

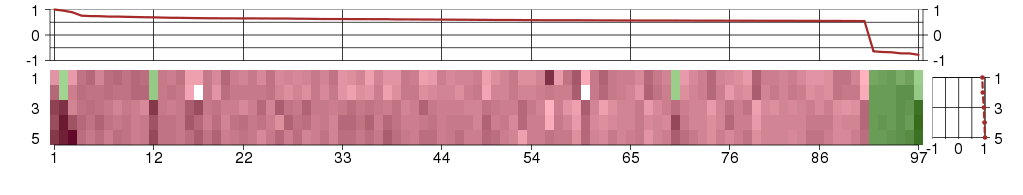

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways, including anabolism and catabolism, by which living organisms transform chemical substances. Metabolic processes typically transform small molecules, but also include macromolecular processes such as DNA repair and replication, and protein synthesis and degradation.
alcohol metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving alcohols, any of a class of compounds containing one or more hydroxyl groups attached to a saturated carbon atom.
organic acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving organic acids, any acidic compound containing carbon in covalent linkage.
cellular amino acid and derivative metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving amino acids, organic acids containing one or more amino substituents, and compounds derived from amino acids, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular amino acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving amino acids, organic acids containing one or more amino substituents.
lipid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving lipids, compounds soluble in an organic solvent but not, or sparingly, in an aqueous solvent. Includes fatty acids; neutral fats, other fatty-acid esters, and soaps; long-chain (fatty) alcohols and waxes; sphingoids and other long-chain bases; glycolipids, phospholipids and sphingolipids; and carotenes, polyprenols, sterols, terpenes and other isoprenoids.
steroid biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of steroids, compounds with a 1,2,cyclopentanoperhydrophenanthrene nucleus; includes de novo formation and steroid interconversion by modification.
nitrogen compound metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving various organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds; includes nitrogen fixation, nitrification, denitrification, assimilatory/dissimilatory nitrate reduction and the interconversion of nitrogenous organic matter and ammonium.
organelle organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of an organelle within a cell. An organelle is an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
peroxisome organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of a peroxisome. A peroxisome is a small, membrane-bounded organelle that uses dioxygen (O2) to oxidize organic molecules.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
steroid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving steroids, compounds with a 1,2,cyclopentanoperhydrophenanthrene nucleus.
bile acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving bile acids, any of a group of steroid carboxylic acids occurring in bile, where they are present as the sodium salts of their amides with glycine or taurine.
lipid biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of lipids, compounds soluble in an organic solvent but not, or sparingly, in an aqueous solvent.
catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of substances, including the breakdown of carbon compounds with the liberation of energy for use by the cell or organism.
biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances; typically the energy-requiring part of metabolism in which simpler substances are transformed into more complex ones.
amine metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving any organic compound that is weakly basic in character and contains an amino or a substituted amino group, as carried out by individual cells. Amines are called primary, secondary, or tertiary according to whether one, two, or three carbon atoms are attached to the nitrogen atom.
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
cellular component organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of a cellular component.
organic acid biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of organic acids, any acidic compound containing carbon in covalent linkage.
organic acid catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of organic acids, any acidic compound containing carbon in covalent linkage.
carboxylic acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving carboxylic acids, any organic acid containing one or more carboxyl (COOH) groups or anions (COO-).
monocarboxylic acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving monocarboxylic acids, any organic acid containing one carboxyl (COOH) group or anion (COO-).
cellular nitrogen compound metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving various organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular ketone metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving any of a class of organic compounds that contain the carbonyl group, CO, and in which the carbonyl group is bonded only to carbon atoms, as carried out by individual cells. The general formula for a ketone is RCOR, where R and R are alkyl or aryl groups.
oxoacid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving any oxoacid; an oxoacid is a compound which contains oxygen, at least one other element, and at least one hydrogen bound to oxygen, and which produces a conjugate base by loss of positive hydrogen ion(s) (hydrons).
cellular amine metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving any organic compound that is weakly basic in character and contains an amino or a substituted amino group, as carried out by individual cells. Amines are called primary, secondary, or tertiary according to whether one, two, or three carbon atoms are attached to the nitrogen atom.
