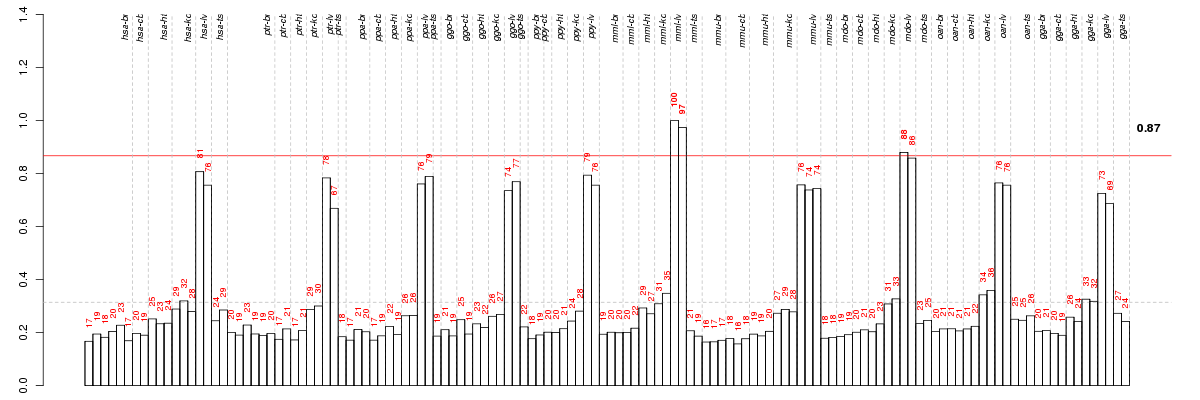

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways, including anabolism and catabolism, by which living organisms transform chemical substances. Metabolic processes typically transform small molecules, but also include macromolecular processes such as DNA repair and replication, and protein synthesis and degradation.
adaptive immune response
An immune response based on directed amplification of specific receptors for antigen produced through a somatic diversification process, and allowing for enhanced response to subsequent exposures to the same antigen (immunological memory).
immune effector process
Any process of the immune system that occurs as part of an immune response.
activation of immune response
Any process that initiates an immune response.
immune system process
Any process involved in the development or functioning of the immune system, an organismal system for calibrated responses to potential internal or invasive threats.
leukocyte mediated immunity
Any process involved in the carrying out of an immune response by a leukocyte.
lymphocyte mediated immunity
Any process involved in the carrying out of an immune response by a lymphocyte.
humoral immune response mediated by circulating immunoglobulin
An immune response dependent upon secreted immunoglobulin. An example of this process is found in Mus musculus.
adaptive immune response based on somatic recombination of immune receptors built from immunoglobulin superfamily domains
An immune response based on directed amplification of specific receptors for antigen produced through a somatic diversification process that includes somatic recombination of germline gene segments encoding immunoglobulin superfamily domains, and allowing for enhanced responses upon subsequent exposures to the same antigen (immunological memory). Recombined receptors for antigen encoded by immunoglobulin superfamily domains include T cell receptors and immunoglobulins (antibodies). An example of this is the adaptive immune response found in Mus musculus.
acute inflammatory response
Inflammation which comprises a rapid, short-lived, relatively uniform response to acute injury or antigenic challenge and is characterized by accumulations of fluid, plasma proteins, and granulocytic leukocytes. An acute inflammatory response occurs within a matter of minutes or hours, and either resolves within a few days or becomes a chronic inflammatory response.
activation of plasma proteins involved in acute inflammatory response
Any process activating plasma proteins by proteolysis as part of an acute inflammatory response.
regulation of immune system process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of an immune system process.
positive regulation of immune system process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of an immune system process.
defense response
Reactions, triggered in response to the presence of a foreign body or the occurrence of an injury, which result in restriction of damage to the organism attacked or prevention/recovery from the infection caused by the attack.
blood coagulation
The sequential process by which the multiple coagulation factors of the blood interact, ultimately resulting in the formation of an insoluble fibrin clot; it may be divided into three stages: stage 1, the formation of intrinsic and extrinsic prothrombin converting principle; stage 2, the formation of thrombin; stage 3, the formation of stable fibrin polymers.
