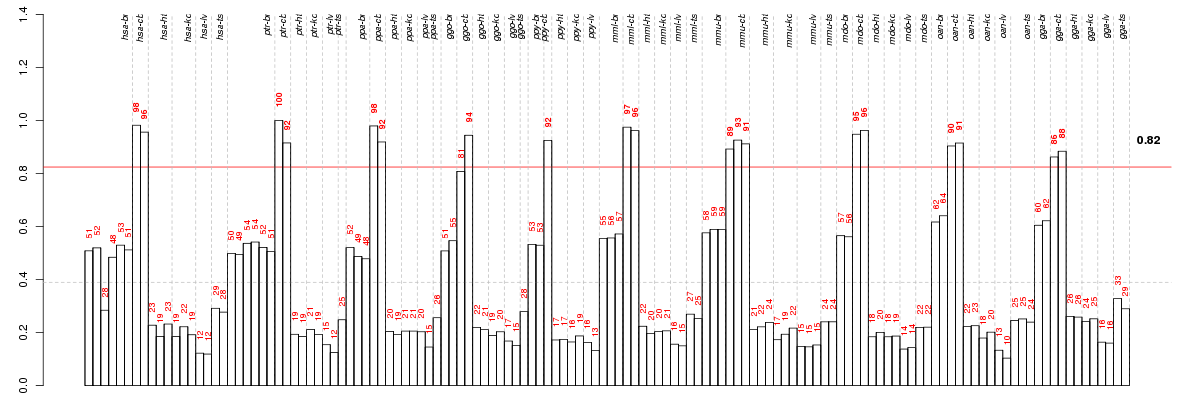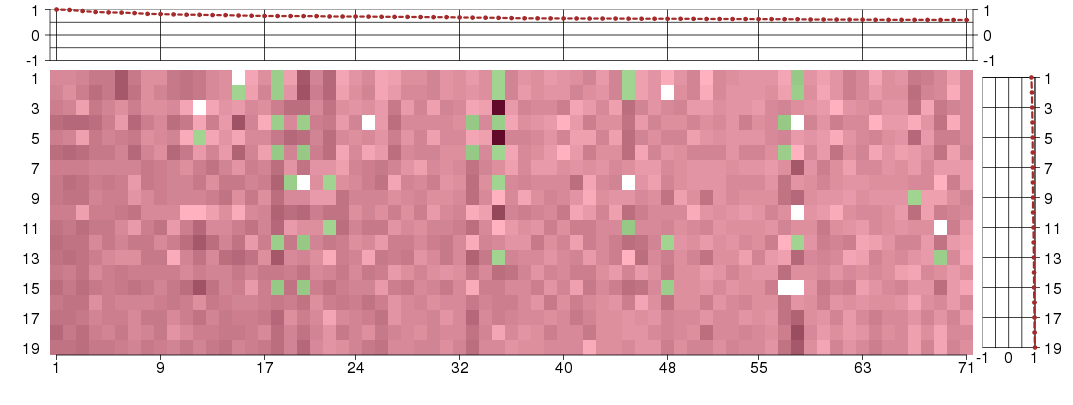

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

system process
A multicellular organismal process carried out by any of the organs or tissues in an organ system. An organ system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a biological objective.
cell communication
Any process that mediates interactions between a cell and its surroundings. Encompasses interactions such as signaling or attachment between one cell and another cell, between a cell and an extracellular matrix, or between a cell and any other aspect of its environment.
cell-cell signaling
Any process that mediates the transfer of information from one cell to another.
synaptic transmission
The process of communication from a neuron to a target (neuron, muscle, or secretory cell) across a synapse.
nerve-nerve synaptic transmission
The process of communication from a neuron to another neuron across a synapse.
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
nervous system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of nervous tissue over time, from its formation to its mature state.
neurological system process
A organ system process carried out by any of the organs or tissues of neurological system.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
transmission of nerve impulse
The neurological system process by which a signal is transmitted through the nervous system by synaptic transmission and the sequential electrochemical polarization and depolarization that travels across the membrane of a nerve cell (neuron) in response to stimulation.
signaling process
Any biological process involved in the generation, transmission, reception, or interpretation of a signal. A signal is an entity used to transmit or convey information.
signaling
The entirety of a process whereby information is transmitted. This process begins with the initiation of the signal and ends when a response has been triggered.
signal transmission
The process whereby a signal is released and/or conveyed from one location to another.
multicellular organismal process
Any biological process, occurring at the level of a multicellular organism, pertinent to its function.
developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an integrated living unit: an anatomical structure (which may be a subcellular structure, cell, tissue, or organ), or organism over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
synaptic transmission, glutamatergic
The process of communication from a neuron to another neuron across a synapse using the neurotransmitter glutamate.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
anatomical structure development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an anatomical structure from an initial condition to its mature state. This process begins with the formation of the structure and ends with the mature structure, whatever form that may be including its natural destruction. An anatomical structure is any biological entity that occupies space and is distinguished from its surroundings. Anatomical structures can be macroscopic such as a carpel, or microscopic such as an acrosome.
all
NA
signaling process
Any biological process involved in the generation, transmission, reception, or interpretation of a signal. A signal is an entity used to transmit or convey information.