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
primary metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving those compounds which are formed as a part of the normal anabolic and catabolic processes. These processes take place in most, if not all, cells of the organism.
cellular catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of substances, carried out by individual cells.
cellular biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
small molecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving small molecules, any monomeric molecule of small relative molecular mass.
small molecule catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of small molecules, any monomeric molecule of small relative molecular mass.
small molecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of small molecules, any monomeric molecule of small relative molecular mass.
carboxylic acid biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of carboxylic acids, any organic acid containing one or more carboxyl (-COOH) groups.
carboxylic acid catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of carboxylic acids, any organic acid containing one or more carboxyl (-COOH) groups.
all
NA
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
organelle organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of an organelle within a cell. An organelle is an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
cellular nitrogen compound metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving various organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of substances, carried out by individual cells.
cellular biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
cellular amino acid and derivative metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving amino acids, organic acids containing one or more amino substituents, and compounds derived from amino acids, as carried out by individual cells.
organic acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving organic acids, any acidic compound containing carbon in covalent linkage.
cellular amino acid and derivative metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving amino acids, organic acids containing one or more amino substituents, and compounds derived from amino acids, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular ketone metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving any of a class of organic compounds that contain the carbonyl group, CO, and in which the carbonyl group is bonded only to carbon atoms, as carried out by individual cells. The general formula for a ketone is RCOR, where R and R are alkyl or aryl groups.
small molecule catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of small molecules, any monomeric molecule of small relative molecular mass.
small molecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of small molecules, any monomeric molecule of small relative molecular mass.
cellular amine metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving any organic compound that is weakly basic in character and contains an amino or a substituted amino group, as carried out by individual cells. Amines are called primary, secondary, or tertiary according to whether one, two, or three carbon atoms are attached to the nitrogen atom.
organic acid catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of organic acids, any acidic compound containing carbon in covalent linkage.
organic acid biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of organic acids, any acidic compound containing carbon in covalent linkage.
organic acid biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of organic acids, any acidic compound containing carbon in covalent linkage.
organic acid catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of organic acids, any acidic compound containing carbon in covalent linkage.
oxoacid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving any oxoacid; an oxoacid is a compound which contains oxygen, at least one other element, and at least one hydrogen bound to oxygen, and which produces a conjugate base by loss of positive hydrogen ion(s) (hydrons).
lipid biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of lipids, compounds soluble in an organic solvent but not, or sparingly, in an aqueous solvent.
cellular amino acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving amino acids, organic acids containing one or more amino substituents.
steroid biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of steroids, compounds with a 1,2,cyclopentanoperhydrophenanthrene nucleus; includes de novo formation and steroid interconversion by modification.
cellular amino acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving amino acids, organic acids containing one or more amino substituents.
carboxylic acid biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of carboxylic acids, any organic acid containing one or more carboxyl (-COOH) groups.
carboxylic acid catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of carboxylic acids, any organic acid containing one or more carboxyl (-COOH) groups.
bile acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving bile acids, any of a group of steroid carboxylic acids occurring in bile, where they are present as the sodium salts of their amides with glycine or taurine.

intracellular
The living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
membrane
Double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
integral to membrane
Penetrating at least one phospholipid bilayer of a membrane. May also refer to the state of being buried in the bilayer with no exposure outside the bilayer. When used to describe a protein, indicates that all or part of the peptide sequence is embedded in the membrane.
endoplasmic reticulum
The irregular network of unit membranes, visible only by electron microscopy, that occurs in the cytoplasm of many eukaryotic cells. The membranes form a complex meshwork of tubular channels, which are often expanded into slitlike cavities called cisternae. The ER takes two forms, rough (or granular), with ribosomes adhering to the outer surface, and smooth (with no ribosomes attached).
