
Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

urogenital system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the urogenital system over time, from its formation to the mature structure.
kidney development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the kidney over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The kidney is an organ that filters the blood and/or excretes the end products of body metabolism in the form of urine.
transport
The directed movement of substances (such as macromolecules, small molecules, ions) into, out of, within or between cells, or within a multicellular organism by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
ion transport
The directed movement of charged atoms or small charged molecules into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
cation transport
The directed movement of cations, atoms or small molecules with a net positive charge, into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
metal ion transport
The directed movement of metal ions, any metal ion with an electric charge, into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
cellular component organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of a cellular component.
extracellular matrix organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of an extracellular matrix.
multicellular organismal process
Any biological process, occurring at the level of a multicellular organism, pertinent to its function.
developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an integrated living unit: an anatomical structure (which may be a subcellular structure, cell, tissue, or organ), or organism over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
glomerulus development
The progression of the glomerulus over time from its initial formation until its mature state. The glomerulus is a capillary tuft which forms a close network with the visceral epithelium (podocytes) and the mesangium to form the filtration barrier and is surrounded by Bowman's capsule in nephrons of the vertebrate kidney. The glomerulus is part of the nephron and is restricted to one body segment.
glomerular basement membrane development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the glomerular basement membrane over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The glomerular basement membrane is the basal laminal portion of the glomerulus which performs the actual filtration.
extracellular structure organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of structures in the space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane, and also covers the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.
organ development
Development of a tissue or tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Development pertains to the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a structure over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
anatomical structure development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an anatomical structure from an initial condition to its mature state. This process begins with the formation of the structure and ends with the mature structure, whatever form that may be including its natural destruction. An anatomical structure is any biological entity that occupies space and is distinguished from its surroundings. Anatomical structures can be macroscopic such as a carpel, or microscopic such as an acrosome.
localization
Any process by which a cell, a substance, or a cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, is transported to, and/or maintained in a specific location.
establishment of localization
The directed movement of a cell, substance or cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, to a specific location.
renal system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the renal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The renal system maintains fluid balance and contributes to electrolyte balance, acid/base balance, and disposal of nitrogenous waste products.
nephron development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the nephron over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A nephron is the functional unit of the kidney.
all
NA
extracellular structure organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of structures in the space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane, and also covers the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
establishment of localization
The directed movement of a cell, substance or cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, to a specific location.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
organ development
Development of a tissue or tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Development pertains to the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a structure over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
glomerular basement membrane development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the glomerular basement membrane over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The glomerular basement membrane is the basal laminal portion of the glomerulus which performs the actual filtration.
glomerulus development
The progression of the glomerulus over time from its initial formation until its mature state. The glomerulus is a capillary tuft which forms a close network with the visceral epithelium (podocytes) and the mesangium to form the filtration barrier and is surrounded by Bowman's capsule in nephrons of the vertebrate kidney. The glomerulus is part of the nephron and is restricted to one body segment.
renal system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the renal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The renal system maintains fluid balance and contributes to electrolyte balance, acid/base balance, and disposal of nitrogenous waste products.
kidney development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the kidney over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The kidney is an organ that filters the blood and/or excretes the end products of body metabolism in the form of urine.
nephron development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the nephron over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A nephron is the functional unit of the kidney.

plasma membrane
The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
membrane
Double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
integral to membrane
Penetrating at least one phospholipid bilayer of a membrane. May also refer to the state of being buried in the bilayer with no exposure outside the bilayer. When used to describe a protein, indicates that all or part of the peptide sequence is embedded in the membrane.
extracellular region
The space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.
collagen
Any of the various assemblies in which collagen chains form a left-handed triple helix; may assemble into higher order structures.
cellular_component
The part of a cell or its extracellular environment in which a gene product is located. A gene product may be located in one or more parts of a cell and its location may be as specific as a particular macromolecular complex, that is, a stable, persistent association of macromolecules that function together.