complement activation
Any process involved in the activation of any of the steps of the complement cascade, which allows for the direct killing of microbes, the disposal of immune complexes, and the regulation of other immune processes; the initial steps of complement activation involve one of three pathways, the classical pathway, the alternative pathway, and the lectin pathway, all of which lead to the terminal complement pathway.
protein maturation by peptide bond cleavage
The hydrolysis of a peptide bond or bonds within a protein as part of protein maturation, the process leading to the attainment of the full functional capacity of a protein.
cellular aromatic compound metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving aromatic compounds, any organic compound characterized by one or more planar rings, each of which contains conjugated double bonds and delocalized pi electrons, as carried out by individual cells.
response to stress
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a disturbance in organismal or cellular homeostasis, usually, but not necessarily, exogenous (e.g. temperature, humidity, ionizing radiation).
inflammatory response
The immediate defensive reaction (by vertebrate tissue) to infection or injury caused by chemical or physical agents. The process is characterized by local vasodilation, extravasation of plasma into intercellular spaces and accumulation of white blood cells and macrophages.
immune response
Any immune system process that functions in the calibrated response of an organism to a potential internal or invasive threat.
complement activation, alternative pathway
Any process involved in the activation of any of the steps of the alternative pathway of the complement cascade which allows for the direct killing of microbes and the regulation of other immune processes.
complement activation, classical pathway
Any process involved in the activation of any of the steps of the classical pathway of the complement cascade which allows for the direct killing of microbes, the disposal of immune complexes, and the regulation of other immune processes.
humoral immune response
An immune response mediated through a body fluid.
hemostasis
The stopping of bleeding (loss of body fluid) or the arrest of the circulation to an organ or part.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
negative regulation of coagulation
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of coagulation.
response to external stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an external stimulus.
response to wounding
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus indicating damage to the organism.
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
gene expression
The process by which a gene's sequence is converted into a mature gene product or products (proteins or RNA). This includes the production of an RNA transcript as well as any processing to produce a mature RNA product or an mRNA (for protein-coding genes) and the translation of that mRNA into protein. Some protein processing events may be included when they are required to form an active form of a product from an inactive precursor form.
immunoglobulin mediated immune response
An immune response mediated by immunoglobulins, whether cell-bound or in solution.
protein processing
Any protein maturation process achieved by the cleavage of peptide bonds.
protein metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving a specific protein, rather than of proteins in general. Includes protein modification.
B cell mediated immunity
Any process involved with the carrying out of an immune response by a B cell, through, for instance, the production of antibodies or cytokines, or antigen presentation to T cells.
regulation of blood coagulation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of blood coagulation.
positive regulation of blood coagulation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of blood coagulation.
negative regulation of blood coagulation
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of blood coagulation.
regulation of response to external stimulus
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a response to an external stimulus.
multicellular organismal process
Any biological process, occurring at the level of a multicellular organism, pertinent to its function.
wound healing
The series of events that restore integrity to a damaged tissue, following an injury.
response to chemical stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a chemical stimulus.
fibrinolysis
An ongoing process that solubilizes fibrin, chiefly by the proteolytic action of plasmin, resulting in the removal of small blood clots.
macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
primary metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving those compounds which are formed as a part of the normal anabolic and catabolic processes. These processes take place in most, if not all, cells of the organism.
innate immune response
Innate immune responses are defense responses mediated by germline encoded components that directly recognize components of potential pathogens.
positive regulation of biological process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
negative regulation of biological process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of response to stimulus
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a response to a stimulus. Response to stimulus is a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
positive regulation of response to stimulus
Any process that activates, maintains or increases the rate of a response to a stimulus. Response to stimulus is a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
regulation of immune response
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the immune response, the immunological reaction of an organism to an immunogenic stimulus.
positive regulation of immune response
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the immune response, the immunological reaction of an organism to an immunogenic stimulus.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
coagulation
The process by which a fluid solution, or part of it, changes into a solid or semisolid mass.
regulation of coagulation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of coagulation, the process by which a fluid solution, or part of it, changes into a solid or semisolid mass.
positive regulation of coagulation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of coagulation.