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
cell-cell signaling
Any process that mediates the transfer of information from one cell to another.
transmission of nerve impulse
The neurological system process by which a signal is transmitted through the nervous system by synaptic transmission and the sequential electrochemical polarization and depolarization that travels across the membrane of a nerve cell (neuron) in response to stimulation.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
synaptic transmission
The process of communication from a neuron to a target (neuron, muscle, or secretory cell) across a synapse.
transmission of nerve impulse
The neurological system process by which a signal is transmitted through the nervous system by synaptic transmission and the sequential electrochemical polarization and depolarization that travels across the membrane of a nerve cell (neuron) in response to stimulation.

intracellular
The living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
cellular_component
The part of a cell or its extracellular environment in which a gene product is located. A gene product may be located in one or more parts of a cell and its location may be as specific as a particular macromolecular complex, that is, a stable, persistent association of macromolecules that function together.
cell
The basic structural and functional unit of all organisms. Includes the plasma membrane and any external encapsulating structures such as the cell wall and cell envelope.
cytoskeleton
Any of the various filamentous elements that form the internal framework of cells, and typically remain after treatment of the cells with mild detergent to remove membrane constituents and soluble components of the cytoplasm. The term embraces intermediate filaments, microfilaments, microtubules, the microtrabecular lattice, and other structures characterized by a polymeric filamentous nature and long-range order within the cell. The various elements of the cytoskeleton not only serve in the maintenance of cellular shape but also have roles in other cellular functions, including cellular movement, cell division, endocytosis, and movement of organelles.
postsynaptic density
The post synaptic density is a region that lies adjacent to the cytoplasmic face of the postsynaptic membrane at excitatory synapse. It forms a disc that consists of a range of proteins with different functions, some of which contact the cytoplasmic domains of ion channels in the postsynaptic membrane. The proteins making up the disc include receptors, and structural proteins linked to the actin cytoskeleton. They also include signalling machinery, such as protein kinases and phosphatases.
organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, and prokaryotic structures such as anammoxosomes and pirellulosomes. Excludes the plasma membrane.
non-membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, not bounded by a lipid bilayer membrane. Includes ribosomes, the cytoskeleton and chromosomes.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular non-membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, not bounded by a lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes ribosomes, the cytoskeleton and chromosomes.
organelle part
Any constituent part of an organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, but excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
cytoskeletal part
Any constituent part of the cytoskeleton, a cellular scaffolding or skeleton that maintains cell shape, enables some cell motion (using structures such as flagella and cilia), and plays important roles in both intra-cellular transport (e.g. the movement of vesicles and organelles) and cellular division. Includes constituent parts of intermediate filaments, microfilaments, microtubules, and the microtrabecular lattice.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
synapse part
Any constituent part of a synapse, the junction between a nerve fiber of one neuron and another neuron or muscle fiber or glial cell.
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
synapse
The junction between a nerve fiber of one neuron and another neuron or muscle fiber or glial cell; the site of interneuronal communication. As the nerve fiber approaches the synapse it enlarges into a specialized structure, the presynaptic nerve ending, which contains mitochondria and synaptic vesicles. At the tip of the nerve ending is the presynaptic membrane; facing it, and separated from it by a minute cleft (the synaptic cleft) is a specialized area of membrane on the receiving cell, known as the postsynaptic membrane. In response to the arrival of nerve impulses, the presynaptic nerve ending secretes molecules of neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft. These diffuse across the cleft and transmit the signal to the postsynaptic membrane.
all
NA
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
organelle part
Any constituent part of an organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, but excludes the plasma membrane.
synapse part
Any constituent part of a synapse, the junction between a nerve fiber of one neuron and another neuron or muscle fiber or glial cell.
intracellular non-membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, not bounded by a lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes ribosomes, the cytoskeleton and chromosomes.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
postsynaptic density
The post synaptic density is a region that lies adjacent to the cytoplasmic face of the postsynaptic membrane at excitatory synapse. It forms a disc that consists of a range of proteins with different functions, some of which contact the cytoplasmic domains of ion channels in the postsynaptic membrane. The proteins making up the disc include receptors, and structural proteins linked to the actin cytoskeleton. They also include signalling machinery, such as protein kinases and phosphatases.
cytoskeletal part
Any constituent part of the cytoskeleton, a cellular scaffolding or skeleton that maintains cell shape, enables some cell motion (using structures such as flagella and cilia), and plays important roles in both intra-cellular transport (e.g. the movement of vesicles and organelles) and cellular division. Includes constituent parts of intermediate filaments, microfilaments, microtubules, and the microtrabecular lattice.