peroxisome
A small, membrane-bounded organelle that uses dioxygen (O2) to oxidize organic molecules; contains some enzymes that produce and others that degrade hydrogen peroxide (H2O2).
peroxisomal membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding a peroxisome.
cellular_component
The part of a cell or its extracellular environment in which a gene product is located. A gene product may be located in one or more parts of a cell and its location may be as specific as a particular macromolecular complex, that is, a stable, persistent association of macromolecules that function together.
cell
The basic structural and functional unit of all organisms. Includes the plasma membrane and any external encapsulating structures such as the cell wall and cell envelope.
cytoplasm
All of the contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures.
integral to peroxisomal membrane
Penetrating at least one phospholipid bilayer of a peroxisomal membrane. May also refer to the state of being buried in the bilayer with no exposure outside the bilayer.
peroxisomal part
Any constituent part of a peroxisome, a small, membrane-bounded organelle that uses dioxygen (O2) to oxidize organic molecules; contains some enzymes that produce and others that degrade hydrogen peroxide (H2O2).
endoplasmic reticulum membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding the endoplasmic reticulum.
endomembrane system
A collection of membranous structures involved in transport within the cell. The main components of the endomembrane system are endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi bodies, vesicles, cell membrane and nuclear envelope. Members of the endomembrane system pass materials through each other or though the use of vesicles.
organelle membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding an organelle.
intrinsic to membrane
Located in a membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
intrinsic to peroxisomal membrane
Located in the peroxisomal membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
intrinsic to organelle membrane
Located in an organelle membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
integral to organelle membrane
Penetrating at least one phospholipid bilayer of an organelle membrane. May also refer to the state of being buried in the bilayer with no exposure outside the bilayer.
microbody membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding a microbody.
nuclear membrane-endoplasmic reticulum network
The continuous network of membranes encompassing the outer nuclear membrane and the endoplasmic reticulum.
microbody
Cytoplasmic organelles, spherical or oval in shape, that are bounded by a single membrane and contain oxidative enzymes, especially those utilizing hydrogen peroxide (H2O2).
organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, and prokaryotic structures such as anammoxosomes and pirellulosomes. Excludes the plasma membrane.
membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
organelle part
Any constituent part of an organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, but excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
membrane part
Any constituent part of a membrane, a double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
endoplasmic reticulum part
Any constituent part of the endoplasmic reticulum, the irregular network of unit membranes, visible only by electron microscopy, that occurs in the cytoplasm of many eukaryotic cells. The membranes form a complex meshwork of tubular channels, which are often expanded into slitlike cavities called cisternae.
microbody part
Any constituent part of a microbody, a cytoplasmic organelle, spherical or oval in shape, that is bounded by a single membrane and contains oxidative enzymes, especially those utilizing hydrogen peroxide (H2O2).
cytoplasmic part
Any constituent part of the cytoplasm, all of the contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
subsynaptic reticulum
An elaborate tubulolamellar membrane system that underlies the postsynaptic cell membrane.
all
NA
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
organelle part
Any constituent part of an organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, but excludes the plasma membrane.
organelle membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding an organelle.
intracellular membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
intrinsic to organelle membrane
Located in an organelle membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
organelle membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding an organelle.
membrane part
Any constituent part of a membrane, a double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
nuclear membrane-endoplasmic reticulum network
The continuous network of membranes encompassing the outer nuclear membrane and the endoplasmic reticulum.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
endoplasmic reticulum membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding the endoplasmic reticulum.
nuclear membrane-endoplasmic reticulum network
The continuous network of membranes encompassing the outer nuclear membrane and the endoplasmic reticulum.
endoplasmic reticulum membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding the endoplasmic reticulum.
endoplasmic reticulum membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding the endoplasmic reticulum.
cytoplasmic part
Any constituent part of the cytoplasm, all of the contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures.
endoplasmic reticulum
The irregular network of unit membranes, visible only by electron microscopy, that occurs in the cytoplasm of many eukaryotic cells. The membranes form a complex meshwork of tubular channels, which are often expanded into slitlike cavities called cisternae. The ER takes two forms, rough (or granular), with ribosomes adhering to the outer surface, and smooth (with no ribosomes attached).