regulation of body fluid levels
Any process that modulates the levels of body fluids.
response to stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
regulation of multicellular organismal process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a multicellular organismal process, the processes pertinent to the function of a multicellular organism above the cellular level; includes the integrated processes of tissues and organs.
positive regulation of multicellular organismal process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of an organismal process, any of the processes pertinent to the function of an organism above the cellular level; includes the integrated processes of tissues and organs.
negative regulation of multicellular organismal process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of an organismal process, the processes pertinent to the function of an organism above the cellular level; includes the integrated processes of tissues and organs.
protein maturation
Any process leading to the attainment of the full functional capacity of a protein.
regulation of fibrinolysis
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of fibrinolysis, an ongoing process that solubilizes fibrin, resulting in the removal of small blood clots.
negative regulation of fibrinolysis
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of fibrinolysis, an ongoing process that solubilizes fibrin, resulting in the removal of small blood clots.
regulation of wound healing
Any process that modulates the rate, frequency, or extent of the series of events that restore integrity to a damaged tissue, following an injury.
biological regulation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of any biological process, quality or function.
regulation of biological quality
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological quality. A biological quality is a measurable attribute of an organism or part of an organism, such as size, mass, shape, color, etc.
regulation of response to stress
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a response to stress. Response to stress is a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a disturbance in organismal or cellular homeostasis, usually, but not necessarily, exogenous (e.g. temperature, humidity, ionizing radiation).
all
NA
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
positive regulation of immune system process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of an immune system process.
positive regulation of multicellular organismal process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of an organismal process, any of the processes pertinent to the function of an organism above the cellular level; includes the integrated processes of tissues and organs.
negative regulation of multicellular organismal process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of an organismal process, the processes pertinent to the function of an organism above the cellular level; includes the integrated processes of tissues and organs.
regulation of immune system process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of an immune system process.
positive regulation of biological process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
negative regulation of biological process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of multicellular organismal process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a multicellular organismal process, the processes pertinent to the function of a multicellular organism above the cellular level; includes the integrated processes of tissues and organs.
immune response
Any immune system process that functions in the calibrated response of an organism to a potential internal or invasive threat.
regulation of response to stimulus
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a response to a stimulus. Response to stimulus is a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
positive regulation of response to stimulus
Any process that activates, maintains or increases the rate of a response to a stimulus. Response to stimulus is a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
protein metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving a specific protein, rather than of proteins in general. Includes protein modification.
complement activation
Any process involved in the activation of any of the steps of the complement cascade, which allows for the direct killing of microbes, the disposal of immune complexes, and the regulation of other immune processes; the initial steps of complement activation involve one of three pathways, the classical pathway, the alternative pathway, and the lectin pathway, all of which lead to the terminal complement pathway.
positive regulation of immune system process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of an immune system process.
immune effector process
Any process of the immune system that occurs as part of an immune response.
regulation of immune response
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the immune response, the immunological reaction of an organism to an immunogenic stimulus.
positive regulation of immune response
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the immune response, the immunological reaction of an organism to an immunogenic stimulus.
regulation of coagulation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of coagulation, the process by which a fluid solution, or part of it, changes into a solid or semisolid mass.
positive regulation of multicellular organismal process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of an organismal process, any of the processes pertinent to the function of an organism above the cellular level; includes the integrated processes of tissues and organs.
negative regulation of multicellular organismal process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of an organismal process, the processes pertinent to the function of an organism above the cellular level; includes the integrated processes of tissues and organs.
positive regulation of coagulation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of coagulation.
negative regulation of coagulation
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of coagulation.
positive regulation of immune response
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the immune response, the immunological reaction of an organism to an immunogenic stimulus.
positive regulation of response to stimulus
Any process that activates, maintains or increases the rate of a response to a stimulus. Response to stimulus is a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
regulation of immune response
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the immune response, the immunological reaction of an organism to an immunogenic stimulus.
negative regulation of fibrinolysis
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of fibrinolysis, an ongoing process that solubilizes fibrin, resulting in the removal of small blood clots.
regulation of response to stress
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a response to stress. Response to stress is a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a disturbance in organismal or cellular homeostasis, usually, but not necessarily, exogenous (e.g. temperature, humidity, ionizing radiation).
