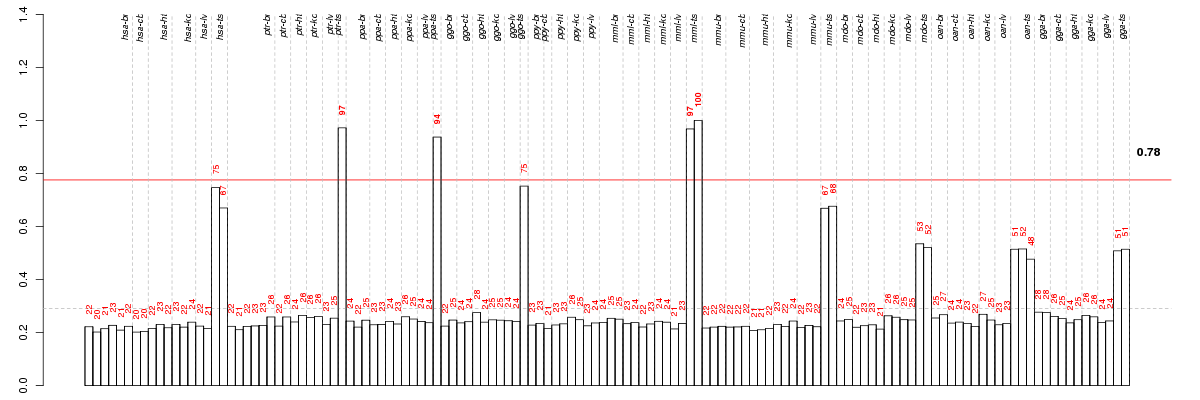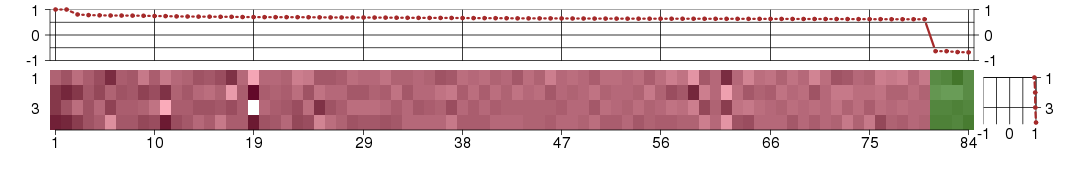

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

M phase of mitotic cell cycle
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which a cell progresses through M phase, the part of the mitotic cell cycle during which mitosis takes place.
mitotic cell cycle
Progression through the phases of the mitotic cell cycle, the most common eukaryotic cell cycle, which canonically comprises four successive phases called G1, S, G2, and M and includes replication of the genome and the subsequent segregation of chromosomes into daughter cells. In some variant cell cycles nuclear replication or nuclear division may not be followed by cell division, or G1 and G2 phases may be absent.
M phase
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which a cell progresses through M phase, the part of the cell cycle comprising nuclear division.
nuclear division
A process by which a cell nucleus is divided into two nuclei, with DNA and other nuclear contents distributed between the daughter nuclei.
organelle organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of an organelle within a cell. An organelle is an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
cell cycle
The progression of biochemical and morphological phases and events that occur in a cell during successive cell replication or nuclear replication events. Canonically, the cell cycle comprises the replication and segregation of genetic material followed by the division of the cell, but in endocycles or syncytial cells nuclear replication or nuclear division may not be followed by cell division.
mitosis
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell divides; the process involves condensation of chromosomal DNA into a highly compacted form. Canonically, mitosis produces two daughter nuclei whose chromosome complement is identical to that of the mother cell.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
cellular component organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of a cellular component.
cell cycle process
A cellular process that is involved in the progression of biochemical and morphological phases and events that occur in a cell during successive cell replication or nuclear replication events.
cell cycle phase
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which a cell progresses through one of the biochemical and morphological phases and events that occur during successive cell replication or nuclear replication events.