microbody
Cytoplasmic organelles, spherical or oval in shape, that are bounded by a single membrane and contain oxidative enzymes, especially those utilizing hydrogen peroxide (H2O2).
endoplasmic reticulum part
Any constituent part of the endoplasmic reticulum, the irregular network of unit membranes, visible only by electron microscopy, that occurs in the cytoplasm of many eukaryotic cells. The membranes form a complex meshwork of tubular channels, which are often expanded into slitlike cavities called cisternae.
microbody part
Any constituent part of a microbody, a cytoplasmic organelle, spherical or oval in shape, that is bounded by a single membrane and contains oxidative enzymes, especially those utilizing hydrogen peroxide (H2O2).
subsynaptic reticulum
An elaborate tubulolamellar membrane system that underlies the postsynaptic cell membrane.
intrinsic to organelle membrane
Located in an organelle membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
endoplasmic reticulum part
Any constituent part of the endoplasmic reticulum, the irregular network of unit membranes, visible only by electron microscopy, that occurs in the cytoplasm of many eukaryotic cells. The membranes form a complex meshwork of tubular channels, which are often expanded into slitlike cavities called cisternae.
microbody membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding a microbody.
microbody part
Any constituent part of a microbody, a cytoplasmic organelle, spherical or oval in shape, that is bounded by a single membrane and contains oxidative enzymes, especially those utilizing hydrogen peroxide (H2O2).
endoplasmic reticulum part
Any constituent part of the endoplasmic reticulum, the irregular network of unit membranes, visible only by electron microscopy, that occurs in the cytoplasm of many eukaryotic cells. The membranes form a complex meshwork of tubular channels, which are often expanded into slitlike cavities called cisternae.
integral to peroxisomal membrane
Penetrating at least one phospholipid bilayer of a peroxisomal membrane. May also refer to the state of being buried in the bilayer with no exposure outside the bilayer.
intrinsic to peroxisomal membrane
Located in the peroxisomal membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
peroxisomal membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding a peroxisome.
intrinsic to peroxisomal membrane
Located in the peroxisomal membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
integral to organelle membrane
Penetrating at least one phospholipid bilayer of an organelle membrane. May also refer to the state of being buried in the bilayer with no exposure outside the bilayer.
peroxisomal part
Any constituent part of a peroxisome, a small, membrane-bounded organelle that uses dioxygen (O2) to oxidize organic molecules; contains some enzymes that produce and others that degrade hydrogen peroxide (H2O2).

molecular_function
Elemental activities, such as catalysis or binding, describing the actions of a gene product at the molecular level. A given gene product may exhibit one or more molecular functions.
catalytic activity
Catalysis of a biochemical reaction at physiological temperatures. In biologically catalyzed reactions, the reactants are known as substrates, and the catalysts are naturally occurring macromolecular substances known as enzymes. Enzymes possess specific binding sites for substrates, and are usually composed wholly or largely of protein, but RNA that has catalytic activity (ribozyme) is often also regarded as enzymatic.
binding
The selective, non-covalent, often stoichiometric, interaction of a molecule with one or more specific sites on another molecule.
oxidoreductase activity
Catalysis of an oxidation-reduction (redox) reaction, a reversible chemical reaction in which the oxidation state of an atom or atoms within a molecule is altered. One substrate acts as a hydrogen or electron donor and becomes oxidized, while the other acts as hydrogen or electron acceptor and becomes reduced.
steroid dehydrogenase activity
Catalysis of an oxidation-reduction (redox) reaction in which one substrate is a sterol derivative.
amino acid binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with an amino acid, organic acids containing one or more amino substituents.
vitamin binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with a vitamin, one of a number of unrelated organic substances that occur in many foods in small amounts and that are necessary in trace amounts for the normal metabolic functioning of the body.
pyridoxal phosphate binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with pyridoxal 5' phosphate, 3-hydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)-2-methyl4-pyridine carboxaldehyde 5' phosphate, the biologically active form of vitamin B6.