proteinaceous extracellular matrix
A layer consisting mainly of proteins (especially collagen) and glycosaminoglycans (mostly as proteoglycans) that forms a sheet underlying or overlying cells such as endothelial and epithelial cells. The proteins are secreted by cells in the vicinity. An example of this component is found in Mus musculus.
collagen type IV
A collagen heterotrimer containing type IV alpha chains; [alpha1(IV)]2alpha2(IV) trimers are commonly observed, although more type IV alpha chains exist and may be present in type IV trimers; type IV collagen triple helices associate to form nets within basement membranes.
basement membrane
A thin layer of dense material found in various animal tissues interposed between the cells and the adjacent connective tissue. It consists of the basal lamina plus an associated layer of reticulin fibers.
cell
The basic structural and functional unit of all organisms. Includes the plasma membrane and any external encapsulating structures such as the cell wall and cell envelope.
brush border
Dense covering of microvilli on the apical surface of epithelial cells in tissues such as the intestine, kidney, and choroid plexus; the microvilli aid absorption by increasing the surface area of the cell.
sheet-forming collagen
Any collagen polymer in which collagen triple helices associate to form sheet-like networks.
extracellular matrix
A structure lying external to one or more cells, which provides structural support for cells or tissues; may be completely external to the cell (as in animals) or be part of the cell (as in plants).
intrinsic to membrane
Located in a membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
cell projection
A prolongation or process extending from a cell, e.g. a flagellum or axon.
extracellular matrix part
Any constituent part of the extracellular matrix, the structure lying external to one or more cells, which provides structural support for cells or tissues; may be completely external to the cell (as in animals) or be part of the cell (as often seen in plants).
extracellular region part
Any constituent part of the extracellular region, the space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers constituent parts of the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.
membrane part
Any constituent part of a membrane, a double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
all
NA
extracellular region part
Any constituent part of the extracellular region, the space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers constituent parts of the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
extracellular matrix part
Any constituent part of the extracellular matrix, the structure lying external to one or more cells, which provides structural support for cells or tissues; may be completely external to the cell (as in animals) or be part of the cell (as often seen in plants).
membrane part
Any constituent part of a membrane, a double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
collagen
Any of the various assemblies in which collagen chains form a left-handed triple helix; may assemble into higher order structures.
basement membrane
A thin layer of dense material found in various animal tissues interposed between the cells and the adjacent connective tissue. It consists of the basal lamina plus an associated layer of reticulin fibers.
