG00000147689), score: 1 FGBfibrinogen beta chain (ENSG00000171564), score: 0.58 FGGfibrinogen gamma chain (ENSG00000171557), score: 0.59 FOXF1forkhead box F1 (ENSG00000103241), score: 0.55 FSTfollistatin (ENSG00000134363), score: 0.68 GDF2growth differentiation factor 2 (ENSG00000128802), score: 0.55 GPR183G protein-coupled receptor 183 (ENSG00000169508), score: 0.52 GPR97G protein-coupled receptor 97 (ENSG00000182885), score: 0.72 HALhistidine ammonia-lyase (ENSG00000084110), score: 0.52 HGFhepatocyte growth factor (hepapoietin A; scatter factor) (ENSG00000019991), score: 0.58 HPXhemopexin (ENSG00000110169), score: 0.53 HRGhistidine-rich glycoprotein (ENSG00000113905), score: 0.52 IGFBP1insulin-like growth factor binding protein 1 (ENSG00000146678), score: 0.6 IHHIndian hedgehog (ENSG00000163501), score: 0.52 IL18RAPinterleukin 18 receptor accessory protein (ENSG00000115607), score: 0.8 IL1R2interleukin 1 receptor, type II (ENSG00000115590), score: 0.6 IL2RBinterleukin 2 receptor, beta (ENSG00000100385), score: 0.58 IL7Rinterleukin 7 receptor (ENSG00000168685), score: 0.61 IRF4interferon regulatory factor 4 (ENSG00000137265), score: 0.64 ITKIL2-inducible T-cell kinase (ENSG00000113263), score: 0.63 MTHFD2Lmethylenetetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase (NADP+ dependent) 2-like (ENSG00000163738), score: 0.58 MYO1Bmyosin IB (ENSG00000128641), score: 0.53 MYO1Fmyosin IF (ENSG00000142347), score: 0.55 NCF2neutrophil cytosolic factor 2 (ENSG00000116701), score: 0.51 NFKBIZnuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells inhibitor, zeta (ENSG00000144802), score: 0.52 NR5A2nuclear receptor subfamily 5, group A, member 2 (ENSG00000116833), score: 0.52 NRBF2nuclear receptor binding factor 2 (ENSG00000148572), score: 0.52 OIT3oncoprotein induced transcript 3 (ENSG00000138315), score: 0.59 PPIBpeptidylprolyl isomerase B (cyclophilin B) (ENSG00000166794), score: 0.51 PRDM1PR domain containing 1, with ZNF domain (ENSG00000057657), score: 0.55 RND3Rho family GTPase 3 (ENSG00000115963), score: 0.58 S1PR4sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 4 (ENSG00000125910), score: 0.63 SAMSN1SAM domain, SH3 domain and nuclear localization signals 1 (ENSG00000155307), score: 0.65 SERPINA10serpin peptidase inhibitor, clade A (alpha-1 antiproteinase, antitrypsin), member 10 (ENSG00000140093), score: 0.58 SERPINC1serpin peptidase inhibitor, clade C (antithrombin), member 1 (ENSG00000117601), score: 0.52 SLC13A5solute carrier family 13 (sodium-dependent citrate transporter), member 5 (ENSG00000141485), score: 0.53 TATtyrosine aminotransferase (ENSG00000198650), score: 0.53 TDO2tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase (ENSG00000151790), score: 0.56 TFPItissue factor pathway inhibitor (lipoprotein-associated coagulation inhibitor) (ENSG00000003436), score: 0.53 TM4SF4transmembrane 4 L six family member 4 (ENSG00000169903), score: 0.56 TMED6transmembrane emp24 protein transport domain containing 6 (ENSG00000157315), score: 0.55 TOB1transducer of ERBB2, 1 (ENSG00000141232), score: 0.56 TRPM8transient receptor potential cation channel, subfamily M, member 8 (ENSG00000144481), score: 0.59 USP2ubiquitin specific peptidase 2 (ENSG00000036672), score: -0.59
| Id | species | tissue | sex | individual |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ggo_lv_f_ca1 | ggo | lv | f | _ |
| ggo_lv_m_ca1 | ggo | lv | m | _ |
| ppy_lv_m_ca1 | ppy | lv | m | _ |
| ppa_lv_f_ca1 | ppa | lv | f | _ |
| ppy_lv_f_ca1 | ppy | lv | f | _ |