organelle fission
The creation of two or more organelles by division of one organelle.
all
NA
organelle organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of an organelle within a cell. An organelle is an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
cell cycle process
A cellular process that is involved in the progression of biochemical and morphological phases and events that occur in a cell during successive cell replication or nuclear replication events.
mitosis
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell divides; the process involves condensation of chromosomal DNA into a highly compacted form. Canonically, mitosis produces two daughter nuclei whose chromosome complement is identical to that of the mother cell.
mitosis
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell divides; the process involves condensation of chromosomal DNA into a highly compacted form. Canonically, mitosis produces two daughter nuclei whose chromosome complement is identical to that of the mother cell.
M phase of mitotic cell cycle
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which a cell progresses through M phase, the part of the mitotic cell cycle during which mitosis takes place.

intracellular
The living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
cellular_component
The part of a cell or its extracellular environment in which a gene product is located. A gene product may be located in one or more parts of a cell and its location may be as specific as a particular macromolecular complex, that is, a stable, persistent association of macromolecules that function together.
cell
The basic structural and functional unit of all organisms. Includes the plasma membrane and any external encapsulating structures such as the cell wall and cell envelope.
cytoplasm
All of the contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures.
centrosome
A structure comprised of a core structure (in most organisms, a pair of centrioles) and peripheral material from which a microtubule-based structure, such as a spindle apparatus, is organized. Centrosomes occur close to the nucleus during interphase in many eukaryotic cells, though in animal cells it changes continually during the cell-division cycle.
microtubule organizing center
A cytoplasmic structure that can catalyze gamma-tubulin-dependent microtubule nucleation and that can anchor microtubules by interacting with their minus ends, plus ends or sides.
spindle
The array of microtubules and associated molecules that forms between opposite poles of a eukaryotic cell during mitosis or meiosis and serves to move the duplicated chromosomes apart.
cytoskeleton
Any of the various filamentous elements that form the internal framework of cells, and typically remain after treatment of the cells with mild detergent to remove membrane constituents and soluble components of the cytoplasm. The term embraces intermediate filaments, microfilaments, microtubules, the microtrabecular lattice, and other structures characterized by a polymeric filamentous nature and long-range order within the cell. The various elements of the cytoskeleton not only serve in the maintenance of cellular shape but also have roles in other cellular functions, including cellular movement, cell division, endocytosis, and movement of organelles.
microtubule
Any of the long, generally straight, hollow tubes of internal diameter 12-15 nm and external diameter 24 nm found in a wide variety of eukaryotic cells; each consists (usually) of 13 protofilaments of polymeric tubulin, staggered in such a manner that the tubulin monomers are arranged in a helical pattern on the microtubular surface, and with the alpha/beta axes of the tubulin subunits parallel to the long axis of the tubule; exist in equilibrium with pool of tubulin monomers and can be rapidly assembled or disassembled in response to physiological stimuli; concerned with force generation, e.g. in the spindle.
spindle microtubule
Any microtubule that is part of a mitotic or meiotic spindle; anchored at one spindle pole.
microtubule cytoskeleton
The part of the cytoskeleton (the internal framework of a cell) composed of microtubules and associated proteins.
macromolecular complex
A stable assembly of two or more macromolecules, i.e. proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates or lipids, in which the constituent parts function together.
organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, and prokaryotic structures such as anammoxosomes and pirellulosomes. Excludes the plasma membrane.
non-membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, not bounded by a lipid bilayer membrane. Includes ribosomes, the cytoskeleton and chromosomes.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular non-membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, not bounded by a lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes ribosomes, the cytoskeleton and chromosomes.
protein complex
Any macromolecular complex composed of two or more polypeptide subunits, which may or may not be identical. Protein complexes may have other associated non-protein prosthetic groups, such as nucleotides, metal ions or other small molecules.