carboxylic acid binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with a carboxylic acid, any organic acid containing one or more carboxyl (COOH) groups or anions (COO-).
monocarboxylic acid binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with a monocarboxylic acid, any organic acid containing one carboxyl (COOH) group or anion (COO-).
amine binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with any organic compound that is weakly basic in character and contains an amino or a substituted amino group.
cofactor binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with a cofactor, a substance that is required for the activity of an enzyme or other protein. Cofactors may be inorganic, such as the metal atoms zinc, iron, and copper in certain forms, or organic, in which case they are referred to as coenzymes. Cofactors may either be bound tightly to active sites or bind loosely with the substrate.
vitamin B6 binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with any of the vitamin B6 compounds: pyridoxal, pyridoxamine and pyridoxine and the active form, pyridoxal phosphate.
all
NA
amino acid binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with an amino acid, organic acids containing one or more amino substituents.
pyridoxal phosphate binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with pyridoxal 5' phosphate, 3-hydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)-2-methyl4-pyridine carboxaldehyde 5' phosphate, the biologically active form of vitamin B6.
| Id | Pvalue | ExpCount | Count | Size | Term |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 00120 | 2.345e-03 | 0.09228 | 3 | 3 | Primary bile acid biosynthesis |
| 04146 | 1.216e-02 | 0.9228 | 6 | 30 | Peroxisome |
| 00140 | 1.441e-02 | 0.1538 | 3 | 5 | Steroid hormone biosynthesis |
| 04610 | 1.648e-02 | 0.646 | 5 | 21 | Complement and coagulation cascades |
| 00260 | 2.150e-02 | 0.3999 | 4 | 13 | Glycine, serine and threonine metabolism |
| 02010 | 2.709e-02 | 0.4306 | 4 | 14 | ABC transporters |
| 00910 | 4.710e-02 | 0.2461 | 3 | 8 | Nitrogen metabolism |
ABCA1ATP-binding cassette, sub-family A (ABC1), member 1 (ENSG00000165029), score: 0.63 ABCB11ATP-binding cassette, sub-family B (MDR/TAP), member 11 (ENSG00000073734), score: 0.61 ABCD3ATP-binding cassette, sub-family D (ALD), member 3 (ENSG00000117528), score: 0.74 ABCG5ATP-binding cassette, sub-family G (WHITE), member 5 (ENSG00000138075), score: 0.64 ACBD5acyl-CoA binding domain containing 5 (ENSG00000107897), score: 0.65 ACOT12acyl-CoA thioesterase 12 (ENSG00000172497), score: 0.6 ACSL5acyl-CoA synthetase long-chain family member 5 (ENSG00000197142), score: 0.58 AKR1D1aldo-keto reductase family 1, member D1 (delta 4-3-ketosteroid-5-beta-reductase) (ENSG00000122787), score: 0.55 ALAS1aminolevulinate, delta-, synthase 1 (ENSG00000023330), score: 0.56 ALBalbumin (ENSG00000163631), score: 0.56 ATL2atlastin GTPase 2 (ENSG00000119787), score: 0.56 AVPR1Aarginine vasopressin receptor 1A (ENSG00000166148), score: 0.57 C5complement component 5 (ENSG00000106804), score: 0.61 C8Acomplement component 8, alpha polypeptide (ENSG00000157131), score: 0.59 C9orf150chromosome 9 open reading frame 150 (ENSG00000153714), score: 0.56 CA1carbonic anhydrase I (ENSG00000133742), score: 0.68 CCBL2cysteine conjugate-beta lyase 2 (ENSG00000137944), score: 0.62 CCDC92coiled-coil domain containing 92 (ENSG00000119242), score: -0.64 CCRL1chemokine (C-C motif) receptor-like 1 (ENSG00000129048), score: 0.62 CNR2cannabinoid receptor 2 (macrophage) (ENSG00000188822), score: 1 CPB2carboxypeptidase B2 (plasma) (ENSG00000080618), score: 0.56 CREB3L3cAMP responsive element binding protein 3-like 3 (ENSG00000060566), score: 0.63 CTHcystathionase (cystathionine gamma-lyase) (ENSG00000116761), score: 0.57 CYP39A1cytochrome P450, family 39, subfamily A, polypeptide 1 (ENSG00000146233), score: 0.57 CYP7B1cytochrome P450, family 7, subfamily B, polypeptide 1 (ENSG00000172817), score: 0.65 DNAJC22DnaJ (Hsp40) homolog, subfamily C, member 22 (ENSG00000178401), score: 0.56 DNTTdeoxynucleotidyltransferase, terminal (ENSG00000107447), score: 0.57 EGFRepidermal growth factor receptor (ENSG00000146648), score: 0.64 ERN1endoplasmic reticulum to nucleus signaling 1 (ENSG00000178607), score: 0.62 F9coagulation factor IX (ENSG00000101981), score: 0.55 FABP2fatty acid binding protein 2, intestinal (ENSG00000145384), score: 0.96 FAM160B1family with sequence similarity 160, member B1 (ENSG00000151553), score: 0.58 FETUBfetuin B (ENSG00000090512), score: 0.7 FN1fibronectin 1 (ENSG00000115414), score: 0.56 GNEglucosamine (UDP-N-acetyl)-2-epimerase/N-acetylmannosamine kinase (ENSG00000159921), score: 0.66 GNMTglycine N-methyltransferase (ENSG00000124713), score: 0.63 GPLD1glycosylphosphatidylinositol specific phospholipase D1 (ENSG00000112293), score: 0.61 H6PDhexose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (glucose 1-dehydrogenase) (ENSG00000049239), score: 0.56 HALhistidine ammonia-lyase (ENSG00000084110), score: 0.74 HAO1hydroxyacid oxidase (glycolate oxidase) 1 (ENSG00000101323), score: 0.57 HTRA1HtrA serine peptidase 1 (ENSG00000166033), score: -0.72 IGF1insulin-like growth factor 1 (somatomedin C) (ENSG00000017427), score: 0.72 IL6STinterleukin 6 signal transducer (gp130, oncostatin M receptor) (ENSG00000134352), score: 0.56 IYDiodotyrosine deiodinase (ENSG00000009765), score: 0.56 KLBklotho beta (ENSG00000134962), score: 0.65 LECT2leukocyte cell-derived chemotaxin 2 (ENSG00000145826), score: 0.7 LIFRleukemia inhibitory factor receptor alpha (ENSG00000113594), score: 0.67 LPIN1lipin 1 (ENSG00000134324), score: 0.57 LPIN2lipin 2 (ENSG00000101577), score: 0.58 LRATlecithin retinol acyltransferase (phosphatidylcholine--retinol O-acyltransferase) (ENSG00000121207), score: 0.57 MAT1Amethionine adenosyltransferase I, alpha (ENSG00000151224), score: 0.6 MCM10minichromosome maintenance complex component 10 (ENSG00000065328), score: 0.66 MIA3melanoma inhibitory activity family, member 3 (ENSG00000154305), score: 0.62 MTTPmicrosomal triglyceride transfer protein (ENSG00000138823), score: 0.56 NR5A2nuclear receptor subfamily 5, group A, member 2 (ENSG00000116833), score: 0.61 ONECUT1one cut homeobox 1 (ENSG00000169856), score: 0.58 OTCornithine carbamoyltransferase (ENSG00000036473), score: 0.71 P4HTMprolyl 4-hydroxylase, transmembrane (endoplasmic reticulum) (ENSG00000178467), score: -0.68 PDP2pyruvate dehyrogenase phosphatase catalytic subunit 2 (ENSG00000172840), score: 0.58 PEX11Aperoxisomal biogenesis factor 11 alpha (ENSG00000166821), score: 0.55 PEX16peroxisomal biogenesis factor 16 (ENSG00000121680), score: 0.59 PEX7peroxisomal