regulation of response to external stimulus
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a response to an external stimulus.
regulation of body fluid levels
Any process that modulates the levels of body fluids.
protein maturation
Any process leading to the attainment of the full functional capacity of a protein.
positive regulation of immune response
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the immune response, the immunological reaction of an organism to an immunogenic stimulus.
activation of immune response
Any process that initiates an immune response.
complement activation
Any process involved in the activation of any of the steps of the complement cascade, which allows for the direct killing of microbes, the disposal of immune complexes, and the regulation of other immune processes; the initial steps of complement activation involve one of three pathways, the classical pathway, the alternative pathway, and the lectin pathway, all of which lead to the terminal complement pathway.
complement activation, alternative pathway
Any process involved in the activation of any of the steps of the alternative pathway of the complement cascade which allows for the direct killing of microbes and the regulation of other immune processes.
negative regulation of blood coagulation
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of blood coagulation.
negative regulation of coagulation
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of coagulation.
regulation of blood coagulation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of blood coagulation.
positive regulation of coagulation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of coagulation.
positive regulation of blood coagulation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of blood coagulation.
blood coagulation
The sequential process by which the multiple coagulation factors of the blood interact, ultimately resulting in the formation of an insoluble fibrin clot; it may be divided into three stages: stage 1, the formation of intrinsic and extrinsic prothrombin converting principle; stage 2, the formation of thrombin; stage 3, the formation of stable fibrin polymers.
regulation of blood coagulation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of blood coagulation.
innate immune response
Innate immune responses are defense responses mediated by germline encoded components that directly recognize components of potential pathogens.
inflammatory response
The immediate defensive reaction (by vertebrate tissue) to infection or injury caused by chemical or physical agents. The process is characterized by local vasodilation, extravasation of plasma into intercellular spaces and accumulation of white blood cells and macrophages.
B cell mediated immunity
Any process involved with the carrying out of an immune response by a B cell, through, for instance, the production of antibodies or cytokines, or antigen presentation to T cells.
complement activation, classical pathway
Any process involved in the activation of any of the steps of the classical pathway of the complement cascade which allows for the direct killing of microbes, the disposal of immune complexes, and the regulation of other immune processes.
positive regulation of blood coagulation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of blood coagulation.
negative regulation of blood coagulation
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of blood coagulation.
negative regulation of fibrinolysis
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of fibrinolysis, an ongoing process that solubilizes fibrin, resulting in the removal of small blood clots.
regulation of blood coagulation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of blood coagulation.
blood coagulation
The sequential process by which the multiple coagulation factors of the blood interact, ultimately resulting in the formation of an insoluble fibrin clot; it may be divided into three stages: stage 1, the formation of intrinsic and extrinsic prothrombin converting principle; stage 2, the formation of thrombin; stage 3, the formation of stable fibrin polymers.
regulation of wound healing
Any process that modulates the rate, frequency, or extent of the series of events that restore integrity to a damaged tissue, following an injury.
regulation of fibrinolysis
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of fibrinolysis, an ongoing process that solubilizes fibrin, resulting in the removal of small blood clots.
negative regulation of fibrinolysis
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of fibrinolysis, an ongoing process that solubilizes fibrin, resulting in the removal of small blood clots.
activation of plasma proteins involved in acute inflammatory response
Any process activating plasma proteins by proteolysis as part of an acute inflammatory response.
humoral immune response mediated by circulating immunoglobulin
An immune response dependent upon secreted immunoglobulin. An example of this process is found in Mus musculus.
complement activation
Any process involved in the activation of any of the steps of the complement cascade, which allows for the direct killing of microbes, the disposal of immune complexes, and the regulation of other immune processes; the initial steps of complement activation involve one of three pathways, the classical pathway, the alternative pathway, and the lectin pathway, all of which lead to the terminal complement pathway.