organelle part
Any constituent part of an organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, but excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
cytoskeletal part
Any constituent part of the cytoskeleton, a cellular scaffolding or skeleton that maintains cell shape, enables some cell motion (using structures such as flagella and cilia), and plays important roles in both intra-cellular transport (e.g. the movement of vesicles and organelles) and cellular division. Includes constituent parts of intermediate filaments, microfilaments, microtubules, and the microtrabecular lattice.
cytoplasmic part
Any constituent part of the cytoplasm, all of the contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
all
NA
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
organelle part
Any constituent part of an organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, but excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular non-membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, not bounded by a lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes ribosomes, the cytoskeleton and chromosomes.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
spindle
The array of microtubules and associated molecules that forms between opposite poles of a eukaryotic cell during mitosis or meiosis and serves to move the duplicated chromosomes apart.
microtubule
Any of the long, generally straight, hollow tubes of internal diameter 12-15 nm and external diameter 24 nm found in a wide variety of eukaryotic cells; each consists (usually) of 13 protofilaments of polymeric tubulin, staggered in such a manner that the tubulin monomers are arranged in a helical pattern on the microtubular surface, and with the alpha/beta axes of the tubulin subunits parallel to the long axis of the tubule; exist in equilibrium with pool of tubulin monomers and can be rapidly assembled or disassembled in response to physiological stimuli; concerned with force generation, e.g. in the spindle.
cytoplasmic part
Any constituent part of the cytoplasm, all of the contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures.
microtubule organizing center
A cytoplasmic structure that can catalyze gamma-tubulin-dependent microtubule nucleation and that can anchor microtubules by interacting with their minus ends, plus ends or sides.
spindle microtubule
Any microtubule that is part of a mitotic or meiotic spindle; anchored at one spindle pole.
cytoskeletal part
Any constituent part of the cytoskeleton, a cellular scaffolding or skeleton that maintains cell shape, enables some cell motion (using structures such as flagella and cilia), and plays important roles in both intra-cellular transport (e.g. the movement of vesicles and organelles) and cellular division. Includes constituent parts of intermediate filaments, microfilaments, microtubules, and the microtrabecular lattice.
centrosome
A structure comprised of a core structure (in most organisms, a pair of centrioles) and peripheral material from which a microtubule-based structure, such as a spindle apparatus, is organized. Centrosomes occur close to the nucleus during interphase in many eukaryotic cells, though in animal cells it changes continually during the cell-division cycle.
microtubule organizing center
A cytoplasmic structure that can catalyze gamma-tubulin-dependent microtubule nucleation and that can anchor microtubules by interacting with their minus ends, plus ends or sides.
spindle
The array of microtubules and associated molecules that forms between opposite poles of a eukaryotic cell during mitosis or meiosis and serves to move the duplicated chromosomes apart.
microtubule
Any of the long, generally straight, hollow tubes of internal diameter 12-15 nm and external diameter 24 nm found in a wide variety of eukaryotic cells; each consists (usually) of 13 protofilaments of polymeric tubulin, staggered in such a manner that the tubulin monomers are arranged in a helical pattern on the microtubular surface, and with the alpha/beta axes of the tubulin subunits parallel to the long axis of the tubule; exist in equilibrium with pool of tubulin monomers and can be rapidly assembled or disassembled in response to physiological stimuli; concerned with force generation, e.g. in the spindle.

molecular_function
Elemental activities, such as catalysis or binding, describing the actions of a gene product at the molecular level. A given gene product may exhibit one or more molecular functions.
nucleic acid binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with any nucleic acid.
binding
The selective, non-covalent, often stoichiometric, interaction of a molecule with one or more specific sites on another molecule.