molecular_function
Elemental activities, such as catalysis or binding, describing the actions of a gene product at the molecular level. A given gene product may exhibit one or more molecular functions.
transporter activity
Enables the directed movement of substances (such as macromolecules, small molecules, ions) into, out of, within or between cells.
transmembrane transporter activity
Enables the transfer of a substance from one side of a membrane to the other.
channel activity
Catalysis of energy-independent facilitated diffusion, mediated by passage of a solute through a transmembrane aqueous pore or channel. Stereospecificity is not exhibited but this transport may be specific for a particular molecular species or class of molecules.
passive transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a solute from one side of the membrane to the other, down the solute's concentration gradient.
gated channel activity
Catalysis of the transmembrane transfer of a solute by a channel that opens in response to a specific stimulus.
all
NA
| Id | Pvalue | ExpCount | Count | Size | Term |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 04730 | 2.028e-03 | 0.38 | 5 | 30 | Long-term depression |
| 04080 | 4.289e-02 | 1.292 | 6 | 102 | Neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction |
ADAM22ADAM metallopeptidase domain 22 (ENSG00000008277), score: 0.63 BICD1bicaudal D homolog 1 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000151746), score: 0.6 C15orf27chromosome 15 open reading frame 27 (ENSG00000169758), score: 0.7 C7orf16chromosome 7 open reading frame 16 (ENSG00000106341), score: 0.74 C8orf79chromosome 8 open reading frame 79 (ENSG00000170941), score: 0.72 CA10carbonic anhydrase X (ENSG00000154975), score: 0.61 CA8carbonic anhydrase VIII (ENSG00000178538), score: 0.74 CACNB4calcium channel, voltage-dependent, beta 4 subunit (ENSG00000182389), score: 0.6 CBLN1cerebellin 1 precursor (ENSG00000102924), score: 0.89 CDH7cadherin 7, type 2 (ENSG00000081138), score: 0.75 CHGBchromogranin B (secretogranin 1) (ENSG00000089199), score: 0.62 CHN2chimerin (chimaerin) 2 (ENSG00000106069), score: 0.65 CHRNA3cholinergic receptor, nicotinic, alpha 3 (ENSG00000080644), score: 0.62 CLVS2clavesin 2 (ENSG00000146352), score: 0.63 CNR1cannabinoid receptor 1 (brain) (ENSG00000118432), score: 0.6 CNTN6contactin 6 (ENSG00000134115), score: 0.62 CRHR1corticotropin releasing hormone receptor 1 (ENSG00000120088), score: 0.63 CRTAMcytotoxic and regulatory T cell molecule (ENSG00000109943), score: 0.74 DNM3dynamin 3 (ENSG00000197959), score: 0.6 DOPEY2dopey family member 2 (ENSG00000142197), score: 0.59 EPC1enhancer of polycomb homolog 1 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000120616), score: 0.64 FAT2FAT tumor suppressor homolog 2 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000086570), score: 1 FGF5fibroblast growth factor 5 (ENSG00000138675), score: 0.79 GALNT7UDP-N-acetyl-alpha-D-galactosamine:polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase 7 (GalNAc-T7) (ENSG00000109586), score: 0.66 GDF10growth differentiation factor 10 (ENSG00000107623), score: 0.59 GNG13guanine nucleotide binding protein (G protein), gamma 13 (ENSG00000127588), score: 0.71 GRIA4glutamate receptor, ionotrophic, AMPA 4 (ENSG00000152578), score: 0.64 GRID2glutamate receptor, ionotropic, delta 2 (ENSG00000152208), score: 0.86 GRM1glutamate receptor, metabotropic 1 (ENSG00000152822), score: 0.74 KCNA1potassium voltage-gated channel, shaker-related subfamily, member 1 (episodic ataxia with myokymia) (ENSG00000111262), score: 0.64 KCNC1potassium voltage-gated channel, Shaw-related subfamily, member 1 (ENSG00000129159), score: 0.69 KCNK10potassium channel, subfamily K, member 10 (ENSG00000100433), score: 0.72 KCNK9potassium channel, subfamily K, member 9 (ENSG00000169427), score: 0.76 LGI2leucine-rich repeat LGI family, member 2 (ENSG00000153012), score: 0.59 LRCH1leucine-rich repeats and calponin homology (CH) domain containing 1 (ENSG00000136141), score: 0.65 LRRC38leucine rich repeat containing 38 (ENSG00000162494), score: 0.65 MAB21L1mab-21-like 1 (C. elegans) (ENSG00000180660), score: 0.98 MAML3mastermind-like 3 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000196782), score: 0.8 MDGA1MAM domain containing glycosylphosphatidylinositol anchor 1 (ENSG00000112139), score: 0.68 MEIS1Meis homeobox 1 (ENSG00000143995), score: 0.64 MLLmyeloid/lymphoid or mixed-lineage leukemia (trithorax homolog, Drosophila) (ENSG00000118058), score: 0.6 MYT1myelin transcription factor 1 (ENSG00000196132), score: 0.78 NRG2neuregulin 2 (ENSG00000158458), score: 0.7 PAX3paired box 3 (ENSG00000135903), score: 0.61 PAX6paired box 6 (ENSG00000007372), score: 0.83 PLCB4phospholipase C, beta 4 (ENSG00000101333), score: 0.7 PLCXD3phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C, X domain containing 3 (ENSG00000182836), score: 0.59 PLD5phospholipase D family, member 5 (ENSG00000180287), score: 0.66 PTCH1patched 1 (ENSG00000185920), score: 0.64 PTCHD1patched domain containing 1 (ENSG00000165186), score: 0.72 PTPRRprotein tyrosine phosphatase, receptor type, R (ENSG00000153233), score: 0.62 PVALBparvalbumin (ENSG00000100362), score: 0.64 RGS8regulator of G-protein signaling 8 (ENSG00000135824), score: 0.64 RIT2Ras-like without CAAX 2 (ENSG00000152214), score: 0.59 SHFSrc homology 2 domain containing F (ENSG00000138606), score: 0.65 SKIv-ski sarcoma viral oncogene homolog (avian) (ENSG00000157933), score: 0.63 SKOR1SKI family transcriptional corepressor 1 (ENSG00000188779), score: 0.78 SLC35F4solute carrier family 35, member F4 (ENSG00000151812), score: 0.76 SLC6A5solute carrier family 6 (neurotransmitter transporter, glycine), member 5 (ENSG00000165970), score: 0.67 SPHKAPSPHK1 interactor, AKAP domain containing (ENSG00000153820), score: 0.65 SRRM4serine/arginine repetitive matrix 4 (ENSG00000139767), score: 0.59 SYT4synaptotagmin IV (ENSG00000132872), score: 0.63 TIAM1T-cell lymphoma invasion and metastasis 1 (ENSG00000156299), score: 0.71 TLL1tolloid-like 1 (ENSG00000038295), score: 0.88 TRIM67tripartite motif-containing 67 (ENSG00000119283), score: 0.9 TRPC3transient receptor potential cation channel, subfamily C, member 3 (ENSG00000138741), score: 0.73 UPF0639UPF0639 protein (ENSG00000175985), score: 0.81 ZFPM2zinc finger protein, multitype 2 (ENSG00000169946), score: 0.68 ZIC4Zic family member 4 (ENSG00000174963), score: 0.94 ZNF238zinc finger protein 238 (ENSG00000179456), score: 0.71 ZNF521zinc finger protein 521 (ENSG00000198795), score: 0.82
| Id | species | tissue | sex | individual |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| gga_cb_m_ca1 | gga | cb | m | _ |
| gga_cb_f_ca1 | gga | cb | f | _ |
| mmu_cb_m1_ca1 | mmu | cb | m | 1 |
| oan_cb_m_ca1 | oan | cb | m | _ |
| mmu_cb_f_ca1 | mmu | cb | f | _ |
| oan_cb_f_ca1 | oan | cb | f | _ |
| ptr_cb_f_ca1 | ptr | cb | f | _ |
| ppa_cb_f_ca1 | ppa | cb | f | _ |
| ppy_cb_f_ca1 | ppy | cb | f | _ |
| mmu_cb_m2_ca1 | mmu | cb | m | 2 |
| ggo_cb_f_ca1 | ggo | cb | f | _ |
| mdo_cb_m_ca1 | mdo | cb | m | _ |
| hsa_cb_f_ca1 | hsa | cb | f | _ |
| mml_cb_f_ca1 | mml | cb | f | _ |
| mdo_cb_f_ca1 | mdo | cb | f | _ |
| mml_cb_m_ca1 | mml | cb | m | _ |
| ppa_cb_m_ca1 | ppa | cb | m | _ |
| hsa_cb_m_ca1 | hsa | cb | m | _ |
| ptr_cb_m_ca1 | ptr | cb | m | _ |