intracellular
The living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
extracellular region
The space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.
cellular_component
The part of a cell or its extracellular environment in which a gene product is located. A gene product may be located in one or more parts of a cell and its location may be as specific as a particular macromolecular complex, that is, a stable, persistent association of macromolecules that function together.
fibrinogen complex
A highly soluble, elongated protein complex found in blood plasma and involved in clot formation. It is converted into fibrin monomer by the action of thrombin. In the mouse, fibrinogen is a hexamer, 46 nm long and 9 nm maximal diameter, containing two sets of nonidentical chains (alpha, beta, and gamma) linked together by disulfide bonds.
extracellular space
That part of a multicellular organism outside the cells proper, usually taken to be outside the plasma membranes, and occupied by fluid.
cell
The basic structural and functional unit of all organisms. Includes the plasma membrane and any external encapsulating structures such as the cell wall and cell envelope.
cytoplasm
All of the contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures.
stored secretory granule
A small subcellular vesicle, surrounded by a membrane, that is formed from the Golgi apparatus and contains a highly concentrated protein destined for secretion. Secretory granules move towards the periphery of the cell and upon stimulation, their membranes fuse with the cell membrane, and their protein load is exteriorized. Processing of the contained protein may take place in secretory granules.
cytoplasmic membrane-bounded vesicle
A membrane-bounded vesicle found in the cytoplasm of the cell.
platelet alpha granule
A secretory organelle found in blood platelets, which is unique in that it exhibits further compartmentalization and acquires its protein content via two distinct mechanisms: (1) biosynthesis predominantly at the megakaryocyte (MK) level (with some vestigial platelet synthesis) (e.g. platelet factor 4) and (2) endocytosis and pinocytosis at both the MK and circulating platelet levels (e.g. fibrinogen (Fg) and IgG).
platelet alpha granule lumen
The volume enclosed by the membrane of the platelet alpha granule.
cytoplasmic vesicle
A vesicle formed of membrane or protein, found in the cytoplasm of a cell.
membrane-enclosed lumen
The enclosed volume within a sealed membrane or between two sealed membranes. Encompasses the volume enclosed by the membranes of a particular organelle, e.g. endoplasmic reticulum lumen, or the space between the two lipid bilayers of a double membrane surrounding an organelle, e.g. nuclear envelope lumen.
vesicle
Any small, fluid-filled, spherical organelle enclosed by membrane or protein.
vesicle lumen
The volume enclosed by the membrane or protein that forms a vesicle.
membrane-bounded vesicle
Any small, fluid-filled, spherical organelle enclosed by a lipid bilayer.
macromolecular complex
A stable assembly of two or more macromolecules, i.e. proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates or lipids, in which the constituent parts function together.
organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, and prokaryotic structures such as anammoxosomes and pirellulosomes. Excludes the plasma membrane.
membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
organelle lumen
The internal volume enclosed by the membranes of a particular organelle; includes the volume enclosed by a single organelle membrane, e.g. endoplasmic reticulum lumen, or the volume enclosed by the innermost of the two lipid bilayers of an organelle envelope, e.g. nuclear lumen.
protein complex
Any macromolecular complex composed of two or more polypeptide subunits, which may or may not be identical. Protein complexes may have other associated non-protein prosthetic groups, such as nucleotides, metal ions or other small molecules.
extracellular region part
Any constituent part of the extracellular region, the space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers constituent parts of the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.
organelle part
Any constituent part of an organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, but excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
cytoplasmic vesicle part
Any constituent part of cytoplasmic vesicle, a vesicle formed of membrane or protein, found in the cytoplasm of a cell.
cytoplasmic part
Any constituent part of the cytoplasm, all of the contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
cytoplasmic membrane-bounded vesicle lumen
The volume enclosed by the membrane of a cytoplasmic membrane-bounded vesicle.
all
NA
extracellular region part
Any constituent part of the extracellular region, the space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers constituent parts of the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
organelle part
Any constituent part of an organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, but excludes the plasma membrane.
organelle lumen
The internal volume enclosed by the membranes of a particular organelle; includes the volume enclosed by a single organelle membrane, e.g. endoplasmic reticulum lumen, or the volume enclosed by the innermost of the two lipid bilayers of an organelle envelope, e.g. nuclear lumen.
fibrinogen complex
A highly soluble, elongated protein complex found in blood plasma and involved in clot formation. It is converted into fibrin monomer by the action of thrombin. In the mouse, fibrinogen is a hexamer, 46 nm long and 9 nm maximal diameter, containing two sets of nonidentical chains (alpha, beta, and gamma) linked together by disulfide bonds.