all
NA
ABTB1ankyrin repeat and BTB (POZ) domain containing 1 (ENSG00000114626), score: -0.68 ACBD6acyl-CoA binding domain containing 6 (ENSG00000135847), score: 0.64 ADAD1adenosine deaminase domain containing 1 (testis-specific) (ENSG00000164113), score: 0.65 ANKLE2ankyrin repeat and LEM domain containing 2 (ENSG00000176915), score: 0.63 ARHGAP28Rho GTPase activating protein 28 (ENSG00000088756), score: 0.7 ARMC4armadillo repeat containing 4 (ENSG00000169126), score: 0.65 BARX1BARX homeobox 1 (ENSG00000131668), score: 0.71 BOLLbol, boule-like (Drosophila) (ENSG00000152430), score: 0.64 BRIP1BRCA1 interacting protein C-terminal helicase 1 (ENSG00000136492), score: 0.73 BTG4B-cell translocation gene 4 (ENSG00000137707), score: 0.72 C10orf96chromosome 10 open reading frame 96 (ENSG00000182645), score: 0.7 C13orf18chromosome 13 open reading frame 18 (ENSG00000102445), score: 0.67 C7orf62chromosome 7 open reading frame 62 (ENSG00000164645), score: 0.62 CCDC83coiled-coil domain containing 83 (ENSG00000150676), score: 0.73 CEP152centrosomal protein 152kDa (ENSG00000103995), score: 0.62 CEP350centrosomal protein 350kDa (ENSG00000135837), score: 0.63 CEP55centrosomal protein 55kDa (ENSG00000138180), score: 0.64 CHODLchondrolectin (ENSG00000154645), score: 0.63 CLCA2chloride channel accessory 2 (ENSG00000137975), score: 1 CTLA4cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4 (ENSG00000163599), score: 0.7 DDX20DEAD (Asp-Glu-Ala-Asp) box polypeptide 20 (ENSG00000064703), score: 0.65 DNAJC21DnaJ (Hsp40) homolog, subfamily C, member 21 (ENSG00000168724), score: 0.66 DNAJC5BDnaJ (Hsp40) homolog, subfamily C, member 5 beta (ENSG00000147570), score: 0.66 DR1down-regulator of transcription 1, TBP-binding (negative cofactor 2) (ENSG00000117505), score: 0.63 DTLdenticleless homolog (Drosophila) (ENSG00000143476), score: 0.69 DYDC1DPY30 domain containing 1 (ENSG00000170788), score: 0.7 E2F7E2F transcription factor 7 (ENSG00000165891), score: 0.64 FAM194Afamily with sequence similarity 194, member A (ENSG00000163645), score: 0.68 FAM81Bfamily with sequence similarity 81, member B (ENSG00000153347), score: 0.63 GJA8gap junction protein, alpha 8, 50kDa (ENSG00000121634), score: 0.64 GMPSguanine monphosphate synthetase (ENSG00000163655), score: 0.66 GSG1germ cell associated 1 (ENSG00000111305), score: 0.76 HIAT1hippocampus abundant transcript 1 (ENSG00000156875), score: 0.68 HOXA13homeobox A13 (ENSG00000106031), score: 0.81 HSF2BPheat shock transcription factor 2 binding protein (ENSG00000160207), score: 0.66 IFT88intraflagellar transport 88 homolog (Chlamydomonas) (ENSG00000032742), score: 0.68 ISG20L2interferon stimulated exonuclease gene 20kDa-like 2 (ENSG00000143319), score: 0.69 KDM1Alysine (K)-specific demethylase 1A (ENSG00000004487), score: 0.62 KDM4Alysine (K)-specific demethylase 4A (ENSG00000066135), score: -0.67 KIF11kinesin family member 11 (ENSG00000138160), score: 0.62 KIF15kinesin family member 15 (ENSG00000163808), score: 0.65 KIF18Akinesin family member 18A (ENSG00000121621), score: 0.7 KNTC1kinetochore associated 1 (ENSG00000184445), score: 0.63 LASS3LAG1 homolog, ceramide synthase 3 (ENSG00000154227), score: 0.78 