biogenesis factor 7 (ENSG00000112357), score: 0.56 PLK3polo-like kinase 3 (ENSG00000173846), score: 0.58 PM20D1peptidase M20 domain containing 1 (ENSG00000162877), score: 0.55 PPP1R15Bprotein phosphatase 1, regulatory (inhibitor) subunit 15B (ENSG00000158615), score: 0.65 PPP2R5Aprotein phosphatase 2, regulatory subunit B', alpha (ENSG00000066027), score: 0.59 PRKD3protein kinase D3 (ENSG00000115825), score: 0.59 PRLRprolactin receptor (ENSG00000113494), score: 0.63 PSEN2presenilin 2 (Alzheimer disease 4) (ENSG00000143801), score: 0.65 PYGLphosphorylase, glycogen, liver (ENSG00000100504), score: 0.55 SARDHsarcosine dehydrogenase (ENSG00000123453), score: 0.55 SDR42E1short chain dehydrogenase/reductase family 42E, member 1 (ENSG00000184860), score: 0.55 SERPINC1serpin peptidase inhibitor, clade C (antithrombin), member 1 (ENSG00000117601), score: 0.57 SLC16A10solute carrier family 16, member 10 (aromatic amino acid transporter) (ENSG00000112394), score: 0.72 SLC17A8solute carrier family 17 (sodium-dependent inorganic phosphate cotransporter), member 8 (ENSG00000179520), score: 0.89 SLC19A2solute carrier family 19 (thiamine transporter), member 2 (ENSG00000117479), score: 0.6 SLC25A47solute carrier family 25, member 47 (ENSG00000140107), score: 0.65 SLC2A9solute carrier family 2 (facilitated glucose transporter), member 9 (ENSG00000109667), score: 0.57 SLC35D1solute carrier family 35 (UDP-glucuronic acid/UDP-N-acetylgalactosamine dual transporter), member D1 (ENSG00000116704), score: 0.62 SLC38A4solute carrier family 38, member 4 (ENSG00000139209), score: 0.68 SLC7A2solute carrier family 7 (cationic amino acid transporter, y+ system), member 2 (ENSG00000003989), score: 0.65 SLC7A6solute carrier family 7 (cationic amino acid transporter, y+ system), member 6 (ENSG00000103064), score: -0.72 SMARCA1SWI/SNF related, matrix associated, actin dependent regulator of chromatin, subfamily a, member 1 (ENSG00000102038), score: -0.67 SPP2secreted phosphoprotein 2, 24kDa (ENSG00000072080), score: 0.57 SRD5A2steroid-5-alpha-reductase, alpha polypeptide 2 (3-oxo-5 alpha-steroid delta 4-dehydrogenase alpha 2) (ENSG00000049319), score: 0.56 STARD5StAR-related lipid transfer (START) domain containing 5 (ENSG00000172345), score: 0.65 TATtyrosine aminotransferase (ENSG00000198650), score: 0.66 TDO2tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase (ENSG00000151790), score: 0.67 TMEM135transmembrane protein 135 (ENSG00000166575), score: 0.59 TOR1Atorsin family 1, member A (torsin A) (ENSG00000136827), score: 0.58 TSPAN3tetraspanin 3 (ENSG00000140391), score: -0.78 TTC39Ctetratricopeptide repeat domain 39C (ENSG00000168234), score: 0.61 TTPAtocopherol (alpha) transfer protein (ENSG00000137561), score: 0.6 UBR2ubiquitin protein ligase E3 component n-recognin 2 (ENSG00000024048), score: 0.55 XCR1chemokine (C motif) receptor 1 (ENSG00000173578), score: 0.58 XKR9XK, Kell blood group complex subunit-related family, member 9 (ENSG00000221947), score: 0.76 ZNF750zinc finger protein 750 (ENSG00000141579), score: 0.69
| Id | species | tissue | sex | individual |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| mdo_lv_f_ca1 | mdo | lv | f | _ |
| mdo_lv_m_ca1 | mdo | lv | m | _ |
| mmu_lv_m1_ca1 | mmu | lv | m | 1 |
| mmu_lv_f_ca1 | mmu | lv | f | _ |
| mmu_lv_m2_ca1 | mmu | lv | m | 2 |