cytoplasmic vesicle
A vesicle formed of membrane or protein, found in the cytoplasm of a cell.
intracellular membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
fibrinogen complex
A highly soluble, elongated protein complex found in blood plasma and involved in clot formation. It is converted into fibrin monomer by the action of thrombin. In the mouse, fibrinogen is a hexamer, 46 nm long and 9 nm maximal diameter, containing two sets of nonidentical chains (alpha, beta, and gamma) linked together by disulfide bonds.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
cytoplasmic vesicle part
Any constituent part of cytoplasmic vesicle, a vesicle formed of membrane or protein, found in the cytoplasm of a cell.
cytoplasmic membrane-bounded vesicle
A membrane-bounded vesicle found in the cytoplasm of the cell.
vesicle lumen
The volume enclosed by the membrane or protein that forms a vesicle.
cytoplasmic membrane-bounded vesicle
A membrane-bounded vesicle found in the cytoplasm of the cell.
cytoplasmic membrane-bounded vesicle lumen
The volume enclosed by the membrane of a cytoplasmic membrane-bounded vesicle.
cytoplasmic part
Any constituent part of the cytoplasm, all of the contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures.
cytoplasmic vesicle
A vesicle formed of membrane or protein, found in the cytoplasm of a cell.
cytoplasmic vesicle part
Any constituent part of cytoplasmic vesicle, a vesicle formed of membrane or protein, found in the cytoplasm of a cell.
cytoplasmic membrane-bounded vesicle lumen
The volume enclosed by the membrane of a cytoplasmic membrane-bounded vesicle.
platelet alpha granule lumen
The volume enclosed by the membrane of the platelet alpha granule.

molecular_function
Elemental activities, such as catalysis or binding, describing the actions of a gene product at the molecular level. A given gene product may exhibit one or more molecular functions.
enzyme inhibitor activity
Stops, prevents or reduces the activity of an enzyme.
endopeptidase inhibitor activity
Stops, prevents or reduces the activity of an endopeptidase, any enzyme that hydrolyzes nonterminal peptide bonds in polypeptides.
binding
The selective, non-covalent, often stoichiometric, interaction of a molecule with one or more specific sites on another molecule.
endopeptidase regulator activity
Modulates the activity of a peptidase, any enzyme that hydrolyzes nonterminal peptide bonds in polypeptides.
amino acid binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with an amino acid, organic acids containing one or more amino substituents.
peptidase inhibitor activity
Stops, prevents or reduces the activity of a peptidase, any enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis peptide bonds.
vitamin binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with a vitamin, one of a number of unrelated organic substances that occur in many foods in small amounts and that are necessary in trace amounts for the normal metabolic functioning of the body.
pyridoxal phosphate binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with pyridoxal 5' phosphate, 3-hydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)-2-methyl4-pyridine carboxaldehyde 5' phosphate, the biologically active form of vitamin B6.
enzyme regulator activity
Modulates the activity of an enzyme.
carboxylic acid binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with a carboxylic acid, any organic acid containing one or more carboxyl (COOH) groups or anions (COO-).
amine binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with any organic compound that is weakly basic in character and contains an amino or a substituted amino group.
cofactor binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with a cofactor, a substance that is required for the activity of an enzyme or other protein. Cofactors may be inorganic, such as the metal atoms zinc, iron, and copper in certain forms, or organic, in which case they are referred to as coenzymes. Cofactors may either be bound tightly to active sites or bind loosely with the substrate.
peptidase regulator activity
Modulates the activity of a peptidase, any enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis peptide bonds.
vitamin B6 binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with any of the vitamin B6 compounds: pyridoxal, pyridoxamine and pyridoxine and the active form, pyridoxal phosphate.
all
NA
amino acid binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with an amino acid, organic acids containing one or more amino substituents.
peptidase inhibitor activity
Stops, prevents or reduces the activity of a peptidase, any enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis peptide bonds.
pyridoxal phosphate binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with pyridoxal 5' phosphate, 3-hydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)-2-methyl4-pyridine carboxaldehyde 5' phosphate, the biologically active form of vitamin B6.
endopeptidase inhibitor activity
Stops, prevents or reduces the activity of an endopeptidase, any enzyme that hydrolyzes nonterminal peptide bonds in polypeptides.