LOC81691exonuclease NEF-sp (ENSG00000005189), score: 0.76 LRRCC1leucine rich repeat and coiled-coil domain containing 1 (ENSG00000133739), score: 0.67 MC2Rmelanocortin 2 receptor (adrenocorticotropic hormone) (ENSG00000185231), score: 1 MGAT4Cmannosyl (alpha-1,3-)-glycoprotein beta-1,4-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase, isozyme C (putative) (ENSG00000182050), score: 0.64 MTHFSDmethenyltetrahydrofolate synthetase domain containing (ENSG00000103248), score: 0.62 MYO15Amyosin XVA (ENSG00000091536), score: 0.71 NEK2NIMA (never in mitosis gene a)-related kinase 2 (ENSG00000117650), score: 0.63 NSMCE4Anon-SMC element 4 homolog A (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000107672), score: -0.63 NSUN4NOP2/Sun domain family, member 4 (ENSG00000117481), score: 0.67 PAX3paired box 3 (ENSG00000135903), score: 0.74 PIAS4protein inhibitor of activated STAT, 4 (ENSG00000105229), score: 0.63 POLKpolymerase (DNA directed) kappa (ENSG00000122008), score: 0.65 PPM1Gprotein phosphatase, Mg2+/Mn2+ dependent, 1G (ENSG00000115241), score: 0.72 PRKAA1protein kinase, AMP-activated, alpha 1 catalytic subunit (ENSG00000132356), score: 0.69 PRTGprotogenin (ENSG00000166450), score: 0.69 RAE1RAE1 RNA export 1 homolog (S. pombe) (ENSG00000101146), score: 0.67 RASSF8Ras association (RalGDS/AF-6) domain family (N-terminal) member 8 (ENSG00000123094), score: 0.65 RNF141ring finger protein 141 (ENSG00000110315), score: 0.7 RTKN2rhotekin 2 (ENSG00000182010), score: 0.69 SERPINB12serpin peptidase inhibitor, clade B (ovalbumin), member 12 (ENSG00000166634), score: 0.74 SERPINB5serpin peptidase inhibitor, clade B (ovalbumin), member 5 (ENSG00000206075), score: 0.77 SLC38A9solute carrier family 38, member 9 (ENSG00000177058), score: 0.67 SMCHD1structural maintenance of chromosomes flexible hinge domain containing 1 (ENSG00000101596), score: 0.64 SPATA17spermatogenesis associated 17 (ENSG00000162814), score: 0.64 STX7syntaxin 7 (ENSG00000079950), score: -0.64 TFAP2Dtranscription factor AP-2 delta (activating enhancer binding protein 2 delta) (ENSG00000008197), score: 0.7 TIPARPTCDD-inducible poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (ENSG00000163659), score: 0.62 TMC5transmembrane channel-like 5 (ENSG00000103534), score: 0.66 TMEM170Atransmembrane protein 170A (ENSG00000166822), score: 0.65 TMEM215transmembrane protein 215 (ENSG00000188133), score: 0.76 TMPRSS3transmembrane protease, serine 3 (ENSG00000160183), score: 0.76 TRIP12thyroid hormone receptor interactor 12 (ENSG00000153827), score: 0.64 TTC16tetratricopeptide repeat domain 16 (ENSG00000167094), score: 0.62 TTC29tetratricopeptide repeat domain 29 (ENSG00000137473), score: 0.63 USP6NLUSP6 N-terminal like (ENSG00000148429), score: 0.64 VPRBPVpr (HIV-1) binding protein (ENSG00000145041), score: 0.64 VRK3vaccinia related kinase 3 (ENSG00000105053), score: 0.62 ZNF318zinc finger protein 318 (ENSG00000171467), score: 0.63
| Id | species | tissue | sex | individual |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ppa_ts_m_ca1 | ppa | ts | m | _ |
| mml_ts_m1_ca1 | mml | ts | m | 1 |
| ptr_ts_m_ca1 | ptr | ts | m | _ |
| mml_ts_m2_ca1 | mml | ts | m | 2 |