collagen type IV
A collagen heterotrimer containing type IV alpha chains; [alpha1(IV)]2alpha2(IV) trimers are commonly observed, although more type IV alpha chains exist and may be present in type IV trimers; type IV collagen triple helices associate to form nets within basement membranes.

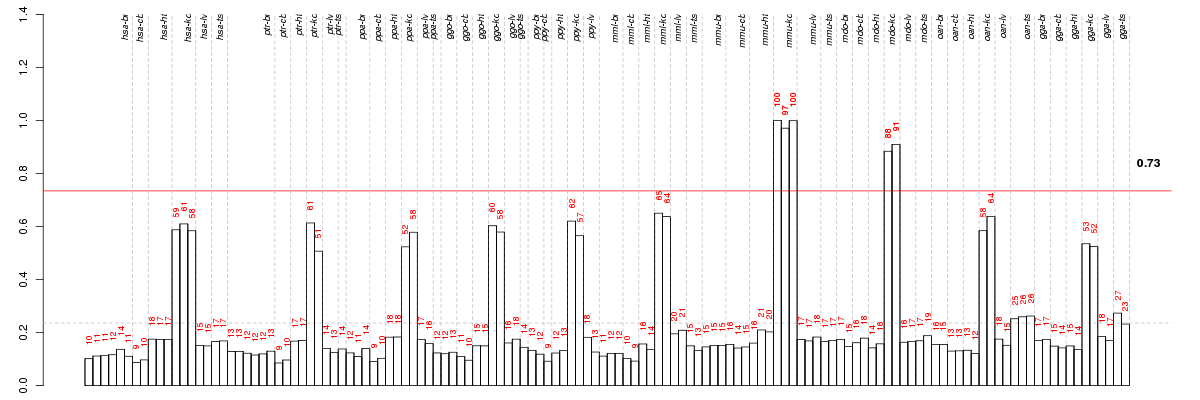
A4GNTalpha-1,4-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase (ENSG00000118017), score: 0.98 ANKRD13Cankyrin repeat domain 13C (ENSG00000118454), score: 0.62 ARHGEF38Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) 38 (ENSG00000138784), score: 0.76 BPNT13'(2'), 5'-bisphosphate nucleotidase 1 (ENSG00000162813), score: 0.69 CASRcalcium-sensing receptor (ENSG00000036828), score: 0.63 CLDN16claudin 16 (ENSG00000113946), score: 0.61 CLDN19claudin 19 (ENSG00000164007), score: 0.65 COL4A3collagen, type IV, alpha 3 (Goodpasture antigen) (ENSG00000169031), score: 0.69 COL4A4collagen, type IV, alpha 4 (ENSG00000081052), score: 0.77 EGFepidermal growth factor (ENSG00000138798), score: 0.85 ESRP1epithelial splicing regulatory protein 1 (ENSG00000104413), score: 0.62 GCM1glial cells missing homolog 1 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000137270), score: 0.71 HOXB7homeobox B7 (ENSG00000120087), score: 0.62 ILDR1immunoglobulin-like domain containing receptor 1 (ENSG00000145103), score: 0.68 KCNJ1potassium inwardly-rectifying channel, subfamily J, member 1 (ENSG00000151704), score: 0.62 KLklotho (ENSG00000133116), score: 0.66 KRT23keratin 23 (histone deacetylase inducible) (ENSG00000108244), score: 0.63 KRT80keratin 80 (ENSG00000167767), score: 0.78 LYPD2LY6/PLAUR domain containing 2 (ENSG00000197353), score: 0.62 MEP1Ameprin A, alpha (PABA peptide hydrolase) (ENSG00000112818), score: 0.92 MEP1Bmeprin A, beta (ENSG00000141434), score: 0.94 NOX4NADPH oxidase 4 (ENSG00000086991), score: 0.69 OSBPL3oxysterol binding protein-like 3 (ENSG00000070882), score: 0.72 PKD2polycystic kidney disease 2 (autosomal dominant) (ENSG00000118762), score: 0.61 SLC10A2solute carrier family 10 (sodium/bile acid cotransporter family), member 2 (ENSG00000125255), score: 0.74 SLC13A1solute carrier family 13 (sodium/sulfate symporters), member 1 (ENSG00000081800), score: 0.72 SLC18A1solute carrier family 18 (vesicular monoamine), member 1 (ENSG00000036565), score: 0.69 SLC34A1solute carrier family 34 (sodium phosphate), member 1 (ENSG00000131183), score: 0.62 SLC5A12solute carrier family 5 (sodium/glucose cotransporter), member 12 (ENSG00000148942), score: 0.66 SUSD2sushi domain containing 2 (ENSG00000099994), score: 0.65 TCN2transcobalamin II (ENSG00000185339), score: 0.62 TMEM27transmembrane protein 27 (ENSG00000147003), score: 0.65 TMIGD1transmembrane and immunoglobulin domain containing 1 (ENSG00000182271), score: 0.85 TNFAIP8tumor necrosis factor, alpha-induced protein 8 (ENSG00000145779), score: 0.71 TRPM6transient receptor potential cation channel, subfamily M, member 6 (ENSG00000119121), score: 0.63 UPK3Auroplakin 3A (ENSG00000100373), score: 1 ZPLD1zona pellucida-like domain containing 1 (ENSG00000170044), score: 0.99
| Id | species | tissue | sex | individual |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| mdo_kd_m_ca1 | mdo | kd | m | _ |
| mdo_kd_f_ca1 | mdo | kd | f | _ |
| mmu_kd_m2_ca1 | mmu | kd | m | 2 |
| mmu_kd_f_ca1 | mmu | kd | f | _ |
| mmu_kd_m1_ca1 | mmu | kd | m | 1 |