ABCG5ATP-binding cassette, sub-family G (WHITE), member 5 (ENSG00000138075), score: 0.61 ACP2acid phosphatase 2, lysosomal (ENSG00000134575), score: 0.62 AGXTalanine-glyoxylate aminotransferase (ENSG00000172482), score: 0.61 AIFM2apoptosis-inducing factor, mitochondrion-associated, 2 (ENSG00000042286), score: 0.56 AKR1D1aldo-keto reductase family 1, member D1 (delta 4-3-ketosteroid-5-beta-reductase) (ENSG00000122787), score: 0.61 ALBalbumin (ENSG00000163631), score: 0.55 AMBPalpha-1-microglobulin/bikunin precursor (ENSG00000106927), score: 0.55 ANXA10annexin A10 (ENSG00000109511), score: 0.58 ATRNattractin (ENSG00000088812), score: 0.55 C1orf130chromosome 1 open reading frame 130 (ENSG00000184454), score: 0.6 C5complement component 5 (ENSG00000106804), score: 0.58 C8Acomplement component 8, alpha polypeptide (ENSG00000157131), score: 0.65 CDC42BPACDC42 binding protein kinase alpha (DMPK-like) (ENSG00000143776), score: -0.67 CLDN14claudin 14 (ENSG00000159261), score: 0.6 CPB2carboxypeptidase B2 (plasma) (ENSG00000080618), score: 0.56 CREB3L3cAMP responsive element binding protein 3-like 3 (ENSG00000060566), score: 0.57 CYP39A1cytochrome P450, family 39, subfamily A, polypeptide 1 (ENSG00000146233), score: 0.57 DDOSTdolichyl-diphosphooligosaccharide--protein glycosyltransferase (ENSG00000244038), score: 0.57 DKK2dickkopf homolog 2 (Xenopus laevis) (ENSG00000155011), score: 0.61 EDEM1ER degradation enhancer, mannosidase alpha-like 1 (ENSG00000134109), score: 0.54 EPHA1EPH receptor A1 (ENSG00000146904), score: 0.56 EPHX1epoxide hydrolase 1, microsomal (xenobiotic) (ENSG00000143819), score: 0.6 F2coagulation factor II (thrombin) (ENSG00000180210), score: 0.58 F9coagulation factor IX (ENSG00000101981), score: 0.59 FETUBfetuin B (ENSG00000090512), score: 0.71 FGBfibrinogen beta chain (ENSG00000171564), score: 0.55 FGGfibrinogen gamma chain (ENSG00000171557), score: 0.55 FN1fibronectin 1 (ENSG00000115414), score: 0.63 FPGSfolylpolyglutamate synthase (ENSG00000136877), score: 0.63 FSTfollistatin (ENSG00000134363), score: 0.57 GDF2growth differentiation factor 2 (ENSG00000128802), score: 0.67 GPLD1glycosylphosphatidylinositol specific phospholipase D1 (ENSG00000112293), score: 0.58 HPXhemopexin (ENSG00000110169), score: 0.56 HRGhistidine-rich glycoprotein (ENSG00000113905), score: 0.63 IGF1insulin-like growth factor 1 (somatomedin C) (ENSG00000017427), score: 0.66 IGFBP1insulin-like growth factor binding protein 1 (ENSG00000146678), score: 0.71 IL10RAinterleukin 10 receptor, alpha (ENSG00000110324), score: 0.58 IL1R2interleukin 1 receptor, type II (ENSG00000115590), score: 0.82 IL28RAinterleukin 28 receptor, alpha (interferon, lambda receptor) (ENSG00000185436), score: 0.62 INHBAinhibin, beta A (ENSG00000122641), score: 0.73 LAG3lymphocyte-activation gene 3 (ENSG00000089692), score: 0.54 LECT2leukocyte cell-derived chemotaxin 2 (ENSG00000145826), score: 0.67 LEPRE1leucine proline-enriched proteoglycan (leprecan) 1 (ENSG00000117385), score: 0.55 MASP2mannan-binding lectin serine peptidase 2 (ENSG00000009724), score: 0.62 MAT1Amethionine adenosyltransferase I, alpha (ENSG00000151224), score: 0.59 MOCOSmolybdenum cofactor sulfurase (ENSG00000075643), score: 0.58 MYO5Cmyosin VC (ENSG00000128833), score: 0.55 NADKNAD kinase (ENSG00000008130), score: 0.54 NGFRnerve growth factor receptor (ENSG00000064300), score: 0.6 NR5A2nuclear receptor subfamily 5, group A, member 2 (ENSG00000116833), score: 0.55 NUDT12nudix (nucleoside diphosphate linked moiety X)-type motif 12 (ENSG00000112874), score: 0.55 ONECUT1one cut homeobox 1 (ENSG00000169856), score: 0.69 OTCornithine carbamoyltransferase (ENSG00000036473), score: 0.68 PEMTphosphatidylethanolamine N-methyltransferase (ENSG00000133027), score: 0.57 PPAPDC1Bphosphatidic acid phosphatase type 2 domain containing 1B (ENSG00000147535), score: 0.72 PROZprotein Z, vitamin K-dependent plasma glycoprotein (ENSG00000126231), score: 0.61 PTBP2polypyrimidine tract binding protein 2 (ENSG00000117569), score: -0.59 RANBP10RAN binding protein 10 (ENSG00000141084), score: 0.57 RAPH1Ras association (RalGDS/AF-6) and pleckstrin homology domains 1 (ENSG00000173166), score: 0.58 RGS18regulator of G-protein signaling 18 (ENSG00000150681), score: 0.55 SCARB1scavenger receptor class B, member 1 (ENSG00000073060), score: 0.66 SDC2syndecan 2 (ENSG00000169439), score: 0.69 SEC16BSEC16 homolog B (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000120341), score: 0.62 SERPINC1serpin peptidase inhibitor, clade C (antithrombin), member 1 (ENSG00000117601), score: 0.58 SGPL1sphingosine-1-phosphate lyase 1 (ENSG00000166224), score: 0.59 SLC2A10solute carrier family 2 (facilitated glucose transporter), member 10 (ENSG00000197496), score: 0.66 SLC35C1solute carrier family 35, member C1 (ENSG00000181830), score: 0.57 SLC38A4solute carrier family 38, member 4 (ENSG00000139209), score: 0.6 SLC46A1solute carrier family 46 (folate transporter), member 1 (ENSG00000076351), score: 0.83 SPP2secreted phosphoprotein 2, 24kDa (ENSG00000072080), score: 0.55 STAB2stabilin 2 (ENSG00000136011), score: 0.64 STARD5StAR-related lipid transfer (START) domain containing 5 (ENSG00000172345), score: 0.62 TATtyrosine aminotransferase (ENSG00000198650), score: 0.62 TDO2tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase (ENSG00000151790), score: 0.54 TGFBItransforming growth factor, beta-induced, 68kDa (ENSG00000120708), score: 0.61 TMEM104transmembrane protein 104 (ENSG00000109066), score: 0.57 TMEM20transmembrane protein 20 (ENSG00000176273), score: 0.61 TRAF2TNF receptor-associated factor 2 (ENSG00000127191), score: 0.64 TRPM1transient receptor potential cation channel, subfamily M, member 1 (ENSG00000134160), score: 0.63 TSKUtsukushi small leucine rich proteoglycan homolog (Xenopus laevis) (ENSG00000182704), score: 0.59 TTPAtocopherol (alpha) transfer protein (ENSG00000137561), score: 0.55 VSIG4V-set and immunoglobulin domain containing 4 (ENSG00000155659), score: 0.59 XCR1chemokine (C motif) receptor 1 (ENSG00000173578), score: 0.61
| Id | species | tissue | sex | individual |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| mdo_lv_m_ca1 | mdo | lv | m | _ |
| mml_lv_f_ca1 | mml | lv | f | _ |
| mml_lv_m_ca1 | mml | lv | m | _ |